The global heat exchanger market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing energy efficiency demands across industries such as oil & gas, power generation, and HVAC. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 20.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% through 2028. This growth trajectory underscores the rising emphasis on thermal efficiency, process optimization, and sustainability in industrial operations. As energy costs climb and environmental regulations tighten, manufacturers are prioritizing high-performance heat exchangers that maximize heat transfer while minimizing energy loss. Against this backdrop, a select group of innovators has emerged as leaders in efficiency-driven design, advanced materials, and smart thermal solutions. Here’s a data-informed look at the top 10 heat exchanger manufacturers setting the benchmark for performance and reliability in today’s evolving industrial landscape.
Top 10 Heat Exchanger Efficiency Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Heat Exchangers for Industrial & Mobile Applications
Domain Est. 1997
Website: thermaltransfer.com
Key Highlights: Leading US-based manufacturer of heat exchangers for industrial and mobile applications. Custom, pre-engineered and off-the-shelf solutions with fast lead ……
#2 Tranter: Responsive Heat Exchangers
Domain Est. 1995
Website: tranter.com
Key Highlights: At Tranter, we specialize in advanced gasketed and welded plate heat exchangers. As a global manufacturer, we are committed to precision and localized service….
#3 Heat exchangers – brazed and gasketed
Domain Est. 1995
Website: danfoss.com
Key Highlights: Our cutting-edge heat exchangers are engineered to deliver exceptional heat transfer efficiency, optimized for both HVAC systems and a wide range of industrial ……
#4 Global Manufacturer of Heat Exchangers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: heatex.com
Key Highlights: Heatex specializes in plate and rotary heat exchangers used in ventilation and thermal management applications worldwide….
#5 Heat Exchanger Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2001
Website: heatexchangermanufacturers.com
Key Highlights: At Ward Vessel and Exchanger, we take pride in designing and manufacturing heat exchangers and pressure vessels that reflect the depth of our engineering ……
#6 Kelvion
Domain Est. 2005
Website: kelvion.com
Key Highlights: Our high-quality heat exchangers for the HVAC industry are specially designed to ensure maximum performance and efficiency. With years of experience in the ……
#7 Heat Exchanger Repair & Fabrication
Domain Est. 2012
Website: altexinc.com
Key Highlights: Altex Industries designs and manufactures high-performance industrial heat exchangers for energy, chemical, and process industries with superior efficiency ……
#8 FUNKE
Website: funke.de
Key Highlights: FUNKE Wärmeaustauscher Apparatebau GmbH is a leading specialist in the development and production of heat exchangers for industrial use. Find out more now!…
#9 Exchanger Industries
Website: exchangerindustries.com
Key Highlights: We have more than six decades of experience in engineering, manufacturing & designing efficient industrial heat exchangers & heat recovery solutions for a ……
#10 Alfa Laval
Domain Est. 2002
Website: alfalaval.us
Key Highlights: Alfa Laval is a global leader in the design and manufacture of fluid handling equipment, epitomizing innovation, efficiency and reliability….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Heat Exchanger Efficiency

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Heat Exchanger Efficiency
As the global push for energy efficiency, sustainability, and decarbonization intensifies, the heat exchanger market is undergoing transformative changes heading into 2026. Driven by industrial modernization, regulatory pressures, and technological innovation, improvements in heat exchanger efficiency have become a central focus across sectors such as power generation, oil & gas, HVAC, chemical processing, and renewable energy. Below are the key market trends shaping heat exchanger efficiency in 2026:
1. Adoption of Advanced Materials for Enhanced Thermal Performance
In 2026, manufacturers are increasingly utilizing high-performance materials such as titanium alloys, advanced composites, and nano-coated surfaces to improve thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. These materials enable thinner walls and higher heat transfer rates while maintaining durability under extreme conditions. The integration of graphene-based coatings is emerging as a breakthrough for reducing fouling and enhancing thermal efficiency by up to 25% in certain applications.
2. Rise of Compact and Modular Heat Exchanger Designs
Compact heat exchangers—such as plate-fin, printed circuit (PCHE), and microchannel types—are gaining traction due to their high surface-area-to-volume ratios and reduced footprint. These designs are particularly favored in aerospace, LNG processing, and electric vehicle thermal management systems. Modular and scalable units allow for easier integration into existing systems and support rapid deployment in distributed energy systems, aligning with the industrial shift toward flexibility and digitalization.
