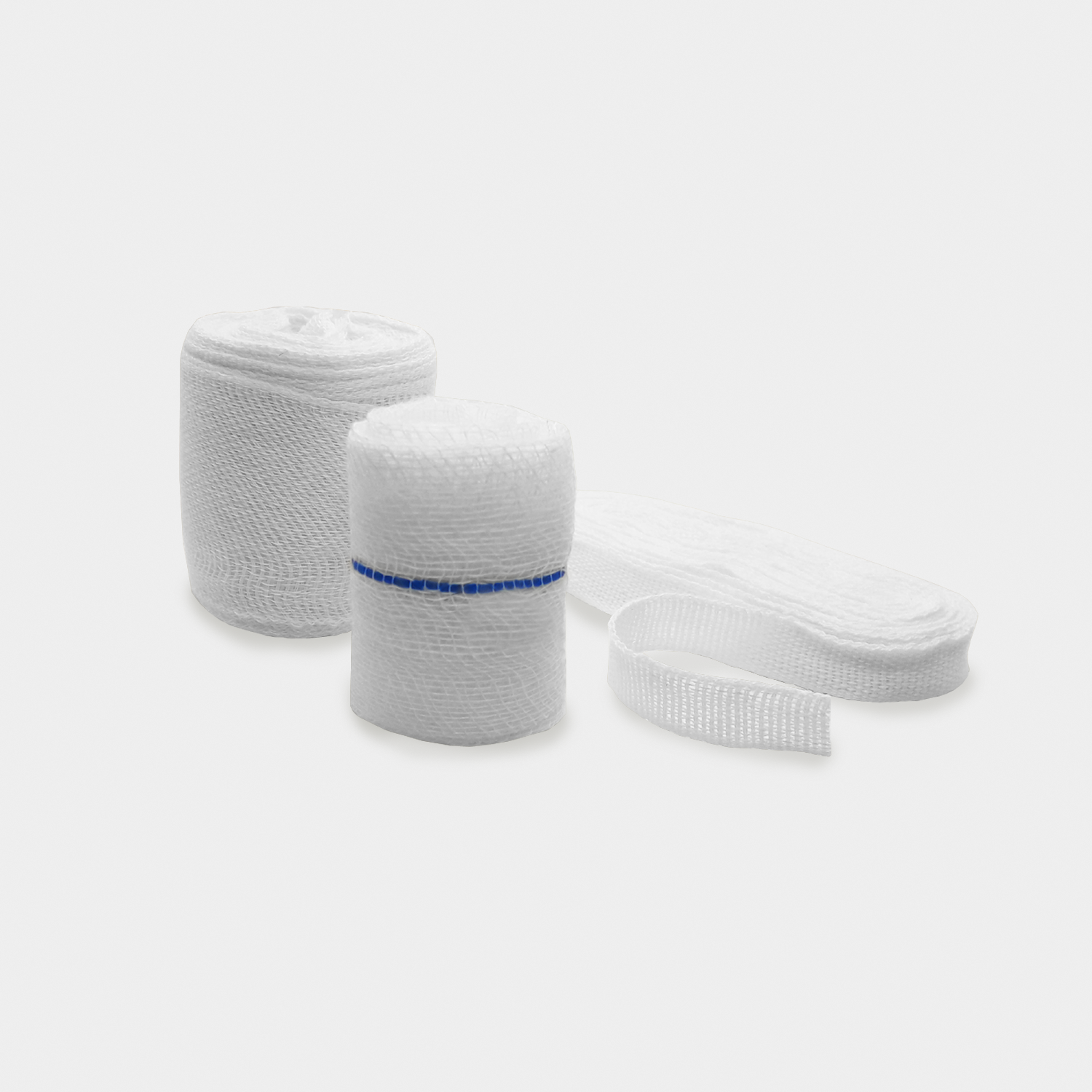
The global wound care market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising incidences of chronic wounds, surgical procedures, and trauma cases. According to Grand View Research, the global wound care market size was valued at USD 22.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2030. A key segment within this domain—gauze-based wound packing materials—remains a cornerstone in both acute and chronic wound management due to its versatility, absorbency, and cost-effectiveness. With increasing demand for advanced yet reliable dressing solutions, manufacturers are enhancing gauze formulations through antimicrobial treatments and improved fiber technologies. As healthcare systems prioritize infection control and efficient healing outcomes, the role of high-quality gauze packing products continues to grow. Here, we spotlight the top seven gauze wound packing manufacturers leading innovation, scalability, and clinical trust in this evolving market landscape.
