The global gas range regulator market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for reliable and safe gas pressure control solutions in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. According to Grand View Research, the global gas pressure regulator market was valued at USD 5.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of approximately 4.1% over the forecast period (2023–2028), underpinned by increasing urbanization, stricter safety regulations, and the expansion of natural gas distribution networks. As energy efficiency and appliance safety become critical priorities, manufacturers of gas range regulators are innovating to meet performance standards and consumer expectations. Against this backdrop, identifying the top players shaping the industry becomes essential for stakeholders across the supply chain. Below are the top 10 gas range regulator manufacturers leading the market through technological advancement, global reach, and compliance excellence.
Top 10 Gas Range Regulator Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Pressure Tech
Domain Est. 2003
Website: pressure-tech.com
Key Highlights: Pressure Tech manufacturers high-quality ISO-9001 pressure regulators for use on critical high-pressure control systems up to 1380 bar (20000 psi)….
#2 Industrial Regulators
Website: cavagnagroup.com
Key Highlights: Cavagna Group offers a wide range of industrial regulators for industrial gases, specifically designed for different kinds of applications….
#3 Gas Regulators
Domain Est. 1988
Website: process.honeywell.com
Key Highlights: Honeywell offers a range of low pressure residential regulators specifically designed to meet various national requirements. They are for natural gas and other ……
#4 TESCOM
Domain Est. 1995
Website: discreteautomation.emerson.com
Key Highlights: TESCOM designs and manufactures a wide range of standard and custom engineered pressure control regulator and valve solutions for a diverse, global market….
#5 Robertshaw
Domain Est. 1995
Website: robertshaw.com
Key Highlights: Robertshaw’s new patent-pending master gas regulator reduces gas stove methane leakage across the entire system to 90% below the agency standard. Learn More – ……
#6 Western Enterprises: High
Domain Est. 1996
Website: westernenterprises.com
Key Highlights: Western Enterprises offers premier solutions for high-pressure gas control, storage, and transmission. Ensure safety and efficiency with our products….
#7 Rotarex Valves Regulators Systems
Domain Est. 1997
Website: rotarex.com
Key Highlights: Rotarex is a global company that designs and manufactures premium quality gas valves, pressure regulators and systems….
#8 Maxitrol
Domain Est. 1997
Website: maxitrol.com
Key Highlights: International leaders in the design and manufacture of gas pressure regulators, modulation systems and safety devices….
#9
Domain Est. 1997
Website: conoflow.com
Key Highlights: We design and manufacture natural gas vehicle (NGV), low pressure and high pressure regulators along with filter and specialty regulators….
#10 Marshall Excelsior Company
Domain Est. 2003
Website: marshallexcelsior.com
Key Highlights: For over half a century, Marshall Excelsior has delivered advanced, precision-engineered gas control solutions trusted across the globe. Our expertise is built ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Gas Range Regulator

H2: Projected Market Trends for Gas Range Regulators in 2026
The global market for gas range regulators is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological innovation, regulatory changes, and shifting consumer preferences. As households and commercial kitchens increasingly prioritize safety, energy efficiency, and smart home integration, gas range regulators are undergoing transformative development to meet these demands.
-
Growing Emphasis on Safety and Compliance
By 2026, stringent safety regulations in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific will continue to shape product design. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) and the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) are expected to enforce stricter performance and durability standards for gas regulators. This will drive demand for regulators equipped with automatic shut-off features, leak detection sensors, and overpressure protection, enhancing consumer confidence and reducing accident risks. -
Integration of Smart Technology
Smart home ecosystems are rapidly expanding, and gas range regulators are no exception. By 2026, the integration of IoT-enabled regulators will gain momentum. These smart regulators will offer remote monitoring via smartphone apps, real-time gas pressure diagnostics, and predictive maintenance alerts. Brands like Honeywell, Robertshaw, and newer entrants are likely to lead this segment, providing seamless connectivity with home automation systems such as Google Nest and Amazon Alexa. -
Rise in Demand for Energy-Efficient Appliances
With increasing global focus on carbon emissions and energy conservation, consumers are favoring gas appliances that optimize fuel use. Advanced regulators with precision pressure control will enable more consistent flame output, improving combustion efficiency. This trend will be particularly strong in markets with government incentives for energy-efficient appliances, such as Japan, Germany, and South Korea. -
Growth in Emerging Markets
Urbanization and improving living standards in regions like Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa will drive demand for modern cooking solutions. As liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) remains a primary cooking fuel in these areas, the need for reliable and affordable gas range regulators will escalate. Local manufacturing and partnerships with global suppliers are expected to expand market access and reduce costs. -
Sustainability and Material Innovation
By 2026, sustainability will influence material choices in regulator manufacturing. Companies will increasingly adopt recyclable metals and reduce reliance on hazardous materials. Additionally, modular designs that allow for easy replacement of worn components (rather than full-unit disposal) will support circular economy goals. -
Consolidation and Competition Among Suppliers
The market is likely to see consolidation as larger players acquire niche innovators to strengthen their smart regulator portfolios. At the same time, competition from low-cost manufacturers in China and India will pressure pricing, prompting established brands to differentiate through quality, certification, and after-sales service.
