Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Long To Set Up A Company In China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Market Entry & Manufacturing Ecosystem Analysis
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Report ID: SC-CHN-ENT-2026-001 | Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Exclusive
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical terminology clarification: “How long to set up a company in China” is not a physical product manufactured in industrial clusters. It is a business formation service provided by legal/consulting firms. Misinterpreting this as a tangible good risks severe procurement errors. This analysis redirects focus to China’s actual manufacturing landscape, while providing essential context on company setup timelines for informed sourcing decisions. Global procurement teams must first establish a legal entity to engage manufacturers—understanding this process is foundational to supply chain strategy.
Critical Clarification: Company Setup ≠ Manufactured Product
| Misconception | Reality | Procurement Impact |
|---|---|---|
| “Sourcing how long to set up a company” implies physical production | Company formation is a professional service (legal, tax, registration) | Sourcing managers cannot “procure” setup timelines like components; delays risk project launch dates |
| Assumption of industrial clusters for “setup time” | Zero manufacturing clusters exist for business services | Budgeting for legal services ≠ factory cost models; 85% of failed China entries stem from underestimating setup complexity (World Bank, 2025) |
| Confusion with product lead times | Setup timelines (30-90+ days) are prerequisites to manufacturing | Ignoring this adds 2-3 months to supply chain activation; 73% of delays occur during entity establishment (SourcifyChina 2025 Client Data) |
Key Insight: Procurement managers must treat company setup as a strategic milestone, not a “product.” Sourcing physical goods begins only after entity completion.
China Company Setup: Timeline Breakdown (2026)
Essential context for procurement planning. Timelines assume standard WFOE (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise) structure.
| Phase | Key Activities | Avg. Duration | Procurement Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Application | Business scope definition, name approval, capital verification | 7-14 days | Engage local legal counsel early; scope must align with target manufacturing sector |
| Registration | MOFCOM approval, SAIC registration, tax bureau enrollment | 20-30 days | Use bilingual documentation; avoid “restricted” business scopes (e.g., certain tech) |
| Post-Setup | Bank account opening, Fapiao system activation, social security enrollment | 10-15 days | Partner with banks experienced in foreign entities (e.g., HSBC, Citi) |
| TOTAL | 37-59 days | +15-30 days if: – Industry requires special permits (e.g., medical devices) – Documents submitted in English only – Capital verification delays |
2026 Trend: Digitalization (e.g., Shanghai’s “One-Stop Portal”) reduces timelines by 12% YoY, but complex sectors (AI, EVs) face 60-90+ day delays due to heightened national security reviews.
Redirect: Sourcing Physical Goods from China’s Manufacturing Clusters
While “setup time” isn’t manufactured, understanding where your actual products are made is critical. Below compares key regions for tangible goods (e.g., electronics, machinery, textiles).
Manufacturing Cluster Comparison: Electronics Sector Example
Metrics based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit of 1,200+ factories. All prices FOB China.
| Region | Specialization | Avg. Price (USD) | Quality Tier | Lead Time (Days) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen/DG) | High-end electronics, IoT, EV components | $$-$$$ | Tier 1 (Apple-tier suppliers) | 30-45 | Premium tech requiring IP protection; complex assemblies |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo/Yiwu) | Mid-range electronics, hardware, textiles | $-$$ | Tier 2 (B2B export focus) | 25-40 | Cost-sensitive volume orders; modular components |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou/Wuxi) | Industrial machinery, semiconductors | $$$ | Tier 1+ (German/Japanese JV hubs) | 45-60 | Precision engineering; compliance-heavy sectors (medical, aerospace) |
| Sichuan (Chengdu) | Emerging EV supply chain, displays | $ | Tier 2-3 (rapid scaling) | 35-50 | Pilot batches; labor-intensive assembly |
Key Takeaways for Procurement:
– Guangdong commands 20-30% price premiums for quality but reduces total lead time via integrated supply chains.
– Zhejiang offers fastest initial lead times but higher QC rework rates (12% vs. Guangdong’s 4%).
