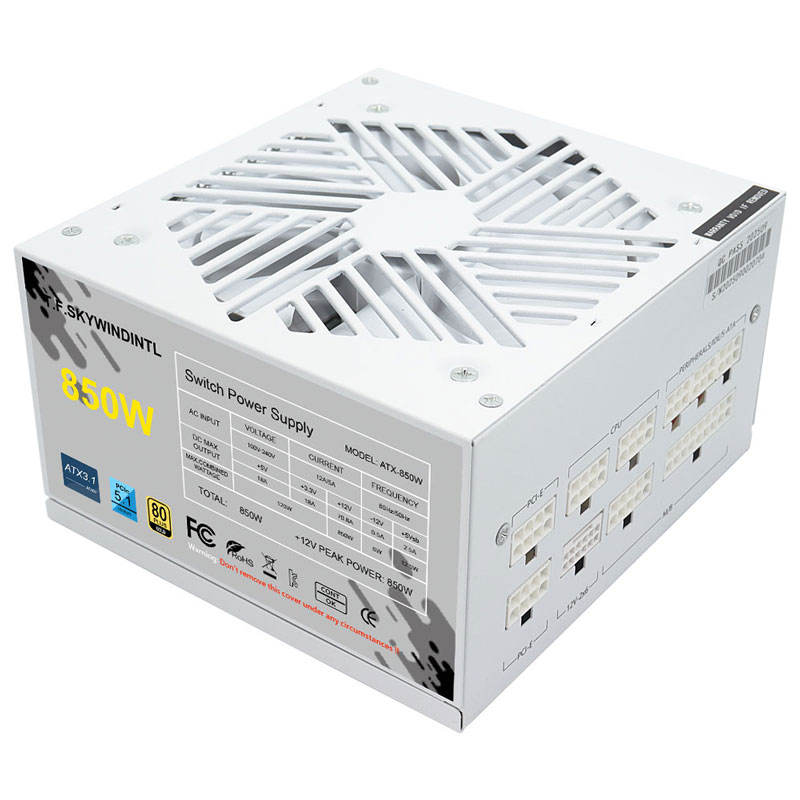
The global power supply unit (PSU) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient computing systems, data center expansion, and advancements in gaming and high-performance hardware. According to Mordor Intelligence, the PSU market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2023 to 2028, with high power units (800W and above) witnessing accelerated adoption across gaming PCs, workstations, and AI-enabled systems. This surge is further supported by increasing investments in cloud infrastructure and the proliferation of power-hungry GPUs and CPUs, which require reliable, high-efficiency power delivery. As energy standards tighten and consumer expectations for performance and reliability rise, manufacturers specializing in high power PSUs are positioned at the forefront of innovation. Based on market share, efficiency certifications, technological advancements, and customer trust, the following five companies have emerged as leaders in the high power PSU segment.
Top 5 High Power Psu Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Gaming PSU
Domain Est. 2008
Website: highpower-tech.com
Key Highlights: HIGH POWER Brand. About Us · Company Profile · Why High Power · Contact Us · Products … SFX-250 BR. Copyright © HIGH POWER ELECTRONIC CO., LTD. All rights ……
#2 Highpower Technology
Domain Est. 2010
Website: highpowertech.com
Key Highlights: Highpower Technology (stock code: 001283) was found in 2002, and committed to the research, design, manufacturing and sales of Li-ion and Ni-MH batteries, ……
#3 How good are High Power PSUs?
Domain Est. 1997
Website: forums.tomshardware.com
Key Highlights: I know High Power makes decent PSUs, but this one is better to avoid as there is no info anywhere, not even on 80 plus list of PSUs….
#4 HIGH POWER® power supply
Domain Est. 2001
Website: highpowersupply.com
Key Highlights: High quality computer power supply units and building block components for servers, compact PCs, and gaming computers. Designed in California…
#5 New DIY Eurorack High Power Supply
Domain Est. 2021
Website: modwiggler.com
Key Highlights: New DIY Eurorack High Power Supply. From circuitbending to homebrew stompboxes & synths, keep the DIY spirit alive! 14 posts • Page 1 of 1….
