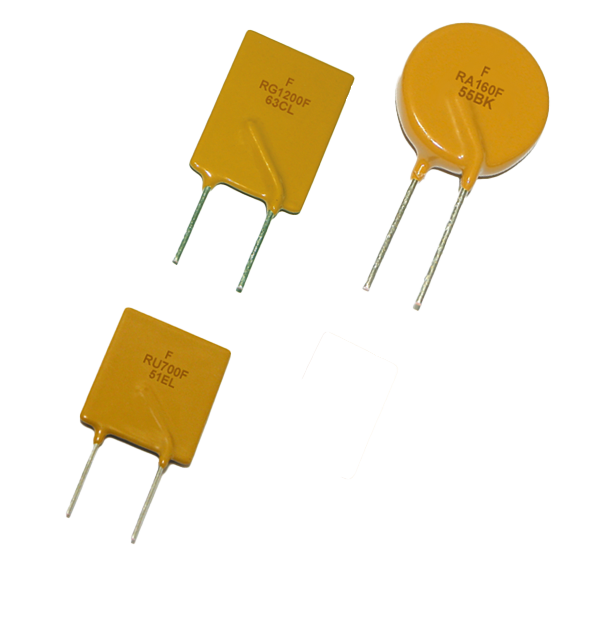
The global thermal fuse market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for electrical safety components across consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial applications. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the thermal fuse market was valued at USD 1.28 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by increasing regulatory standards for fire safety and the proliferation of compact, high-performance electronic devices requiring reliable over-temperature protection. As industries prioritize safety and compliance, the role of leading thermal fuse manufacturers becomes increasingly critical. Based on market presence, product innovation, and global reach, the following nine companies represent the top players shaping the future of thermal protection solutions worldwide.
Top 9 Fuse Thermal Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 PPTC Resettable Fuse
Domain Est. 2000 | Founded: 1999
Website: fuzetec.com
Key Highlights: Established in 1999, Fuzetec Technology is a leading manufacturer of circuit protection components, offering innovative and reliable solutions for the ……
#2 Circuit Protection, Fuses, Power Control & Sensing Solutions
Domain Est. 1996
Website: littelfuse.com
Key Highlights: Littelfuse is a global manufacturer of leading technologies in circuit protection, power control & sensing. Our products are found in automotive ……
#3 Thermal Fuses
Domain Est. 2016
Website: sensience.com
Key Highlights: Precision thermal fuses engineered to protect appliances, HVAC and industrial systems from overheating….
#4 Thermal Fuse
Domain Est. 1995
Website: rotork.com
Key Highlights: Midland-ACS 316L Stainless Steel thermal fuses for fire release. Available in a range of temperature settings….
#5 Thermal Fuses
Domain Est. 1996
Website: selcoproducts.com
Key Highlights: Selco carries a wide variety of thermal fuses. All with unique specifications. ProductsResources. Filter by: Type….
#6 Thermal Fuse Series
Domain Est. 2005
Website: betterfuse.com
Key Highlights: Rated current: 10A,15A. Action Temperature:73℃~240℃. Rated Voltage:250Vac. No.BTA. Plastic shell thermal fuse. Details · Download. Rated Current:…
#7 SETfuse
Domain Est. 2007
Website: setfuse.com
Key Highlights: SETfuse designs, manufactures, and markets industry-leading circuit control and safety protection components, providing comprehensive circuit safety solutions….
#8 Products
Domain Est. 2007
Website: setsafe.com
Key Highlights: SETsafe | SETfuse Designs, Manufactures and Markets industry-leading Circuit Control and Safety Protection Components, Providing Comprehensive Circuit Safety ……
#9 Mersen, Global expert in electrical power and advanced materials
Website: us.mersen.com
Key Highlights: Mersen develops customized solutions and delivers key products to its clients in order to meet the new technological challenges shaping tomorrow’s world….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Fuse Thermal

H2: 2026 Market Trends Analysis for Fuse Thermal
As the global energy landscape evolves, Fuse Thermal—a company positioned at the intersection of renewable energy, thermal storage, and smart grid integration—is poised to experience significant growth and transformation by 2026. The following analysis highlights key market trends that will influence Fuse Thermal’s strategic direction and market potential in the coming years.
