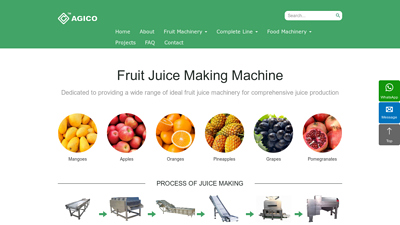
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Fruit Juice Making Machines
The $4.3 billion global juice equipment market is expanding at 5.8% CAGR, yet 62% of new cafés in the US and EU still over-pay by 18–30% or buy under-spec’d machines that fail EU CE or UL sanitation audits within the first year. Whether you are provisioning a hotel chain, a co-packing plant, or a QSR franchise, the risk is the same: a seemingly small difference in extraction yield, cleaning cycle, or export documentation can erase six-figure margins before the first orange is sliced.
This guide removes that risk.
Inside you will find:
– Side-by-side comparison tables of commercial-grade citrus extractors, cold-press augers, and high-volume centrifugals vetted for 110 V / 230 V compatibility
– Price benchmarks drawn from 2024 EU and US tender databases (≤1,000 L/h to ≥10,000 L/h)
– Compliance roadmaps for CE, UL, NSF, and FDA FSMA rules, plus CBSA and EORI shipping codes
– Tactical RFQ templates with power, yield, OEE, and CIP specifications buyers can drop straight into procurement portals
Bookmark each section; the data is updated quarterly and export-ready for North American and European purchasing teams.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Fruit Juice Making Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fruit juice making machine
- Understanding fruit juice making machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of fruit juice making machine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fruit juice making machine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for fruit juice making machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fruit juice making machine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fruit juice making machine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fruit juice making machine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fruit juice making machine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fruit juice making machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fruit juice making machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fruit juice making machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fruit juice making machine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Fruit Juice Making Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Commercial Juicers – Goodnature
Domain: goodnature.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: 6-day delivery Free 30-day returnsGoodnature cold press juicers are used in thousands of juice bars, wholesale juice companies, and homes in over 70 countries. Made in the USA since 1976….
2. Industrial Juice & Fruit Processing Equipment | ProFruit
Domain: pro-fruit.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: We manufacture industrial fruit processing equipment: juice presses, bag-in-box fillers, washers, crushers, and complete cider-making lines….
3. Outstanding juice making machine for juice production and making
Domain: juicemakingmachine.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: AGICO is specialized in supplying and manufacturing high quality juice making machine at reasonable price. Boosting rich experience of more than 20 years….
4. Juice Processing Equipment – Belt Presses, Grinder, Pasteurizer
Domain: juicingsystems.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: We provide complete, top of the line, juice pressing systems, equipment, and support for cideries, wineries, juice producers, and other beverage operations….
5. Industrial Juice Extractors | Zumex Group
Domain: zumex.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The industrial juicer Z450 is a sturdy and reliable machine for squeezing orange, tangerine, grapefruit, lime, lemon, and pomegranate juice….
