The global galvanized steel coil market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand from key end-use sectors such as construction, automotive, and appliances. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global galvanized steel market was valued at USD 74.9 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by increasing infrastructure development, especially in emerging economies, and the growing need for corrosion-resistant materials that ensure longevity and reduce maintenance costs. Hot-dipped galvanized steel coils, in particular, remain a preferred choice due to their superior coating thickness and enhanced durability. As demand continues to rise, a core group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in production capacity, technological innovation, and global reach. Based on market presence, annual output, and industry reputation, the following are the top 10 hot-dipped galvanized steel coil manufacturers shaping the future of the industry.
Top 10 Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Coil Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Hot Dipped Galvanized GI Steel Coil
Domain Est. 2009
Website: sino-steel.net
Key Highlights: As a leading galvanized steel coil manufacturer, Qingdao Sino Steel Co..Ltd. adheres to strict quality standards to produce our galvanized steelcoils/sheets….
#2 Hot
Domain Est. 2023
Website: sumikosteel.com
Key Highlights: Hot-dip galvanized steel coil is produced by immersing a steel sheet into a bath of molten zinc. This process creates a zinc coating on the surface of the ……
#3 Hot Dip Galvanized Coil
Website: ansteel-group.com
Key Highlights: Hot dip galvanizing is to make the molten metal react with the iron substrate to produce an alloy layer, so that the substrate and the coating are combined….
#4 SSAB high
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ssab.com
Key Highlights: SSAB is a Nordic and US-based steel company. SSAB offers value added … Hot dip galvanized · Color coated coils and sheets · Overlay products · Tool steel ……
#5 AZZ
Domain Est. 1997
Website: azz.com
Key Highlights: We are North America’s leading independent provider of hot-dip galvanizing and coil coating services. At AZZ, we provide sustainable, unmatched metal coating ……
#6 Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Sheet & Coil
Domain Est. 1998
Website: chesterfieldsteel.com
Key Highlights: Chesterfield Steel supplies hot dipped galvanized steel sheet & coil for use in the automotive, transportation, & solar industries. Get a quote now!…
#7 Hot
Domain Est. 2001
Website: curtissteelco.com
Key Highlights: Our extensive inventory includes hot-dipped galvanized sheets and coils, designed for durability, corrosion resistance, and long-term performance….
#8 Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Sheet & Coil Supplier
Domain Est. 2006
Website: alliancesteel.net
Key Highlights: Alliance Steel’s hot-dipped galvanized steel sheet and coil service capabilities include slitting, multi-blanking and cut-to-length, metallurgical support….
#9 hot dipped galvanized steel coil sghc
Domain Est. 2022
Website: lsdsteel.com
Key Highlights: We can provide you with custom hot dipped galvanized steel coils and we will try our best to meet the specifications you want.We know many hot dipped galvanized ……
#10 Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Coils
Domain Est. 2023
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Coil

2026 Market Trends for Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Coil
H2: Steady Growth Driven by Infrastructure and Automotive Demand, Amidst Cost and Sustainability Pressures
The global market for Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel (HDG) Coil is projected for steady, albeit moderate, growth through 2026. Key drivers include robust demand from infrastructure development and the automotive sector, particularly in emerging economies. However, this growth trajectory faces significant headwinds from escalating input costs and increasing environmental regulations. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the prevailing trends shaping the market:
- Resilient Demand from Core Sectors: The construction industry remains the largest consumer of HDG coil, benefiting from ongoing urbanization, government infrastructure spending (especially in Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and parts of Africa), and the need for durable, corrosion-resistant building materials (roofing, cladding, structural sections). Simultaneously, the automotive sector continues to be a major driver, utilizing HDG steel for body panels, chassis components, and underbody parts to meet stringent safety and longevity requirements, even as electric vehicle (EV) adoption grows (EVs still require significant structural steel).
