The global laboratory consumables market, which includes precision tools such as glass Pasteur pipettes, is experiencing steady expansion driven by rising demand in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and academic research. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the laboratory consumables market was valued at USD 49.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.3% through 2028. This growth trajectory reflects increasing investment in R&D infrastructure and stringent quality control requirements, particularly in high-throughput environments where precision instruments like capillary glass pipettes are essential. Pasteur pipettes with controlled inner diameters—often ranging from 1.0 mm to 3.0 mm—are critical for accurate liquid handling in micro-scale applications. As demand for standardized, high-quality glass pipettes rises, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in precision engineering, diameter consistency, and volume calibration. These companies combine stringent ISO certifications, advanced glass-drawing techniques, and large-scale production capabilities to meet the evolving needs of modern laboratories worldwide. In this data-driven landscape, the top eight glass Pasteur pipette diameter manufacturers stand out for their technical accuracy, regulatory compliance, and market reach.
Top 8 Glass Pasteur Pipette Diameter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Pasteur Pipets
Domain Est. 1995
Website: fishersci.com
Key Highlights: Corning™ Disposable Glass Pasteur Pipets are ideal for nonvolumetric transfer work in bacteriology, immunology, hematology and serology studies….
#2 Pasteur Pipettes
Domain Est. 1996
Website: dwk.com
Key Highlights: Explore DWK’s range of pasteur pipettes, designed for accurate and safe fluid handling in laboratories. Available in non-sterile and sterile!…
#3 Pasteur Pipettes, Disposable
Domain Est. 1996
#4 250PK Disposable Pasteur Pipettes, Soda Glass, No Teat
Domain Est. 2000
Website: eiscolabs.com
Key Highlights: The product measures 5.9 inches (150.77mm) in length and an outer diameter of 7mm. Whether you’re in a professional laboratory, classroom, or conducting ……
#5 Pasteur pipettes
Domain Est. 2002
Website: dutscher.com
Key Highlights: Pasteur pipette VOLAC. Discover. Low capillary diameter: 1.5 mm. Soda-lime glass. Glass Pasteur pipettes, non-cottoned. Discover. • Made from soda-lime glass…
#6 Pasteur Pipets for Transfer & Sampling
Domain Est. 2002
Website: seco.us
Key Highlights: 2–6 day delivery · 7-day returnsPasteur pipets for sample transfer and aliquoting. Choose glass or plastic formats, sterile options, and bulb compatibility for clean handling….
#7 Volac Pasteur pipette 230 mm
Domain Est. 2014
Website: ddbiolab.com
Key Highlights: Volac Pasteur pipette 230 mm. 320248. Print Share. Sales Unit : 1000. Brand : DIVERS DUTSCHER. Part Number : D812. See specific terms. 127.20 €….
#8 Glass Pasteur pipettes
Website: deltalab.es
Key Highlights: Dimensions: Ø mouth: 6.95 ± 0.15 mm; Ø tip: 1.2 ± 0.15 mm; 0.53 ± 0.03 thick. Closed: Made of neutral soda glass, with the tip closed and cotton in the mouth….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Glass Pasteur Pipette Diameter

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Glass Pasteur Pipette Diameter
The global market for laboratory consumables, including glass Pasteur pipettes, is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by increasing demand in life sciences, pharmaceutical research, and academic laboratories. Within this market, specific trends related to glass Pasteur pipette diameter are emerging due to evolving application requirements, automation integration, and standardization efforts.