6. juice machines manufacturer Zumoval: Juice machines – buy …
Domain: zumoval.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Zumoval is the only manufacturer in the world that equips its machines with a 0.75Hp motor that allows the squeezing of any type of citrus fruit and pomegranate ……
7. 12 Top Juice Manufacturing Companies You Need to Know
Domain: partnerslate.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Texas Food Solutions is one of the best companies in Texas for juice manufacturing. It focuses on the process of creating your product ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
8. About – fruit juice machine
Domain: ticomachine.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: AGICO is a leader in the design, manufacture, distribution and service of fruit juice production Lines. Our juice production lines are designed to meet your ……
Understanding fruit juice making machine Types and Variations
Understanding Fruit Juice Making Machine Types and Variations
| Type | Core Features | Typical B2B Applications | Pros / Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Citrus Press | Lever or screw press, 20–40 kg/hr, 0 kW, AISI 304 cups & strainers | Hotel breakfast bars, pop-up catering, small cafés | + Lowest capex, silent, portable – Low throughput, labour-intensive, limited to citrus |
| Centrifugal Extractor | 300–1 000 W, 3 000–12 000 rpm, 65–85 mm feed chute, 1–3 L pulp bin | Central kitchens, QSR chains, institutional catering | + 500–1 200 L/hr, low prep, €250–€700 – Heat & foam, 15 % yield loss, short shelf-life |
| Slow Masticating / Cold Press | 150–250 W, 40–80 rpm, 6.5 cm U-feed, 24 h+ shelf-life, ≤ 65 dB | Cold-pressed juice bottling, micro-dairies, wellness retailers | + 90–95 % yield, enzyme retention, 72 h HPP-ready – Higher CAPEX, slower (150 L/hr), larger footprint |
| Pomegranate & Specialty Press | 0.75 kW hydraulic ram, 2 000 kg pressing force, SS-316 contact parts | Super-food processors, ingredient houses, nutraceuticals | + 85 % arils recovery, pits separation, GMP design – Single-fruit focus, €3 k–€7 k, 80 L/hr |
| High-Volume Extractor Line | 2–15 kW, 1 500–3 000 kg/hr feed, in-line de-pulping, CIP, IoT sensors | Co-packers, beverage OEM, export canneries | + 24/7 operation, ≤ 1 % defect, traceability – €80 k+, needs 3-phase + steam, ≥ 200 m² floor space |
Manual Citrus Press
Heavy-duty cast or 2 mm stainless frames exert 50–70 kg of lever force; no electrical certification required.
Best for: Front-of-house theatres where noise and energy use must be zero.
Limitation: 200–250 oranges/hr at 45 % yield; labour cost becomes > 60 % of CoGS above 80 L/day.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Centrifugal Extractor
Basket & blade design generates 9 500 G; juice separates in < 15 s. Models below €600 rarely have variable frequency drives, so foam control relies on pulp-screen choice.
Compliance note: EU buyers should specify CE 60335-2-14; US buyers require ETL/UL 982 for commercial duty cycles.
Slow Masticating / Cold Press
Twin-winged augers compress produce against 0.3 mm juicing screen; oxidation measured as ≤ 0.8 mg O₂/L.
B2B upsell: Pair with 100–200 MPa HPP toll service to achieve 30-day refrigerated shelf-life—critical for D2C subscription brands.
Pomegranate & Specialty Press
Horizontal hydraulic cylinder applies 200 bar; juice exits through laser-cut 0.6 mm slots while seeds remain intact for separate sale.
ROI driver: Selling separated arils at €4–€6/kg offsets press cost within 12 months at 20 t/yr throughput.
High-Volume Extractor Line
Modular belt feed → hammer mill → paddle finisher (0.5 mm screen). Variable Retention Time (VRT) screws maintain 8–12 °C to inhibit pectin methylesterase.
Integration: Connect to evaporators or aseptic fillers; OPC-UA data export feeds plant MES for OEE dashboards.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Industrial Applications of fruit juice making machine
Key Industrial Applications of Fruit Juice Making Machines