Expert Sourcing Insights for High Power Psu

H2: 2026 Market Trends for High Power PSUs
The High Power Power Supply Unit (PSU) market in 2026 is poised for dynamic growth and significant transformation, driven by escalating energy demands from advanced computing, industrial automation, and the global push for sustainability. Key trends shaping this market include:
1. Surging Demand from AI and Data Centers: The exponential growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and high-performance computing (HPC) will be the primary engine for high-power PSU adoption. AI training clusters and next-generation data centers housing thousands of GPUs/TPUs (requiring 700W, 1000W, 1200W, and even 1600W+ per unit) will demand PSUs with extreme power density, superior efficiency (approaching or exceeding Titanium standards), and exceptional thermal management. Liquid-cooled PSUs are expected to emerge as a critical solution to manage the intense heat generated.
2. Advancement in Efficiency and Power Density: Regulatory pressures (like updated ENERGY STAR and EU CoC Tier 2 standards) and operational cost concerns will push manufacturers towards even higher efficiency levels. Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) semiconductor technologies will become more mainstream, enabling smaller, lighter, and significantly more efficient PSUs (e.g., >96% efficiency at 50% load). This focus on power density will be crucial for space-constrained applications like dense server racks and advanced workstations.
3. Rise of Modular and Customizable Solutions: Flexibility will be key. The market will see increased demand for highly modular PSUs (especially in industrial and telecom sectors) allowing users to configure voltage rails, power levels, and form factors. Custom high-power solutions for specialized applications (e.g., medical imaging, semiconductor manufacturing, renewable energy integration) will grow, moving beyond standard off-the-shelf units.
4. Integration of Smart Features and Digital Control: High-power PSUs will increasingly incorporate digital control (e.g., PMBus, digital twins) and smart monitoring. Features like real-time telemetry (voltage, current, temperature, fan speed), predictive maintenance alerts, remote configuration, and seamless integration into broader power management systems (DCIM) will become standard, enhancing reliability, uptime, and energy optimization.
5. Focus on Reliability, Redundancy, and Sustainability: As critical infrastructure depends on high-power PSUs, reliability and Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) will be paramount. N+1 and N+N redundant configurations will remain essential in data centers. Simultaneously, sustainability will drive the use of recyclable materials, reduced packaging, and designs focused on longevity and repairability. The carbon footprint of manufacturing and operation will be a key differentiator.
6. Expansion Beyond Traditional Computing: While data centers and high-end PCs remain core markets, growth will accelerate in adjacent sectors:
* Industrial Automation: Robotics, advanced CNC machines, and large-scale PLCs require robust, high-reliability PSUs.
* Telecommunications: 5G/6G network densification and edge computing nodes need efficient, compact high-power solutions.
* Renewable Energy & EVs: Integration with solar/wind inverters and fast-charging EV infrastructure will create new demand for specialized high-power conversion units.
* Gaming and Content Creation: Enthusiast desktops with multiple high-end GPUs will sustain demand for 1000W+ PSUs with advanced features.
In summary, the 2026 high-power PSU market will be characterized by relentless innovation driven by AI’s voracious appetite for power, a technological shift towards wide-bandgap semiconductors for efficiency and density, the integration of intelligence and connectivity, and expanding applications across diverse high-tech industries, all underpinned by an increasing emphasis on sustainability and reliability.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing High-Power PSUs (Quality & IP)
Sourcing high-power power supply units (PSUs) requires careful evaluation to ensure reliability, safety, and long-term performance. Overlooking key aspects can lead to system failures, downtime, or safety hazards. Below are common pitfalls related to quality and ingress protection (IP) ratings that buyers should be aware of.
Overlooking Component Quality and Build Standards
Many low-cost PSUs use substandard components such as electrolytic capacitors with short lifespans, poorly wound transformers, or inadequate PCB layouts. These compromises may not be visible externally but significantly impact efficiency, thermal performance, and longevity. Always verify the use of industrial-grade components and check for certifications like UL, CE, or 80 PLUS (where applicable) to ensure minimum quality benchmarks.