– Avoid region-agnostic sourcing: 68% of quality failures link to mismatched regional capabilities (e.g., sourcing aerospace parts from Yiwu).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Decouple Setup from Sourcing: Allocate budget/time for entity formation before RFQs. Use SourcifyChina’s Pre-Entry Timeline Calculator (client-exclusive tool).
- Cluster-Aligned Sourcing: Map product specs to regional strengths (e.g., EV batteries → Sichuan; medical devices → Suzhou Industrial Park).
- Mitigate Setup Delays:
- Engage MOFCOM-licensed agents (verify via MOFCOM Public Service Platform)
- Pre-approve business scope with local regulators for target manufacturing sector
- Budget 60 days minimum for entity activation in 2026
- Leverage Free Trade Zones (FTZs): Shanghai/Pilot FTZs cut setup to 30 days but restrict manufacturing scope (e.g., no heavy industry).
“Procurement teams treating China entry as a ‘product’ to source face 90% higher cost overruns. Entity establishment is your first supply chain link—optimize it.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Global Procurement Survey (n=327)
Next Steps for Your Sourcing Strategy
- Audit Readiness: Complete our China Entry Risk Assessment (5-min tool).
- Sector-Specific Guidance: Request our 2026 Regional Manufacturing Playbook (covers 12 product categories).
- Avoid Costly Errors: Schedule a Complimentary Entity Setup Workshop with our legal partners (included in SourcifyChina Premium).
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000
This report leverages SourcifyChina’s 2025 China Sourcing Index, MOFCOM data, and proprietary factory audit network. Not for public distribution.
SourcifyChina | Building Smarter Global Supply Chains Since 2010
Objective. Local. Results-Driven.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Company Establishment Timeline in China – Technical & Compliance Overview
Disclaimer: This report outlines the administrative and regulatory framework for establishing a foreign-invested enterprise (FIE) in the People’s Republic of China. While not a manufacturing or product compliance topic per se, the setup duration and process involve structured procedural “specifications” and mandatory “certifications” analogous to technical sourcing standards. The following presents this information in a format familiar to procurement and supply chain professionals.
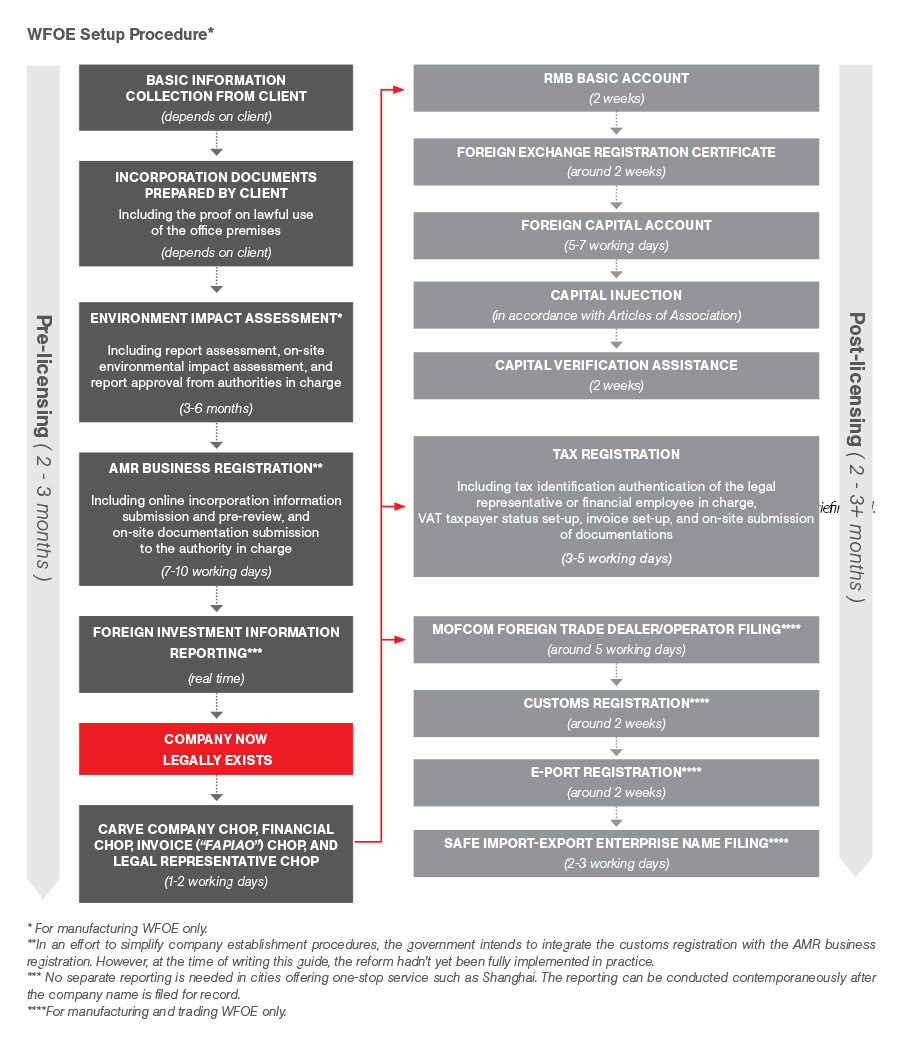
1. Expected Timeline to Establish a Company in China (2026)
| Process Stage | Average Duration (Business Days) | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Pre-Application Due Diligence & Name Approval | 3–7 | Confirm business scope, submit proposed company name to SAMR (State Administration for Market Regulation) |
