The global headphone connector market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for audio devices across consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial applications. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global audio connectors market was valued at USD 4.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by the proliferation of smartphones, wireless technologies, and high-fidelity audio equipment—though wired connections remain critical in professional audio, aviation, and industrial sectors where reliability and latency matter. As headphone design evolves, so too does the need for durable, high-performance connectors that support analog, digital, and hybrid signals. Amid this demand, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, precision engineering, and global supply. These top nine headphone connector manufacturers not only dominate in terms of product range and quality but also play a pivotal role in shaping the future of audio connectivity.
Top 9 Headphone Connector Types Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Neutrik
Domain Est. 1996
Website: neutrik.com
Key Highlights: Neutrik is the leading manufacturer of audio connectors and receptacles. Neutrik produces XLR, plugs, jacks, speaker and power connectors, patch panels, ……
#2 Cable Selection Guidance
Domain Est. 2017
Website: audiophileninja.com
Key Highlights: Headphone Connector Types. Dual SMC; Dual 3.5mm; Dual 2.5mm Long; Dual 2.5mm … Please contact your headphone manufacturer to confirm cable configuration….
#3 A2DC-Connector
Domain Est. 1996
Website: audio-technica.com
Key Highlights: This is a rich lineup of cables made for a variety of headphone types and equipped with different output connectors, from a standard 3.5 mm connector to 2.5 mm ……
#4 Jacks and Plugs
Domain Est. 1996
Website: switchcraft.com
Key Highlights: The Switchcraft line of jacks and plugs are designed with our customers in mind. Perfect for power plugs for instrumentation and audio connections….
#5 Audio-Video Connectors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: amphenol.com
Key Highlights: Amphenol 164 series connectors are water-resistant, polarized, five and six contact electrical connectors for use in low voltage audio frequency circuits and ……
#6 Furutech
Domain Est. 1998
Website: furutech.com
Key Highlights: RCA Connectors · XLR Connectors · Spade Connectors · Banana Connectors · BNC Connectors · Phono Connectors · Headphone Connectors · RCA Sockets · XLR sockets ……
#7 Grado 12
Domain Est. 1998
Website: gradolabs.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free deliveryThe mini adaptor cable has a 1/8 inch (3.5mm) plug then 8 inches (20cm) of cable connected to a 1/4 inch (6.3mm) jack….
#8 Headphone
Domain Est. 2002
Website: bluejeanscable.com
Key Highlights: Here are some pictures of our common connectors. Note that the terminology “TS,” “TRS,” “TRRS” and the like refers, on a phone-plug type connector, to how ……
#9 REAN Connectors
Domain Est. 2004
Website: rean-connectors.com
Key Highlights: REAN offers designers of audio, video and lighting products a comprehensive range of connectors featuring ultra-robust, high-reliability designs….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Headphone Connector Types

2026 Market Trends for Headphone Connector Types
As we approach 2026, the market for headphone connector types continues to evolve rapidly, shaped by advancements in wireless technology, shifting consumer preferences, and industry-wide design philosophies. The traditional dominance of physical connectors is being steadily challenged, leading to a fragmented but highly dynamic landscape.
Wireless Dominance Accelerates
By 2026, wireless connectivity—primarily via Bluetooth 5.4 and the emerging Bluetooth LE Audio standard—will solidify its position as the leading headphone interface. Key drivers include seamless integration with smartphones (most of which have eliminated headphone jacks), improved battery life, enhanced audio quality through codecs like LC3, and greater user convenience. True wireless stereo (TWS) earbuds represent the fastest-growing segment, further diminishing reliance on physical connectors. Innovations such as multi-point pairing and audio sharing will further entrench wireless as the default choice for mainstream consumers.
3.5mm Jack Persists in Niche and Pro Markets
Despite the wireless surge, the 3.5mm analog headphone jack will maintain relevance in specific segments. Audiophiles and professional audio users continue to favor it for its lossless signal transmission, zero latency, and compatibility with high-end audio equipment. Additionally, budget-conscious consumers, travelers using in-flight entertainment systems, and users in regions with lower smartphone upgrade cycles will sustain demand. Some premium smartphones and audio devices may reintroduce the jack as a differentiator, appealing to purists and enhancing brand loyalty.
