The global generator control systems market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising power demand, increased backup power needs across critical infrastructure, and the expansion of decentralized energy systems. According to Mordor Intelligence, the generator control systems market was valued at USD 10.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.3% during the forecast period 2024–2029. This growth is further fueled by advancements in automation, the integration of IoT-enabled monitoring, and the push toward smart grid technologies. As industries—from healthcare to data centers—prioritize uninterrupted power supply, demand for reliable, intelligent generator control systems has surged. In this evolving landscape, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders, delivering innovative, scalable, and efficient control solutions. Based on market presence, technological advancement, and product performance, here are the top 9 generator control systems manufacturers shaping the industry today.
Top 9 Generator Control Systems Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Electric Power Systems
Domain Est. 1993
Website: cat.com
Key Highlights: 2-day deliveryTrust Caterpillar, leader in electric power systems. Our diesel & gas generator sets are solutions for commercial, industrial facilities & more….
#2 Shop Generator Controls by Manufacturer from General Power
Domain Est. 2001
Website: genpowerusa.com
Key Highlights: Customized Solutions: Generator control systems are tailored to your specific power generation requirements, ensuring a seamless fit for your unique setup….
#3 Cummins Generator Sets
Domain Est. 1990
Website: cummins.com
Key Highlights: We design, manufacture, and test all major components of our generator sets – the engine, alternator, and control systems – so they work in harmony from the ……
#4 Energy Management Solutions for Business & Service
Domain Est. 1995
Website: generac.com
Key Highlights: Explore a range of solutions that will work together to streamline your systems across every stage of the energy journey. An image of a Generac generator….
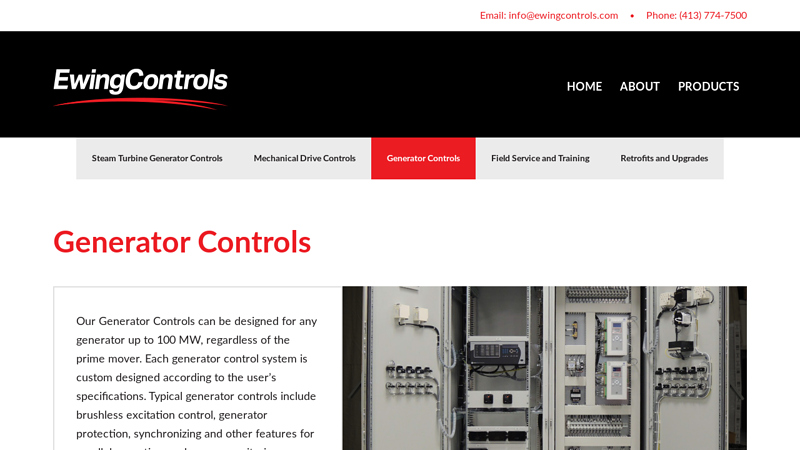
#5 Generator Controls
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ewingcontrols.com
Key Highlights: Our Generator Controls can be designed for any generator up to 100 MW, regardless of the prime mover. Each generator control system is custom designed….
#6 DSEGenset
Domain Est. 2002
Website: deepseaelectronics.com
Key Highlights: A complete range of genset control modules including synchronising & load sharing applications. Lighting tower, engine only and G59 protection solutions….
#7
Domain Est. 2004
Website: smartgen.cn
Key Highlights: The product range includes generator set controllers, low-voltage distribution controllers, marine engine and power management systems (PMS), construction ……
#8 Power Generation Products
Domain Est. 2018
Website: mtu-solutions.com
Key Highlights: We supply all the expertise, equipment and services you need to integrate your complete power solutions – from fuel supply through to electrical design….
#9 Taylor Power Systems
Domain Est. 2019
Website: taylorpowergenerators.com
Key Highlights: Taylor Power Systems combines over 30 years of innovation and reliability to deliver world-class power solutions for industries and homes around the globe….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Generator Control Systems

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Generator Control Systems
The Generator Control Systems (GCS) market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by the global push for energy resilience, decarbonization, digitalization, and grid modernization. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Accelerated Integration of Smart Grid & Digital Technologies:
By 2026, advanced digitalization will be central to GCS. Adoption of IoT-enabled controllers, cloud-based monitoring platforms, and AI-driven predictive maintenance will be mainstream. These technologies enable real-time performance analytics, remote diagnostics, and optimized generator operation, reducing downtime and operational costs. Edge computing will enhance decision-making speed at the generator site, supporting faster response to grid fluctuations.