-
Standardization of Diameter Sizes
By 2026, industry demand for consistency and compatibility with automated liquid handling systems is expected to reinforce the dominance of standard diameter ranges. The most commonly used outer diameters—ranging from 5 mm to 7 mm—are likely to remain prevalent. Manufacturers are increasingly aligning production with ISO and ASTM standards to ensure interoperability with pipette bulbs, fillers, and dispensing equipment, particularly in high-throughput environments. -
Shift Toward Precision and Consistency
Laboratories engaged in sensitive applications such as cell culture, microinjection, and analytical chemistry are demanding tighter tolerances in pipette diameter. This trend is driving innovation in manufacturing processes, with suppliers investing in precision glass-drawing technologies. Pipettes with diameters optimized for low dead volume and controlled flow rates (e.g., narrow 5–5.5 mm variants) are gaining traction in specialized research settings. -
Demand for Specialized Diameters in Niche Applications
While standard diameters dominate, there is growing market segmentation for specialized pipettes. For example, micro-volume applications may require ultra-fine diameters (<5 mm) for precise droplet control, particularly in embryology and nanoliter-scale assays. Conversely, industrial-scale transfer applications favor wider diameters (7 mm and above) for higher flow rates. By 2026, niche suppliers are expected to expand offerings in these specialized diameter categories to meet demand from biotech startups and contract research organizations (CROs). -
Impact of Material Innovation on Diameter Performance
Advancements in borosilicate glass formulation are enhancing durability and chemical resistance, allowing for thinner-walled designs without sacrificing strength. This enables manufacturers to maintain or slightly reduce outer diameter while preserving inner bore integrity. These innovations support the production of lightweight, high-precision pipettes that meet the ergonomic and functional needs of modern labs. -
Regional Market Variations
In North America and Europe, regulatory emphasis on reproducibility and GLP compliance is reinforcing demand for calibrated pipettes with certified diameters. In contrast, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America show higher demand for cost-effective, general-purpose pipettes with standard diameters. However, as these regions expand their R&D infrastructure, demand for precision-diameter glass pipettes is expected to rise, narrowing the gap by 2026. -
Sustainability and Reusability Influences
While plastic alternatives are gaining ground, reusable glass Pasteur pipettes retain a strong foothold in environmentally conscious and high-temperature applications. The durability of glass allows for repeated sterilization, making diameter consistency over multiple uses a key selling point. Suppliers are emphasizing long-term performance metrics, including diameter stability after autoclaving, as a competitive advantage.
In summary, the 2026 market for glass Pasteur pipette diameter will be characterized by a dual trend: consolidation around standardized dimensions for broad compatibility and innovation in specialized diameters for precision applications. Manufacturers that balance scalability, precision, and sustainability will be best positioned to capture growth in both established and emerging laboratory sectors.
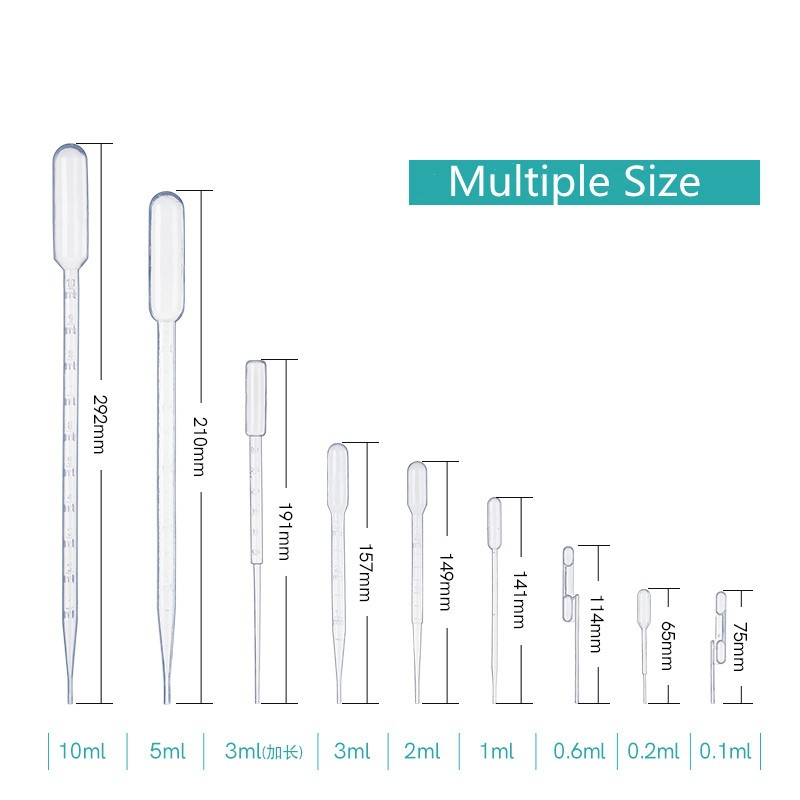

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Glass Pasteur Pipettes by Diameter (Quality & IP Considerations)
Sourcing glass Pasteur pipettes based on diameter involves more than just matching a size specification. Overlooking quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to compromised performance, regulatory non-compliance, or legal risks. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Assuming All Pipettes of the Same Diameter Perform Equally
A common mistake is treating pipettes with identical nominal diameters (e.g., 5 mm outer diameter) as functionally interchangeable. In reality, variations in glass thickness, bore consistency, and tip geometry—often not specified in basic product descriptions—can significantly affect liquid handling precision, flow rate, and breakage resistance. Lower-quality pipettes may have inconsistent wall thickness, leading to unpredictable performance during aspiration and dispensing.