3. Integration of Digital Twin and AI-Driven Optimization
By 2026, digital transformation is significantly impacting heat exchanger performance monitoring and maintenance. The adoption of digital twin technology enables real-time simulation of heat transfer dynamics, allowing operators to optimize flow rates, detect fouling early, and predict maintenance needs. Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms analyze operational data to continuously tune control parameters, improving system efficiency by 10–20% and reducing downtime.
4. Focus on Fouling Mitigation and Self-Cleaning Technologies
Fouling remains one of the largest contributors to efficiency loss in heat exchangers. In response, 2026 sees increased deployment of anti-fouling surface treatments, ultrasonic cleaning systems, and pulsating flow technologies. Electromagnetic and acoustic-based cleaning mechanisms are being integrated directly into heat exchanger units, minimizing cleaning cycles and extending operational life.
5. Regulatory and Energy Efficiency Standards Driving Innovation
Stricter environmental regulations, such as the EU’s Ecodesign Directive and U.S. DOE efficiency standards, are compelling industries to upgrade legacy heat exchange systems. In particular, industries subject to carbon pricing or emissions caps are investing in high-efficiency recuperators and regenerators to recover waste heat. This regulatory pressure is accelerating R&D in next-generation designs that achieve over 90% thermal recovery efficiency.
6. Growth in Renewable and Low-Carbon Applications
The expansion of green hydrogen production, geothermal energy, and concentrated solar power (CSP) is creating new demand for highly efficient heat exchangers capable of operating with non-conventional fluids and at extreme temperatures. Supercritical CO₂ (sCO₂) power cycles, which require compact and highly efficient heat exchangers, are expected to be a major growth area, especially in next-gen nuclear and solar thermal plants.
7. Regional Market Dynamics and Supply Chain Resilience
Asia-Pacific, led by China and India, dominates the heat exchanger market in 2026 due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. However, North America and Europe are seeing strong growth in retrofitting and efficiency upgrades, driven by sustainability mandates. Supply chain localization is also a trend, as manufacturers seek to reduce dependency on raw material imports and ensure continuity for critical components.
Conclusion
By 2026, the heat exchanger market is increasingly defined by efficiency as a key performance indicator. Technological advancements, digital integration, and regulatory pressures are collectively pushing the industry toward smarter, more sustainable, and higher-performing solutions. Companies that invest in innovative designs, predictive maintenance, and material science will lead the market, positioning heat exchangers as pivotal enablers of global energy transition and industrial efficiency.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Heat Exchanger Efficiency (Quality, Intellectual Property)
Sourcing heat exchangers involves critical decisions beyond just price and delivery. Focusing solely on upfront cost can lead to significant long-term penalties related to performance, reliability, and intellectual property (IP) risks. Here are key pitfalls to avoid, particularly concerning efficiency, quality, and IP:
1. Prioritizing Lowest Initial Cost Over Lifecycle Efficiency
The most common and costly mistake is selecting a supplier based purely on the lowest purchase price. This often leads to:
* Compromised Materials: Suppliers may use thinner tubes, lower-grade alloys (e.g., inferior stainless steel), or substandard gasket materials to cut costs, reducing corrosion resistance and lifespan.
* Poor Design & Manufacturing Tolerances: Inadequate design optimization (e.g., suboptimal baffle spacing, tube layout) or sloppy fabrication (poor tube-to-tubesheet joints, misaligned baffles) creates flow maldistribution, hotspots, and increased pressure drop, drastically lowering actual efficiency below theoretical or quoted figures.
* Hidden Costs: Lower efficiency means higher energy consumption (pumping power, reduced heat recovery), more frequent cleaning, shorter service life, and increased downtime, far outweighing the initial savings.
2. Inadequate Verification of Efficiency Claims & Performance Guarantees
Relying solely on supplier-provided data sheets or vague “high efficiency” claims is risky:
* Unverified Simulations: Suppliers may use overly optimistic simulation results (e.g., assuming perfect flow distribution, clean surfaces) that don’t reflect real-world conditions.
* Lack of Test Certificates: Failure to demand and verify independent performance testing (e.g., according to TEMA, HEI, or ASME standards) under representative conditions.
