The high pressure pasteurization (HPP) market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for minimally processed, preservative-free foods with extended shelf life. According to Grand View Research, the global high pressure processing equipment market was valued at USD 810.3 million in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.4% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by rising adoption across the food and beverage, meat and poultry, dairy, and ready-to-eat meal sectors. As food safety regulations tighten and clean-label trends gain momentum, HPP technology has become a critical solution for ensuring microbial safety without compromising flavor, texture, or nutritional quality. With North America and Europe leading in adoption and Asia-Pacific emerging as a high-growth region, the demand for reliable and scalable HPP machines is escalating. In this evolving landscape, manufacturers are innovating to deliver higher throughput, improved energy efficiency, and automation—making the selection of the right equipment partner essential. Below is a data-driven overview of the top 9 high pressure pasteurization machine manufacturers shaping the future of food preservation.
Top 9 High Pressure Pasteurization Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Avure Technologies
Domain Est. 2002
Website: jbtc.com
Key Highlights: JBT Avure’s high pressure processing (HPP) solutions offer food and beverage producers high output, expandability, and low operating costs….
#2 Idus HPP Systems
Domain Est. 2018
Website: idushpp.com
Key Highlights: Using the latest technologies and materials, we offer first quality 6000 bar HPP machines with the most economic rates among the western manufacturers….
#3 High Pressure Food Processor (HPP) Equipment
Website: kobelco.co.jp
Key Highlights: This technology has been used for processing meat products, dairy products, seafoods, grains, including packed cooked rice these days….
#4 High Pressure Cold Processing
Domain Est. 2006
Website: nw-naturals.net
Key Highlights: High pressure cold processing systems employ pressures to inactivate many food-borne pathogens such as Salmonella, E. coli and Listeria….
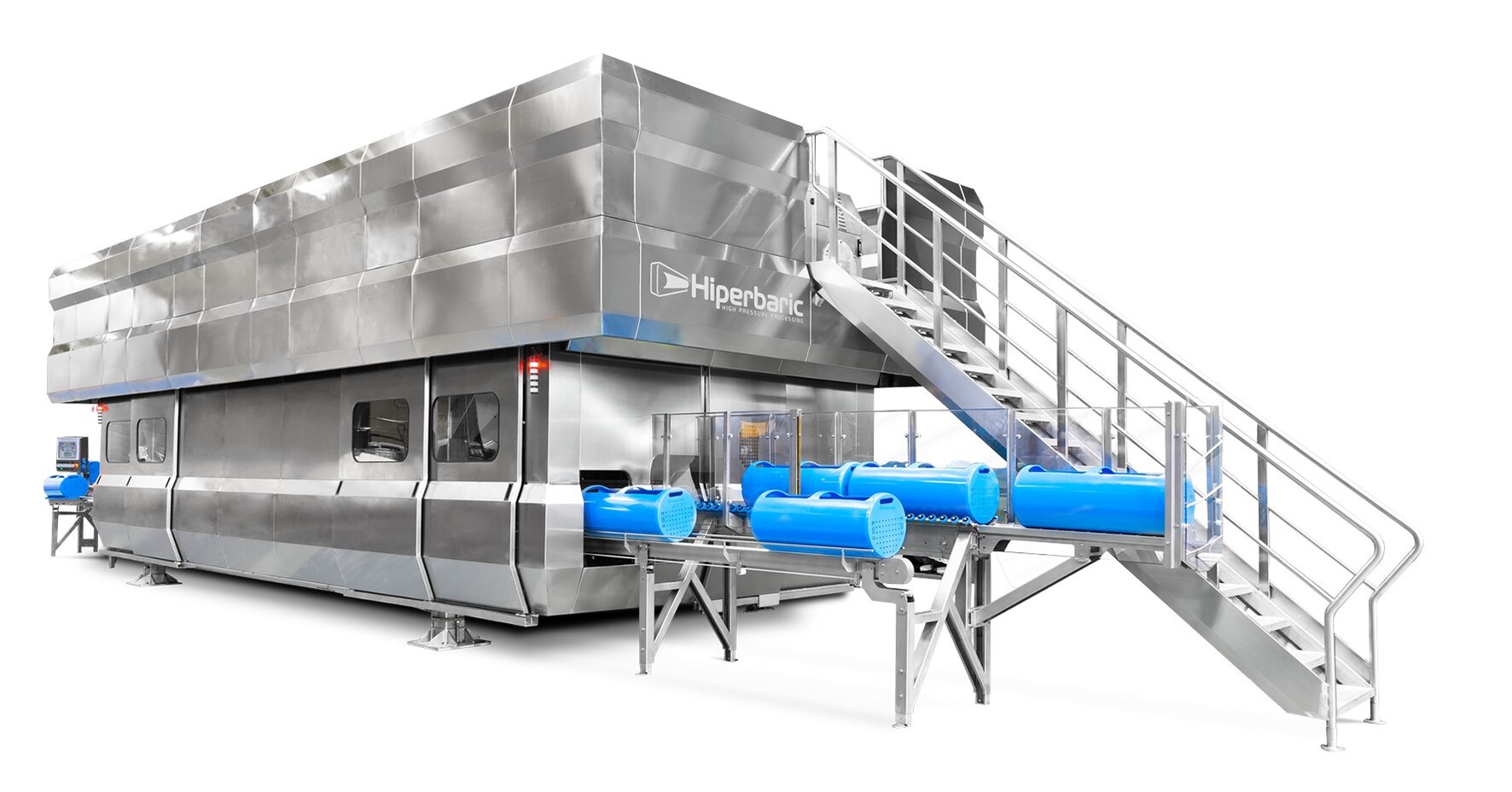
#5 Hiperbaric
Domain Est. 2011
Website: hiperbaric.com
Key Highlights: Hiperbaric designs, manufactures and market High Pressure Processing equipment since its foundation in 1999….
#6 High Pressure Processing (HPP)
Domain Est. 2011
Website: thyssenkrupp-uhde.com
Key Highlights: High pressure processing by thyssenkrupp allows gentle preservation of food by high pressure – without additives or heat….
#7 American Pasteurization Company
Domain Est. 2013
Website: americanpasteurizationcompany.com
Key Highlights: American Pasteurization Company (APC) is the first company in the United States to offer High Pressure Processing (HPP) on a commercial tolling basis….
#8 HPP Los Angeles
Domain Est. 2014
Website: hpplosangeles.com
Key Highlights: We are excited to offer high pressure pasteurization services for all food types as well as contract packaging for juices and related product lines to the Los ……
#9 Universal Pure
Domain Est. 2017
Website: universalpure.com
Key Highlights: High Pressure Processing services partnership – supporting your food safety and product quality needs nationwide….
Expert Sourcing Insights for High Pressure Pasteurization Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for High Pressure Pasteurization (HPP) Machines
