The global healds manufacturing market is witnessing steady growth, driven by increasing demand from the textile industry for advanced weaving technologies. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global textile machinery market—which encompasses key components like healds—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2023 to 2028. Healds, essential for guiding warp yarns in looms, are critical to improving weaving efficiency and fabric quality, particularly in high-speed shuttleless looms. As textile producers expand production capacity and upgrade to automated systems, the need for precision-engineered, durable healds has intensified. This demand is further amplified in emerging economies across Asia-Pacific, where countries like India and Vietnam are scaling up textile manufacturing. Leveraging insights from Grand View Research, which notes a rising adoption of smart textile machinery, the healds sector is evolving with innovations in materials and surface treatments to enhance performance and longevity. Against this backdrop, the following list highlights the top 10 healds manufacturers leading the industry through technological advancement, global reach, and consistent product quality.
Top 10 Healds Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Greetings
Domain Est. 2007
Website: negentec.co.kr
Key Highlights: Aprt from these, NEGENTEC CO., LTD. is manufacturing and supplying industrial plastic healds, etc used in P.P loom, air bag weave….
#2 Maksteel
Domain Est. 2000 | Founded: 1980
Website: maksteelindia.com
Key Highlights: Maksteel Wire Healds Pvt. Ltd. Established in 1980 is a leading textile weaving machine accessories manufacturer in India. Maksteel has made rapid progress ……
#3 Profile
Domain Est. 2014
Website: healdsindia.com
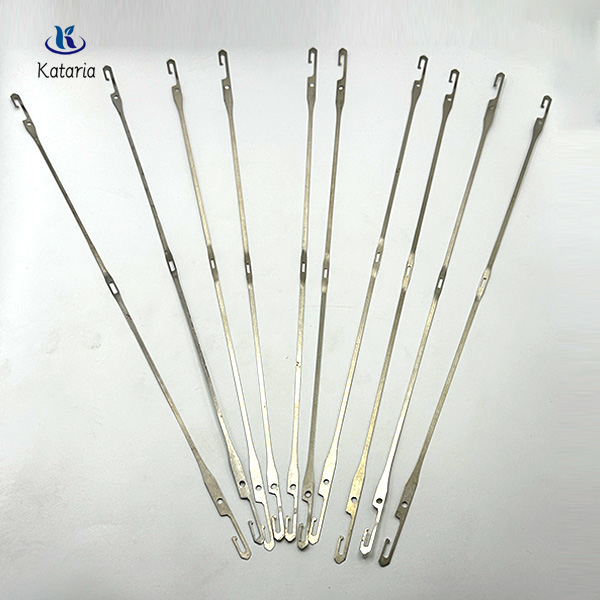
Key Highlights: AMBICA TEXTILE INDUSTRIES is one of the leading manufacturers, exporters & suppliers of riderless flat healds, narrow fabric healds, leno doup healds, drop pin, ……
#4 About Us
Domain Est. 2021
Website: healdanddropwire.com
Key Highlights: We are a professional manufacturer of automatic warp crossing healds, steel healds, warp stopper healds, gauze healds, twisted healds, woven healds, ribbon ……
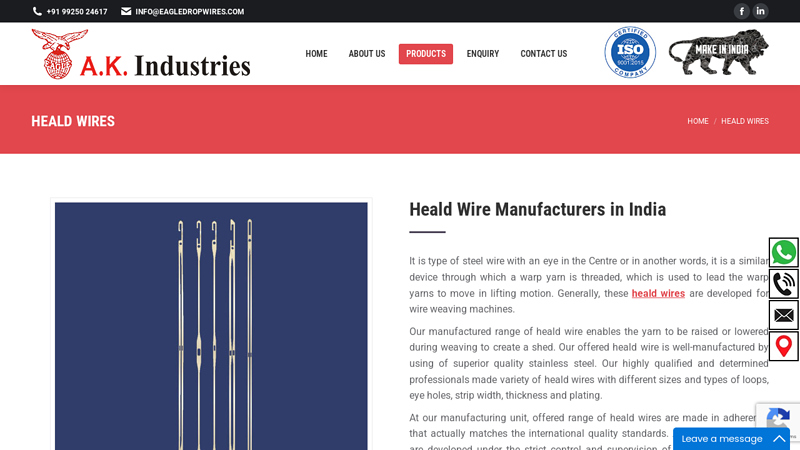
#5 Heald Wire Manufacturers in India
Domain Est. 2021
Website: eagledropwires.com
Key Highlights: Our manufactured range of heald wire enables the yarn to be raised or lowered during weaving to create a shed. Our offered heald wire is well-manufactured by ……
#6 Wire Heald
Domain Est. 2008
Website: healdindia.co.in
Key Highlights: Our product range includes wire Healds for: Carpet felt and filter fabrics; Frame Weaving; Plastic woven sac; Jute weaving; Jacquard Weaving ……
#7 Wire Heald
Domain Est. 2008
Website: guryaytekstil.com
Key Highlights: NON-STOP WEAVING, HIGH EFFICIENCY. Güryay Textile has been manufacturing complete spring wire healds and jacquard accessories for weaving looms….
