The global hammer press machine market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand from industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing for high-precision metal forming solutions. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global forging market—which includes hammer press machines—was valued at USD 113.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.2% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights increasing industrial automation and infrastructure development as key growth catalysts, with the metal forming machinery segment expected to expand significantly due to advancements in energy-efficient and CNC-controlled forging equipment. As manufacturers prioritize productivity and precision, leading hammer press machine producers are innovating to meet stringent quality standards and evolving production needs. In this competitive landscape, six companies stand out for their technological expertise, global reach, and comprehensive product portfolios.
Top 6 Hammer Press Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Hammer Presses
Domain Est. 2019
Website: hammerpresses.com
Key Highlights: Metal Stamping Presses from 15-2500 ton. Built to JIS First Class Industrial Standard and CE Certified. Press models for all various metal forming ……
#2 Hammer Strength Select Chest Press
Domain Est. 1995
Website: lifefitness.com
Key Highlights: Hammer Strength Select Chest Press: Customize your workout with five pressing arm positions. Explore our inviting range of 22 Hammer Strength Select pieces….
#3 Scot Forge
Domain Est. 1997
Website: scotforge.com
Key Highlights: Recognized as the industry leader in open die forging and rolled ring forging, we’re the world’s premier provider of high-quality metal forging solutions….
#4 Big BLU Hammer
Domain Est. 2003
Website: secure.bigbluhammer.com
Key Highlights: American Made Forging Tools. Power Hammer, Presses, Anvils and more….
#5 closed die forging hammers and presses,Electric Screw Press …
Domain Est. 2013 | Founded: 1956
Website: anyanghammer.com
Key Highlights: Anyang Forging Press since 1956, produce forging hammers and presses for closed die forging and open die forging, steel ball machine etc….
#6 Premium Hammer Strength Machine for Your Gym
Domain Est. 2015
Website: fitnessequipmentempire.com
Key Highlights: Browse premium Hammer Strength machines, leg press machines, and Life Fitness gear at Fitness Equipment Empire. Upgrade your workouts with top-quality ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hammer Press Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Hammer Press Machines
The hammer press machine market is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving manufacturing demands, and regional industrial growth. These machines—used primarily in forging, metal shaping, and automotive component production—are adapting to the broader shifts toward automation, energy efficiency, and smart manufacturing. Below are the key trends expected to shape the hammer press machine industry in 2026:
-
Increased Adoption of Automation and Smart Technologies
By 2026, hammer press machines are expected to integrate advanced automation, IoT connectivity, and real-time monitoring systems. Manufacturers are investing in smart presses equipped with sensors and AI-driven analytics to improve precision, reduce downtime, and optimize energy use. These features support Industry 4.0 initiatives and enhance overall productivity in high-volume production environments. -
Growth in Automotive and Aerospace Sectors
The automotive and aerospace industries remain primary consumers of forged metal components. As demand for lightweight, high-strength materials rises—especially in electric vehicles (EVs) and fuel-efficient aircraft—the need for reliable hammer press machines will increase. This trend is expected to fuel demand for high-capacity, precision-controlled hammer presses capable of handling complex alloys. -
Shift Toward Energy-Efficient and Hydraulic Hybrid Systems
Traditional steam or air-powered hammer presses are gradually being replaced by energy-efficient hydraulic and electro-mechanical variants. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to favor hybrid systems that reduce energy consumption and operational noise, aligning with global sustainability goals and stricter environmental regulations. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Regions such as Southeast Asia, India, and parts of Latin America are witnessing rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. These areas are expected to drive demand for affordable, durable hammer press machines. Local manufacturing hubs in these regions will likely increase imports or develop domestic production capabilities to meet growing needs. -
Customization and Modular Designs
As production requirements become more diverse, suppliers are offering modular and customizable hammer press solutions. By 2026, OEMs will focus on flexible systems that can be reconfigured for different forging tasks, reducing capital expenditure and increasing machine utilization across multiple applications. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Following disruptions caused by global events in recent years, manufacturers are reevaluating supply chains. The trend toward localized production is expected to boost regional hammer press manufacturing, particularly in North America and Europe, to ensure faster delivery and reduce dependency on imports. -
Focus on Operator Safety and Ergonomics
Regulatory standards and workplace safety concerns are pushing manufacturers to design hammer presses with enhanced safety features—such as automated clamping, emergency stops, and enclosed work zones. By 2026, compliance with international safety norms (e.g., CE, OSHA) will be a key factor in procurement decisions.
In summary, the 2026 hammer press machine market will be defined by digital integration, energy efficiency, and responsiveness to sector-specific demands. Companies that innovate in automation, sustainability, and regional market adaptation will be best positioned to lead in this evolving landscape.
