The global gears and wheels market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across automotive, industrial machinery, and aerospace sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global gear market size was valued at USD 68.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by advancements in precision engineering, rising automation, and the proliferation of electric vehicles requiring sophisticated transmission systems. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence projects steady growth in gearwheel demand, particularly in Asia-Pacific, due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. As competition intensifies, a select group of manufacturers has emerged at the forefront, combining technological innovation, scale, and global reach to dominate the landscape. The following list highlights the top 8 gears and wheels manufacturers shaping the future of motion control and mechanical power transmission.
Top 8 Gears Wheels Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
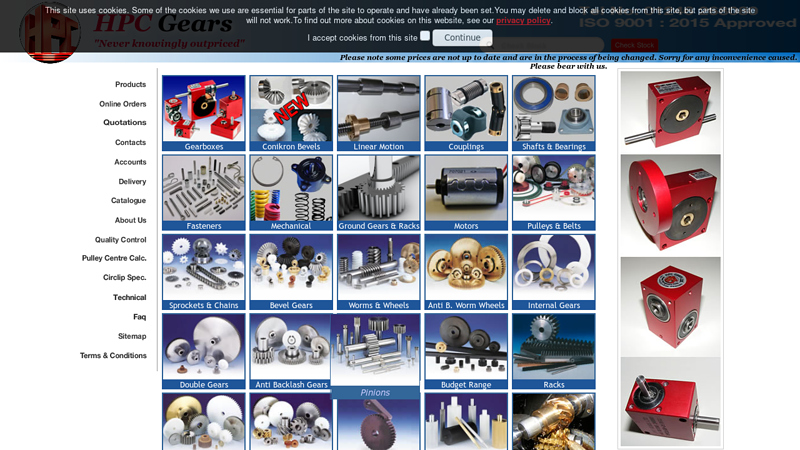
#1 HPC Gears
Domain Est. 2000
Website: hpcgears.com
Key Highlights: MANUFACTURER AND STOCKIST OF GEAR TRANSMISSION PRODUCTS. … Worms & Wheels. Worm & Wheels. Anti Backlash Worm Wheels. AntiB.Worm Wheels….
#2 Types of Gears
Domain Est. 2015
Website: khkgears.net
Key Highlights: There are many types of gears. This page explains the various types of gears, including spur gears, bevel gears, worm gears and helical gears….
#3 Gleason Corporation
Domain Est. 1991
Website: gleason.com
Key Highlights: We are a leader in the development and manufacture of production systems for all types of gears including gear and transmission design software, machines, ……
#4 Gear Off Road
Domain Est. 1992
Website: atd.com
Key Highlights: Access Gear Off Road’s top-rated portfolio of offerings. The wheels you love, and your consumers ask for by name….
#5 Yukon Gear & Axle
Domain Est. 1999
Website: yukongear.com
Key Highlights: Shop Yukon Gear & Axle for premium drivetrain components including gears, axles, lockers, and differentials. Trusted by professionals and enthusiasts alike, ……
#6 Method Race Wheels
Domain Est. 2009
Website: methodracewheels.com
Key Highlights: Method Race Wheels is committed to bringing you the finest quality products with the most complete lineup of wheels for off-road trucks, off-road buggies, ……
#7 Gear Off Road
Domain Est. 2014
Website: gearoffroad.com
Key Highlights: Discover Gear Off Road. High quality cast aluminum wheels built to accommodate the most demanding off-road environments with a design aesthetic fit for the ……
#8 HD WHEELS
Domain Est. 2019
Website: hpdwheels.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to HD Wheels. Home of the Original Spinout Wheels. CLICK – To Check out our latest wheel & rim offerings now. At HD Wheels we strive to be different ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Gears Wheels

H2: Projected Market Trends for Gears and Wheels in 2026
The global gears and wheels market is poised for substantial transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifts in industrial demand, and evolving regulatory landscapes. As critical components in automotive, industrial machinery, aerospace, and renewable energy sectors, gears and wheels are undergoing innovation to meet efficiency, sustainability, and performance goals. Below is an analysis of key market trends expected to shape the industry in 2026.