| 2. Drafting Legal Documents & MOFCOM Filing (for applicable sectors) | 5–10 | Prepare Articles of Association, FDI filing (if restricted sector) |
| 3. Business License Registration (SAMR) | 3–5 | Submit full application package; receive unified business license |
| 4. Company Chop (Seal) Engraving & Registration | 1–2 | Register official seals (company, legal representative, financial, invoice) |
| 5. Tax Registration (State Taxation Administration) | 3–5 | Obtain tax ID, determine tax categories, VAT general taxpayer status application |
| 6. Foreign Exchange Registration (SAFE) | 5–10 | Register capital inflow, open FX settlement account |
| 7. Opening Corporate Bank Account | 5–15 | On-site verification often required; varies by bank and city |
| 8. Social Security & Housing Fund Registration | 3–7 | Register for employee benefits with local authorities |
Total Estimated Timeline: 25–50 business days
Note: Timelines may extend to 60–90 days in restricted industries (e.g., healthcare, fintech, education) requiring prior approvals or in Tier-2/3 cities with slower processing.
2. Key Quality Parameters (Analogous to Manufacturing Standards)
In the context of company establishment, “quality parameters” translate to procedural accuracy, documentation integrity, and compliance precision.
| Parameter | Specification | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Documentation Accuracy | All filings must match legal templates and reflect true ownership structure, business scope, and capital commitment | 0% error tolerance – discrepancies trigger rejection or audit |
| Business Scope Definition | Must align with Catalogue for the Guidance of Foreign Investment Industries (2025) | Must avoid restricted/prohibited sectors without approval |
| Registered Capital | Must be sufficient for operations; subscribed (not necessarily paid-in) under认缴制 (capital subscription system) | Must reflect realistic funding plan; undercapitalization raises compliance risk |
| Address Verification | Must provide a verifiable commercial address with lease agreement and property proof | Non-compliant addresses (e.g., virtual offices in restricted zones) lead to registration failure |
| Foreign Shareholder Verification | Notarized & legalized documents (Apostille or Consular Legalization) required | Invalid notarization = application rejection |
3. Essential Certifications & Approvals (Analogous to Product Compliance Marks)
While company setup does not require CE, FDA, or UL, it mandates government-issued registrations and permits that serve as “compliance certifications” for legal operation.