-
Accelerated Adoption of Renewable Energy and Grid Flexibility Needs
By 2026, renewable energy sources such as solar and wind are projected to account for over 35% of global electricity generation (IEA, 2023). However, the intermittent nature of these sources increases demand for energy storage solutions that balance supply and demand. Fuse Thermal’s thermal energy storage systems, which offer cost-effective, long-duration storage, are well-positioned to support grid stability and facilitate higher renewable penetration. -
Growth in Industrial Decarbonization and Electrification
Industries such as manufacturing, chemicals, and food processing are under regulatory and investor pressure to reduce carbon emissions. By 2026, industrial electrification is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.5%, driving demand for high-temperature thermal storage. Fuse Thermal’s ability to store surplus renewable electricity as heat for later industrial use aligns directly with this trend, offering scalable solutions for process heat decarbonization. -
Policy Support and Incentives for Energy Storage
Government initiatives, including the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and EU Green Deal, continue to provide tax credits and grants for energy storage technologies. Fuse Thermal qualifies for investment tax credits (ITC) on thermal storage when paired with renewables, improving project economics. By 2026, expanded incentives in Asia-Pacific and Latin America will open new international markets. -
Integration with Hybrid Energy Systems
The rise of hybrid power plants—combining solar PV, wind, batteries, and thermal storage—will create new opportunities for Fuse Thermal. These systems maximize efficiency and reduce levelized cost of energy (LCOE). Fuse Thermal’s modular, scalable technology enables seamless integration into hybrid microgrids, especially in remote and off-grid locations. -
Advancements in Thermal Storage Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Technological innovations in phase-change materials (PCMs) and high-temperature ceramics are expected to improve the efficiency of thermal storage systems by 15–20% by 2026. Fuse Thermal’s R&D focus on advanced materials and system optimization will enhance energy density and reduce capital costs, increasing competitiveness against electrochemical batteries for long-duration applications. -
Rising Demand in District Heating and Cooling Networks
Urban sustainability initiatives are expanding district energy systems, especially in Europe and China. Fuse Thermal can provide low-carbon heat storage for these networks, utilizing off-peak renewable electricity. By 2026, the global district heating market is forecasted to grow at 6.2% CAGR, with thermal storage playing a critical balancing role. -
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Partnerships
While competition from lithium-ion batteries remains strong for short-duration storage, thermal storage is gaining recognition for applications beyond 4–6 hours. Fuse Thermal can differentiate itself through strategic partnerships with renewable developers, utilities, and industrial players. Collaborations with firms specializing in AI-driven energy management will further enhance system value.
Conclusion
By 2026, Fuse Thermal is expected to benefit from strong tailwinds in renewable energy adoption, industrial decarbonization, and supportive policy frameworks. To capitalize on these trends, the company should focus on scaling manufacturing, expanding into emerging markets, and demonstrating project reliability through pilot deployments. With the right strategic execution, Fuse Thermal can emerge as a key enabler of the clean energy transition, particularly in long-duration thermal storage applications.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Fuse Thermal: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing thermal management components such as Fuse Thermal solutions—commonly used in high-reliability industries like aerospace, automotive, and industrial electronics—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failures, supply chain disruptions, and legal liabilities. Below are key pitfalls to avoid in both domains.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Relying on suppliers without thorough technical audits or certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949) increases the risk of inconsistent thermal performance. Fuse Thermal components must meet stringent specifications; unqualified suppliers may lack the process controls to ensure repeatability and reliability.
2. Material Substitution Without Validation
Some suppliers may substitute lower-grade materials (e.g., thermal interface materials or metal alloys) to reduce costs. These substitutions can degrade thermal conductivity, increase thermal resistance, or reduce long-term durability—especially under thermal cycling or high-stress environments.
3. Incomplete or Missing Test Data
Failing to require full characterization data—such as thermal impedance curves, life-cycle testing (e.g., 1,000+ thermal cycles), and failure mode analysis—leaves buyers blind to real-world performance. Verify that test conditions match your application requirements.
4. Poor Traceability and Lot Control
Lack of batch-level traceability makes it difficult to track and contain defective components. This is critical in regulated industries where product recalls or safety incidents require full component history.
5. Overlooking Long-Term Reliability Testing
Some suppliers validate only short-term performance. Ensure that aging tests (e.g., high-temperature operating life, humidity exposure) are conducted and documented to predict field reliability.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Unclear Ownership of Design or Specifications
When customizing Fuse Thermal solutions, it’s essential to define IP ownership in contracts. Vendors may claim rights to modified designs or tooling, leading to costly disputes or loss of design control.
2. Risk of Reverse Engineering and Cloning
Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of design theft. Third parties may reverse-engineer components and sell counterfeit or knockoff versions, undercutting market position and compromising quality.