USB-C Emerges as the Primary Wired Alternative
USB-C is becoming the de facto wired connector for headphones, especially in the Android ecosystem. By 2026, it will serve dual purposes: digital audio transmission and device charging. Its advantages—reversible design, high data throughput, and support for active noise cancellation and high-resolution audio—make it ideal for modern headphones. The EU’s common charger mandate has accelerated adoption, pushing manufacturers to standardize on USB-C across devices, including headphones. Expect growth in USB-C wired earbuds and over-ear models that leverage the connector for enhanced functionality.
Decline of Proprietary and Legacy Connectors
Proprietary connectors (e.g., Apple’s Lightning) and older standards like 2.5mm or 6.35mm jacks will continue to decline. Apple’s shift toward USB-C across its product line, mandated by regulatory pressures, will phase out Lightning-based headphones. While 6.35mm connectors remain in professional studio environments, their consumer presence will shrink. Adapters and dongles will persist as transitional tools, but their market share will wane as native USB-C and wireless solutions become ubiquitous.
Rise of Smart and Adaptive Connectivity
Beyond physical interfaces, intelligent audio routing and contextual connectivity will gain prominence. Headphones will increasingly use AI to switch seamlessly between devices, optimize connection stability, and adapt audio profiles based on environment. Features like automatic device pairing, presence detection, and spatial audio sync rely less on connectors and more on integrated ecosystems—foreshadowing a future where the connector itself becomes functionally invisible.
In summary, the 2026 headphone connector market is defined by the ascendancy of wireless technologies, the strategic retreat of analog jacks to specialized domains, and the consolidation around USB-C as the dominant wired standard. The trajectory points toward a cable-free future, where convenience, integration, and ecosystem synergy outweigh the need for physical connections.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Headphone Connector Types (Quality, IP)
Sourcing headphone connectors involves more than just selecting a standard plug type—overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) factors can lead to product failures, legal risks, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control Leading to Mechanical or Electrical Failures
One of the most frequent issues is procuring connectors with inconsistent build quality. Low-cost suppliers may use substandard materials such as brittle plastics or inferior plating (e.g., thin or non-uniform gold plating), leading to premature wear, intermittent connections, or complete plug failure. Sourcing without verifying mechanical durability (insertion cycles, strain relief) or electrical performance (contact resistance, signal integrity) increases the risk of field failures and customer complaints.
Lack of IP Clearance for Proprietary or Patented Designs
Many headphone connector designs, especially locking mechanisms, smart connectors (e.g., with integrated electronics), or novel form factors, are protected by patents or utility models. Sourcing from manufacturers that replicate patented designs without licensing exposes your company to infringement lawsuits, product recalls, and supply chain disruption. Always conduct due diligence on IP ownership and ensure suppliers can provide freedom-to-operate assurances.
Inconsistent Compliance with Industry Standards
Connectors may claim compatibility with standards like IEC 61076 or JEITA RC-6801, but non-compliant parts often slip through due to inadequate supplier vetting. Misaligned tip-ring-sleeve (TRS) dimensions, incorrect pinouts, or failure to meet environmental ratings (e.g., temperature, humidity) can result in interoperability issues across devices. Always request test reports and conduct independent verification.
Overlooking Environmental and IP Ratings for Intended Use
For ruggedized or outdoor audio equipment, sourcing connectors without appropriate Ingress Protection (IP) ratings (e.g., IP54 or higher for dust and splash resistance) can compromise reliability. Many standard 3.5mm or 2.5mm connectors are not sealed, leading to corrosion or short circuits in harsh environments. Ensure the connector’s IP rating matches the product’s use case and verify through supplier documentation or testing.
Dependence on Obsolete or Discontinued Connector Types
Some niche or legacy connector types may be discontinued or nearing end-of-life. Sourcing these without checking long-term availability risks production halts and costly redesigns. Always confirm the connector’s lifecycle status and consider second sourcing or standardization on widely available types.
Insufficient Supplier Qualification and Traceability
Relying on unqualified or opaque supply chains—especially from brokers or secondary markets—increases the risk of counterfeit or re-marked components. These may fail prematurely or not meet specifications. Implement supplier qualification processes, demand full traceability (batch/lot numbers), and consider audits or third-party testing for high-volume or safety-critical applications.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough technical evaluation, legal review, and supply chain diligence to ensure both performance and compliance in headphone connector sourcing.