2. Overlooking Glass Quality and Manufacturing Standards
Not all borosilicate glass is created equal. Inferior pipettes may use substandard glass with higher coefficients of thermal expansion or reduced chemical resistance, increasing the risk of cracking during sterilization or exposure to solvents. Always verify compliance with established standards such as ISO 7786 or ASTM E969, which govern material composition and dimensional tolerances. Failure to do so can result in contamination or safety hazards in sensitive applications.
3. Ignoring Tip Geometry and Calibration Accuracy
Diameter specifications typically refer to the shaft, but tip diameter and taper are critical for accurate liquid delivery and compatibility with pipette bulbs or dispensers. Poorly formed tips—either too blunt or inconsistently shaped—can cause dripping, inaccurate volume transfer, or difficulty in accessing narrow containers. Ensure that pipettes are manufactured under tight tolerances and, where applicable, are individually inspected or calibrated.
4. Disregarding Intellectual Property in Proprietary Designs
Some suppliers offer pipettes with patented designs—such as specialized tip coatings, color-coding systems, or ergonomic features—protected under IP law. Sourcing generic versions that mimic these designs without authorization may lead to infringement claims, especially in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals or diagnostics. Always verify that the product does not violate existing patents or trademarks, particularly when sourcing from third-party or offshore manufacturers.
5. Prioritizing Cost Over Traceability and Certification
Choosing the lowest-cost option often means sacrificing documentation. Reputable suppliers provide lot traceability, certificates of conformance, and material safety data sheets (MSDS). Lack of these can be a major pitfall in regulated environments (e.g., GLP, GMP labs), where audit trails and quality assurance are mandatory. Pipettes without proper certification may be excluded from use in validated processes.
6. Failing to Validate Supplier Claims
Marketing materials may claim “precision-bore” or “laboratory-grade” without substantiating evidence. Without independent validation or access to quality audit reports, buyers risk receiving non-conforming products. Conduct supplier audits or request sample testing before large-scale procurement, particularly when diameter consistency is critical for automated systems or high-throughput workflows.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—focusing on material quality, dimensional consistency, regulatory compliance, and IP integrity—organizations can ensure reliable performance and mitigate risks when sourcing glass Pasteur pipettes by diameter.
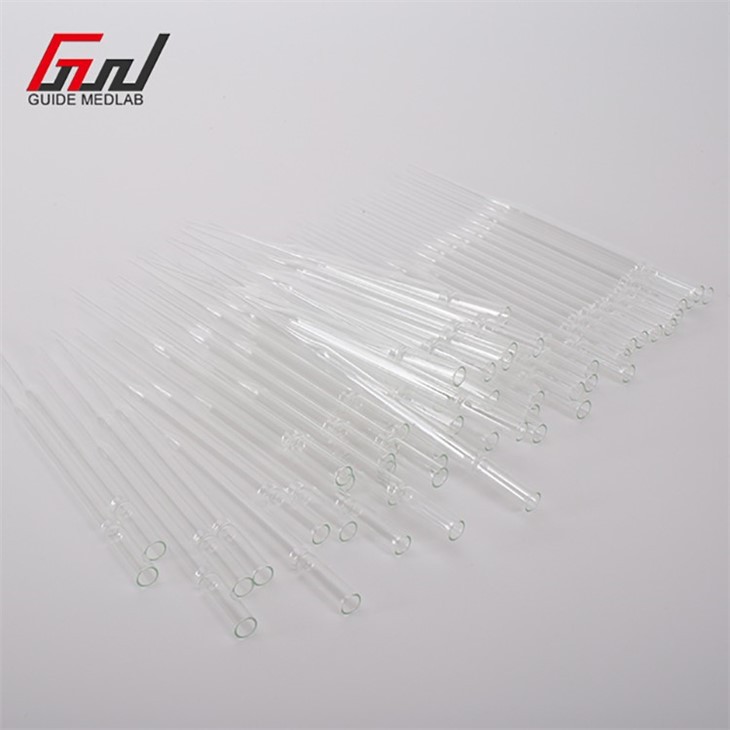

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Glass Pasteur Pipettes: Diameter Specifications
Understanding Diameter Variability in Glass Pasteur Pipettes
Glass Pasteur pipettes are widely used in laboratories for the transfer of small liquid volumes. Unlike volumetric or micropipettes, Pasteur pipettes are non-graduated and typically used with pipette bulbs or pumps. A critical yet often overlooked specification is the pipette’s inner and outer diameter, which can affect fluid flow, dispensing accuracy, and compatibility with accessories.
