The global grocery cart market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand in supermarkets and hypermarkets worldwide. According to Mordor Intelligence, the shopping cart market was valued at USD 1.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is supported by increasing investments in retail infrastructure, urbanization, and the modernization of shopping facilities—factors that elevate the need for durable, efficient, and innovative grocery cart components. As retailers prioritize customer experience and operational efficiency, the demand for high-quality cart parts such as wheels, baskets, handles, and nesting systems has surged. In this competitive landscape, manufacturers specializing in reliable and ergonomically designed components are playing a critical role. Below are the top six grocery cart parts manufacturers that are shaping the future of retail mobility through advanced engineering and scalable production.
Top 6 Grocery Cart Parts Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
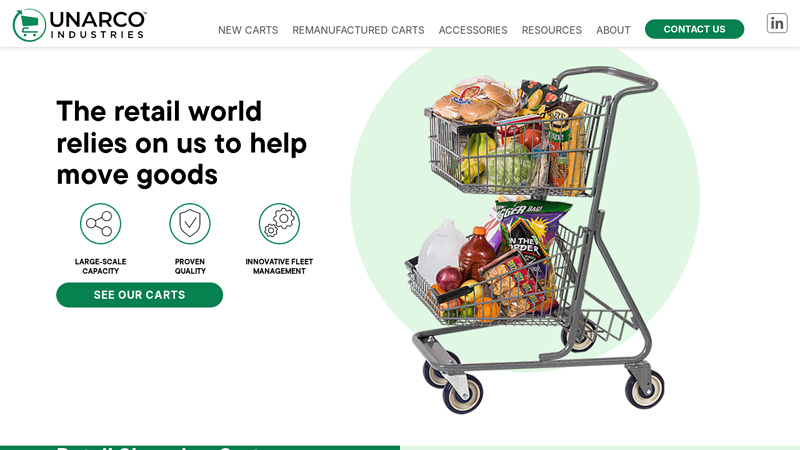
#1 Retail Shopping Carts
Domain Est. 1996
Website: unarco.com
Key Highlights: Unarco is the leading North American shopping cart manufacturer that supports the volume, scale & fleet management needs of retailers….
#2 Carts & Parts Inc
Domain Est. 2000
Website: cartsandparts.com
Key Highlights: Carts and Parts, Inc, is America’s leading source for shopping carts and more. We carry items used by grocery stores and retail outlets nationwide….
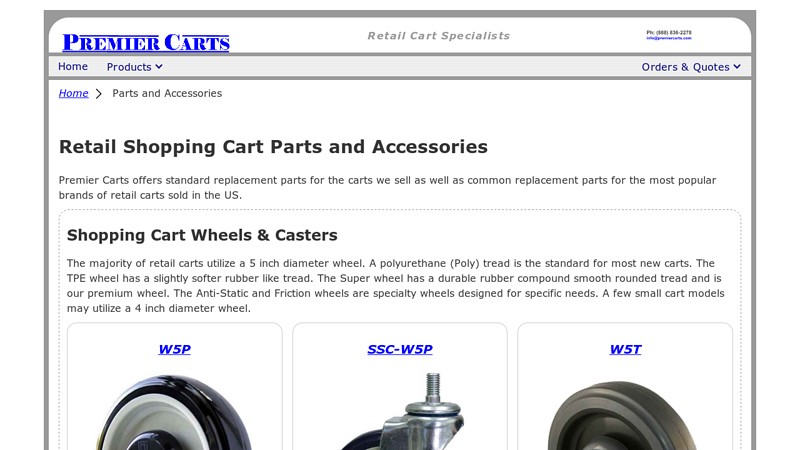
#3 Parts and Accessories for Retail Shopping Carts
Domain Est. 2000
Website: premiercarts.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsPremier Carts offers standard replacement parts for the carts we sell as well as common replacement parts for the most popular brands of retail carts so…
#4 to Nationwide Cart Parts
Domain Est. 2010
#5 Americana Companies
Domain Est. 2022
Website: americanacarts.com
Key Highlights: Large variety of metal-wire shopping carts, plastic shopping carts, hand baskets, and shopping cart parts for grocery stores, convenience stores, ……
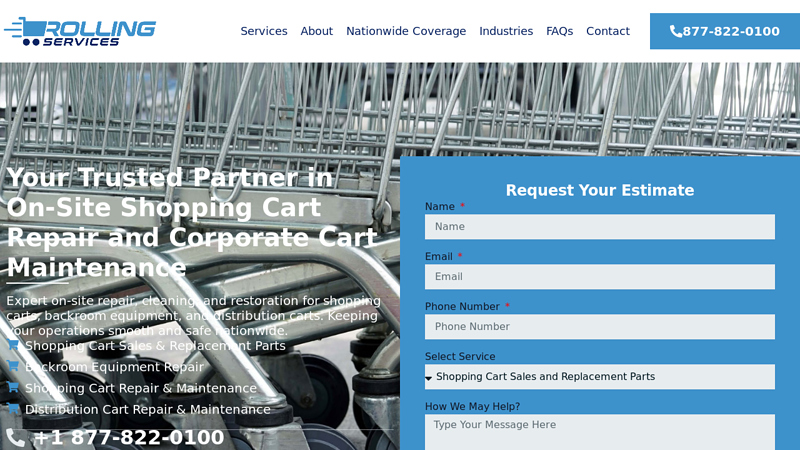
#6 Rolling Services