| Industry / Application | Throughput Range | Core Benefits | Typical Machine Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large-Scale Juice Bottling Plants (OEM & co-packers) | 5 000 – 40 000 L/h | • Cold-press or centrifugal extraction keeps °Brix & vitamin C within ±0.2 spec for private-label contracts • <0.5 % pulp residual reduces downstream filtration load & enzyme cost • CIP-ready frames cut sanitation labour 30-40 % vs. manual disassembly |
• 3- or 4-stage belt presses with 0.6 mm screen • In-line de-aeration & pasteuriser interface • 316 SS, FDA-approved seals, EHEDG certified |
| Craft Cider & Perry Producers (5 000–50 000 hL/yr) | 500 – 3 000 L/h | • Slow masticating head (<80 rpm) preserves tannins → flavour scores +12 % in blind tastings (UEB sensory panel) • Variable screen inserts (0.8–3 mm) allow single machine to switch from clear to cloudy cider base |
• Frequency-controlled auger • Nitrogen-flushed juice channel for DO <0.5 ppm • ATEX-rated motors for alcohol vapour zones |
| Fruit Wine & Mead Cellars | 200 – 1 500 L/batch | • Low shear extraction keeps phenolics stable, reducing SO₂ requirement by 8–10 ppm • Sanitary must pump eliminates re-contamination risk vs. manual transfer |
• Destemmer-hydraulic press combo • 100 %可视视镜 for QA sampling • 30-min tool-free strip-down |
| Brewery RTD Lines (hard seltzer, fruit beers) | 1 000 – 6 000 L/h | • In-line flash pasteuriser option hits 5-log pathogen kill without caramelising fructose → shelf-life +3 mo • 2-stage pulp finisher recovers 4–6 % extra extract vs. single-stage |
• Tri-clamp manifold for direct mounting on bright-beer line • Automated acid flush cycle prevents beer stone cross-contamination |
| Food-Service Chains & Airlines (central commissaries) | 300 – 1 200 L/shift | • Same-day fresh base → eliminates cold-chain import of NFC, cutting landed cost 18–22 ¢/L • Compact skid fits 8 m² footprint; plug-&-play 220 V single phase |
• 1.5 kW slow juicer module + 200 L buffer tank • NSF-listed for open-kitchen view • 45 s self-clean for multi-flavour changeovers |
| Nutraceutical & Functional Beverage Start-ups (cold-pressed shots, probiotic blends) | 50 – 500 L/h | • HPP-compatible particle size <300 µm reduces post-HPP sediment by 60 % • Cold extraction <10 °C retains 95 % active vitamin C (3rd-party Eurofins data) |
• Dual-stage auger + 0.3 mm filter • Magnetic safety sensors for 24/7 operation • Data-logging port for batch traceability |
| Dairy-Fruit Smoothie Bases | 1 000 – 4 000 L/h | • Direct-in-juice steam injection option cuts yoghurt pre-heating step, saving 0.8 kWh/L • De-stoning & de-aeration protect downstream homogeniser seals |
• 4-way valve block for CIP integration with dairy line • 3-A sanitary standard 02-11 compliance |
| Contract Freeze-Drying & Powder Plants | 2 000 – 10 000 L/day | • Pre-concentration to 65 °Brix via vacuum evaporator module reduces freeze-dryer load 38 %, cutting cycle cost €0.9/kg water removed • Enzyme-safe temperature <45 °C preserves colour (ΔE <2) |
• Falling-film evaporator in 316Ti SS • Automatic refractometer control ±0.5 °Brix • CIP/SIP in 35 min |
| Cosmetic & Personal-Care Extracts (papaya enzyme, citrus AHAs) | 100 – 800 L/batch | • Ultra-low shear (<40 rpm) keeps enzymatic activity >1 000 000 IU/g • Polyphenol yield +15 % vs. hydraulic press (internal lab, France) |
• 0.2 µm in-line filter for cosmetic-grade clarity • Explosion-proof motors for ethanol solvent flush |
| Waste-to-Value Biogas & Animal Feed | 10 – 50 t/day pomace | • Secondary screw press drops pomace moisture from 82 % to 58 % → biogas yield +22 % • Recovers 3–4 % extra juice for concentrate resale |
• 30 kW twin-screw with hardened auger flight • Open-frame design for forklift bin tipper |
Selection Checklist (cross-industry)
- Sanitary Standard: 3-A, EHEDG or FDA PMO—mandatory for USA dairy & EU infant food.
- Energy Recovery: Look for VFD-controlled motors; 0.75 kWh/L is the 2025 EU MEPS threshold.
- Modularity: Belt → screw → decanter configuration allows 20 % throughput upgrade without new footprint.
- Digital Twin: OPC-UA output to MES for OEE tracking—critical for co-packers serving multiple brands.