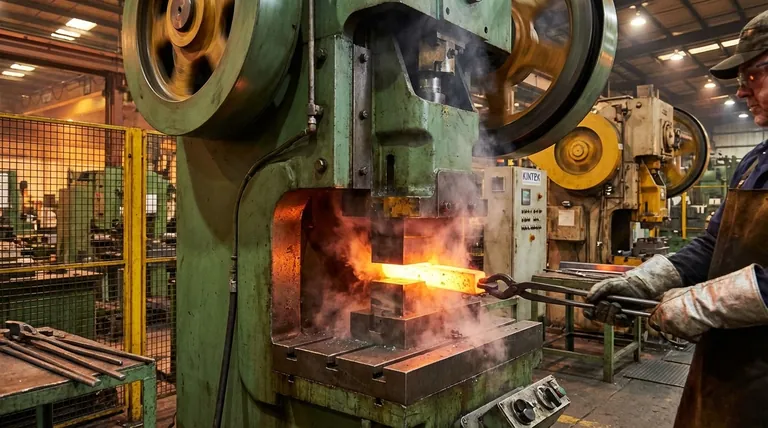

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Hammer Press Machine (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a hammer press machine involves significant investment and technical complexity. Overlooking key factors can lead to poor performance, safety hazards, and intellectual property (IP) risks. Below are critical pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material and Build Quality Assessment
Many suppliers use substandard steel alloys or poor welding practices, resulting in frame deformation, premature wear, or catastrophic failure under load. Always verify material certifications (e.g., ASTM standards), inspect weld quality, and request third-party test reports before purchase.
Lack of Dynamic Load Testing and Certification
Some hammer presses are rated based on static load assumptions, not real-world dynamic impact conditions. Machines without dynamic load testing or certifications (e.g., CE, ISO) may not perform reliably. Ensure the supplier provides impact energy ratings and fatigue test data.
Poor Tolerance and Alignment in Critical Components
Misalignment in the ram, guide columns, or anvil can cause uneven wear, tool breakage, and poor forging quality. Avoid machines without precision-machined components and documented alignment tolerances. Request inspection reports on geometric accuracy.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Low-cost machines from unknown manufacturers often lack local service support or spare parts inventory. This leads to extended downtimes. Confirm the supplier’s service network, response time, and spare parts lead times before procurement.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Sourcing from Suppliers with Questionable IP Ownership
Some manufacturers reverse-engineer or copy patented hammer press designs. Purchasing such equipment may expose your company to IP infringement claims, especially in regulated markets. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s design origin and request proof of IP ownership or licensing.
Lack of Customization Protection
If you collaborate with a supplier to modify or customize a hammer press for your specific application, ensure your design inputs are protected via Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and clear IP clauses in contracts. Otherwise, the supplier may reuse your innovations for competitors.
Inadequate Documentation and Software Licensing
Modern hammer presses often include proprietary control systems or software. Failing to verify software licenses or obtain full technical documentation can lead to compliance issues or hinder maintenance. Demand full documentation packages and confirm software is legally licensed.
Risk of Trade Secret Exposure During Site Visits or Trials
Allowing supplier engineers unrestricted access to your production facility during machine trials may expose proprietary processes. Implement strict access controls and define permitted observation scopes in visit agreements.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, buyers can ensure a reliable, compliant, and legally secure acquisition of hammer press machinery.
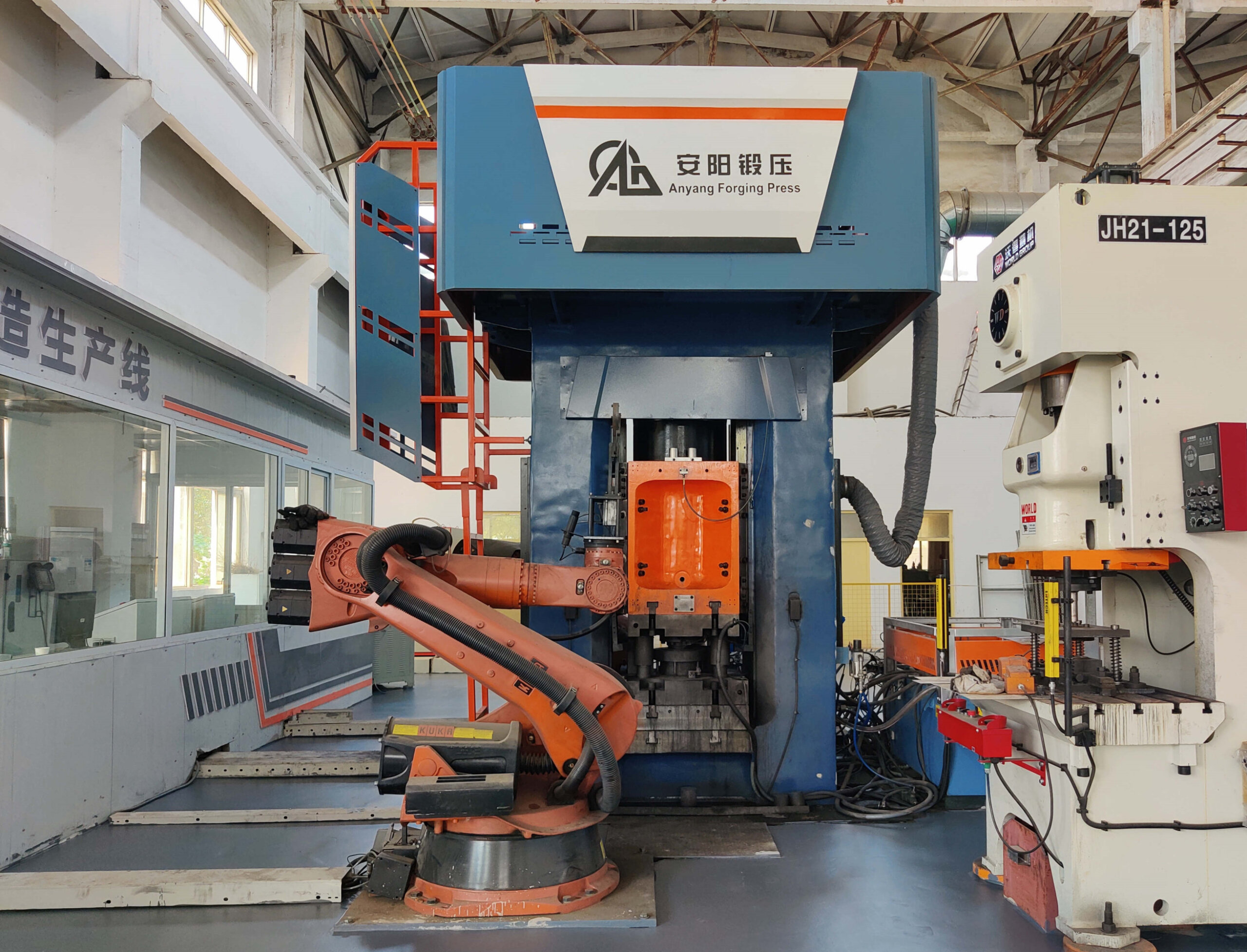

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Hammer Press Machine
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, legal, and efficient transportation, handling, and operation of a hammer press machine.
Transportation & Handling
Ensure the hammer press machine is securely packaged and transported according to manufacturer specifications and freight regulations. Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., forklifts, cranes with slings rated for the machine’s weight) during loading, unloading, and positioning. Confirm the transport vehicle has sufficient load capacity and secure tie-down points. Protect hydraulic lines, electrical components, and precision surfaces from damage during transit.
Import/Export Regulations