Domain Est. 2024
Website: rollingservicesllc.com
Key Highlights: Rolling Services offers nationwide on-site shopping cart repair, maintenance, and cleaning. Call us at 877-822-0100 for service!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Grocery Cart Parts
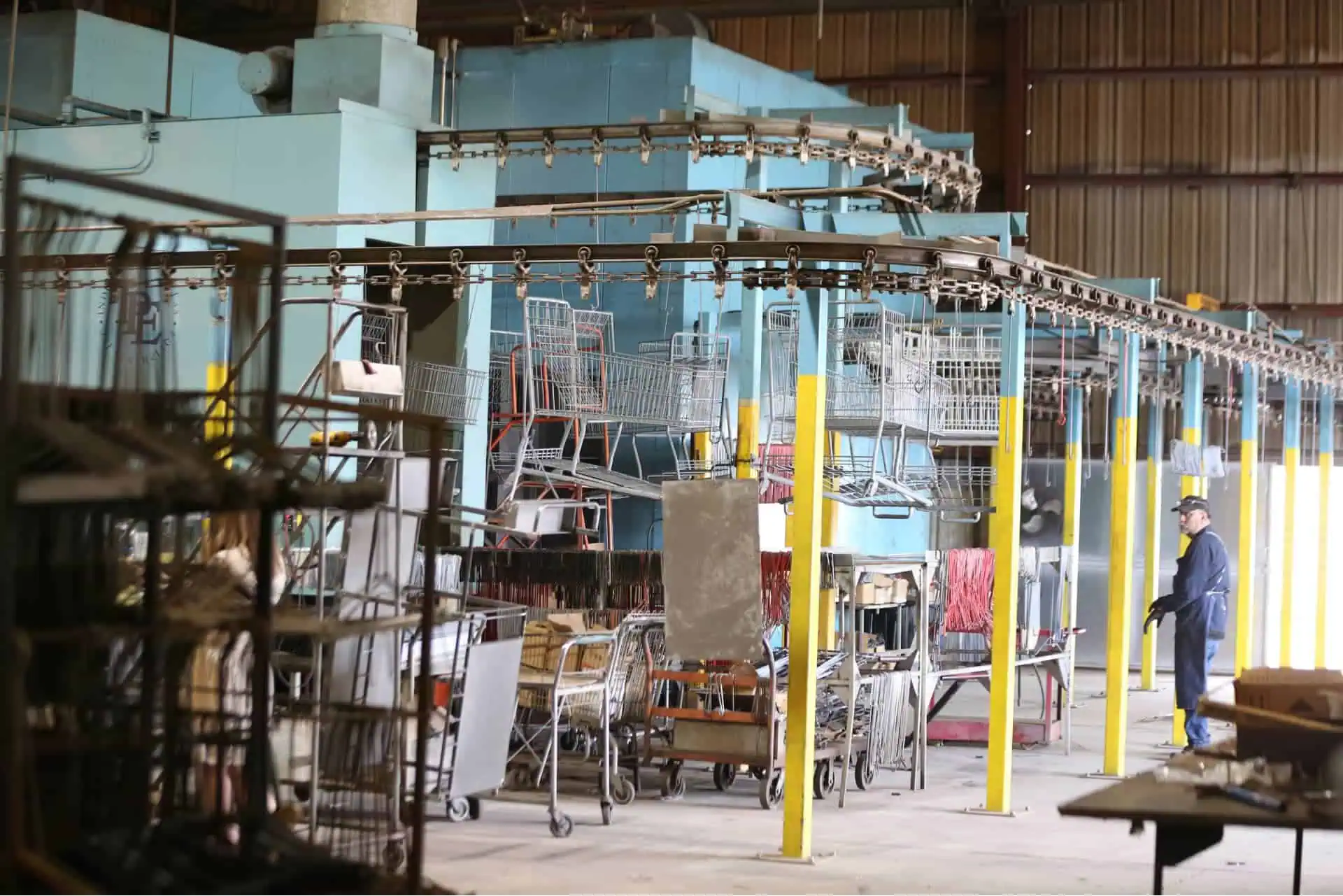

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Grocery Cart Parts
The global market for grocery cart parts is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by evolving retail infrastructure, sustainability demands, technological innovation, and shifts in consumer behavior. As supermarkets and hypermarkets modernize operations to enhance efficiency and customer experience, the demand for durable, smart, and eco-friendly cart components is set to rise. Below are the key market trends expected to shape the grocery cart parts industry through 2026.
1. Increased Demand for Durable and Recyclable Materials
By 2026, retailers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, leading to a shift from traditional steel and plastic components to recycled, recyclable, or composite materials such as recycled polyethylene and aluminum alloys. This transition is fueled by corporate environmental goals and consumer preference for eco-conscious brands. As a result, manufacturers of cart wheels, baskets, and frames are investing in materials that reduce environmental impact while maintaining structural integrity and longevity.
2. Growth in Smart Cart Technology Integration
The rise of smart grocery carts equipped with digital displays, inventory scanners, and contactless payment systems is creating new demand for advanced cart components. By 2026, parts such as embedded electronic housings, battery compartments, sensor mounts, and connectivity modules are expected to see significant growth. Retailers in North America and Europe are leading this trend, integrating IoT-enabled carts to streamline shopping and collect consumer data.
3. Expansion of E-commerce and Click-and-Collect Services