2. Rising Demand for Hybrid and Renewable Integration:
As microgrids and hybrid power systems (combining diesel, natural gas, solar, wind, and battery storage) gain traction, GCS will evolve to manage complex multi-source environments. Advanced control algorithms will be essential for seamless load sharing, fuel optimization, and ensuring stability when integrating intermittent renewables. This trend is particularly strong in off-grid and remote applications, as well as in mission-critical facilities seeking energy independence.
3. Focus on Sustainability and Emissions Compliance:
Stricter environmental regulations worldwide will drive demand for GCS that support low-emission operations. Systems will increasingly incorporate features like automatic start/stop based on load demand, load management to minimize fuel consumption, and integration with carbon monitoring tools. Natural gas and biogas generators, which require precise control for efficiency and emissions compliance, will benefit from next-generation GCS solutions.
4. Growth in Decentralized Energy and Resilience Needs:
The increasing frequency of extreme weather events and grid instability is spurring investment in backup and primary power solutions. Data centers, healthcare facilities, and industrial sites will deploy more sophisticated GCS with enhanced automation, faster switchover times, and improved synchronization capabilities. This supports business continuity and aligns with corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) goals.
5. Cybersecurity as a Critical Requirement:
With greater connectivity comes increased cyber risk. By 2026, cybersecurity will be a non-negotiable feature in GCS design. Manufacturers will prioritize secure firmware updates, encrypted communications, and compliance with standards like IEC 62443. End-users will demand control systems with built-in threat detection and robust access controls.
6. Consolidation and Platform-Based Solutions:
Market consolidation among equipment manufacturers and control system providers will lead to integrated, vendor-agnostic platforms. These platforms will offer unified control across diverse generator fleets and energy assets, simplifying operations for facility managers and energy service companies (ESCOs).
In summary, the 2026 GCS market will be defined by intelligent, connected, and sustainable control solutions that support the transition toward resilient, low-carbon energy systems. Players who innovate in digital integration, hybrid energy management, and cybersecurity will lead the market.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Generator Control Systems: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing Generator Control Systems (GCS) involves significant technical and legal considerations, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational failures, safety hazards, financial losses, and legal disputes.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Failing to thoroughly vet suppliers based on certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, IEC 60255), industry experience, and proven track record can result in substandard control systems. Suppliers without a history of delivering reliable GCS may lack robust design, testing, and manufacturing processes, increasing the risk of premature failures or non-compliance with environmental and safety standards.
Insufficient Testing and Validation Protocols
Many organizations assume that factory acceptance tests (FAT) are sufficient, but skipping site acceptance tests (SAT) or real-world simulation under varying load conditions can mask latent defects. Inadequate validation against grid codes, fault ride-through requirements, or transient response criteria may lead to system instability or non-compliance during operation.
Use of Non-Standard or Obsolete Components
Some suppliers cut costs by incorporating outdated or non-industrial-grade components that degrade under harsh operating conditions (e.g., high temperature, vibration). This compromises long-term reliability and increases maintenance costs. Additionally, reliance on obsolete components can lead to supply chain disruptions and lack of future support.
Poor Documentation and Software Version Control
Incomplete or inaccurate documentation—such as control logic diagrams, programming code, or configuration files—hinders troubleshooting and maintenance. Poor version control increases the risk of configuration errors during upgrades or repairs, potentially leading to unplanned downtime.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unclear Ownership of Control Software and Firmware
Many suppliers retain full IP rights to embedded software, even when the system is custom-developed. This can restrict the buyer’s ability to modify, service, or transfer the system without vendor dependency. Ambiguous licensing terms may also prohibit reverse engineering or third-party integration, limiting operational flexibility.
Hidden Use of Third-Party or Open-Source Code
Suppliers may incorporate third-party or open-source software components without proper disclosure or licensing compliance. This exposes the buyer to legal risks, including infringement claims or obligations under open-source licenses (e.g., GPL), which could require the release of proprietary modifications.
Lack of Escrow Agreements for Critical Software
Without a software escrow agreement, buyers risk losing access to source code and configuration tools if the supplier goes out of business or refuses support. This can cripple long-term maintenance and upgrades, especially for mission-critical power generation systems.