- Geographic Shifts and Capacity Expansion: Asia-Pacific, led by China and India, will dominate both production and consumption. China is focusing on consolidating its industry and shifting towards higher-value, advanced high-strength galvanized grades. India is witnessing significant capacity additions to meet its domestic infrastructure and automotive boom. Southeast Asia and the Middle East are also emerging as growth pockets.
- Price Volatility and Cost Pressures: The market will remain sensitive to fluctuations in the prices of key inputs: hot-rolled coil (HRC) and zinc. Geopolitical tensions, energy costs (especially for the energy-intensive galvanizing process), and supply chain disruptions continue to pose risks, potentially squeezing margins for producers and impacting end-user pricing.
- Technological Advancements and Product Evolution: Demand is shifting towards higher-performance HDG products. This includes:
- Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS): Increased adoption in automotive for lightweighting without sacrificing safety.
- Improved Coating Adhesion and Formability: Essential for complex automotive parts.
- Thinner Coatings with Enhanced Performance: Balancing cost and corrosion protection.
- Digitalization in Production: Implementation of AI and IoT for process optimization, quality control, and predictive maintenance.
- Sustainability and Regulatory Focus: Environmental concerns are becoming paramount:
- Energy Consumption: The galvanizing process is energy-intensive, driving investment in energy efficiency and potential shifts towards renewable energy sources.
- Zinc Emissions: Stricter regulations on zinc fume emissions from galvanizing lines are pushing investments in advanced filtration and closed-loop systems.
- Recyclability: HDG steel’s inherent recyclability remains a strong environmental advantage, but the industry faces pressure to further reduce its overall carbon footprint across the lifecycle.
- Competition from Substitutes: While HDG’s corrosion resistance is hard to match for many applications, competition from alternatives like Galvalume (aluminum-zinc alloy), organic coatings, and composites persists, particularly in cost-sensitive or niche applications. However, HDG’s cost-effectiveness and proven performance ensure its dominant position in core markets.
In conclusion, the 2026 HDG coil market outlook is one of moderate growth underpinned by fundamental demand, but navigated through a landscape of economic volatility, rising costs, and intensifying environmental scrutiny. Success for producers will depend on operational efficiency, investment in high-value products, geographic diversification, and proactive management of sustainability challenges.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Coil: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing hot dipped galvanized steel coil (HDG) from international or unfamiliar suppliers can be cost-effective, but it comes with significant risks—especially regarding quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Buyers must be vigilant to avoid common pitfalls that can lead to production delays, safety issues, and legal complications.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Coating Thickness and Adhesion
One of the most frequent quality issues is non-uniform galvanized coating thickness. Some suppliers may meet minimum standards on paper but fail to maintain consistency across batches. Thin or uneven coatings reduce corrosion resistance, leading to premature rust and failure in end-use applications. Additionally, poor adhesion can result in flaking or peeling during forming or welding.
2. Substandard Base Steel Quality
The performance of HDG coil depends heavily on the quality of the base steel. Unreliable suppliers may use low-grade raw materials to cut costs, resulting in coils with poor mechanical properties—such as tensile strength, elongation, and formability. This can compromise the structural integrity of final products.
3. Inaccurate or Falsified Test Reports
Some suppliers provide forged or misleading mill test certificates (MTCs) that claim compliance with international standards (e.g., ASTM, JIS, or EN), but the actual product fails to meet these specifications. Without independent third-party inspection, buyers may unknowingly accept subpar material.
4. Surface Defects and Contamination
Common surface issues include ash spots, zinc dross inclusions, scratches, and oil residue. These defects not only affect appearance but can interfere with downstream processes like painting, powder coating, or welding. Poor handling and storage practices during production or shipping can exacerbate contamination.