Misinterpreting or Falsifying IP Ratings
A common pitfall is assuming the advertised IP (Ingress Protection) rating reflects real-world performance. Some manufacturers may claim high IP ratings (e.g., IP67) without third-party validation. Always request test reports or certification documents from accredited labs. An IP67 rating, for example, requires the PSU to withstand dust ingress and temporary immersion in water—ensure it has been properly tested under these conditions.
Inadequate Thermal Management
High-power PSUs generate significant heat. If thermal design is poor—such as insufficient heatsinking, lack of airflow optimization, or low-quality thermal interface materials—the unit can overheat, leading to derating or failure. Check whether the PSU maintains full output power across its specified temperature range and verify if forced air cooling is required.
Ignoring Real-World Efficiency and Load Behavior
Efficiency ratings (e.g., 90%) are often quoted at ideal load conditions (e.g., 50–75% load). However, performance may degrade significantly at low or maximum loads. Review full load efficiency curves and ensure the PSU operates efficiently within your expected load profile. Poor efficiency increases operating costs and heat output.
Assuming Uniform Quality Across Brands and Suppliers
Not all PSUs labeled with the same specs perform equally. Reputable industrial suppliers often provide better quality control, traceability, and after-sales support compared to generic or grey-market alternatives. Beware of counterfeit or rebranded units that mimic well-known brands but fail under sustained load.
Overlooking Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Ensure the PSU meets relevant safety (e.g., IEC/UL 62368-1), EMC (e.g., EN 55032), and environmental standards (e.g., RoHS, REACH). Non-compliant units may pass initial testing but fail under regulatory audit or cause interference with sensitive equipment.
Underestimating the Importance of Mechanical and Mounting Design
High-power PSUs often require secure mounting and proper cable strain relief. Units with flimsy enclosures or poor connector retention can fail mechanically over time, especially in environments with vibration or frequent handling. Verify build quality, ingress protection at cable entry points, and compatibility with your enclosure or rack system.
Skipping Long-Term Reliability and MTBF Data
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) figures can be misleading if based on ideal lab conditions. Scrutinize how MTBF was calculated (e.g., MIL-HDBK-217 vs. Telcordia), and look for field reliability data or customer feedback. High-power PSUs used in critical applications should have proven track records.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: request detailed technical documentation, demand third-party certifications, and consider pilot testing before full-scale deployment. Investing time upfront ensures a robust, safe, and reliable power solution.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for High Power PSU
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
High Power Power Supply Units (PSUs) are subject to a range of international and regional regulations due to their electrical nature, energy consumption, and potential environmental impact. Compliance ensures market access, safety, and environmental responsibility.
Safety Standards
– IEC/UL 62368-1: Primary safety standard for audio/video, information, and communication technology equipment, including high power PSUs. Mandates protection against electric shock, fire, and mechanical hazards.
– UL 1310 (Class 2 Power Units): Applies if the PSU operates within Class 2 output limits; otherwise, full IEC 62368-1 compliance is required.
– Regional equivalents include:
– EN 62368-1 (Europe)
– CSA C22.2 No. 62368-1 (Canada)
– CCC (China)
– PSE (Japan)
– KC (South Korea)
EMC & EMI Regulations
– EMC Directive 2014/30/EU (Europe): Requires electromagnetic compatibility—PSUs must not interfere with other devices and must withstand interference.
– FCC Part 15 Subpart B (USA): Regulates unintentional radiators; Class A or B depending on use environment.
– CISPR 32: International standard for multimedia equipment emissions, widely adopted globally.
Energy Efficiency & Environmental Directives
– DoE Level VI (USA): Mandates minimum efficiency and no-load power consumption limits.
– EU Ecodesign Directive (Lot 6, Regulation 2019/1782): Sets efficiency and no-load performance requirements for external power supplies.
– Energy Star (80 PLUS Certification for PSUs): Voluntary but market-advantageous, especially for computing and data center applications.
– RoHS (EU), REACH, and China RoHS: Restrict hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and phthalates in electrical components.