The surge in online grocery shopping and curbside pickup has altered cart usage patterns. Retailers are now deploying specialized carts for order assembly and delivery logistics. This has created demand for modular cart parts—such as detachable baskets, adjustable shelves, and ergonomic handles—designed for efficiency in backroom operations. By 2026, these specialized components are expected to represent a growing segment of the market.
4. Rising Replacement and Aftermarket Demand
As existing fleets of grocery carts age, maintenance and replacement of worn parts (especially wheels, child seats, and basket linings) are becoming a key revenue stream. The aftermarket for replacement parts is expanding, particularly in regions with large supermarket chains and cost-conscious operators seeking to extend the life of their carts. Online distribution platforms are making it easier for retailers to source individual components, further fueling this trend.
5. Regional Market Diversification and Emerging Market Growth
While North America and Europe remain dominant markets due to high supermarket penetration and technological adoption, regions such as Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa are witnessing rapid retail modernization. By 2026, these emerging markets are expected to drive demand for affordable, low-maintenance cart parts suited to local conditions, such as rugged wheels for uneven surfaces and corrosion-resistant materials in humid climates.
6. Focus on Ergonomics and Accessibility
Retailers are placing greater emphasis on inclusive shopping experiences, prompting redesigns of cart components for improved ergonomics and accessibility. By 2026, demand is rising for adjustable-height handles, smoother-rolling wheels, and lightweight frames that benefit elderly and disabled shoppers. Regulatory standards and consumer advocacy are accelerating this trend.
7. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Post-pandemic supply chain disruptions have prompted grocery cart parts manufacturers to reevaluate sourcing strategies. By 2026, there is a growing shift toward regional production and supplier diversification to mitigate risks. This trend supports the localization of component manufacturing, particularly in North America and Europe, reducing lead times and transportation costs.