In conclusion, the 2026 gas range regulator market will be defined by smarter, safer, and more sustainable solutions. Stakeholders who invest in innovation, compliance, and emerging market outreach will be best positioned to capture growth in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Gas Range Regulator (Quality & IP)
Sourcing a gas range regulator involves critical considerations for safety, performance, and legal compliance. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to significant risks, including product failures, safety hazards, and legal liabilities. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Quality Materials and Construction
One of the most frequent issues is selecting regulators made from substandard materials. Low-cost suppliers may use inferior brass, plastic, or elastomers that degrade quickly when exposed to gas, heat, or pressure. This can lead to leaks, inconsistent pressure output, or complete regulator failure—posing serious fire or explosion risks.
Impact: Reduced product lifespan, safety incidents, and costly recalls.
Lack of Certification and Compliance
Many suppliers, especially in unregulated markets, offer regulators without proper certification (e.g., UL, CSA, CE, or local gas safety standards). Using uncertified regulators violates building codes and voids insurance coverage. Additionally, non-compliant products may not withstand required pressure tests or environmental conditions.
Impact: Legal non-compliance, liability exposure, and rejection during inspections.
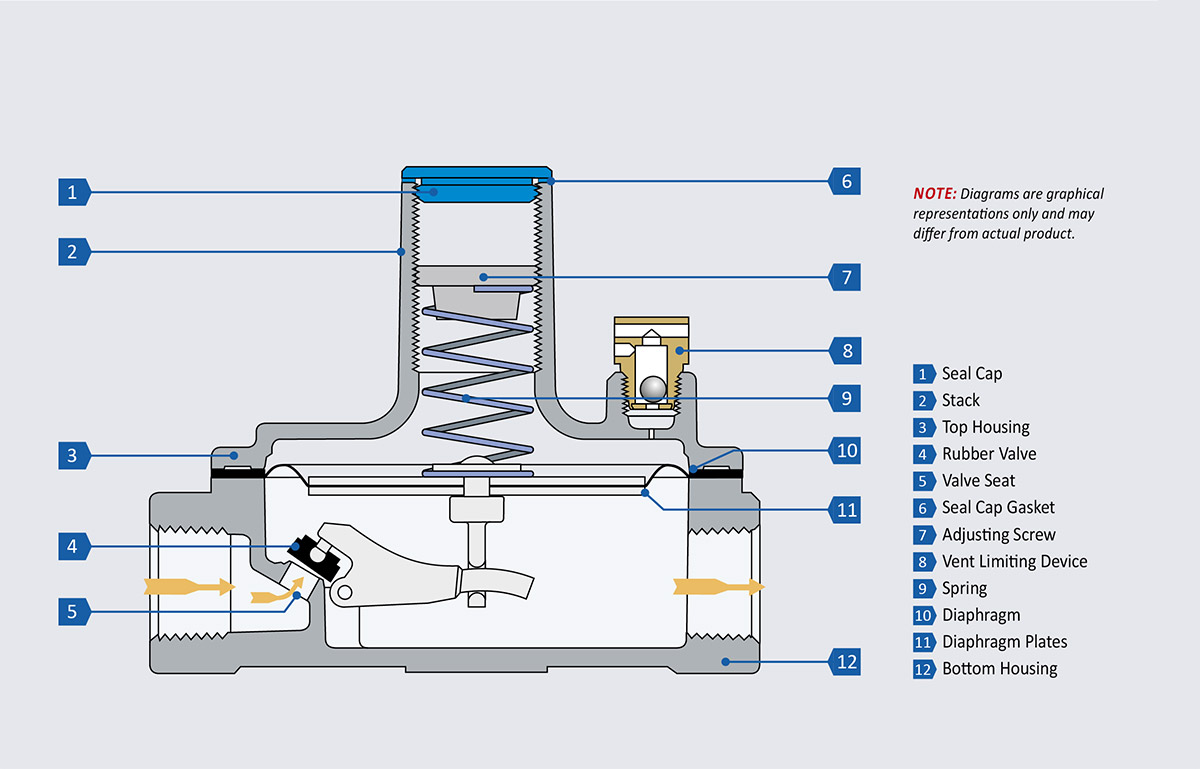
Inconsistent Pressure Regulation
Low-quality regulators often fail to maintain a consistent outlet pressure. Fluctuating gas pressure affects burner performance—leading to uneven cooking, flame lift, or flameouts. This typically results from imprecise spring tension, poor diaphragm design, or lack of calibration.