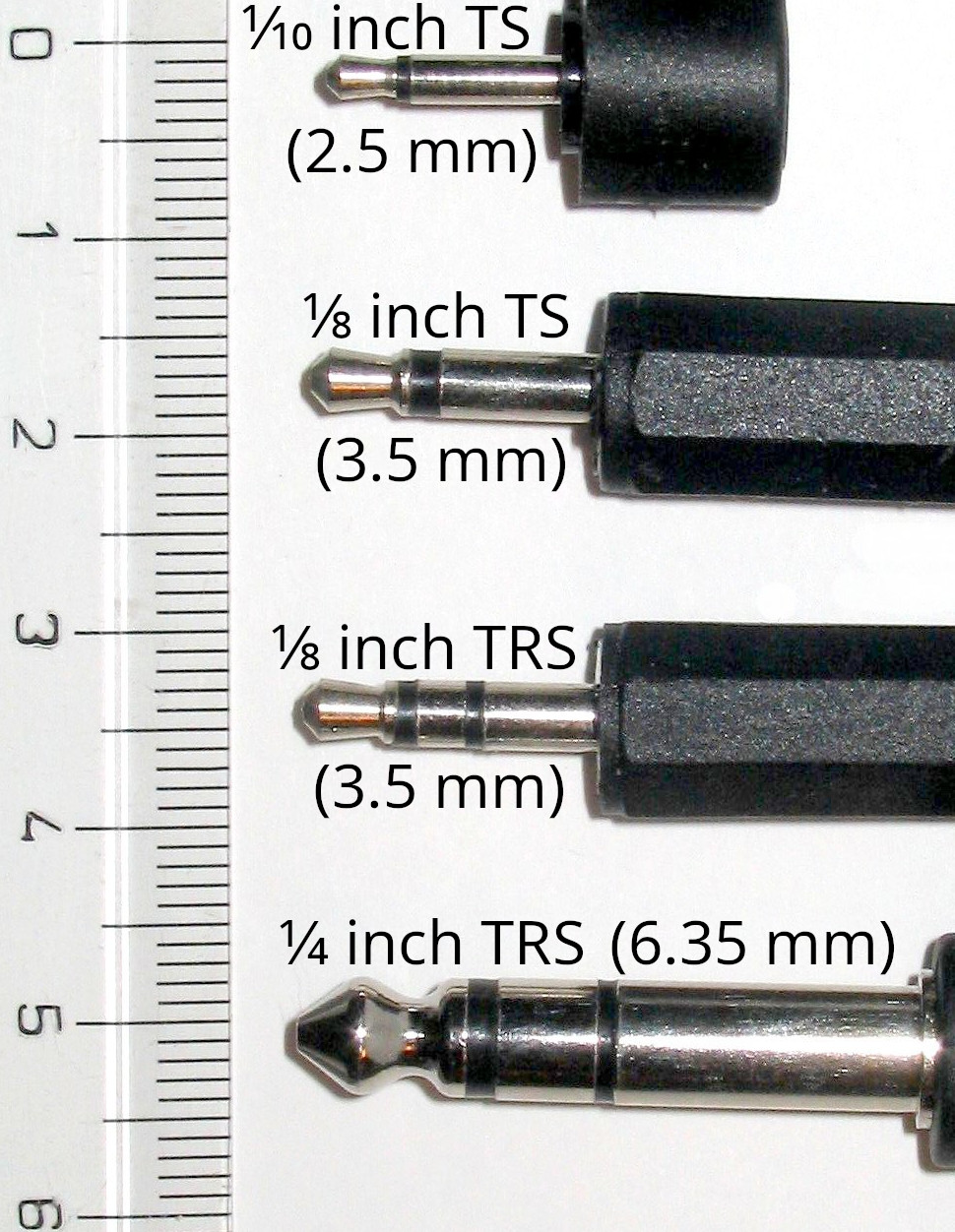

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Headphone Connector Types
Understanding the various headphone connector types is essential for logistics, inventory management, and regulatory compliance across global markets. This guide outlines common connector types, their logistical considerations, and compliance requirements to ensure smooth distribution and adherence to international standards.
3.5 mm (1/8 inch) TRS and TRRS
The 3.5 mm connector is the most widely used headphone jack, found in consumer electronics such as smartphones, laptops, and audio devices. TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve) supports stereo audio, while TRRS adds a fourth conductor for microphone and control signals (common in smartphones).
Logistical Considerations:
– High-volume demand due to broad device compatibility.
– Standardized packaging and labeling for retail and B2B shipments.
– Compatibility with legacy and current devices makes it a staple in inventory.
Compliance Requirements:
– Must comply with IEC 61076-2-103 (connectors for electronic equipment).