Conclusion
By 2026, the grocery cart parts market will be shaped by sustainability, digitization, and operational efficiency. Manufacturers who innovate in materials, embrace smart technology, and adapt to regional demands will be best positioned to capture growth. As retailers continue to modernize, the role of cart components will expand beyond utility to become integral to the shopping experience and environmental goals.
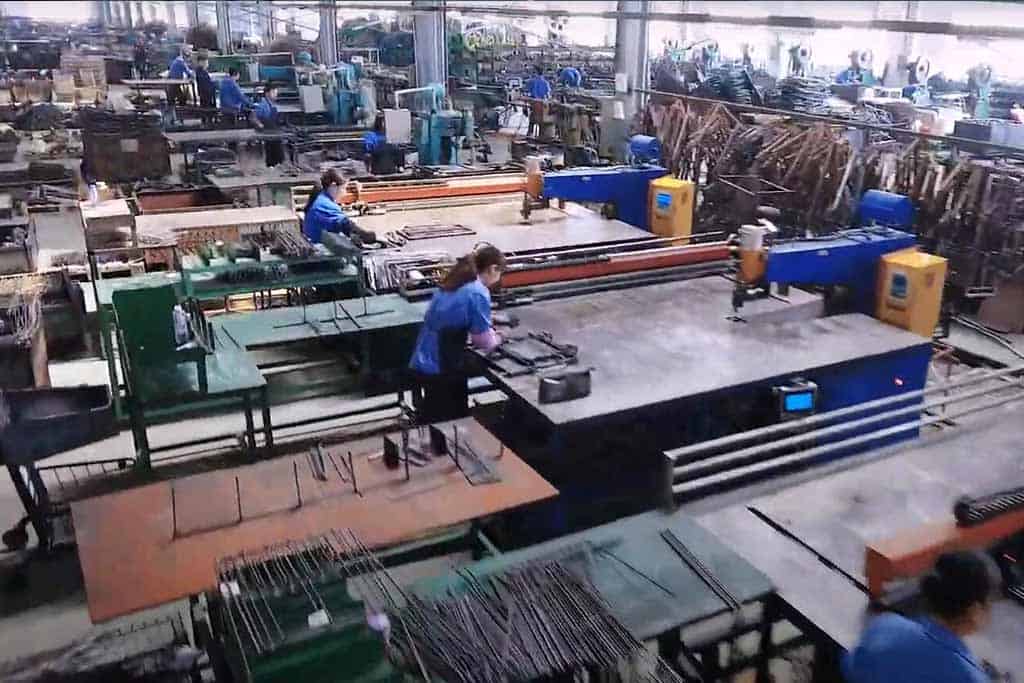

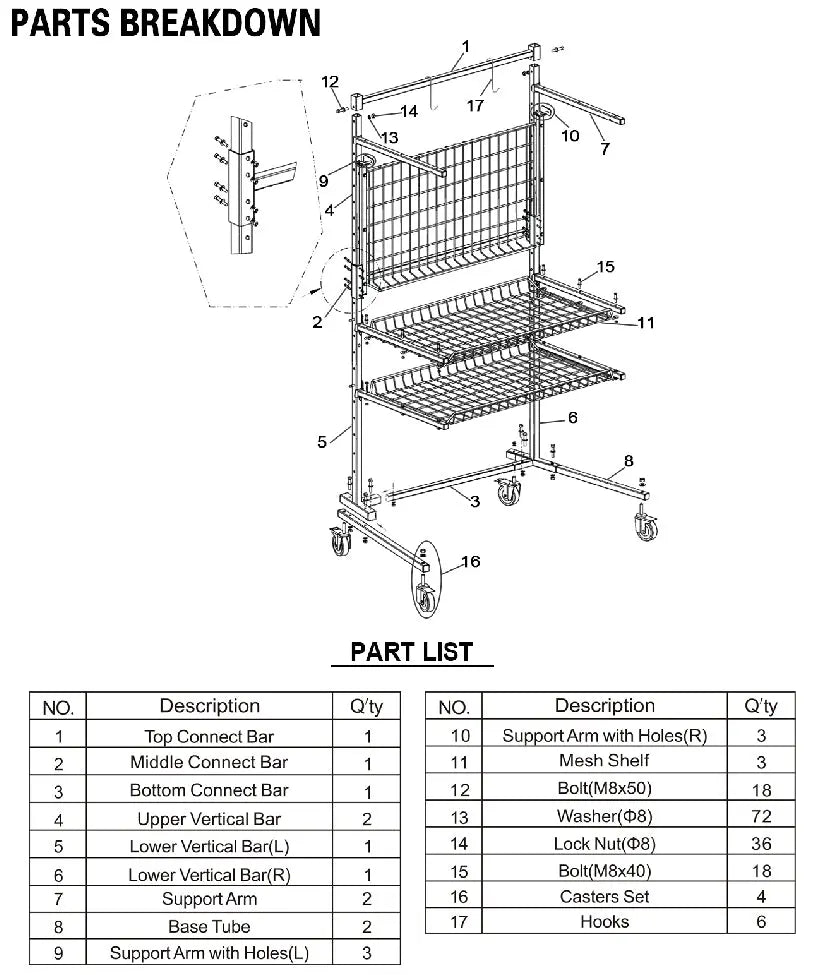
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Grocery Cart Parts (Quality, IP)
Sourcing grocery cart parts can seem straightforward, but businesses often encounter significant challenges related to part quality and intellectual property (IP). Avoiding these pitfalls is crucial to maintaining operational efficiency, ensuring customer safety, and protecting your brand from legal risks.
Poor Part Quality Leading to Premature Failures
One of the most frequent issues is receiving grocery cart parts—such as wheels, baskets, or handles—that do not meet durability or performance standards. Low-quality materials, such as brittle plastics or thin-gauge steel, can result in parts cracking, breaking, or wearing out quickly under daily use. This leads to increased maintenance costs, frequent replacements, and customer dissatisfaction due to malfunctioning carts.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances
Even if individual parts appear well-made, inconsistent manufacturing tolerances can make assembly difficult or cause misalignment in the final cart. Wheels that don’t track straight, baskets that don’t fit properly, or handlebars that wobble reduce usability and create safety hazards. These inconsistencies are often the result of working with suppliers who lack robust quality control processes.
Lack of Compliance with Safety and Regulatory Standards
Some sourced parts may not comply with regional safety standards (e.g., ASTM F963 in the U.S. for consumer products). Using non-compliant parts exposes retailers to liability in case of accidents and can result in regulatory penalties or recalls. This is especially critical for components like child seats or folding mechanisms that bear weight or pose entrapment risks.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Many grocery cart designs, especially proprietary components like patented wheel assemblies or unique basket geometries, are protected by intellectual property rights. Sourcing generic or “compatible” parts from third-party suppliers can inadvertently infringe on patents, trademarks, or design rights. This exposes the buyer to legal action, cease-and-desist orders, or costly litigation, particularly if the parts closely mimic a branded original equipment manufacturer (OEM) design.