Impact: Poor end-user experience, increased customer complaints, and returns.
Counterfeit or Cloned Products
Some suppliers offer regulators that mimic well-known brands but lack authorized manufacturing rights. These counterfeit or cloned products may bear fake certifications or logos, deceiving buyers into believing they are purchasing genuine, IP-protected components.
Impact: Intellectual property infringement, legal action from rights holders, and reputational damage.
No IP Rights or Licensing Agreements
When sourcing OEM or custom regulators, failing to secure proper IP rights—such as design patents, trademarks, or technical know-how—can result in dependency on a single supplier or future legal disputes. Some manufacturers may use patented technologies without licensing, exposing buyers to infringement claims.
Impact: Supply chain vulnerability, litigation risk, and loss of exclusivity.
Inadequate Testing and Quality Control
Suppliers with weak QC processes may ship regulators without proper leak testing, pressure cycling, or environmental stress testing. Without documented test results or traceability, it’s difficult to ensure batch-to-batch consistency or troubleshoot field failures.
Impact: High failure rates in the field, warranty claims, and brand damage.
Ignoring Regional Gas Specifications
Gas composition (natural gas vs. LPG), inlet pressure, and temperature ranges vary by region. Sourcing a regulator designed for one market (e.g., 21 mbar natural gas in Europe) for use in another (e.g., 11” WC in North America) leads to poor performance or unsafe operation.
Impact: Safety risks, non-compliance, and product incompatibility.
Overlooking Long-Term Supplier Reliability
Choosing a supplier solely on price without evaluating their long-term reliability, technical support, and manufacturing stability risks future shortages or quality drift. If the supplier loses certification or ceases operations, replacement becomes difficult—especially if the design is IP-locked.
Impact: Supply chain disruption and potential requalification costs.
By carefully vetting suppliers, demanding certifications, verifying IP legitimacy, and insisting on rigorous quality standards, businesses can avoid these common pitfalls and ensure safe, reliable, and legally compliant gas range regulators.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Gas Range Regulators
Regulatory Compliance
Gas range regulators are safety-critical components that must meet stringent regulatory standards to ensure safe operation in residential and commercial settings. Compliance is mandatory across multiple jurisdictions.
International and Regional Standards
Gas range regulators must conform to recognized international and regional safety standards. Key standards include:
– ISO 27957: Specifies requirements for pressure regulators used with liquefied petroleum gases (LPG) in domestic applications.
– EN 12864: European standard for automatic change-over and pressure regulators for LPG.
– CSA 6.14: Canadian standard for regulators for use with gas appliances.
– AS/NZS 5645: Australian and New Zealand standard for gas pressure regulators.
Manufacturers must ensure their regulators are tested and certified by accredited bodies such as TÜV, UL, CSA Group, or SAI Global.
North American Requirements
In the United States and Canada, gas range regulators must be certified to meet:
– ANSI Z21.24 / CSA 6.14: Standard for automatic gas valve shutoff and pressure regulators.
– DOT 4BA or 4BW: For regulators used with propane cylinders in portable applications (DOT-regulated).