1. Increased Demand from the Automotive and EV Sectors
The automotive industry remains the largest consumer of gears and wheels, with electric vehicles (EVs) emerging as a key growth driver. By 2026, the global EV market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 20%, increasing demand for high-precision transmission gears and lightweight wheel systems. Unlike traditional internal combustion engines, EVs require fewer gears but rely on highly efficient, low-noise gear systems such as single-speed transmissions and planetary gear sets. This shift is prompting manufacturers to focus on precision engineering and advanced materials like high-strength alloys and composites.
2. Adoption of Lightweight and High-Performance Materials
To improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, both in ICE and EV platforms, manufacturers are increasingly adopting lightweight materials such as aluminum alloys, magnesium, and carbon fiber-reinforced polymers for wheels and gear housings. By 2026, the use of advanced materials is expected to grow significantly, supported by advancements in additive manufacturing (3D printing) and metal injection molding. These technologies allow for complex gear geometries and reduced part weight without sacrificing durability.
3. Growth in Industrial Automation and Robotics
The rise of smart factories and industrial automation is fueling demand for precision gears and wheels used in robotics, CNC machines, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). By 2026, the global industrial robotics market is expected to surpass $100 billion, directly benefiting gear and wheel suppliers. High-torque, low-backlash gears—such as harmonic and cycloidal drives—are seeing increased adoption, particularly in applications requiring precision motion control.
4. Expansion in Renewable Energy Applications
Wind turbines rely heavily on large-scale gearboxes (e.g., planetary and helical gears) to convert low rotor speeds into high-speed electrical generation. As global investments in wind energy continue to rise, the gears market for renewable applications is expected to expand steadily. By 2026, offshore wind projects—particularly in Europe and Asia—are anticipated to drive demand for durable, corrosion-resistant gear systems designed for harsh environments.
5. Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Reconfiguration
Asia-Pacific, led by China, India, and Japan, will remain the dominant region for gears and wheels production and consumption due to robust automotive and industrial manufacturing. However, reshoring and nearshoring trends in North America and Europe—driven by supply chain resilience and trade policy changes—are expected to boost local manufacturing. By 2026, increased investment in domestic gear production is likely in the U.S. and Germany, particularly for defense, aerospace, and EV applications.
6. Digitalization and Predictive Maintenance
The integration of IoT sensors and digital twins in gear and wheel systems is enabling predictive maintenance and real-time performance monitoring. By 2026, smart gearboxes equipped with condition-monitoring systems will become standard in industries such as mining, transportation, and energy. This trend enhances equipment uptime, reduces maintenance costs, and supports the growth of servitization business models among gear manufacturers.
7. Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt greener production methods. By 2026, expect increased recycling of gear and wheel materials, use of bio-based lubricants, and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. Some leading companies are exploring remanufacturing programs to extend product lifecycles—a practice that aligns with circular economy principles and reduces waste.
Conclusion
By 2026, the gears and wheels market will be characterized by innovation in materials, digital integration, and sustainability. Growth will be fueled by electric mobility, automation, and renewable energy, while regional diversification and supply chain resilience reshape global production networks. Companies that invest in R&D, adopt smart manufacturing, and align with environmental standards will be best positioned to capture emerging opportunities in this evolving landscape.