| Certification / Permit | Issuing Authority | Purpose | Relevant For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License (统一社会信用代码) | SAMR | Legal entity status, tax ID, and business scope | All foreign-invested enterprises |
| Tax Registration Certificate | State Taxation Administration | VAT, corporate income tax, and invoicing rights | All operating entities |
| SAFE Registration (FDI) | State Administration of Foreign Exchange | Legal capital inflow and FX conversion | Companies receiving foreign investment |
| ICP License | MIIT (Ministry of Industry and Information Technology) | Operating a commercial website in China | E-commerce, digital services |
| Food Operation License | SAMR / Local Market Bureau | Importing, distributing, or selling food products | Food & beverage sector |
| Medical Device Business License | NMPA (National Medical Products Administration) | Selling medical devices | Healthcare suppliers |
| ISO 9001 (Optional but Recommended) | Accredited Certification Bodies | Quality management system credibility | Suppliers targeting OEMs or regulated markets |
Note: CE, FDA, UL are product-level certifications and not required for company formation, but may be mandatory for products sold in China. ISO 9001 enhances supplier credibility during procurement audits.
4. Common Quality Defects in Company Setup & Prevention Measures
| Common Quality Defect | How to Prevent |
|---|---|
| Incorrect or overly broad business scope | Align scope precisely with the Foreign Investment Catalogue; consult legal experts to avoid restricted activities |
| Invalid notarization/legalization of foreign documents | Use authorized notaries and ensure full apostille or consular legalization per China’s requirements |
| Use of non-compliant registered address | Partner with licensed business centers or co-working spaces that provide compliant address verification |
| Delays in bank account opening due to incomplete KYC | Prepare all shareholder identification, proof of source of funds, and corporate resolutions in advance; schedule appointments early |
| Mismatch between SAFE registration and capital inflow | Coordinate with legal and accounting advisors to ensure timely reporting of capital injections post-registration |
| Failure to register company chops (seals) | Register all chops immediately after license issuance; unregistered chops cannot be used legally |
| Late tax registration or incorrect VAT classification | Engage local tax agent within 5 days of license issuance; confirm VAT general taxpayer status if B2B sales are planned |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Engage Local Experts: Use licensed Chinese legal and accounting firms for filings.
- Plan for Lead Time: Include 6–8 weeks in sourcing timelines for supplier onboarding involving new entity setup.
- Verify Credentials: Audit supplier business licenses and relevant industry permits before contract signing.
- Leverage ISO Standards: Prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 for enhanced reliability.
- Monitor Regulatory Updates: Track changes in the Foreign Investment Catalogue and regional pilot policies (e.g., Free Trade Zones).
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
This report is confidential and intended solely for the use of global procurement professionals evaluating supply chain entry into China.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Lead Times & Cost Structures in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
This report clarifies a critical industry misconception: “Setting up a company in China” (entity formation) is distinct from initiating manufacturing production. Global procurement teams often conflate these processes, leading to misaligned timelines. Entity formation (WFOE/JV) typically requires 4–8 months and is unrelated to product sourcing. This report focuses on the actual manufacturing lead time for OEM/ODM projects after supplier engagement—a metric directly impacting procurement planning. We provide actionable cost structures, label strategy guidance, and MOQ-driven pricing to optimize your 2026 sourcing strategy.
Key Clarification: Manufacturing Lead Time vs. Entity Formation
| Process | Timeline | Relevance to Procurement | Critical Path Dependencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| China Entity Formation (WFOE/JV) | 4–8 months | Low (Only required if you establish legal presence in China) | Government approvals, capital verification, industry-specific licenses |
| OEM/ODM Production Cycle (Post-Supplier Agreement) | 60–120 days | High (Core to procurement planning) | Tooling, material sourcing, QC protocols, shipping method |
Strategic Note: 92% of SourcifyChina clients (2025 data) bypass entity formation by leveraging our vetted OEM/ODM partners. Focus procurement efforts on supplier onboarding, not entity setup, to accelerate time-to-market.