While standardized in length and general design, the diameter of glass Pasteur pipettes is not uniformly regulated under a single international standard, leading to variability between manufacturers. Typical outer diameters range from 5 mm to 7 mm, with inner diameters generally between 1 mm to 3 mm. This variation can impact:
- Compatibility with rubber bulbs, pipette fillers, or automated liquid handling systems
- Capillary action and droplet formation
- Suitability for viscous or particulate-laden liquids
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
ISO and ASTM Standards
Currently, no dedicated ISO or ASTM standard governs the dimensional specifications of general-purpose glass Pasteur pipettes. However, related standards may apply indirectly:
- ISO 758:2020 – Specifies requirements for glass measuring cylinders, which reference glass quality and tolerances but not Pasteur pipettes directly.
- ASTM E969 – Standard Specification for Glass Volumetric Pipets – Applies to volumetric (not transfer or Pasteur) pipettes and does not cover non-graduated types.
As a result, compliance relies heavily on manufacturer specifications and adherence to Good Laboratory Practice (GLP).
Material and Safety Compliance
Glass Pasteur pipettes must comply with general laboratory safety and material regulations:
- REACH (EU) and TSCA (USA): Ensure the glass and any coatings are free from restricted substances.
- USP <381> Pharmaceutical Glass Containers: While not directly applicable, borosilicate glass used in high-quality pipettes often meets Type I glass criteria for chemical resistance.
- Sharps Safety: Due to their pointed tips, glass Pasteur pipettes are considered sharps. Disposal must comply with OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard (29 CFR 1910.1030) and local biohazard waste regulations.
Logistics and Handling Best Practices
Procurement and Inventory Management
- Specify inner and outer diameter requirements in procurement orders to ensure consistency.
- Source from reputable suppliers who provide Certificate of Conformance (CoC) and batch traceability.
- Store in original packaging to prevent breakage and contamination, in a dry, temperature-stable environment.
Packaging and Shipping
- Glass Pasteur pipettes are typically shipped in rigid cardboard tubes or plastic trays to prevent breakage.
- Ensure UN-rated packaging if shipping internationally or transporting biohazard-contaminated items.
- Label shipments with “Fragile” and “Laboratory Glassware” identifiers.
Import/Export Compliance
- Verify HS Code classification: Typically under 7017 20 00 (Laboratory glassware, not optical).
- Confirm compliance with destination country regulations (e.g., Health Canada, TGA Australia, NMPA China) if pipettes are sold as part of diagnostic or medical kits.
- For autoclavable or sterile pipettes, ensure sterilization method (e.g., gamma irradiation) is documented and compliant with medical device directives if applicable.
Recommendations for Laboratories
- Standardize by Diameter: Define acceptable diameter ranges in SOPs to minimize variability in experimental outcomes.
- Vendor Qualification: Audit suppliers for quality control practices, including dimensional consistency checks.
- Labeling: Clearly label pipette storage with manufacturer, dimensions, and sterility status (if applicable).
- Training: Train personnel on proper handling, disposal, and risks associated with glass pipettes.
By proactively managing diameter specifications and aligning logistics with regulatory expectations, laboratories can ensure safety, reproducibility, and compliance in their operations.
In conclusion, sourcing glass Pasteur pipettes with a specific or consistent diameter requires careful consideration of the manufacturer specifications, quality control standards, and intended application. While traditional Pasteur pipettes are not typically standardized to precise diameter tolerances like volumetric glassware, variations in tip bore and shaft diameter can significantly impact performance—especially in applications requiring precise liquid handling, filtration, or compatibility with rubber bulbs or automated systems.
To ensure consistency and suitability, it is recommended to source pipettes from reputable suppliers who provide detailed product specifications, including average outer and inner diameters. Where tight dimensional control is critical, consideration should be given to calibrated or precision glassware alternatives. Additionally, batch testing and visual inspection upon receipt can help verify diameter uniformity. Ultimately, clear communication with suppliers and alignment with application requirements are key to successfully sourcing glass Pasteur pipettes with the appropriate diameter characteristics.