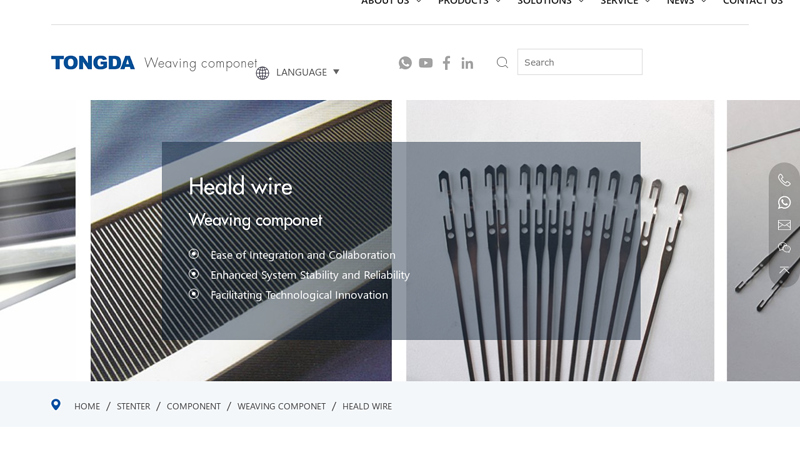
#8 Heald wire
Domain Est. 2011
Website: china-tongda.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture various types of heald wire, such as closed O type flat steel healds, opened J type steel healds, opened C type flat steel healds, and more….
#9 Healds Tech
Domain Est. 2024
Website: healds.tech
Key Highlights: We don’t just manufacture the heald spring assembly set – we engineer performance. From our unique dual-eye, dual-material healds to high-precision tubes ……
#10 Company
Website: heald.uk.com
Key Highlights: For over three decades, Heald has been securing some of the world’s most high profile locations with advanced protection against hostile vehicle attacks….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Healds

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Healds
As of 2026, the global market for healds—critical components in textile looms used to control warp yarn movement during weaving—is experiencing notable transformation driven by technological advancements, shifting manufacturing dynamics, and increased demand for high-efficiency textile production. Below is an analysis of key market trends shaping the healds industry in 2026.
1. Growth in Technical Textiles and Smart Fabrics
The rising demand for technical textiles—used in automotive, medical, geotextile, and protective apparel sectors—is driving innovation in weaving technologies. Healds are being redesigned to accommodate finer, stronger, and more diverse yarn types, including composite and smart fibers. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting precision-engineered healds compatible with high-speed air jet and rapier looms to meet these specialized needs.
2. Automation and Industry 4.0 Integration
The textile industry’s shift toward automation is extending to auxiliary components like healds. In 2026, digitally monitored heald frames equipped with sensors are gaining traction, enabling real-time detection of wear, tension imbalances, and misalignment. This predictive maintenance capability reduces downtime and improves weaving efficiency, particularly in large-scale smart factories across Asia and Europe.