The global market for High Pressure Pasteurization (HPP) machines is projected to experience substantial growth by 2026, driven by increasing consumer demand for clean-label, minimally processed foods and beverages, alongside advancements in food safety technology. Key trends shaping the HPP machinery market in 2026 include:
-
Rising Demand for Clean-Label and Natural Products
Consumers are increasingly avoiding artificial preservatives and chemical additives. HPP enables food manufacturers to extend shelf life without heat or chemicals, preserving nutritional value, flavor, and texture. This aligns perfectly with clean-label trends, particularly in ready-to-eat meals, cold-pressed juices, deli meats, and dairy alternatives. By 2026, the clean-label movement is expected to remain a dominant force, propelling HPP adoption across diverse food segments. -
Expansion in the Cold-Pressed Juice and Functional Beverage Sector
The cold-pressed juice market has been a primary early adopter of HPP technology. By 2026, this segment continues to grow, with increased interest in functional beverages—such as probiotic drinks, plant-based smoothies, and immunity-boosting formulations—further fueling demand for HPP machines. Manufacturers are investing in larger-capacity and more efficient HPP systems to meet rising production needs. -
Technological Advancements and Automation
HPP machine manufacturers are focusing on innovation to improve throughput, energy efficiency, and ease of integration into existing production lines. By 2026, next-generation HPP systems feature advanced automation, real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and Industry 4.0 compatibility. These improvements reduce operational costs and downtime, making HPP more accessible to mid-sized food processors. -
Growth in Emerging Markets
While North America and Europe remain leading adopters of HPP technology, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East are witnessing accelerated adoption. Increasing urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and greater awareness of food safety are driving investments in HPP infrastructure. Countries such as China, India, Brazil, and Mexico are expected to see a surge in HPP machine installations by 2026. -
Regulatory Support and Food Safety Standards
Global food safety regulations are becoming more stringent, particularly in response to foodborne illness outbreaks. HPP is recognized by regulatory bodies such as the FDA and USDA as an effective pathogen reduction method. This regulatory endorsement enhances confidence among producers and retailers, encouraging wider implementation of HPP across perishable food categories. -
Sustainability and Waste Reduction Initiatives
HPP contributes to sustainability by extending product shelf life, reducing food waste, and eliminating the need for thermal processing, which has a higher carbon footprint. By 2026, food companies under pressure to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are increasingly turning to HPP as part of their sustainability strategies. -
Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The HPP equipment market is seeing increased consolidation, with key players forming strategic partnerships, acquiring smaller technology firms, or collaborating with food processors to offer integrated solutions. Equipment providers are also offering HPP-as-a-Service (HaaS) models, allowing smaller brands to access the technology without heavy capital investment.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for High Pressure Pasteurization machines is characterized by strong growth, technological innovation, and expanding applications. Driven by consumer preferences, regulatory trends, and sustainability goals, HPP is poised to become a cornerstone technology in the global food safety and preservation landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing High Pressure Pasteurization (HPP) Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing a High Pressure Pasteurization (HPP) machine is a significant investment, and overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to costly problems, operational failures, and legal disputes. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Underestimating Quality and Manufacturing Standards
- Choosing Based Solely on Price: Opting for the lowest-cost machine often means sacrificing critical components, materials, and engineering rigor. Cheap alternatives may use inferior seals, weaker vessel materials, or substandard control systems, leading to frequent breakdowns, safety hazards, product inconsistency, and higher total cost of ownership.
- Ignoring Material Compatibility and Certification: The pressure vessel, seals, and wetted parts must be compatible with your specific products (e.g., acidic juices, high-fat meats) and meet stringent food safety standards (e.g., FDA, EU 1935/2004, 3-A Sanitary Standards). Failure to verify certifications (ASME, PED) for the pressure vessel can result in regulatory non-compliance and safety risks.
- Overlooking Proven Reliability and Uptime: HPP machines are complex. Sourcing from a supplier without a strong track record of reliability in your specific application (e.g., pouch size, throughput) can lead to excessive downtime, missed production schedules, and lost revenue. Request references and verify actual uptime data.
- Neglecting Service and Support Infrastructure: A machine is only as good as the support behind it. Sourcing from a supplier without readily available spare parts, trained technicians, and responsive customer service in your region can turn minor issues into major production stoppages. Ensure clear service level agreements (SLAs).
2. Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
- Purchasing Machines with Infringing Technology: Some suppliers, particularly newer or less reputable ones, may incorporate patented technologies (e.g., specific valve designs, control algorithms, sealing mechanisms, water management systems) without proper licensing. As the end-user, you could be drawn into costly infringement lawsuits, face machine seizure, or be forced to pay retroactive licensing fees.
- Lack of IP Verification: Failing to conduct due diligence on the supplier’s IP position is a major risk. Reputable HPP leaders (e.g., Hiperbaric, Avure/BAE Systems) hold extensive patent portfolios. Ensure the supplier can demonstrate freedom-to-operate or provide proof of necessary licenses for all critical components and processes used in their machine.
- Unclear Ownership of Customizations: If you require specific modifications or integrations, the contract must explicitly define who owns the IP for these custom elements. Ambiguity can lead to disputes later, especially if the machine is resold or the supplier becomes uncooperative.
- Vulnerability to Trade Secret Theft: Sharing detailed product formulations or processing parameters during machine qualification with an untrusted supplier risks exposing sensitive trade secrets. Ensure robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are in place before sharing confidential information.