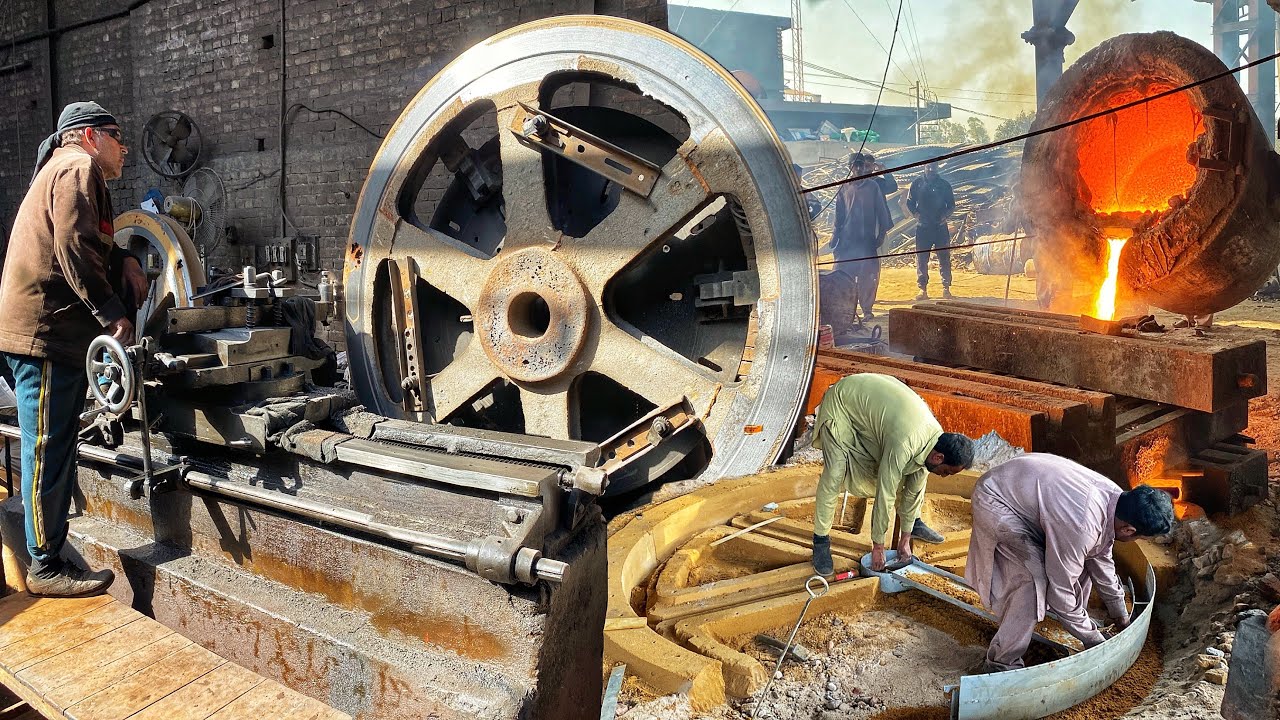

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Gears and Wheels: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing gears and wheels—especially for precision machinery, automotive, or industrial applications—exposes buyers to significant risks if not managed carefully. Two of the most critical areas where companies face challenges are quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) violations. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to production delays, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality Inconsistencies and Material Deficiencies
One of the most prevalent issues in sourcing gears and wheels is inconsistent product quality. Suppliers, particularly low-cost manufacturers in certain regions, may use substandard materials or fail to adhere to precise engineering tolerances. Forged or case-hardened steel gears, for instance, require strict heat treatment processes; deviations can result in premature wear or catastrophic failure. Dimensional inaccuracies, improper tooth profiles, or poor surface finishes can compromise performance and lead to excessive noise, vibration, or system breakdowns. Buyers often discover these defects only after installation, making remediation costly and disruptive.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Many suppliers fail to provide proper material certifications, test reports, or traceability documentation. Without mill test certificates (MTCs), ISO compliance records, or inspection reports (e.g., CMM reports), it becomes impossible to verify whether components meet specified standards like AGMA, DIN, or ISO 1328. This lack of documentation increases the risk of receiving non-compliant parts and complicates quality audits or root-cause analysis in the event of a failure.
Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
Sourcing from unauthorized or unverified suppliers raises the risk of receiving counterfeit or reverse-engineered gears and wheels. These components may visually resemble original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts but lack the proprietary metallurgy, heat treatment, or geometric precision. In addition to performance issues, using such parts may inadvertently infringe on protected designs or patents, exposing the buyer to legal liability.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
Manufacturers often design custom gear profiles, tooth geometries, or proprietary wheel configurations protected by patents, trade secrets, or design rights. When sourcing from third parties—especially in regions with lax IP enforcement—there’s a significant risk that suppliers may replicate protected designs without authorization. Buyers may unknowingly import or use components that violate IP laws, leading to lawsuits, customs seizures, or forced redesigns. Even if the buyer is not directly responsible for the infringement, proving due diligence can be difficult without proper supplier vetting.