3. Asia-Pacific Dominance in Production and Consumption
China, India, and Bangladesh remain the largest markets for healds due to their expansive textile manufacturing bases. India, in particular, has seen accelerated adoption of modern looms under government initiatives like “Make in India,” boosting demand for high-performance healds. Localization of component manufacturing is reducing import dependency and fostering regional heald production hubs.
4. Material Innovation and Durability Enhancement
Traditional steel healds are being gradually supplemented by advanced materials such as stainless steel alloys, ceramic-coated variants, and composite polymers. These materials offer improved resistance to abrasion, corrosion, and high temperatures—essential for maintaining precision in continuous operation environments. Sustainability considerations are also prompting R&D into recyclable and longer-lasting heald designs.
5. Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The healds market is witnessing consolidation among component suppliers aiming to offer integrated shedding solutions. Companies like Karl Mayer, Sultex, and smaller regional manufacturers are forming partnerships with loom OEMs to co-develop customized heald systems. This vertical integration enhances compatibility and performance, particularly for high-density and complex weave patterns.
6. Sustainability and Circular Economy Pressures
Environmental regulations are pushing textile producers to reduce waste and energy consumption. In response, heald manufacturers are focusing on extending product lifecycles through improved surface treatments and modular designs that allow for easy repair or recycling. Additionally, energy-efficient weaving processes indirectly elevate the demand for low-friction, high-precision healds.
7. Challenges: Supply Chain Volatility and Skilled Labor Shortage
Despite growth, the sector faces hurdles such as fluctuating raw material prices (especially for specialty steels) and geopolitical disruptions affecting supply chains. Moreover, the declining availability of skilled technicians to maintain and align heald systems poses a challenge, emphasizing the need for user-friendly, plug-and-play solutions.
Conclusion
In 2026, the healds market is evolving from a commodity-driven segment to a high-precision, technology-integrated niche within the broader textile machinery ecosystem. Success for manufacturers hinges on innovation in materials, alignment with automation trends, and responsiveness to regional manufacturing shifts. As weaving technology advances, healds are becoming smarter, stronger, and more sustainable—positioning them as critical enablers of next-generation textile production.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Healds: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
When sourcing healds—essential components in weaving looms used to control warp yarns—buyers often encounter challenges related to quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) risks. Understanding these pitfalls is crucial for ensuring reliable textile production and avoiding legal complications.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Specifications
One of the most common quality issues arises from variations in material composition and manufacturing tolerances. Healds made from substandard steel or with inconsistent wire diameter can lead to premature wear, breakage, or uneven shedding. Sourcing from suppliers without strict quality control processes increases the risk of receiving non-conforming batches.
Poor Surface Finish and Coating
Healds are prone to friction and corrosion. A poor surface finish or inadequate anti-corrosion coating (e.g., lack of proper nickel or zinc plating) can result in increased yarn abrasion and shortened lifespan. Buyers may overlook coating specifications during procurement, leading to reduced loom efficiency and higher maintenance costs.
Lack of Standardization
Different loom manufacturers use proprietary heald dimensions and profiles. Sourcing generic or non-OEM healds without verifying compatibility can lead to misalignment, skipped picks, or loom downtime. Ensuring dimensional accuracy and adherence to OEM specifications is essential.
Inadequate Testing and Certification
Reputable suppliers typically provide test reports for tensile strength, dimensional accuracy, and surface quality. However, some low-cost suppliers may skip rigorous testing. Relying on uncertified products increases the risk of field failures and production delays.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Unauthorized Replication of OEM Designs
Many heald designs are protected by patents or trade secrets held by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). Sourcing counterfeit or reverse-engineered healds without proper licensing constitutes IP infringement. This exposes the buyer to legal action, product seizures, or reputational damage.
Ambiguous Supplier Agreements
Contracts with suppliers may fail to clarify IP ownership or liability for infringement. Without explicit clauses stating that the supplier assumes responsibility for IP compliance, the end-user may be held liable in case of disputes.
Grey Market Procurement
Purchasing healds through third-party distributors or grey market channels increases the risk of acquiring IP-violating products. These channels often lack transparency about manufacturing origins, making it difficult to verify legitimacy.