* Vague Guarantees: Accepting performance guarantees without clear, measurable criteria (specific heat transfer rates, pressure drops at defined flow rates/temperatures) and consequences for non-compliance. Guarantees should be tied to the as-delivered unit, not just design.
3. Neglecting Quality Control and Manufacturing Oversight
Assuming compliance with standards (e.g., ASME, PED) is sufficient oversight is a major pitfall:
* Insufficient QA/QC Processes: Suppliers in cost-driven regions may have weak quality systems, leading to inconsistent welding quality, dimensional errors, or improper cleaning/pickling.
* Lack of Witness Points: Not specifying mandatory hold/witness points in the purchase order (e.g., witnessing pressure tests, non-destructive testing – NDT like RT/UT/PT, final dimensional inspection) allows defects to go undetected.
* Material Traceability Gaps: Inadequate documentation (MTRs – Material Test Reports) or inability to verify the actual materials used, raising concerns about authenticity and corrosion resistance.
4. Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Risks and Design Ownership
This is a critical but often underestimated pitfall:
* Copying Proprietary Designs: Sourcing from suppliers known to reverse-engineer or copy patented heat exchanger designs (e.g., specific plate patterns, enhanced tube geometries, proprietary baffle configurations) exposes the buyer to infringement lawsuits. Due diligence on the supplier’s design origin is essential.
* Unclear Design Ownership/Transfer: Failing to explicitly state in contracts whether the design is standard, custom, and who owns the IP rights. Purchasing a custom-designed exchanger without securing the right to future replicas or modifications creates dependency and risk.
* “Grey Market” or Counterfeit Components: Sourcing replacements or spare parts from unauthorized channels risks receiving inferior or counterfeit components that damage the original equipment and void warranties.
5. Ignoring Long-Term Support and Spare Parts Availability
Efficiency and reliability depend on maintainability:
* Supplier Longevity & Commitment: Choosing a supplier with poor financial health or a history of exiting product lines risks being unable to obtain critical spare parts (tubes, plates, gaskets) or technical support for repairs, leading to extended downtime and forced replacement.
* Proprietary vs. Standard Designs: Highly proprietary designs might offer peak efficiency but create vendor lock-in and exorbitant spare part costs. Balancing efficiency with standardization (e.g., using common tube sizes, standard flange types) enhances long-term supportability.
* Inadequate Documentation: Receiving insufficient or poor-quality as-built drawings, operation & maintenance (O&M) manuals, and material certifications hinders effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Mitigation Strategy: Implement a rigorous sourcing process involving detailed technical specifications, mandatory performance testing with clear acceptance criteria, independent quality audits or third-party inspection (e.g., by an NDTI), thorough IP due diligence on designs, and contracts explicitly defining quality requirements, IP ownership, and long-term support obligations. Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), not just the purchase price.
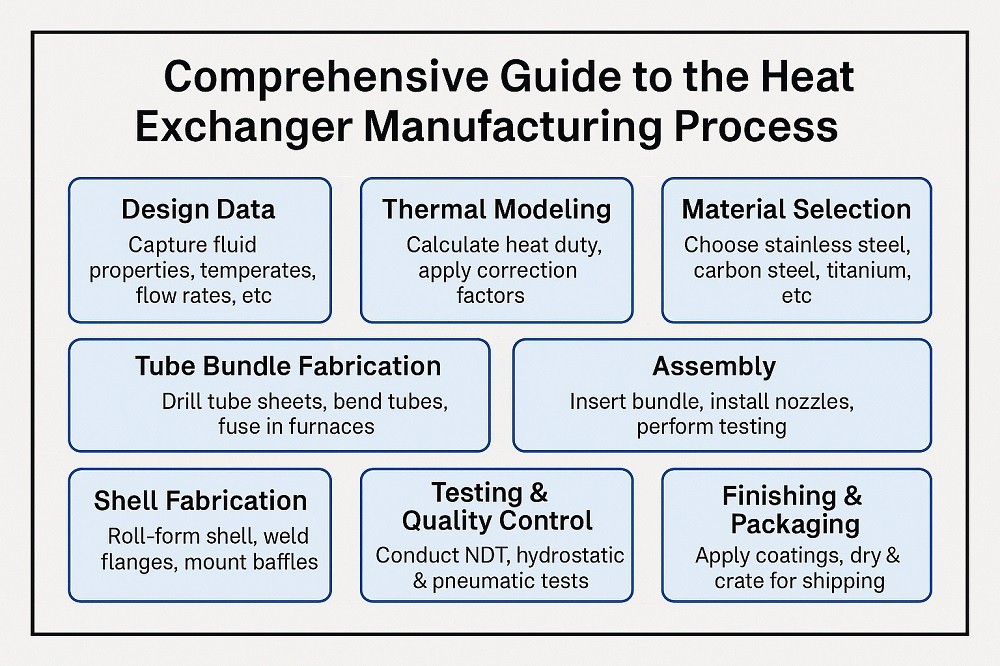
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Heat Exchanger Efficiency
Understanding Regulatory Frameworks and Industry Standards
Heat exchanger efficiency is governed by a range of international, national, and industry-specific regulations and standards. Key compliance frameworks include ISO 14400 (Energy efficiency in thermal systems), ASME BPVC (Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code) for mechanical integrity, and local energy efficiency mandates such as the EU Ecodesign Directive or U.S. DOE regulations. Facilities must ensure that heat exchanger designs, operations, and retrofits align with these standards to avoid penalties and ensure operational legality. Regular audits and certification documentation (e.g., CE marking, ASME stamp) are essential components of compliance.