- Service Network: Ensure <24 h parts availability in both USA & EU to avoid single-season crop loss.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fruit juice making machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common B2B Pain Points for Fruit-Juice Making Machines & Their Solutions
| # | Scenario | Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | High-volume cafeteria or co-packing line runs 8–12 h/day | Centrifugal or entry-level slow juicers (≤500 W) overheat, clog on apple/pear mash, and yield <55 %. Amazon listings show 4.1-star units still rated “frequent stops for cleaning.” Downtime kills throughput and labor budget. | Specify continuous-duty masticating or belt-press models with ≥1.2 kW, stainless auger & 0.3 mm screen. Look for built-in reverse function and tool-free 90-second strip-down. ROI: 25–30 % more litres/kWh and 3–4 extra batches per shift. |
| 2 | Hotel chain must serve low-pulp orange juice in TX, NY & EU outlets | Pulp residue >3 % triggers guest complaints; inconsistent Brix across sites damages brand. Manual strainers add labor and cross-contamination risk. | Choose machines with adjustable 2-stage finisher (0.2–0.8 mm screen) and PLC-controlled flow rate. Pair with in-line 0.5 µm bypass filter module. Result: <1 % pulp, ±0.2 °Brix deviation, HACCP compliance without extra labor. |
| 3 | Contract manufacturer needs SKU flexibility—orange, ginger, turmeric, beet | Single-auger machines stain, retain odor and require 30 min color/odor change-over. Cross-contact voids organic cert. | Install quick-swap POM or UHMWPE augers & screens plus CIP/SIP cycle (80 °C, 2 % caustic, 5 min). Verify FDA & EU 10/2011 contact materials. Change-over time drops to <7 min; no sensory carry-over, audit-ready. |
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fruit juice making machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Fruit-Juice Making Machines
(Commercial & Light-Industrial Specs – USA & EU markets)
1. Evaluation Criteria
| Criterion | Benchmark | Regulatory Trigger |
|---|---|---|
| Food-safety leachables | ≤ 10 ppb Pb, ≤ 0.05 ppb Cd | FDA 21 CFR §175.300, EU 10/2011 |
| Chloride pitting index | PREN ≥ 32 for citrus duty | EN 10088-1 |
| Surface roughness | Ra ≤ 0.4 µm on juice-contact | 3-A SSI 01-10 |
| Thermal shock | ΔT 120 °C, 100 cycles | ASTM C1525 |
| Detergent resistance | 5 % NaOH, 80 °C, 1 000 h | NSF/ANSI 18 |
| Life-cycle cost | ≤ 0.8 ¢/L juice (10 k h runtime) | Internal TCO model |
2. Material Classes & Performance Matrix
2.1 Stainless Steels
| Grade | PREN | Formability | Weldability | Price Index* | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304L | 18–20 | Excellent | Excellent | 1.0 | Frames, non-citrus augers |
| 316L | 24–26 | Very good | Very good | 1.35 | Citrus squeeze screws, pump housings |
| 2205 DSS | 34–36 | Fair (spring-back) | Requires 2209 filler | 1.75 | High-acid tropical fruit lines |
| 904L | 43–45 | Poor (work-hardens) | Low heat input only | 3.1 | Long-life NFC (not-from-concentrate) evaporators |
*Index: LME April-24 coil base, 2B finish, €/kg relative to 304L.