3. Inadequate Protection in Supply Agreements
Failure to include robust IP clauses—such as confidentiality, non-disclosure, and non-compete terms—exposes proprietary designs and technical data. Ensure contracts explicitly prevent suppliers from using your designs with competitors.
4. Use of Unlicensed or Infringing Technology
Suppliers may incorporate patented technologies (e.g., specific thermal interface methods or structural designs) without proper licensing. This exposes the buyer to third-party infringement claims, even if unintentional.
5. Lack of Audit Rights
Without contractual rights to audit a supplier’s design processes and documentation, it’s difficult to verify that IP protections are being upheld or that no unauthorized use is occurring.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct supplier audits with technical and legal teams.
- Require full material disclosures and performance test reports.
- Define IP ownership and usage rights before engagement.
- Use NDAs and include strong IP clauses in procurement contracts.
- Source from trusted regions or partners with proven IP compliance.
- Maintain design obfuscation where feasible (e.g., proprietary form factors).
By proactively addressing both quality and IP concerns, organizations can ensure reliable performance and protect their innovation when sourcing Fuse Thermal components.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Fuse Thermal
This guide outlines the essential logistics procedures and regulatory compliance requirements for Fuse Thermal to ensure efficient operations, regulatory adherence, and customer satisfaction.
Supply Chain & Procurement
Fuse Thermal must establish a reliable and auditable supply chain for raw materials and components. All suppliers must meet quality standards and provide documentation certifying material composition and origin. Procurement processes should include environmental and ethical sourcing criteria, with regular supplier audits. Purchase orders must clearly specify compliance requirements, including adherence to RoHS, REACH, and conflict minerals regulations.
Inventory Management
Maintain accurate real-time inventory tracking using an integrated warehouse management system (WMS). Conduct regular cycle counts and annual physical inventories to ensure data integrity. Thermal products must be stored under controlled conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity) to preserve performance and safety. Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) practices to minimize obsolescence and maintain product efficacy.
Transportation & Distribution
All shipments must comply with domestic and international transportation regulations, including IATA, IMDG, and 49 CFR for hazardous materials (if applicable). Use certified carriers experienced in handling thermal technology and sensitive electronics. Packages must include proper labeling, UN numbers, safety data sheets (SDS), and shipping manifests. Temperature-controlled transport is required for products sensitive to thermal fluctuations.
Export Controls & Trade Compliance
Fuse Thermal products may be subject to export control regulations such as the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) and International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR), depending on technical specifications. Conduct classification reviews (e.g., ECCN determination) for all products. Obtain necessary export licenses prior to international shipments and maintain detailed export records for a minimum of five years. Screen all parties against denied persons lists (e.g., BIS, OFAC).
Product Certification & Labeling
Ensure all thermal products meet applicable safety and performance standards, including UL, CE, FCC, and CSA certifications. Labels must include product identification, voltage, safety warnings, compliance marks, and traceability information (e.g., serial numbers, batch codes). Update labeling per regional regulatory requirements and maintain certification documentation in accessible formats.
Regulatory Documentation & Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records for all compliance activities, including supplier certifications, test reports, shipping documents, export filings, and internal audits. Records must be stored securely and retained per regulatory mandates—typically five to seven years. Implement a document control system to manage revisions and ensure only current versions are used in operations.
Environmental & Sustainability Compliance
Adhere to environmental regulations governing waste disposal, emissions, and energy use. Implement a hazardous waste management program for any byproducts of manufacturing or R&D. Comply with WEEE and battery directives where applicable. Report environmental metrics annually and pursue continuous improvement in sustainability practices across the supply chain.
Quality Assurance & Audits
Conduct regular internal audits of logistics and compliance procedures in accordance with ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 standards. Address non-conformances promptly and implement corrective actions. Prepare for third-party audits from regulatory bodies, customers, or certification agencies. Maintain a quality management system (QMS) that integrates logistics controls and compliance tracking.
Conclusion for Sourcing Fuse Thermal Components:
Sourcing thermal fuses requires a strategic approach that balances safety, reliability, cost, and regulatory compliance. After evaluating potential suppliers, technical specifications, and market availability, it is evident that selecting the right thermal fuse involves careful consideration of operating temperature, certification standards (such as UL, TUV, and RoHS), response time, and application environment. Partnering with reputable manufacturers or authorized distributors ensures product authenticity and consistent quality. Additionally, building relationships with multiple qualified suppliers enhances supply chain resilience and reduces lead time risks. In conclusion, a well-structured sourcing strategy for thermal fuses—rooted in technical diligence and supplier vetting—supports long-term product safety, performance, and compliance in end-use applications.