Inadequate Supplier Vetting and Oversight
Companies often select suppliers based solely on price or lead time, neglecting technical audits, factory inspections, or IP compliance checks. Without verifying a supplier’s engineering capabilities, quality control systems (e.g., ISO 9001), or history of IP compliance, businesses expose themselves to both functional and legal risks. Ongoing oversight, including regular quality audits and sample testing, is frequently neglected after initial procurement.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, companies should:
– Conduct thorough supplier qualification, including technical and legal assessments.
– Require full material and process certifications.
– Perform independent quality inspections (pre-shipment and in-house).
– Include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
– Work with legal counsel to verify freedom-to-operate when sourcing custom-designed components.
– Consider sourcing from reputable, certified manufacturers with transparent supply chains.
Proactive management of quality and IP risks ensures reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and protection against costly disputes.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Gears and Wheels
Product Classification and HS Codes
Accurate classification of gears and wheels is essential for international shipping and customs compliance. Gears typically fall under HS Code 8483.40 (Transmission shafts, cranks, bearing housings, and gears), while wheels may be classified under 8708.70 (Wheels for vehicles) or 8483.60 (Machine parts). Confirm exact codes based on material, application, and design to avoid customs delays or penalties.
Packaging and Handling Standards
Gears and wheels must be packaged to prevent damage during transit. Use moisture-resistant wrapping, anti-corrosion VCI paper for metal components, and secure them in sturdy wooden crates or corrugated boxes with internal bracing. Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”) and include product identification tags.
Shipping and Transportation Requirements
Choose freight methods based on size, weight, and destination. Small components can ship via air or parcel services, while large or heavy wheels may require LTL (Less-Than-Truckload) or FCL (Full Container Load) ocean freight. Ensure compliance with carrier-specific regulations, including weight limits, pallet dimensions, and load securement standards.
Export Controls and Licensing
Verify if gears or wheels are subject to export controls, especially if used in defense, aerospace, or high-performance machinery. Items may require an export license under EAR (Export Administration Regulations) or ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations). Conduct end-use and end-user screening to comply with sanctions and embargoes.
Import Compliance and Duties
Understand destination country regulations, including import duties, taxes, and certification requirements. Provide accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Some markets may require product conformity assessments (e.g., CE marking in the EU, DOT for vehicle wheels in the U.S.).
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Ensure gears and wheels meet relevant industry standards such as ISO, DIN, SAE, or ASTM. For automotive applications, compliance with FMVSS (U.S.) or UNECE regulations (Europe) may be required. Maintain documentation proving material quality, load ratings, and performance testing.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain complete records for at least five years, including shipping manifests, export licenses, certificates of compliance, and customer declarations. Digital tracking systems can help manage documentation and support audits or customs inquiries.
Environmental and RoHS Compliance
Confirm that materials used in gears and wheels comply with environmental regulations such as EU RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH. Provide Declarations of Conformity and material safety data sheets (MSDS) when requested.
Returns and Reverse Logistics
Establish a clear process for handling returns, including inspection for damage, compliance verification, and proper disposal or refurbishment. Ensure returned items are repackaged and documented to meet safety and customs requirements if shipped across borders.
Conclusion for Sourcing Gear Wheels
In conclusion, sourcing gear wheels requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, durability, and supplier reliability. The selection process should be guided by the specific application requirements, including load capacity, speed, torque, environmental conditions, and material compatibility. Whether sourcing standard or custom-designed gears, it is essential to work with reputable manufacturers or suppliers who adhere to industry standards and offer proper certifications.
Partnering with suppliers who provide technical support, consistent quality control, and on-time delivery helps ensure smooth integration into production processes and reduces downtime. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—beyond just the initial purchase price—leads to more sustainable and efficient operations in the long term.
With careful evaluation and due diligence, effective sourcing of gear wheels contributes significantly to the performance, reliability, and longevity of mechanical systems across industries such as automotive, manufacturing, robotics, and renewable energy.