Verify compliance with international trade requirements if shipping across borders. This includes proper classification under the Harmonized System (HS Code), typically under 8462 (Machine tools for forging, stamping, or bending metal). Ensure all necessary export licenses, import permits, certificates of origin, and customs documentation are prepared. Comply with sanctions and dual-use regulations where applicable.
Safety Compliance
The hammer press must meet recognized safety standards such as ISO 16092 (Safety of machinery — Mechanical and hydraulic presses) and relevant local regulations (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC in the EU). Key safety features include emergency stop systems, two-hand control devices, guarding around the point of operation, and overload protection. Conduct a risk assessment and ensure all safety interlocks are functional before operation.
Electrical & Environmental Standards
Confirm the machine’s electrical system complies with regional standards (e.g., NEC in North America, IEC/EN 60204-1 internationally). Ensure proper grounding, voltage compatibility, and protection against electrical hazards. Address noise emissions in accordance with directives such as EU Directive 2000/14/EC or local noise ordinances. Implement measures to control oil leaks and manage waste materials (e.g., metal shavings, used lubricants) in compliance with environmental regulations.
Installation & Commissioning
Install the machine on a stable, level foundation capable of absorbing dynamic loads. Provide adequate clearance for operation, maintenance, and emergency access. Ensure utility connections (power, hydraulic lines, air supply) meet specifications. Commissioning must include alignment checks, functional testing of safety systems, and operator training. Maintain documentation of installation and safety validation.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Retain all compliance-related documents, including CE marking certificate (if applicable), Declaration of Conformity, technical file, safety manuals, maintenance logs, and inspection records. These are critical for audits, regulatory compliance, and liability protection.
Operator Training & Certification
Only trained and authorized personnel should operate the hammer press. Training must cover machine functions, safety procedures, emergency protocols, lockout/tagout (LOTO), and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Maintain training records and conduct periodic refresher sessions.
Maintenance & Inspections
Implement a scheduled preventive maintenance program in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations. Regularly inspect critical components such as dies, clutches, brakes, and structural elements for wear or damage. Document all maintenance and corrective actions to ensure ongoing compliance and machine reliability.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Hammer Press Machine
In conclusion, sourcing a hammer press machine requires a thorough evaluation of production requirements, machine specifications, quality standards, and supplier reliability. After careful assessment of various suppliers and models, it is evident that selecting the right hammer press involves balancing performance, durability, cost-efficiency, and after-sales support. Machines that offer high forging precision, energy efficiency, and low maintenance, coupled with technical support and warranty coverage, provide long-term value and operational reliability.
Prioritizing suppliers with proven industry experience, positive customer feedback, and compliance with international safety and quality standards ensures a sound investment. Additionally, considering future scalability and potential integration into automated production lines enhances operational flexibility.
Ultimately, the successful sourcing of a hammer press machine not only improves manufacturing efficiency and product quality but also contributes to sustainable growth and competitiveness in the forging industry. A well-informed procurement decision today lays the foundation for enhanced productivity and reduced downtime in the years to come.