Top 7 Gauze Wound Packing Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Gauze Packing / Throat Packing / Wound Packing
Domain Est. 2016
Website: sdpmedical.com
Key Highlights: SDP Inc. is a manufacturer and supplier of operating room sponges, dressings and custom products to the US and Canadian healthcare markets….
#2 Wound Packing Gauze Strips
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cardinalhealth.com
Key Highlights: Curity™ packing strips are made of all natural 100% cotton. This fine mesh gauze is ideal for wet-to-dry packing. Available in plain or iodoform….
#3 NAR Wound Packing Gauze
Domain Est. 1996
Website: narescue.com
Key Highlights: North American Rescue’s Wound Packing Gauze is a compact, easy to use, Z-folded gauze designed for both linear wound packing and basic bandaging….
#4 Pak
Domain Est. 2000
Website: gentell.com
Key Highlights: Plain and Iodoform Gauze Strips are sterile and may be used dry to absorb drainage in exuding wounds or soaked with a medication of choice….
#5 QuikClot Combat Gauze
Domain Est. 2002
Website: quikclot.com
Key Highlights: QuikClot Combat Gauze is a sterile, 3 in. x 4 yds. Z-folded, nonwoven gauze with X-ray indicator, and is impregnated with kaolin….
#6 Global
Domain Est. 2006
Website: celoxmedical.com
Key Highlights: CELOX™ Gauze is designed to help stop bleeding from emergency life-threatening injuries. Independent comparative tests in the form of a meta-analysis reported a ……
#7 Hemostatic Gauze • Blood Clotting Gauze Dressings
Domain Est. 2008
Website: omni-stat.com
Key Highlights: Hemostatic Gauzes for hospital and emergency use. Blood Clotting Gauze dressings proven to quickly clot blood and prevent blood loss….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Gauze Wound Packing

H2: Projected Market Trends for Gauze Wound Packing in 2026
The global gauze wound packing market is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by rising incidences of chronic wounds, surgical procedures, and trauma cases. Key trends shaping the market include technological advancements in gauze materials, increasing demand for infection control, and the expansion of home healthcare services.
One major trend is the shift toward advanced gauze products infused with antimicrobial agents such as silver, iodine, or honey. These next-generation gauzes offer enhanced healing properties and reduced infection risks, making them increasingly preferred in both clinical and home settings. By 2026, such value-added products are expected to capture a larger market share, especially in developed regions like North America and Europe.
Another influential factor is the growing geriatric population, which is more susceptible to chronic conditions like diabetes and venous ulcers. This demographic shift is increasing the demand for effective wound management solutions, including gauze packing, particularly in outpatient and long-term care facilities.
Additionally, the expansion of home healthcare and telemedicine is promoting the use of user-friendly, sterile gauze dressings that can be managed by patients or caregivers. This trend is encouraging manufacturers to focus on easy-to-use packaging, clear instructions, and cost-effective solutions suitable for non-clinical environments.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate due to improving healthcare infrastructure, rising medical tourism, and increasing awareness of advanced wound care. Government initiatives in countries like India and China to modernize healthcare delivery are further supporting market expansion.
However, the market also faces challenges such as price sensitivity in low-income regions and competition from alternative wound care products like foams, hydrogels, and films. Nonetheless, gauze wound packing remains a staple in first aid and emergency care, ensuring its continued relevance.
In summary, by 2026, the gauze wound packing market will be characterized by innovation in material science, a focus on infection prevention, and increasing accessibility through home healthcare models. These dynamics will sustain demand and drive moderate but consistent market growth globally.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Gauze Wound Packing: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing gauze wound packing, a critical medical consumable, involves navigating several potential pitfalls, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failure to address these can lead to regulatory non-compliance, patient safety risks, supply chain disruptions, and legal liabilities.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Composition and Purity
A primary quality concern is variability in the raw materials used. Gauze must be made from high-purity, medical-grade cotton or synthetic fibers free from contaminants such as lint, dyes, or chemical residues. Sourcing from suppliers without robust quality control systems may result in inconsistent fiber composition or the presence of allergens and endotoxins, increasing the risk of adverse patient reactions.