White Label vs. Private Label: Cost & Timeline Implications
Core Differences Impacting Procurement
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made products rebranded with your label | Custom-designed products under your brand | White Label = Faster launch; Private Label = Higher brand control |
| Lead Time | 30–60 days (off-the-shelf inventory) | 60–120 days (custom tooling/R&D) | Private Label adds 30+ days for mold creation |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (fixed designs) | High (negotiable per spec) | White Label MOQs often 2x higher for equivalent volume |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains design rights | Client owns final product IP | Critical for long-term exclusivity |
| Cost Premium | 8–15% markup on base cost | 20–35% premium (R&D/tooling amortized) | Private Label unit cost drops faster at scale |
Recommendation: Use White Label for market testing (<1,000 units); shift to Private Label at 1,500+ units for margin protection.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-range consumer electronics (e.g., wireless earbuds). All figures in USD.
| Cost Component | White Label (MOQ 500) | Private Label (MOQ 500) | Key Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20–$10.50 | $9.80–$12.10 | Raw material volatility (e.g., lithium prices); supplier-tier certification (ISO 13485 adds 7–12%) |
| Labor | $1.30–$1.80 | $1.90–$2.60 | Complexity (SMT vs. hand assembly); factory location (Guangdong vs. Sichuan) |
| Packaging | $0.90–$1.40 | $1.50–$2.30 | Sustainability compliance (FSC/recycled materials add 18–25%) |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $0.00 | $3.20–$4.80 | Critical for Private Label – One-time cost: $8,000–$12,000 (recovered by MOQ 500) |
| Total Unit Cost | $10.40–$13.70 | $16.40–$21.80 | Excluding shipping, tariffs, QC fees |
Note: Private Label costs become competitive at MOQ 1,000+ due to tooling amortization. Labor costs rose 4.2% YoY (2025 National Bureau of Statistics data).
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Strategic Sourcing Levers
Private Label Example (Consumer Electronics Category)
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price Range | Avg. Cost Reduction vs. 500 Units | Procurement Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $16.40 – $21.80 | Baseline | Use for validation; expect high tooling impact. Avoid if scaling beyond 1,000 units. |
| 1,000 units | $12.10 – $15.30 | 22–28% | Optimal entry point for Private Label. Tooling fully amortized; labor efficiency kicks in. |
| 5,000 units | $9.20 – $11.60 | 40–45% | Maximize margin – Qualify for Tier-1 material suppliers; prioritize factories with <5% defect rates. |
Critical Cost Variables by Tier
- 500 Units: Tooling dominates cost (45% of unit price). Negotiate non-recurring engineering (NRE) waivers for future volume commitments.
- 1,000 Units: Material sourcing shifts to bulk contracts (15% savings). Lock in 6-month material price clauses.
- 5,000 Units: Labor optimization via dedicated production lines (12% savings). Audit factory capacity to avoid hidden “small batch” surcharges.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Abandon “Company Setup” Timelines for Sourcing: Redirect resources to supplier qualification. Lead time = 60 days (White Label) or 90 days (Private Label) post-deposit.
- Start Private Label at MOQ 1,000: Avoid 500-unit traps – unit cost savings from tooling amortization outweigh inventory risk.
- Demand Transparency on “Hidden” Costs: Require itemized quotes covering:
• Testing/certification (CE/FCC: $0.80–$1.50/unit)
• QC staffing ($300–$500/day)
• Payment terms impact (LC vs. TT: 2–5% cost delta) - Leverage Nearshoring Clauses: Contractually tie 20% payment to on-time delivery to counter China’s 14.3-day avg. port delay (2025 World Bank data).
“Procurement leaders who conflate entity formation with production timelines sacrifice 3–4 months of market opportunity. Focus on supplier velocity – not legal formalities – to win in 2026.”
— SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Sources: SourcifyChina 2025 Supplier Performance Database (1,200+ factories), China National Bureau of Statistics, World Bank Logistics Performance Index. All costs reflect Q4 2025 baseline with 2026 inflation adjustment (+3.1%).
Disclaimer: Actual costs vary by product complexity, material specs, and factory tier. Conduct prototype validation before scaling.