5. Lack of Process Control and Certification
Reputable HDG producers follow strict process controls and hold certifications such as ISO 9001, ISO 14001, or product-specific approvals. Suppliers without such certifications may lack consistent quality management systems, increasing the risk of variability and defects.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Compliance Risks
1. Misrepresentation of Brand and Origin
Some suppliers mislabel or “rebrand” generic or off-spec coils as premium products from well-known mills (e.g., Nippon Steel, ArcelorMittal, or POSCO). This constitutes IP infringement and can deceive buyers into paying premium prices for inferior goods.
2. Use of Counterfeit Mill Certifications
Fraudulent documentation—such as fake heat numbers, counterfeit mill stamps, or falsified test reports—is a growing issue. These documents may mimic legitimate ones but do not correspond to actual production batches, undermining traceability and compliance.
3. Unauthorized Use of Patented Coating Technologies
Certain galvanizing processes or coating formulations (e.g., Galfan, Galvalume, or proprietary anti-fingerprint coatings) are protected by patents. Unlicensed suppliers may replicate these technologies illegally, exposing buyers to IP litigation if the final product enters regulated markets.
4. Supply Chain Opacity and Lack of Traceability
A lack of transparency in the supply chain—where coils change hands through multiple intermediaries—makes it difficult to verify origin, production methods, and compliance. This opacity increases exposure to IP violations and regulatory non-compliance, especially under trade laws like the U.S. Section 301 or anti-dumping regulations.
5. Risk of Customs Seizures and Legal Liability
Importing steel coils that infringe on trademarks or patents can lead to customs detentions, fines, or even legal action against the buyer. Companies may also face reputational damage if discovered using counterfeit or non-compliant materials.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, request third-party inspections, verify certifications, and, where possible, establish direct relationships with reputable mills. Including robust quality and IP clauses in contracts—and working with legal and technical experts—can further protect against costly sourcing failures.
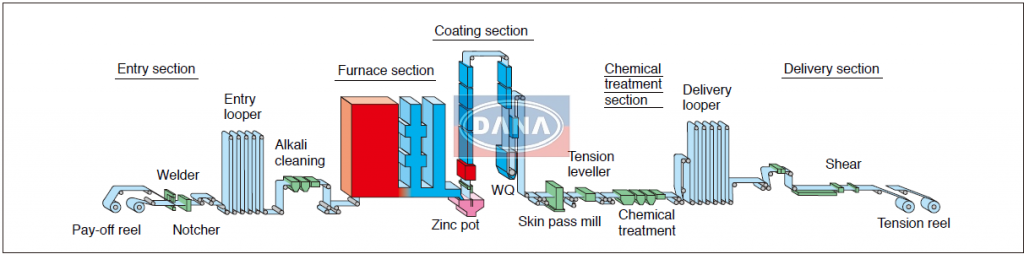
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Coil
Overview and Key Characteristics
Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Coil (HDG Coil) is a widely used material in construction, automotive, and manufacturing industries due to its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and formability. It is produced by immersing cold-rolled steel coil into a bath of molten zinc, creating a metallurgically bonded zinc-iron alloy coating. Understanding its physical and chemical properties is essential for safe and compliant logistics and handling. Key characteristics include weight (typically 5–15 metric tons per coil), diameter (up to 2,000 mm), width (600–1,500 mm), and susceptibility to mechanical damage and moisture exposure.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage during transit and storage. HDG coils are typically wrapped with moisture-resistant inner paper or plastic film, followed by a galvanized or painted steel outer jacket, secured with steel strapping. Wooden or steel pallets or coil cradles are used for support. Handling must be conducted using calibrated forklifts, overhead cranes, or coil grabbers to avoid edge damage or deformation. Coils must always be lifted and transported vertically (on their edge) and never rolled or dragged. Workers should wear appropriate PPE to prevent cuts from sharp edges.