– UL 144: For LPG regulators used with appliances.
All regulators must bear the mark of a recognized certification body (e.g., UL, CSA, ETL) and include permanent labeling with model number, inlet/outlet pressure, gas type, and manufacturer information.
European Union Compliance
Under the EU Gas Appliances Regulation (EU) 2016/426, gas range regulators fall within the scope of regulated products. Key requirements include:
– CE marking indicating conformity with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
– Compliance with EN 12864 and other applicable harmonized standards.
– Involvement of a Notified Body for design examination and production quality assurance (Module B + D, for example).
– Technical documentation and EU Declaration of Conformity must be maintained for 10 years.
Labeling and Documentation
All gas range regulators must include clear, permanent labeling indicating:
– Manufacturer name and contact information
– Model and serial number
– Inlet and outlet pressure ratings
– Approved gas types (e.g., natural gas, propane)
– Date of manufacture
– Certification marks (e.g., CSA, UL, CE)
Accompanying documentation must include installation instructions, safety warnings, and maintenance guidelines in the local language(s) of the destination market.
Transportation and Logistics
Safe and compliant transportation of gas range regulators is essential due to their use in gas systems and potential safety implications.
Packaging Requirements
- Regulators must be individually sealed or wrapped to prevent contamination and damage.
- Use of anti-corrosion packaging (e.g., VCI paper or film) is recommended, especially for export.
- Outer packaging must be sturdy, labeled with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”), and include certification markings if applicable.
- Include compliance labels (e.g., CE, UL) on outer cartons for customs and retailer verification.
Shipping Classifications
Gas range regulators are typically classified as non-hazardous goods for transport when not installed on or connected to gas cylinders. However:
– If shipped with residual gas or pressurized components, they may fall under hazardous materials regulations (e.g., IMDG, IATA, 49 CFR).
– Always verify with testing labs or certification bodies whether the product requires hazardous classification.
– Use UN-certified packaging if shipping pressurized or gas-containing components.
Import and Customs Compliance
- Ensure Harmonized System (HS) Code accuracy (e.g., 9026.20 for pressure regulators).
- Provide Certificates of Conformity, test reports, and Declarations of Performance (DoP) for EU imports.
- Meet country-specific labeling and language requirements (e.g., French labeling in Canada).
- Partner with customs brokers familiar with gas appliance regulations to avoid delays.
Installation and Field Compliance
Qualified Installation
Gas range regulators must be installed by licensed or certified technicians in accordance with:
– National and local gas codes (e.g., NFPA 54 in the U.S., CSA B149.1 in Canada).
– Manufacturer’s installation instructions.
– Local jurisdictional requirements for gas line sizing, venting, and shutoff valves.
Inspection and Maintenance
- Final installation must be inspected and approved by a local authority or utility provider.
- Regulators should be periodically inspected for leaks, corrosion, and proper function.
- Replace regulators if damaged, leaking, or beyond service life (typically 10–15 years).
Record Keeping
Maintain records of:
– Product certifications and compliance documentation.
– Batch testing and quality control reports.
– Shipping and customs documentation.
– Installation and inspection reports (for commercial projects).
Adherence to this logistics and compliance guide ensures safety, regulatory approval, and market access for gas range regulators worldwide.
Conclusion for Sourcing Gas Range Regulator:
After a thorough evaluation of available suppliers, product specifications, cost considerations, and compliance with safety standards, it is evident that sourcing a reliable and high-quality gas range regulator is critical to ensuring safe and efficient appliance operation. The selected regulator must meet regional safety certifications (such as CSA, UL, or CE), be compatible with the gas type (natural gas or propane), and maintain consistent outlet pressure for optimal performance.
Sourcing from reputable manufacturers or certified distributors ensures product reliability, long-term durability, and compliance with industry regulations. While cost is an important factor, prioritizing safety, quality, and technical support over the lowest price helps mitigate potential risks associated with gas leaks, appliance damage, or hazards to end users.
In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach—balancing cost, quality, compliance, and supplier credibility—will lead to the successful integration of a safe and effective gas range regulator into the supply chain or end-use application. Ongoing supplier evaluation and adherence to maintenance and installation guidelines are recommended to ensure continued performance and safety.