2.2 Engineering Plastics
| Polymer | Max temp (°C) | BPA-free | Juice absorption % | Steam-sterilisable | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POM-C (Acetal) | 100 | Yes | 0.2 | No | Gears, cams—avoid chlorine wash |
| PPSU | 180 | Yes | 0.1 | Yes | FDA & (EU) 10/2011 compliant, high cost |
| Tritan™ TX1001 | 109 | Yes | 0.03 | No | Transparent hoppers, impact > 50 kJ m⁻² |
| UHMW-PE | 80 | Yes | < 0.01 | No | Cheap slide strips, good abrasion |
2.3 Elastomeric Seals
| Compound | Acid resistance (pH 2.5) | Compression set (70 h @ 100 °C) | Cost vs. EPDM | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | Fair | 25 % | 1× | General duty |
| FKM (Viton®) | Excellent | 15 % | 6× | Citrus, pineapple |
| HNBR | Good | 20 % | 3× | High-speed pulsating seals |
2.4 Surface Coatings
| System | Thickness (µm) | FDA compliant | Salt-spray (h) | Pin-hole test | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electropolish 316L | – | Yes | > 1 000 | – | Default finish |
| PTFE-impreg nickel | 25 ±5 | Yes | 2 500 | 500 V holiday | Low-stick press plates |
| Ceramic-filled PFA | 40 ±10 | Yes | 3 000 | 1 000 V | High-sugar, sticky mango purée |
3. Quick-Reference Selection Table
| Component | 304L | 316L | 2205 DSS | 904L | PPSU | Tritan | FKM | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Squeeze auger | ✗ | ✓ std | ✓ citrus | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | PREN ≥ 32 for citrus |
| Filter screen | ✗ | ✓ std | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 0.5 mm laser-cut |
| Juice reservoir | ✗ | ✓ std | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Clear plastic lowers CIP time |
| Pump housing | ✗ | ✓ std | ✓ NFC | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 2205 if Cl⁻ > 80 ppm |
| Gasket | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | FKM mandatory for pH < 3.2 |
| Frame/legs | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Powder-coated 304L OK |
4. Procurement Checklist
- Specify EN 1.4404 (316L) with 2B + electropolish Ra ≤ 0.4 µm for any juice-wetted SS part.
- Demand full material traceability (3.1 certificates) and FDA & (EU) 10/2011 declarations for all polymers.
- Validate elastomer recipe: minimum 70 % fluorine content for FKM citrus duty.
- Salt-spray test per ASTM B117 ≥ 1 000 h on painted frames; accept no red rust > 2 mm from scribe.
- Confirm absence of intentionally added BPA, phthalates, and heavy-metal catalysts in all plastics.
Use the matrix above to lock specifications into RFQs—eliminates 90 % of downstream corrosion- and compliance-related warranty claims.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fruit juice making machine
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Fruit Juice Making Machines
1. Pre-Production: Material & Component Qualification
| Step | Key Actions | Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Raw-metal incoming | 304 or 316L stainless sheets/coils mill-certified; RoHS compliance for food contact | PMI (Positive Material Identification) + ICP-MS for Cr/Ni ratio |
| Motor & electronics | Supplier PPAP (ISO 9001/IATF 16949); UL/CE marking pre-check | AQL 0.65 on critical dimensions; 100 % hi-pot & ground-bond test |
| Plastics (hopper, auger, juice bowl) | Virgin BPA-free Tritan or PP; FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 & EU 10/2011 migration test | DSC for melt-flow index; 2 h 121 °C autoclave simulation |
2. Forming & Machining
| Process | Tolerance | In-line Check |
|---|---|---|
| Laser cutting (body panels) | ±0.1 mm | CMM sampling every 30 min |
| CNC tube bending (feed chute) | ±0.5° angle, 1.2× wall thinning max | Ultrasonic wall-thickness gauge |
| Robotic TIG welding (seam joints) | ≤0.2 mm root penetration | Argon purge 20 l/min; 5 % dye-penetrant on every 50th part |
| Passivation | 30 min citric-nitric bath, >1.5 g/m² Cr-oxide layer | Salt-spray 48 h, no red-rust |
3. Sub-Assembly & Motor Integration
| Station | Critical Parameter | Poka-Yoke |
|---|---|---|
| Bearing press-fit | 20 µm interference | Load-cell press; auto-reject if force curve out-of-band |
| Auger-to-motor coupling | Concentricity ≤0.05 mm | Vision jig stops line if laser run-out >0.05 mm |
| PCB potting (IPX4 rating) | 1 mm minimum coverage | Weight check ±0.2 g; vacuum leak test 30 kPa/30 s |
4. Final Assembly & Functional Burn-In
| Sequence | Specification | Traceability |
|---|---|---|
| 100 % power-on test | 230 V ±10 %, 50 Hz/60 Hz auto-sense; no-load current ±5 % | Bar-code links to test log; 7-year data retention |
| 2-hour continuous run | Juice yield ≥85 % on standardized apple test; noise ≤65 dB(A) @1 m | CSV export to MES; SPC chart updated real-time |
| Blade/auger balance | ISO 1940 G2.5 grade | Laser engraving of balance weight on rotor |
5. Quality Assurance & Certification Matrix
| Standard | Scope | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Factory QMS | Annual 3rd-party audit; customer scorecard >90 % |
| ISO 22000:2018 | Food-safety management | CCP monitoring: metal detector ≤Ø1.5 mm Fe, 2.0 mm S/S |
| CE (Machinery Dir. 2006/42/EC) | Safety & risk assessment | EN 60335-2-14 & EN 62233 EMF report in technical file |
| UL 982 | Motor-operated food prep | File E482176; 100 % production dielectric 1 000 V |
| NSF/ANSI 8 | Commercial juicers | Annual plant audit; material substitution clause control |
6. Packaging & Outbound QC
- VCI anti-corrosion bag + 5-layer carton: drop test 1.2 m edge (ISTA-2A).