Transportation Guidelines
HDG coils can be shipped via sea, rail, or road freight. For sea freight, coils are generally transported in open-top or flat-rack containers, or as break-bulk cargo on general cargo vessels. When using containers, proper dunnage and blocking/bracing must be used to prevent movement. On flatbed trucks or railcars, coils must be secured with heavy-duty straps, chains, or coil chocks. The load must be evenly distributed and secured to prevent shifting during transit. Avoid exposure to rain or seawater; tarpaulins or container covers should be used if necessary. Temperature and humidity control are less critical, but prolonged exposure to condensation should be avoided.
Storage Conditions
Store HDG coils indoors in a dry, well-ventilated warehouse to prevent white rust (zinc corrosion due to moisture). If outdoor storage is unavoidable, coils must be elevated on wooden blocks or racks and fully covered with waterproof tarpaulins, ensuring no water pooling. Coils should be stored vertically on their edges with adequate spacing for air circulation. Avoid direct contact with soil or concrete. Stacking should be limited to manufacturer-recommended levels to prevent deformation. Regular inspection for coating integrity and signs of corrosion is advised.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Compliance with international and local regulations is essential. Key standards include ASTM A653/A653M (USA), EN 10346 (Europe), and JIS G3302 (Japan), which define coating mass, mechanical properties, and testing methods. Import/export shipments must comply with customs documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. HDG coils may be subject to anti-dumping or countervailing duties depending on the country of origin and destination. Ensure Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are available, noting that zinc fumes can be hazardous if coils are welded or cut without proper ventilation.
Environmental and Safety Regulations
HDG steel is recyclable and generally considered environmentally stable. However, during cutting, grinding, or welding, zinc oxide fumes may be released, requiring local exhaust ventilation and respiratory protection per OSHA (USA) or similar regulations. Waste packaging materials (plastic, steel strapping) should be disposed of or recycled according to local environmental laws. Spill management plans are not typically required for intact coils, but handling residues (e.g., oil from mill grease) should comply with hazardous waste regulations if applicable.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain full traceability through batch numbers, heat numbers, and mill test certificates (MTCs) that verify chemical composition and mechanical properties. Documentation must accompany the shipment and include coating weight, steel grade, dimensions, and test results. For international trade, ensure Harmonized System (HS) code accuracy—typically 7210.70 or 7225.40 depending on composition and width. Accurate labeling on each coil or package is mandatory for identification and quality control.
Risk Management and Insurance
Given the high value and susceptibility to physical and environmental damage, HDG coils should be insured against loss, theft, corrosion, and transit damage. Common risks include coil collapse, coating scratches, moisture exposure, and improper handling. Use experienced freight forwarders familiar with steel logistics. Include inspection clauses at loading, during transit, and upon delivery. Consider third-party pre-shipment inspections for large orders to verify quality and packaging compliance.
Conclusion
Efficient and compliant logistics for Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Coil require attention to packaging, handling, transportation modes, storage conditions, and regulatory standards. A proactive approach to documentation, safety, and risk mitigation ensures product integrity, customer satisfaction, and adherence to international trade requirements. Regular training for handling personnel and auditing of logistics partners further enhance supply chain reliability.
Conclusion on Sourcing Hot-Dipped Galvanized Steel Coils
Sourcing hot-dipped galvanized steel coils requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and compliance with technical specifications. These coils are essential in industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing due to their excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and cost-effectiveness over the product lifecycle. When sourcing, it is crucial to partner with reputable suppliers or manufacturers who adhere to international standards (such as ASTM, JIS, or ISO) and have consistent quality control processes in place.
Key considerations include the zinc coating weight (e.g., Z60, Z180, Z275), coil dimensions, steel grade, surface finish, and compliance with environmental and safety regulations. Additionally, evaluating logistics, lead times, and total landed cost—including tariffs and transportation—is vital for maintaining supply chain efficiency.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of hot-dipped galvanized steel coils involves comprehensive due diligence, clear communication of technical requirements, and establishing long-term relationships with qualified suppliers. By prioritizing quality and reliability, businesses can ensure optimal performance of the end product while minimizing maintenance and replacement costs.