Design and Installation Compliance Requirements
During the design and installation phase, adherence to engineering standards is critical for achieving optimal efficiency and regulatory approval. Engineers must follow guidelines from organizations such as TEMA (Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association) and API (American Petroleum Institute) to ensure thermal performance, material compatibility, and safety. Documentation, including P&IDs (Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams), material test reports, and pressure testing records, must be maintained. Compliance with local building codes and environmental permits (e.g., air emissions, coolant discharge) is also mandatory prior to commissioning.
Operational Monitoring and Maintenance Logistics
Efficient heat exchanger operation requires continuous monitoring and scheduled maintenance in accordance with OSHA, EPA, and industry best practices. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as approach temperature, pressure drop, and fouling factor must be tracked using SCADA or energy management systems. Maintenance schedules should follow API 510/570 or ISO 55000 for asset management, including cleaning, tube inspections, and leak testing. Proper record-keeping of maintenance logs and efficiency reports supports compliance during regulatory inspections and energy audits.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Reporting
Organizations must report energy consumption and efficiency metrics as part of environmental compliance programs like ISO 50001 (Energy Management) or the U.S. ENERGY STAR program. Heat exchanger efficiency directly impacts overall plant energy performance and carbon footprint. Facilities should conduct regular energy assessments (e.g., ASHRAE Level 2 audits) and submit required data to regulatory bodies such as the EPA’s ENERGY STAR Portfolio Manager or the EU’s Emissions Trading System (ETS). Accurate data logging and third-party verification enhance credibility and support sustainability certifications.
Supply Chain and Procurement Considerations
Procuring heat exchangers and replacement parts requires due diligence to ensure compliance with efficiency and material standards. Suppliers must provide certified materials (e.g., ASTM, ASME) and documentation proving adherence to RoHS, REACH, or other environmental directives. Logistics planning should include lead time management, import/export compliance for international shipments, and adherence to customs regulations for high-efficiency components. Sustainable sourcing policies further support corporate compliance with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals.
Training and Personnel Certification
Personnel involved in the operation, maintenance, and inspection of heat exchangers must be properly trained and certified. Compliance with OSHA 29 CFR 1910 (General Industry Standards) and NFPA 70E (Electrical Safety) is mandatory when working with high-pressure or high-temperature systems. Training programs should cover thermal efficiency principles, safety procedures, and emergency response. Certifications such as Certified Energy Manager (CEM) or ASME accreditation validate competency and are often required during regulatory audits.
In conclusion, sourcing a high-efficiency heat exchanger involves a comprehensive evaluation of design, materials, operating conditions, and lifecycle costs. Key factors such as thermal performance, fouling resistance, pressure drop, and compatibility with process fluids significantly influence efficiency. Advancements in technologies like compact heat exchangers, enhanced surface designs, and smart monitoring systems offer opportunities to optimize thermal transfer and reduce energy consumption. Additionally, working with reputable suppliers who adhere to industry standards and provide reliable performance data ensures long-term operational reliability and energy savings. Therefore, prioritizing efficiency in the sourcing process not only enhances system performance but also contributes to sustainability goals and reduced operational expenses over the equipment’s lifespan.