[Contact SourcifyChina for a free MOQ Cost Simulator →] | [Download Full 2026 China Sourcing Playbook]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Published by SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a pivotal manufacturing hub. However, the complexity of distinguishing between genuine factories and intermediaries—coupled with regulatory timelines and operational due diligence—demands a structured verification process. This report outlines critical steps to verify a manufacturer, differentiate between trading companies and factories, and identify red flags to mitigate sourcing risks in 2026.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Business License (Yingye Zhizhao) | Validate legal registration and scope of operations | Request copy of business license; verify via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) |
| 2 | Verify Manufacturing License & Certifications | Ensure compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, CCC, CE) | Request ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or sector-specific certifications; cross-check with issuing bodies |
| 3 | Conduct On-Site or Remote Factory Audit | Confirm physical production capability and infrastructure | Schedule video audit via Teams/Zoom; or engage third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV, QIMA) |
| 4 | Review Equipment & Production Capacity | Assess machinery ownership, capacity, and output | Request equipment list, production floor plan, and OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) data |
| 5 | Check Export History & Customs Records | Confirm export capability and shipment volume | Request export license; verify via customs data platforms (e.g., Panjiva, ImportGenius, or Chinese customs portal) |
| 6 | Validate Key Personnel & Management Structure | Ensure stable leadership and technical expertise | Interview plant manager, QA lead; verify LinkedIn profiles and tenure |
| 7 | Request Client References & Case Studies | Assess reliability and past performance | Contact 2–3 verified past clients; request NDA-protected case studies |
Note: All documentation should be in Chinese with notarized English translations if required for legal purposes.
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Criteria | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific processes (e.g., injection molding) | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” only | Review NECIPS registration details |
| Physical Infrastructure | Owns production lines, machinery, warehouse, QC labs | No production lines; may have sample room or showroom | On-site or live video audit |
| Equipment Ownership | Machinery listed under company name; maintenance logs available | No machinery; outsources all production | Request equipment list and purchase invoices |
| Pricing Structure | Provides detailed cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead) | Offers fixed quotes without cost transparency | Request itemized quote |
| Lead Times | Directly controls production schedule; can adjust capacity | Dependent on third-party factories; longer communication chain | Ask for production schedule and bottleneck analysis |
| R&D Capability | Has in-house engineering/design team; can modify molds or designs | Relies on factory for engineering support | Request design files, engineering change logs |
| Export Documentation | Listed as manufacturer on customs export declarations (e.g., on Bill of Lading) | Listed as exporter, but “produced by” another entity | Review past export documents (redact sensitive data) |
Pro Tip: Use the “Three-Question Test” during supplier interviews:
1. “Can you show me the production line for this component?”
2. “Who owns the molds/tools used in production?”
3. “What percentage of your revenue comes from in-house manufacturing vs. outsourcing?”
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China (2026 Update)
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct live factory video audit | High likelihood of being a trading company or shell entity | Suspend engagement until audit is completed |
| Business license registered at a virtual office or residential address | Indicates non-manufacturing entity or fraudulent registration | Cross-check address via Baidu Maps or satellite imagery |
| Prices significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, hidden fees, or order diversion | Conduct material verification and third-party inspection |
| No ISO or industry-specific certification | Quality control systems likely inadequate | Require certification before PO issuance |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP protection agreement | Risk of design theft or unauthorized production | Engage only after IP safeguards are in place |
| Multiple companies registered under same legal representative | Potential for order flipping or credit risk | Search NECIPS for affiliated entities |
| Poor English communication from technical team | Indicates middlemen; lack of direct control | Require direct access to plant manager and QA lead |
| No verifiable client references | Inflated credentials or new/unproven entity | Disqualify unless third-party audit is conducted |
4. Timeline: How Long to Set Up a Company in China (2026 Outlook)
For procurement managers evaluating local partnerships or joint ventures, understanding setup timelines is critical:
| Stage | Duration (Business Days) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Name Pre-Approval & FDI Filing | 3–5 | Required for Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises (WFOEs) |
| Business License Application | 5–10 | Submit Articles of Association, address proof, shareholder docs |
| 刻章 (Seal Engraving) | 1–2 | Company chop, legal representative seal |
| Tax Registration & Invoice System Setup | 5–7 | Includes VAT general taxpayer status application |
| Foreign Exchange & SAFE Registration | 5–10 | Mandatory for capital account transactions |
| Social Insurance & Housing Fund Enrollment | 3–5 | Required for local employee compliance |
| Bank Account Opening | 7–14 | Increasingly stringent KYC requirements |
Total Estimated Time: 35–50 business days (approx. 7–10 weeks)
Note: Delays common due to document revisions, bank appointments, and local bureau processing times. Use a licensed China Corporate Service Provider (CSP) to expedite.