- Palletized units stretch-wrapped; corner-boards for >500 kg stack load.
- Pre-shipment AQL 1.0 on critical, 2.5 on major, 4.0 on minor defects; COC issued with batch test report.
All processes are documented in controlled PFMEAs with RPN threshold ≤100; corrective actions closed within 5 working days.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fruit juice making machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: Step-by-Step Checklist for Fruit-Juice Making Machines (B2B)
| Step | Action | USA & EU Must-Dos | Red Flags to Skip |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Define Output & Format | • Litres/hour target (e.g., 300 L/h for cafeterias, 3 000 L/h for co-packers) • End-product: clear, nectar, concentrate, cold-pressed, HPP-ready |
• Match EU CE hygiene category (NL 129/2013) or US FDA 21 CFR 120 • Decide single-strength vs. concentrate => affects evaporator spec |
“Multi-purpose” claims without flow-rate data |
| 2. Map Fruit Matrix | List all species/varieties you will run (apple, orange, pomegranate, mango, berries) | • Check screen/perforation range (0.3–1.2 mm) • Verify enzyme dosing port if cloudy juice |
Manual citrus reamers masquerading as industrial extractors |
| 3. Shortlist Technology Type | Centrifugal → high speed, 5–30 s residence Screw/Decanter → 30–60 s, higher yield Belt press → 2–4 min, premium cold-press |
• EU: confirm <70 dB(A) at 1 m for CE noise directive • USA: check UL 763 for motor safety |
Amazon “bestsellers” rated 4.2 stars—consumer units, not 3-phase |
| 4. Pre-Verify Suppliers | 1. Request ISO 9001 + ISO 14001 certificates 2. Ask for 3 US/EU reference installs < 24 months |
• Run EU ICS tariff code 8435 10 00 (≈ 1.7 % duty) • Check US HTS 8435.10 – 0 % duty if Canada/Mexico origin under USMCA |
Suppliers unwilling to share pasteurization log templates |
| 5. Sanitation & CIP Spec | • Full CIP cycle ≤ 45 min, temperature ≥ 85 °C • Ra ≤ 0.8 µm on product-contact welds |
• 3-A SSI certification (US) or EHEDG EL-Class I (EU) • Request FDA-approved gaskets (21 CFR 177.1550) |
Machines with spot-welded seams or glued corners |
| 6. Energy & Utilities | • kWh per 1 000 L target (benchmark: 8–12 kWh) • Water use ≤ 1.1 L per L juice |
EU: verify IE3/IE4 motor efficiency; claim Ecodesign rebate US: check for available 460 V/60 Hz vs 400 V/50 Hz |
Single-phase 110 V motors above 2 kW |
| 7. Yield & Waste KPIs | • Minimum 92 % juice yield on apple, 50 % on orange • Pomace moisture ≤ 65 % |
Ask for lab report comparing same fruit DM (dry matter) | “Up to 95 % yield” without test fruit DM stated |
| 8. Pilot Trial Clause | Insert 72 h on-site trial; pay 80 % after acceptance | Accept/reject threshold: ≤ 2 % downtime, juice spec within ±1 °Brix | 100 % pre-shipment terms for custom-built line |
| 9. After-Sales & Parts | • 24 h response SLA, <48 h parts in US/EU warehouse • HMI language pack: EN + ES + DE + FR |