Lack of Sterility Assurance
Sterility is non-negotiable for wound packing gauze used in clinical settings. A common pitfall is assuming that all suppliers adhere to validated sterilization processes (e.g., gamma irradiation or ethylene oxide). Inadequate sterilization protocols or poor packaging integrity can lead to microbial contamination, posing serious infection risks. Sourcing without verifying sterilization validation reports and batch-specific certificates of sterility is a significant oversight.
Non-Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Gauze wound packing is classified as a medical device in most jurisdictions (e.g., Class I under FDA 21 CFR 878.4010, or as a Class I under EU MDR). A frequent pitfall is sourcing products that do not meet applicable regulatory requirements, such as FDA 510(k) clearance, CE marking, or adherence to ISO 13485 standards. Suppliers may provide misleading documentation or sell non-compliant products labeled as medical-grade, leading to regulatory penalties and market withdrawal.
Inadequate Absorbency and Linting Performance
Functional performance is critical. Poor-quality gauze may exhibit low absorbency or excessive linting, which can impede wound healing and introduce foreign particles into the wound bed. Relying solely on supplier claims without independent performance testing (e.g., absorbency per ASTM F535 or linting per ASTM F1819) exposes buyers to substandard products.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Inadvertent Infringement of Patented Designs or Processes
Some advanced gauze wound packing products incorporate proprietary technologies, such as antimicrobial coatings (e.g., silver-impregnated gauze), specialized weaves, or delivery systems protected by patents. Sourcing generic equivalents without conducting due diligence on existing patents can result in inadvertent IP infringement, leading to legal disputes, injunctions, and financial damages.
Counterfeit or Misrepresented Products
The medical supply market is vulnerable to counterfeit goods, especially through third-party distributors or online platforms. These products may mimic branded gauze packing but lack proper IP authorization and quality controls. Purchasing counterfeits not only violates IP rights but also compromises patient safety and exposes the buyer to liability.
Unclear Licensing and Authorized Distribution Channels
A key IP risk arises when sourcing through unauthorized distributors who lack proper licensing agreements with the IP holder. Even if the product appears legitimate, distribution without authorization constitutes IP infringement. Buyers must verify that suppliers are on the manufacturer’s official distributor list and possess valid distribution rights.
Insufficient Documentation and Traceability
Lack of proper documentation—such as certificates of conformance, material declarations, and IP clearance statements—makes it difficult to verify both quality and IP legitimacy. This absence of traceability increases exposure to regulatory scrutiny and IP litigation, particularly in global supply chains where sourcing transparency is critical.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, organizations should:
– Conduct thorough supplier audits and request quality management system certifications (e.g., ISO 13485).
– Require test reports for sterility, biocompatibility (ISO 10993), and performance specifications.
– Perform patent landscape analyses when sourcing technologically advanced products.
– Verify IP rights and distribution authorizations through legal counsel.
– Prioritize direct sourcing from OEMs or authorized distributors to ensure authenticity.
Proactively addressing both quality and IP risks ensures the safe, compliant, and legally sound procurement of gauze wound packing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Gauze Wound Packing
Overview
Gauze wound packing is a critical medical supply used in wound care to absorb exudate, promote healing, and maintain a clean environment. Due to its direct application on open wounds, strict logistics and compliance protocols must be followed to ensure patient safety, product efficacy, and regulatory adherence.
Regulatory Classification and Standards
Gauze wound packing is typically classified as a medical device under regulatory frameworks such as:
– United States: Class I or Class II medical device regulated by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) under 21 CFR Part 878.
– European Union: Class I medical device under Regulation (EU) 2017/745 (MDR), requiring CE marking.
– Other Regions: Compliance with local regulations such as Health Canada, TGA (Australia), and PMDA (Japan) is required for market access.
Key standards include:
– ISO 13485 (Quality Management Systems for Medical Devices)
– ISO 10993 (Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices)
– USP <797> (Pharmaceutical Compounding – Sterile Preparations), if applicable for sterile compounding environments
Manufacturing and Quality Control
- Must be produced in a controlled, cleanroom environment compliant with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
- Sterile gauze requires validated sterilization methods (e.g., ethylene oxide, gamma irradiation) with documented sterility assurance levels (SAL of 10⁻⁶).