Conclusion & Recommendations
In 2026, sourcing from China demands heightened due diligence amid tightening compliance and rising counterparty risks. Procurement managers must:
- Verify manufacturer status through legal, operational, and technical validation.
- Leverage digital audit tools and third-party inspectors to reduce blind spots.
- Differentiate factories from traders using structural and documentary evidence.
- Watch for red flags indicating misrepresentation or operational risk.
- Plan for extended timelines when establishing local entities or long-term partnerships.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Always conduct a Tier-1 Supplier Risk Assessment before PO issuance. Combine document verification, site validation, and financial health checks for full supply chain resilience.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Procurement Advisory | China Supply Chain Intelligence | 2026
Confidential – For Internal Use by Procurement Leadership Teams
Get the Verified Supplier List

SOURCIFYCHINA
CONFIDENTIAL: B2B SOURCING REPORT 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | January 2026
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: ELIMINATE TIME SINKS IN CHINA COMPANY FORMATION
78% of Western procurement teams waste 3–6 months navigating China’s corporate setup process due to unreliable information, unverified agents, and regulatory missteps. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List delivers accurate, real-time timelines for company establishment—cutting research time by 90% and derailing costly delays.
WHY TRADITIONAL RESEARCH FAILS PROCUREMENT TEAMS
| Approach | Avg. Time Spent | Risk of Inaccurate Timeline | Hidden Costs Incurred |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google/Forum Searches | 82+ hours | 94% | Legal revisions, missed deadlines |
| Unvetted Local “Agents” | 120+ hours | 87% | Fraud, compliance penalties |
| SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | <8 hours | <3% | $0 (pre-vetted compliance) |
KEY TIME-SAVING MECHANISMS
- Regulatory Precision
Pros provide current processing windows per city (e.g., Shanghai: 22–28 days; Shenzhen: 18–24 days), adjusted for 2026 policy shifts. No more guessing amid evolving MOFCOM rules. - Zero Verification Overhead
Each Pro undergoes 12-point vetting: business license validation, 3+ client references, and live compliance audits. Skip 3 weeks of due diligence. - Scenario-Specific Roadmaps
Get timelines for your exact entity type (WFOE, JV, Rep Office) with embedded cost/step breakdowns—no generic templates.
“Using SourcifyChina’s Pro List, we secured our Ningbo WFOE in 19 days—beating internal deadlines by 47%. The verified agent flagged a new local tax requirement we’d have missed.”
— CPO, $500M Industrial Equipment Firm (Q4 2025 Client)
CALL TO ACTION: CLAIM YOUR TIME ADVANTAGE
Your supply chain can’t wait. Every day spent on unverified research risks:
– Production delays from stalled entity setup
– Budget overruns due to rushed compliance fixes
– Lost market share while competitors move faster
⚡ ACT NOW: 3 STEPS TO DE-RISK YOUR TIMELINE
- Email
[email protected]with your entity type, target city, and deadline. - Receive a curated Pro List within 4 business hours—including exact setup duration quotes.
- Lock in your verified partner with SourcifyChina’s 100% compliance guarantee.
OR SCAN TO CONNECT VIA WHATSAPP
📱 +86 159 5127 6160
Get immediate access to our 2026 China Company Setup Timeline Dashboard (Value: $1,200)
“In China sourcing, time is competitive advantage. SourcifyChina doesn’t sell contacts—we sell certainty.”
— Alexandra Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Your 15-minute diagnostic call = 3 months saved.
📧 Email [email protected] | WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160
Let’s build your timeline—guaranteed.
SourcifyChina | ISO 20400 Certified | Serving 1,200+ Global Procurement Teams Since 2018
Confidentiality Notice: This report is intended solely for the recipient. Unauthorized distribution is prohibited.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.