The global demand for precision marking solutions in industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods has driven significant advancements in laser marking technology—particularly for applications involving glass. With the need for permanent, high-contrast, and non-contact marking on fragile and heat-sensitive materials, glass laser marking machines have emerged as a critical component in modern manufacturing. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global laser marking machines market was valued at USD 2.87 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 4.32 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 7.1% during the forecast period. This growth is fueled by increasing automation, stringent product traceability regulations, and the expansion of high-tech manufacturing sectors. As a result, a select group of manufacturers has risen to prominence by delivering innovative, reliable, and application-specific glass laser marking solutions. The following list highlights the top 10 manufacturers shaping this competitive landscape through technological excellence and strong market presence.
Top 10 Glass Laser Marking Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Marking Machines for Glass
Domain Est. 1996
Website: telesis.com
Key Highlights: You can produce the best glass marking results with a laser marking machine from Telesis Technologies, Inc. Get a quote on a glass laser marker today!…
#2 Laser Marking Machines
Domain Est. 1997
Website: videojet.com
Key Highlights: Shop Videojet laser marking machines and industrial laser marking systems. Get a free quote and optimize your production line today!…
#3 Laser Marking for All Industries
Domain Est. 2006
Website: lasermarktech.com
Key Highlights: Discover innovative laser marking solutions tailored for various industries. Explore our cutting-edge technology as leaders in laser marking and engraving….
#4 Glass Engraving
Domain Est. 1996
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Unlock glass engraving with our laser marking solutions: precision glass marking and etching. Discover our glass engraving machine for exquisite laser glass ……
#5 Laser Engraving & Etching Glass with an Epilog Laser Machine
Domain Est. 1997
Website: epiloglaser.com
Key Highlights: Glass engraving and etching with a CO2 laser produces a beautiful frosted effect, allowing you to etch custom logos and designs on nearly any glass product….
#6 Trotec Laser
Domain Est. 2002
Website: troteclaser.com
Key Highlights: High-end laser machines for precise engraving, marking and cutting. Trotec lasers for printers, manufacturing industry, engravers and schools. Based on over 25 ……
#7 Leader In Permanent Marking Solutions
Domain Est. 2007
Website: gravotech.us
Key Highlights: Gravotech designs, manufactures, and distributes innovative engraving, marking, and cutting solutions….
#8 Laser Equipment Supplier
Domain Est. 2007
Website: radianlaser.com
Key Highlights: Radian Laser Systems is a laser equipment supplier specializing in high-speed, customizable laser machinery, including fiber, CO2, and galvo lasers….
#9 Laser Cutting, Engraving & Marking Machines
Domain Est. 2010
Website: thunderlaser.com
Key Highlights: Thunder Laser offers high-quality, reliable laser machines to meet the needs of a variety of industries. ThunderLaser has become a well-recognized icon in ……
#10 Laser Marking
Domain Est. 2016
Website: cermarkusa.com
Key Highlights: Laser marking is a cost-effective and reliable way to mark parts and components with information such as serial numbers, barcodes, logos, and text….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Glass Laser Marking Machine
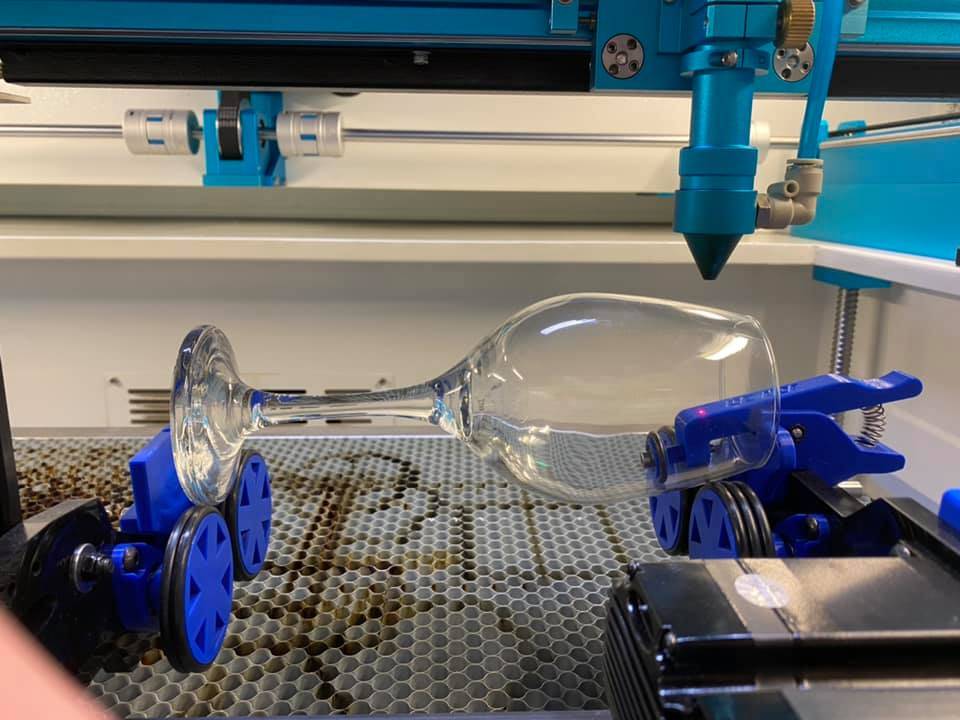

H2: Market Trends for Glass Laser Marking Machines in 2026
By 2026, the global market for glass laser marking machines is expected to witness significant growth, driven by advancements in laser technology, increasing demand for precision marking across industries, and a growing emphasis on product traceability and anti-counterfeiting measures. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Rising Adoption in the Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Sectors
The pharmaceutical industry is increasingly utilizing glass laser marking machines for permanent, high-precision labeling on vials, syringes, and ampoules. Regulatory requirements for unique device identification (UDI) and serialization are accelerating adoption, particularly in North America and Europe. Laser marking ensures compliance with standards such as FDA 21 CFR Part 11 and EU MDR. -
Growth in Consumer Electronics and Smart Devices
The consumer electronics industry relies heavily on glass components—such as smartphone covers, watch faces, and display panels—that require durable, aesthetically pleasing markings. Fiber and UV laser systems are being optimized for cold marking on glass, minimizing thermal stress and micro-cracking, thus supporting the trend toward sleek, high-end product designs. -