- Each batch must undergo quality testing for sterility, endotoxin levels (LAL test), particulate matter, and physical integrity.
- Suppliers must provide Certificates of Conformance (CoC) and, for sterile products, Certificates of Sterility.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- Packaging must maintain sterility and integrity during transportation and storage.
- Labels must include:
- Product name and description (e.g., “Sterile Gauze Wound Packing, 2” x 2””)
- Lot number and expiration date
- Sterile status and sterilization method
- Single-use designation
- Manufacturer name and address
- Regulatory markings (e.g., CE mark, FDA registration number)
- UDI (Unique Device Identification) in compliance with FDA and EU MDR
Storage and Handling
- Store in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 15–30°C).
- Avoid exposure to moisture, direct sunlight, and contaminants.
- Maintain separation between sterile and non-sterile items.
- Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory management to prevent use of expired products.
- Monitor and document storage conditions where required.
Transportation and Distribution
- Use validated shipping methods to maintain product integrity.
- Temperature-sensitive shipments may require cold chain logistics if specified by the manufacturer.
- Transport packaging must protect against physical damage, moisture, and contamination.
- Distributors must be authorized and comply with local medical device distribution regulations.
- Maintain shipment records, including temperature logs (if applicable), delivery dates, and recipient verification.
Import/Export Compliance
- Obtain necessary import permits and customs documentation (e.g., FDA Prior Notice for U.S. imports).
- Ensure Harmonized System (HS) code accuracy (e.g., 5601.21 or 5601.22 for gauze).
- Comply with export control regulations (e.g., EAR or ITAR, if applicable).
- Verify destination country’s medical device registration requirements before shipment.
Inventory Management and Traceability
- Implement a robust inventory system capable of tracking lot numbers and expiration dates.
- Maintain records for traceability in case of recalls or adverse events (minimum 5 years, per FDA and MDR).
- Report any suspected product defects, adverse events, or malfunctions to regulatory authorities as required (e.g., FDA MedWatch, EUDAMED).
Training and Personnel
- Staff involved in handling, storing, or distributing gauze wound packing must be trained in:
- GMP and GDP (Good Distribution Practices)
- Infection control and aseptic techniques
- Regulatory requirements and documentation procedures
- Training records must be maintained and updated regularly.
Recall and Field Safety Procedures
- Establish a recall plan aligned with regulatory requirements.
- Be prepared to execute rapid lot-level recalls in response to contamination, sterility failure, or labeling errors.
- Notify regulatory bodies and customers promptly during a recall event.
- Conduct root cause analysis and implement corrective actions.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
- Non-sterile gauze waste should be disposed of according to local biomedical waste regulations.
- Used gauze from patient care is considered biohazardous and must be handled as regulated medical waste.
- Packaging materials should comply with environmental standards (e.g., recyclable materials where possible).
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for gauze wound packing require a comprehensive approach integrating regulatory adherence, quality assurance, and supply chain integrity. Maintaining sterility, traceability, and documentation throughout the product lifecycle is essential to ensure patient safety and regulatory compliance across global markets.
Conclusion: Sourcing Gauze Wound Packing
Sourcing gauze wound packing requires a strategic balance between quality, cost-effectiveness, regulatory compliance, and supply chain reliability. As a critical component in wound care management, gauze must meet stringent medical standards—including sterility, absorbency, and biocompatibility—to ensure patient safety and treatment efficacy. When selecting suppliers, healthcare providers and procurement teams should prioritize vendors with proven adherence to regulatory requirements (such as FDA, CE, or ISO certifications) and consistent product quality.
Additionally, considerations such as material composition (e.g., cotton, rayon, or non-woven blends), packaging formats, and customization options should align with clinical needs. Building relationships with reputable manufacturers or distributors, evaluating total cost of ownership (including logistics and inventory management), and maintaining supply chain resilience—especially in times of crisis—are essential for uninterrupted patient care.
In conclusion, a well-informed, proactive sourcing strategy for gauze wound packing not only supports optimal clinical outcomes but also enhances operational efficiency and preparedness within healthcare systems.