Labeling & Documentation
– Product labeling must include:
– Manufacturer name/model/serial
– Input/output voltage and current
– Safety certifications (e.g., CE, UL, FCC)
– Efficiency rating (e.g., 80 PLUS Bronze, Gold)
– User manuals and technical documentation must be provided in local languages where required.
Logistics & Transportation Considerations
High power PSUs often involve heavy, sensitive electronic components and may include batteries or hazardous materials, affecting shipping protocols and supply chain planning.
Packaging Requirements
– Use ESD-safe (electrostatic discharge) materials to protect sensitive circuits.
– Include shock-absorbent padding (e.g., foam inserts) to prevent damage during transit.
– Seal in moisture-resistant bags if shipping to humid environments.
– Clearly label packages with:
– “Fragile”
– “This Side Up”
– “Do Not Stack”
– Compliance marks (e.g., CE, UL)
Weight & Dimension Constraints
– High power PSUs (e.g., 1000W+) are often heavy (5–15 kg) and bulky.
– Optimize palletization and container loading; consider LTL (Less Than Truckload) vs. FTL (Full Truckload) based on volume.
– Confirm compliance with carrier size/weight limits (e.g., UPS, FedEx, DHL).
Hazardous Materials & Shipping Restrictions
– Most high power PSUs do not contain hazardous materials if RoHS-compliant.
– If integrated batteries (e.g., backup UPS units) are present, classify under UN 3481 (PI 966) or UN 3091 (PI 967) per IATA/IMDG regulations.
– Always provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) if requested.
Customs & Import Compliance
– Prepare accurate Commercial Invoices, Packing Lists, and Certificates of Origin.
– Include HS (Harmonized System) Code: Typically 8504.40 (electronic power supply units).
– Declare correct value, country of origin, and applicable certifications.
– Be aware of import duties and VAT in destination countries (e.g., EU VAT, US HTSUS tariffs).
Warehousing & Handling
– Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments (10–30°C recommended).
– Avoid stacking beyond specified limits to prevent bottom-unit damage.
– Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory rotation to prevent obsolescence.
– Use anti-static flooring and handling procedures in fulfillment centers.
Market-Specific Compliance Checklist
| Region | Safety | EMC | Efficiency | Labeling |
|————–|—————-|————–|——————|——————|
| USA/Canada | UL/CSA 62368-1 | FCC Part 15 | DoE Level VI | UL, FCC, Energy Guide |
| EU | EN 62368-1 | EMC Directive| Ecodesign Lot 6 | CE, RoHS |
| UK | UKCA | UKCA | UK Ecodesign | UKCA, RoHS |
| China | CCC | China EMC | GB 20943 | CCC, CQC |
| Japan | PSE (METI) | VCCI | Top Runner | PSE Mark |
| South Korea | KC | KC EMC | Energy Efficiency| KC Mark |
Recommended Best Practices
- Pre-Certification Testing: Engage accredited labs to test prototypes early.
- Supplier Compliance Management: Ensure component suppliers are RoHS/REACH compliant.
- Documentation Archive: Maintain compliance certificates, test reports, and design files for audits.
- Logistics Partner Selection: Choose carriers experienced in handling sensitive electronics.
- Traceability: Implement serial number tracking for warranty and recall purposes.
Adhering to this guide ensures your high power PSU meets global standards, reduces supply chain risks, and accelerates time-to-market.
In conclusion, sourcing a high-power power supply unit (PSU) requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure reliability, efficiency, and compatibility with your system’s demands. It is essential to determine the actual power requirements of your components—especially the CPU and GPU—while allowing headroom for peak loads and future upgrades. Prioritizing units with high efficiency ratings (80 Plus Gold, Platinum, or higher), robust build quality, and modular cabling enhances performance and system manageability. Additionally, selecting a reputable brand with strong safety certifications and warranty support minimizes risks of failure and ensures long-term durability. Ultimately, investing in a high-quality, high-power PSU not only safeguards your components but also contributes to a stable, efficient, and future-proof computing setup.