Advancements in Ultrafast and UV Laser Technology
Ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) and UV lasers are gaining traction due to their ability to produce high-contrast, non-ablative marks on sensitive glass surfaces without compromising structural integrity. These technologies enable intricate designs, QR codes, and micro-text, meeting the needs of industries demanding both functionality and aesthetics. -
Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
Glass laser marking machines are increasingly being integrated into automated production lines with IoT-enabled monitoring, real-time data logging, and AI-driven quality control. This connectivity supports predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and ensures consistent marking quality—key factors in high-volume manufacturing environments. -
Expansion in the Food and Beverage Industry
With growing demand for traceability and brand authenticity, beverage manufacturers are adopting laser marking for batch coding, expiration dates, and promotional messages directly on glass bottles. The non-contact nature of laser systems ensures hygiene and reduces contamination risks compared to ink-based methods. -
Sustainability and Regulatory Push Toward Non-Ink Solutions
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are driving a shift away from inkjet coding, which involves solvents and consumables. Laser marking offers a clean, chemical-free alternative with lower long-term operational costs, making it a preferred choice in eco-conscious markets. -
Regional Market Growth in Asia-Pacific
Countries such as China, India, and South Korea are emerging as key growth hubs due to expanding manufacturing bases, rising investments in automation, and supportive government initiatives in advanced manufacturing. Local production of laser components is also reducing equipment costs and improving accessibility. -
Customization and Personalization Trends
Demand for personalized glass products—such as engraved drinkware, luxury packaging, and custom architectural glass—is fueling the adoption of desktop and semi-automated laser marking systems. This trend is particularly strong in the retail and gifting sectors.
In conclusion, the glass laser marking machine market in 2026 will be shaped by technological innovation, regulatory compliance, and cross-industry demand for precision, durability, and sustainability. Companies investing in advanced laser sources, software integration, and application-specific solutions are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Glass Laser Marking Machine (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a glass laser marking machine involves more than just selecting the right technical specifications. Buyers often encounter significant challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for making a reliable and legally sound investment.
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many suppliers, especially low-cost manufacturers, use substandard materials and components to cut costs. This can lead to premature wear, inconsistent performance, and frequent breakdowns. Look out for machines with non-industrial-grade lasers, weak frame construction, or inadequate cooling systems, all of which compromise reliability and longevity.
Inaccurate or Exaggerated Performance Claims
Some suppliers overstate a machine’s capabilities—such as marking speed, precision, or compatibility with various glass types. These misleading claims can result in the machine failing to meet production requirements. Always request real-world test results or live demonstrations with your specific glass materials before purchasing.
Lack of After-Sales Support and Service
A major pitfall is choosing a supplier with limited or no local technical support. If the machine breaks down and spare parts take weeks to arrive or technicians are unavailable, production downtime can be costly. Verify the availability of maintenance services, training, and technical assistance before finalizing a purchase.
Inadequate Safety and Compliance Features
Low-quality machines may not meet international safety standards (e.g., CE, FDA, or ISO). This poses risks to operators and could lead to legal issues or facility shutdowns. Ensure the machine includes proper laser shielding, emergency stops, and ventilation systems, and confirm compliance documentation.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Purchasing machines that incorporate copied or reverse-engineered technology can expose your business to legal liability. Some suppliers use counterfeit control software, clone patented optical systems, or replicate branded designs. This not only supports unethical practices but may result in third-party IP lawsuits or customs seizures.