Unauthorized Use of Brand Logos or Design Elements
Using replacement parts that feature logos, branding, or design elements from original manufacturers without authorization constitutes trademark infringement. Even if the part functions well, attaching a protected logo without a license can lead to legal disputes and damage brand reputation.
Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability Gaps
Without clear visibility into the supply chain, companies may unknowingly source parts from unauthorized or unqualified manufacturers. This lack of traceability complicates quality assurance and increases the risk of counterfeit or substandard components entering the inventory.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, businesses should:
– Partner with reputable, vetted suppliers who provide quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001).
– Conduct regular on-site audits and request material test reports.
– Verify IP status and obtain proper licensing when using OEM-compatible designs.
– Clearly define technical specifications and tolerances in procurement contracts.
– Work with legal counsel to ensure compliance with IP and consumer safety regulations.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, organizations can ensure reliable cart performance, reduce long-term costs, and protect themselves from legal exposure.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Grocery Cart Parts
Overview
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the manufacturing, transportation, storage, and distribution of grocery cart parts. These components—such as wheels, baskets, child seats, handles, and frames—must meet safety, environmental, and regulatory standards while being efficiently managed throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance
Grocery cart parts must comply with national and international regulations depending on the target market. Key requirements include:
- Consumer Product Safety Standards: In the U.S., parts must meet standards set by the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC), particularly for child seats and structural components.