3. Insufficient Due Diligence on the Supplier
- Failing to Validate Claims: Don’t accept brochures and sales pitches at face value. Demand third-party validation, independent test reports, and on-site demonstrations using your products in your packaging. Verify performance claims (throughput, pressure, cycle time).
- Ignoring Financial and Operational Stability: Sourcing from a financially unstable or operationally immature supplier increases the risk of project delays, abandonment, or the company going out of business, leaving you without support or spare parts.
- Overlooking Integration Complexity: HPP machines are not standalone units. They require integration with upstream (loading) and downstream (unloading, potentially secondary packaging) automation. Ensure the supplier has proven experience integrating their machines into complete lines and can provide clear specifications for interfaces.
Mitigation Strategy: Prioritize suppliers with established reputations, verifiable certifications, transparent IP documentation, robust service networks, and a proven history of successful installations in your industry segment. Invest in thorough technical and legal due diligence before committing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for High Pressure Pasteurization (HPP) Machine
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
High Pressure Pasteurization (HPP) machines are subject to numerous regulatory standards to ensure food safety, worker safety, and environmental compliance. Adherence to these regulations is mandatory for legal operation and market access.
Food Safety Regulations
– FSMA (U.S. Food Safety Modernization Act): HPP units must be integrated into a facility’s Hazard Analysis and Risk-Based Preventive Controls (HARPC) plan. Operators must validate that HPP effectively controls identified pathogens (e.g., Listeria, E. coli, Salmonella) in specific product matrices.
– FDA 21 CFR Part 113 (Thermally Processed Low-Acid Foods): While HPP is non-thermal, facilities using HPP on low-acid foods must still comply with relevant aspects of food safety systems, including recordkeeping and process validation.
– USDA FSIS (for meat, poultry, and egg products): HPP treatment of USDA-regulated products requires prior approval. The process must be validated and included in the facility’s HACCP plan. Labeling must reflect HPP use if it impacts product claims (e.g., “cold-pressed,” “no preservatives”).
– Codex Alimentarius & International Standards: For export, compliance with Codex General Principles of Food Hygiene (CXC 1-1969) and specific HPP guidance from bodies like IFT and EFSA may be required.
Machine Safety & Certification
– CE Marking (Europe): HPP machines placed in the EU must comply with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), Pressure Equipment Directive (2014/68/EU), and relevant EN standards (e.g., EN 12100 for safety of machinery).
– ASME Certification (U.S.): Pressure vessels must meet ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (Section VIII) standards and be stamped by an authorized inspector.
– OSHA Compliance: Adhere to OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 (Lockout/Tagout), 1910.146 (Permit-Required Confined Spaces), and 1910.212 (Machine Guarding) to protect personnel.
Environmental & Facility Regulations
– Local Building & Zoning Codes: Installation must conform to structural load limits, utility connections (water, power, drainage), and noise ordinances.
– EPA & Local Water Regulations: Discharge of process water (especially if treated with antimicrobials) may require pretreatment or permits under the Clean Water Act.
Installation & Site Preparation
Proper site preparation is essential for safe and efficient HPP machine operation.
Facility Requirements
– Structural Integrity: The floor must support the machine’s weight (typically 10–20+ tons) with vibration dampening. Reinforced concrete foundations are usually required.
– Utility Supply:
– Water: High-purity water (deionized or reverse osmosis) for pressure transmission, typically 30–100 GPM at 50–60 psi.
– Power: 480V 3-phase electrical supply with dedicated circuit (50–200+ kW depending on unit size).
– Compressed Air: Clean, dry air (90–120 psi) for controls and door actuation.
– Drainage: Floor drains capable of handling high-volume water discharge during depressurization cycles.
– Space Allocation: Allow minimum 3–5 feet clearance on all sides for maintenance, safety zones, and compliance with NFPA 70 (NEC) and fire codes.
Environmental Controls
– Maintain ambient temperature between 50–85°F (10–30°C) and humidity below 80% to protect electrical and hydraulic components.
– Provide adequate ventilation to dissipate heat from pumps and hydraulic systems.
Transportation & Handling
HPP machines are large, heavy, and sensitive systems requiring specialized logistics.
Pre-Shipment Planning
– Confirm machine dimensions, weight, and center of gravity with the manufacturer.