Use of Proprietary Software Without Licensing
Many budget machines run on unlicensed or pirated software, which can lead to system instability, lack of updates, and legal exposure. Ensure the supplier uses legally licensed software and, ideally, provides open or documented APIs for integration and future scalability.
No Clear Warranty or IP Indemnification
Suppliers may offer vague or limited warranties that exclude software or critical components. Even worse, they may refuse to indemnify buyers against IP infringement claims. Always insist on a clear warranty and, when possible, contractual protection from IP-related liabilities.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: verify supplier credentials, inspect machines in person or via video, request references, and involve legal counsel when reviewing contracts. Prioritizing quality and IP integrity protects your operations, reputation, and long-term return on investment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Glass Laser Marking Machine
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the import, export, transportation, and operation of a Glass Laser Marking Machine. Adherence to these guidelines ensures safe handling, legal conformity, and smooth deployment.
Shipping and Transportation
Ensure the glass laser marking machine is securely packaged in a shock-resistant, moisture-proof crate with sufficient internal cushioning (e.g., foam inserts). Use wooden export crates compliant with ISPM-15 standards for international shipments. Clearly label the package with fragile, this-side-up, and laser equipment warnings. Choose carriers experienced in handling precision industrial machinery and provide detailed handling instructions. For air freight, comply with IATA regulations regarding electronic and mechanical equipment. Maintain temperature and humidity control during transit to prevent condensation and internal damage.
Import/Export Regulations
Verify export control classifications such as ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) under the U.S. Commerce Control List or equivalent (e.g., EU Dual-Use Regulation). Laser systems may be subject to export restrictions due to power output or controlled technology. Obtain necessary export licenses if required. For import, confirm compliance with destination country regulations including CE (Europe), UKCA (UK), or other regional conformity marks. Provide accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and a technical specification sheet detailing laser class, power, and wavelength. Consult local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker to ensure tariff code (HS Code) accuracy—common codes include 8456.11 or 8456.12 for laser processing machines.
Safety Compliance
The machine must comply with relevant laser safety standards such as IEC 60825-1 (international), FDA 21 CFR Part 1040.10 (U.S.), and EN 60825-1 (Europe). It must be classified appropriately (typically Class 1 or Class 4 with interlocks). Install safety interlocks, key switches, emergency stop buttons, and protective enclosures. Provide visible warning labels indicating laser radiation hazards. Include a user-accessible laser safety manual and ensure operators are trained in safe operation and emergency procedures. Conduct regular safety audits and maintain a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) if required by local regulations.
Electrical and EMC Standards
Ensure the machine meets voltage, frequency, and plug type requirements of the operating region (e.g., 110V/60Hz in North America, 230V/50Hz in Europe). Use power conditioners or transformers if necessary. Verify compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) directives such as CE EMC Directive 2014/30/EU or FCC Part 15 (U.S.) to prevent interference with other equipment. Ground the machine properly and use shielded cables for all connections.
Environmental and Disposal Regulations
Adhere to RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in applicable regions. The machine should not contain restricted substances such as lead, mercury, or cadmium above permitted levels. Provide information for proper end-of-life disposal, including recycling options for electronic components and laser modules. Follow local environmental laws regarding industrial waste if consumables (e.g., cooling fluids) are used.
Documentation and User Training
Supply complete technical documentation including user manual, safety instructions, maintenance guide, and compliance certificates (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS). Provide multilingual documentation if required by the target market. Conduct on-site or virtual operator training covering machine operation, maintenance, safety protocols, and troubleshooting. Maintain records of training and equipment certification for audits.
Maintenance and Service Compliance
Establish a preventive maintenance schedule in accordance with manufacturer guidelines. Only qualified technicians should perform service, especially on laser optics and power systems. Keep logs of all maintenance, repairs, and component replacements. Ensure spare parts are authentic and meet original compliance standards. Update firmware and software regularly to maintain safety and regulatory compliance.
In conclusion, sourcing a glass laser marking machine requires careful evaluation of several key factors to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and return on investment. It is essential to consider the type of laser (such as CO2 or fiber lasers with appropriate wavelengths for glass), marking precision, speed, and compatibility with various glass types and thicknesses. Additionally, assessing the machine’s durability, ease of integration into existing production lines, software user-friendliness, and after-sales support—including training and maintenance—is crucial. Suppliers should be vetted for reputation, technical expertise, and compliance with industry standards. Ultimately, selecting the right laser marking solution will enhance product traceability, branding, and operational efficiency, making it a strategic investment for industries such as packaging, automotive, pharmaceuticals, and consumer electronics.