Lack of Due Diligence
Buyers may prioritize cost and availability over verifying a supplier’s IP compliance. Failing to audit suppliers or request proof of licensing agreements can inadvertently support counterfeit operations.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Partner with certified, reputable suppliers who comply with OEM specifications.
– Request material test reports and conduct batch inspections.
– Verify IP rights and require suppliers to warrant non-infringement.
– Use formal procurement agreements that include quality and IP clauses.
– Consider OEM or licensed aftermarket healds for critical applications.
By addressing both quality and IP concerns proactively, textile manufacturers can ensure reliable performance, avoid legal exposure, and maintain production continuity.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Healds
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance procedures for handling Healds—critical components in textile weaving machinery—to ensure safe, efficient, and regulation-compliant operations.
Overview of Healds and Their Importance
Healds are flat, vertical wires with an eyelet (or “shed”) used in looms to control the warp yarns during weaving. Proper handling, storage, and transportation are vital to maintain their precision and prevent damage that could disrupt production.
Packaging Requirements
Healds must be packaged to prevent bending, corrosion, and contamination. Use:
– Rigid cardboard boxes or plastic containers with internal dividers.
– Anti-corrosion paper or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) film for metal protection.
– Clearly labeled packaging indicating part number, quantity, and “Fragile – Handle with Care.”
Storage Guidelines
Store Healds in a controlled environment to maintain integrity:
– Temperature: 15–25°C (59–77°F)
– Relative Humidity: Below 60%
– Keep away from direct sunlight, moisture, and corrosive chemicals.
– Store horizontally on shelves in original packaging until use.
Transportation Standards
Ensure safe transit through proper logistics planning:
– Use padded, secure pallets for bulk shipments.
– Avoid stacking excessive weight on Heald boxes.
– Secure loads in vehicles to prevent shifting during transit.
– Prefer climate-controlled transport for long-distance or international shipments.
Import/Export Compliance
Healds may be subject to international trade regulations:
– Classify under correct HS Code (typically 8448.39 for parts of textile machinery).
– Verify export control requirements (e.g., EAR in the U.S.).
– Complete commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin as required.
– Comply with destination country’s customs and safety standards.
Quality and Inspection Protocols
Implement inspection checkpoints:
– Pre-shipment: Verify quantity, packaging integrity, and labeling accuracy.
– Upon receipt: Inspect for physical damage and verify conformity with order specifications.
– Use documented checklists and non-conformance reporting procedures.
Safety and Handling Procedures
Train personnel on safe handling:
– Wear cut-resistant gloves when handling metal Healds.
– Use proper lifting techniques to avoid strain.
– Keep work areas clean and organized to prevent tripping or dropping parts.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain full traceability for compliance and quality assurance:
– Assign batch/lot numbers to all Heald shipments.
– Retain shipping records, inspection reports, and certificates for at least 5 years.
– Use inventory management systems to track stock levels and expiry (if applicable).
Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Adhere to environmental standards:
– Recycle packaging materials where possible.
– Dispose of damaged Healds and packaging in accordance with local waste regulations.
– Comply with REACH (EU), RoHS, and other applicable chemical restriction directives.
Supplier and Vendor Compliance
Ensure all suppliers meet required standards:
– Audit packaging and shipping practices.
– Require compliance with ISO 9001 or equivalent quality management systems.
– Include logistics and compliance clauses in vendor contracts.
Following this guide ensures efficient logistics operations and full regulatory compliance when managing Healds across the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Healds:
In conclusion, sourcing high-quality healds is a critical factor in ensuring optimal weaving performance, fabric quality, and loom efficiency. Selecting reliable suppliers who provide durable materials, consistent dimensions, and excellent surface finishes directly impacts shedding precision and reduces downtime due to breakages or misalignments. Factors such as material type (e.g., steel or composite), compatibility with specific loom models, lead time, and cost-effectiveness must be carefully evaluated during the procurement process. Establishing strong relationships with trusted manufacturers or distributors, along with implementing a quality assurance process for incoming healds, can significantly enhance production reliability and reduce long-term operational costs. Ultimately, strategic sourcing of healds supports smoother weaving operations and contributes to improved textile output and competitiveness in the market.