– Obtain necessary transportation permits for oversized/overweight loads if shipping by road.
– Coordinate with freight forwarder experienced in industrial machinery.
Shipping & Delivery
– Use flatbed trailers with cranes or forklifts rated for the machine’s weight.
– Secure the machine with bracing and protective covers during transit.
– Inspect for damage upon arrival; document and report any issues immediately.
On-Site Handling
– Use slings, lifting beams, or spreader bars attached to designated lifting points only.
– Avoid dragging or tilting the machine. Use rollers or skid systems designed for heavy loads.
– Ensure clear access path with no overhead obstructions or floor weak points.
Operational Compliance & Maintenance
Sustained compliance depends on rigorous operational and maintenance protocols.
Process Validation & Monitoring
– Conduct initial and periodic validation studies (e.g., inoculated pack studies) to prove lethality against target pathogens.
– Maintain logs of pressure (up to 87,000 psi), time, temperature, and product dwell time for each batch.
– Calibrate pressure transducers, temperature probes, and timers annually or per manufacturer’s schedule.
Sanitation & Hygiene
– Implement a preventive maintenance (PM) schedule including:
– Daily: Clean seals, chamber, and water reservoir.
– Weekly: Inspect high-pressure seals and O-rings.
– Quarterly: Flush and replace transmission fluid; inspect hydraulic system.
– Follow a written Sanitation Standard Operating Procedure (SSOP) aligned with GMPs and facility food safety plan.
Recordkeeping
– Retain process records, maintenance logs, calibration certificates, and validation reports for a minimum of 2 years (or as required by customer or regulation).
– Ensure electronic records comply with FDA 21 CFR Part 11 if applicable (audit trails, electronic signatures).
Training & Personnel Safety
Only trained personnel should operate or maintain HPP equipment.
Operator Training
– Provide comprehensive training on:
– Machine startup/shutdown procedures.
– Emergency stop functions and lockout/tagout (LOTO).
– Recognizing seal failures or pressure anomalies.
– Proper loading techniques to prevent chamber damage.
– Require certification before unsupervised operation.
Safety Procedures
– Enforce use of PPE: safety glasses, hearing protection, cut-resistant gloves.
– Install safety interlocks, warning lights, and barriers around the machine.
– Conduct regular safety drills and machine-specific hazard assessments.
Labeling & Consumer Communication
HPP use may impact product labeling and marketing claims.
- Label Accuracy: If HPP enables “preservative-free” or “fresh-like” claims, ensure these are truthful and not misleading (per FTC and FDA guidelines).
- Allergen & Ingredient Disclosure: HPP does not eliminate allergens; standard labeling rules apply.
- Process Transparency: Some retailers or consumers require disclosure of HPP use; verify buyer specifications.
Adhering to this guide ensures safe, compliant, and efficient operation of High Pressure Pasteurization equipment across the supply chain. Always consult machine-specific manuals and regulatory authorities for up-to-date requirements.
Conclusion: Sourcing a High-Pressure Pasteurization (HPP) Machine
Sourcing a High-Pressure Pasteurization (HPP) machine is a strategic investment that can significantly enhance food safety, extend shelf life, and preserve the nutritional and sensory qualities of fresh and minimally processed foods. As consumer demand for clean-label, preservative-free products continues to grow, HPP technology offers a competitive advantage by enabling producers to meet market expectations without compromising product quality.
When sourcing an HPP machine, it is essential to evaluate key factors such as production capacity, equipment reliability, scalability, technical support, and total cost of ownership. Engaging with reputable manufacturers, reviewing case studies, and potentially visiting operational sites can provide valuable insights into real-world performance and reliability.
Additionally, considerations around integration with existing production lines, compliance with food safety regulations, and staff training must not be overlooked. While the initial capital investment may be substantial, the long-term benefits—such as reduced spoilage, expanded distribution reach, and enhanced brand reputation—often justify the expenditure.
Ultimately, selecting the right HPP system requires a balanced approach that aligns technological capabilities with business goals. By carefully assessing vendor offerings and anticipating future growth, companies can successfully implement HPP technology to drive innovation, ensure product safety, and gain a sustainable edge in the evolving food and beverage industry.