- RoHS & REACH Compliance: If parts contain electronic sensors or are made from plastics/metals, they must comply with Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) in the EU and REACH regulations regarding chemical use.
- Proposition 65 (California): Warnings may be required if parts contain chemicals listed under California’s Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act.
- ADA Guidelines: Handle design and cart maneuverability should consider accessibility standards, especially for components affecting usability.
Ensure proper documentation, including Certificates of Compliance (COC), Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), and test reports from accredited labs.
Material Handling & Packaging
Proper packaging safeguards parts during transit and storage:
- Use corrugated cardboard, reusable plastic totes, or wooden crates based on part size and fragility.
- Protect metal components from rust with anti-corrosion wraps or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) packaging.
- Clearly label packages with part numbers, quantities, weight, and handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”).
- Implement barcoding or RFID tags for traceability and inventory management.
Minimize packaging waste to align with sustainability goals and reduce shipping costs.
Transportation & Shipping
Efficient transportation planning is critical:
- Mode Selection: Use full truckload (FTL) or less-than-truckload (LTL) shipping based on volume. For international shipments, consider containerized ocean freight or air freight for urgent components.
- Weight & Dimensions: Optimize load configuration to maximize cubic utilization and minimize freight class (NMFC code).
- Temperature & Environment: Store and ship plastic and rubber parts away from extreme heat or cold to prevent warping or brittleness.
- Customs Documentation: For cross-border shipments, provide accurate HS codes (e.g., 8716.80 for parts of wheeled vehicles), commercial invoices, and packing lists.
Partner with carriers experienced in industrial parts logistics to reduce damage and delays.
Warehousing & Inventory Management
Effective storage practices ensure part availability and integrity:
- Store parts on pallets or shelving to avoid floor contact and moisture damage.
- Implement a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) system for materials prone to degradation (e.g., rubber wheels).
- Use Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) to track stock levels, locations, and reorder points.
- Conduct regular cycle counts to maintain inventory accuracy.
Segregate hazardous materials (e.g., lubricants) according to OSHA and fire safety codes.
Quality Assurance & Traceability
Maintain consistent part quality and compliance:
- Perform incoming inspection of raw materials and outgoing audit of finished parts.
- Keep lot numbers and manufacturing dates for full traceability in case of recalls.
- Maintain records of supplier certifications, quality control (QC) reports, and non-conformance logs.
- Adhere to ISO 9001 standards if applicable for quality management systems.
Sustainability & Environmental Responsibility
Environmental compliance and sustainable practices are increasingly important:
- Recycle metal scrap and plastic offcuts during manufacturing.
- Source recycled materials (e.g., recycled steel or HDPE) where feasible.
- Comply with local waste disposal regulations for industrial byproducts.
- Reduce carbon footprint by optimizing transport routes and using eco-friendly packaging.
Supplier & Vendor Compliance
Ensure all suppliers meet required standards:
- Conduct audits of key suppliers for quality, labor practices, and environmental compliance.
- Require suppliers to provide compliance documentation (e.g., Conflict Minerals reports, ISO certifications).
- Include compliance clauses in procurement contracts.
Incident Response & Recalls
Prepare for potential compliance or safety issues:
- Establish a recall plan detailing notification procedures, return logistics, and root cause analysis.
- Register with relevant authorities (e.g., CPSC in the U.S.) for product incident reporting.
- Train staff on handling customer complaints and safety concerns related to cart parts.
By integrating these logistics and compliance practices, businesses can ensure the safe, efficient, and lawful handling of grocery cart parts across the supply chain.
In conclusion, sourcing grocery cart parts requires a strategic approach that balances cost, quality, durability, and supplier reliability. By identifying key components such as wheels, baskets, handles, and connectors, businesses can target suppliers specializing in durable, interchangeable, and compliant parts that meet industry standards. Exploring both domestic and international suppliers, evaluating materials (such as recyclable plastics and reinforced steel), and considering after-sales support and lead times are critical factors in making informed procurement decisions. Establishing long-term relationships with reputable manufacturers not only ensures consistent quality and timely replacements but also supports sustainability initiatives through repair and reuse programs. Ultimately, effective sourcing of grocery cart parts contributes to improved operational efficiency, reduced long-term costs, and enhanced customer experience in retail environments.