Insufficient IP Clauses in Contracts
Procurement contracts that fail to explicitly define IP ownership, usage rights, and licensing terms leave buyers vulnerable. Ambiguities can lead to disputes over customization rights, system replication, or data ownership from control system logs and diagnostics.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, organizations should:
– Conduct rigorous supplier audits and request references from similar projects.
– Specify comprehensive testing requirements in procurement contracts.
– Require full disclosure of software components and licensing.
– Negotiate clear IP ownership and include software escrow provisions.
– Ensure all deliverables include complete, up-to-date documentation and source code access where applicable.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, buyers can ensure reliable, maintainable, and legally secure generator control systems.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Generator Control Systems
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the procurement, transportation, installation, operation, and maintenance of Generator Control Systems (GCS). Adhering to these practices ensures safety, regulatory adherence, and system reliability.
Procurement and Vendor Selection
Ensure that generator control systems are sourced from reputable manufacturers and suppliers with documented compliance to international and regional standards. Evaluate vendors based on adherence to ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO 14001 (environmental management), and relevant product certifications (e.g., UL, CE, CSA). Confirm that technical documentation, compliance declarations, and cybersecurity protocols are provided prior to purchase.
Transportation and Handling
Transport GCS components in manufacturer-approved packaging to prevent damage from vibration, moisture, and electrostatic discharge. Follow handling guidelines for sensitive electronics—avoid direct exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, or contaminants during transit. Maintain a documented chain of custody and inspect shipments upon arrival for damage or tampering. Store components in a controlled environment (typically 10°C–30°C, 30%–60% RH) until installation.
Import/Export Compliance
Verify that the generator control system meets export control regulations such as the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or Export Administration Regulations (EAR), if applicable. Ensure compliance with destination country import requirements, including CE marking (EU), KC certification (South Korea), or INMETRO (Brazil). Prepare accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes, commercial invoices, and certificates of origin to avoid customs delays.
Installation and Commissioning
Install GCS in accordance with manufacturer specifications and local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC 60364 internationally). Use certified technicians and follow lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during installation. Commissioning must include functional testing, synchronization checks, and integration with supervisory control systems. Document all steps for audit and compliance purposes.
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Ensure GCS complies with applicable safety and performance standards, including:
– IEC 62114 (Functional safety of electrical control systems)
– IEEE 446 (Emergency and standby power systems)
– NFPA 110 (Standard for Emergency and Standby Power Systems)
– Local grid interconnection codes (e.g., IEEE 1547 for distributed energy resources)
Maintain up-to-date records of inspections, certifications, and system modifications.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection
Implement cybersecurity measures in line with NERC CIP (North America), IEC 62443 (industrial communication networks), or NIST SP 800-82. Secure communication ports, apply firmware updates promptly, and restrict access via role-based controls. Conduct regular vulnerability assessments and ensure data logging complies with GDPR, CCPA, or other applicable data privacy laws.
Maintenance and Recordkeeping
Schedule routine maintenance per manufacturer guidelines and regulatory requirements. Keep detailed logs of inspections, repairs, software updates, and calibration. Retain records for a minimum of seven years or as mandated by jurisdiction. Use predictive maintenance tools where possible to enhance system availability and compliance.
Decommissioning and Disposal
Follow environmental regulations (e.g., WEEE in the EU, RCRA in the U.S.) when decommissioning or disposing of GCS components. Ensure proper data sanitization of control units containing sensitive operational data. Recycle electronic waste through certified vendors and document all disposal activities for audit compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Generator Control Systems
In conclusion, sourcing the right generator control system is a critical decision that directly impacts the reliability, efficiency, and safety of power generation operations. A well-chosen control system ensures seamless generator startup, stable voltage and frequency regulation, effective load management, and integration with monitoring and protection systems—especially in critical applications such as healthcare, data centers, and industrial facilities.
When sourcing these systems, it is essential to consider factors such as compatibility with existing generator sets, scalability, ease of maintenance, compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, IEC, NFPA), and cybersecurity features for remote monitoring. Opting for reputable suppliers with proven technical support and service networks further enhances long-term performance and minimizes downtime.
Additionally, investing in advanced digital controls with smart features—such as remote access, predictive diagnostics, and automated testing—can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce lifecycle costs. Ultimately, a strategic approach to sourcing generator control systems, focused on quality, reliability, and future readiness, ensures robust power continuity and supports the overall resilience of critical infrastructure.