– CE marking (EU) for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and low voltage directive (LVD).
– FCC Part 15 (USA) for unintentional radiators if integrated with active circuitry.
– RoHS compliance (restriction of hazardous substances) in electronics.
2.5 mm TRS/TRRS
Smaller than the 3.5 mm variant, the 2.5 mm connector is used in specialized communication equipment, hearing aids, and some professional audio gear.
Logistical Considerations:
– Lower volume demand; often used in niche or enterprise markets.
– Requires careful inventory segregation to avoid mix-ups with 3.5 mm variants.
– May require special handling due to fragile construction.
Compliance Requirements:
– IEC 61076-2-103 also applies to 2.5 mm connectors.
– Must meet medical device standards (e.g., ISO 13485) if used in hearing aids.
– Compliance with REACH and RoHS regulations for material safety.
6.35 mm (1/4 inch) TRS
Commonly used in professional audio equipment such as studio headphones, musical instruments, and amplifiers. Offers superior durability and signal integrity compared to smaller connectors.
Logistical Considerations:
– Used primarily in B2B and professional markets; packaging often bulkier.
– Requires durable shipping materials to prevent damage during transit.
– Lower turnover; typically stored in specialized audio equipment warehouses.
Compliance Requirements:
– Subject to IEC 60603-11 (connectors for electronic equipment).
– CE and UKCA marking for professional audio gear in Europe.
– FCC certification for any active components in connected devices.
– RoHS and REACH compliance mandatory for EU distribution.
USB-A and USB-C Connectors (Digital Audio)
Increasingly common in modern headphones, especially USB-C for smartphones and laptops. These connectors transmit digital audio signals and may provide power.
Logistical Considerations:
– High compatibility with modern devices; rising demand in mobile and computing sectors.
– Inventory must distinguish between USB-A (legacy) and USB-C (current standard).
– Requires compliance with USB-IF certification for interoperability.
Compliance Requirements:
– USB-IF certification required for official USB logo usage.
– CE, FCC, and IC (Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada) for EMC and safety.
– RoHS, REACH, and California Proposition 65 for chemical safety.
– ENERGY STAR or equivalent may apply if power management features are present.
Proprietary Connectors
Some manufacturers (e.g., Apple with Lightning, older Samsung models) use proprietary connectors. These are less common but still relevant in specific ecosystems.
Logistical Considerations:
– High risk of obsolescence; requires careful demand forecasting.
– Often region-specific or tied to product lifecycle; complicates global inventory.
– May require licensing agreements for third-party accessories.
Compliance Requirements:
– Must comply with regional safety and EMC standards (FCC, CE, PSE in Japan).
– Licensing from original manufacturer may be required (e.g., Apple MFi program).
– RoHS and WEEE compliance for end-of-life handling.
General Compliance and Logistics Best Practices
- Labeling and Documentation: All connectors must be clearly labeled with type, compatibility, and compliance marks (CE, FCC, RoHS).
- Global Standards Alignment: Ensure products meet regional requirements (e.g., KC mark for South Korea, CCC for China).
- Packaging and Shipping: Use anti-static and protective packaging, especially for sensitive or small connectors.
- Traceability: Implement serial or batch tracking for recalls and compliance audits.
- Sustainability: Adhere to WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives for end-of-life product handling.
By understanding the logistics and compliance landscape for each headphone connector type, businesses can optimize supply chain efficiency, reduce risk, and ensure global market readiness.
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate headphone connector type depends on the specific application, device compatibility, user needs, and industry standards. The most common connector types—3.5mm, 2.5mm, 6.35mm (1/4 inch), and USB (including USB-C and Lightning)—each serve distinct purposes. The 3.5mm jack remains widely used for its universal compatibility with smartphones, audio players, and computers, though its prevalence is declining in favor of digital alternatives. The 6.35mm connector is ideal for professional audio equipment due to its durability and superior signal quality, while the 2.5mm variant is often used in specialized or balanced audio setups. Meanwhile, USB and USB-C connectors are gaining traction, especially in modern mobile devices, offering digital audio transmission, in-line controls, and power delivery.
When sourcing connectors, it is essential to consider compatibility with end devices, audio quality requirements, durability, and market trends. With the ongoing shift toward wireless audio and digital interfaces, future-proofing sourcing decisions by including support for USB-C or wireless adapters may be advisable. Ultimately, selecting the right headphone connector involves balancing legacy support with emerging technologies to ensure optimal performance and user satisfaction.