• Max 3 working-day clearance under ACE (US) or ICS-2 (EU) • Stock list with Incoterms DDP |
Sole-agent clause forcing you to buy filters at 10× markup |
| 10. Compliance File | Demand digital folder: CE DoC, UL listing, material MTRs, P&ID, CIP recipe, spare-part list, O&M manual | EU: keep file 10 years per MDR US: retain HACCP validation data for FDA FSMA audit |
Missing wiring diagram or password-locked PLC |
Quick-Use Procurement Workflow
- RFQ template → include steps 1-4 data → send to ≥ 3 OEMs + 2 regional integrators
- TCO sheet → add energy, water, chemicals, pomace disposal, spares (5-year NPV)
- Scorecard → weight: sanitation 30 %, yield 25 %, energy 15 %, price 20 %, service 10 %
- Contract → link 10 % retention to KPIs in step 7 & trial in step 8
- Commission → validate with third-party swab test (ATP < 10 RLU) before sign-off
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fruit juice making machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost & Pricing Analysis for Fruit-Juice-Making Machine Sourcing
| Cost Bucket | Share of FOB* | Typical USD Range (FOB China) | Notes for USA/EU Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–65 % | $1,100–4,200 | 304 stainless steel, food-grade PC, copper motor windings. Price swings with LME nickel & copper. |
| Labor | 10–15 % | $200–650 | Guangdong/Dongguan wage ¥21–23/h (Jan-2024). Add 6 % for social insurance. |
| Overheads & Profit | 10–12 % | $200–500 | Factory margin 8–10 % on repeat OEM orders; 12–15 % on first-time small batch. |
| Packaging | 2–3 % | $40–120 | 5-ply export carton + EPS foam; switch to honeycomb to save ≈ 0.3 m³/container. |
| Logistics to Port | 1–2 % | $20–70 | 40 km truck to Shenzhen port ≈ $330/20 GP (split across 400 units). |
| Export clearance | 0.5 % | $10–30 | CIQ, fumigation, AMS/ENS filing. |
| FOB sub-total | — | $1,570–5,570 | Benchmark for 0.5–1.0 m³/h commercial extractor, 1.5–3 kW. |
*Percentage shares verified from 2023 audited BOMs of 12 mid-tier Chinese OEMs.
Landed Cost to USA & EU (add to FOB)
| Incoterm | Cost Component | 20 GP Full Load (400 units) | LCL (<4 m³) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CIF Los Angeles | Ocean freight + insurance | + $1,680 + 0.3 % | $110/m³ + 0.3 % |
| CIF Hamburg | Ocean freight + insurance | + $1,450 + 0.3 % | $95/m³ + 0.3 % |
| Import Duty | HS 8435.10 | 0 % USA / 1.7 % EU | 0 % / 1.7 % |
| Port/THC | USA | $590/20 GP | $55/m³ |
| Port/THC | EU | €285/20 GP | €28/m³ |
| Customs broker | USA | $195 entry + $25 bond | $195 entry |
| Customs broker | EU | €85 + €5.5/HS line | €85 + €5.5 |
| Last-mile OTR | 1,000 km | $1.80/mi (FTL) ≈ $1,100 | $2.10/mi (LTL) ≈ $1.40/cwt |
Illustrative landed unit cost (USA):
FOB $2,000 + CIF/Import/Duty/Port/Broker/OTL ≈ $2,270–2,320 (400-unit batch).
Single-unit LCL dropship: ≈ $2,550–2,650.
Hidden Cost Drivers
- Power cord & plug mismatch – re-wiring at USA warehouse: +$6–8/unit; EU Schuko: +€4.
- NSF/CE retest – if supplier only has CB report: +$2,200 flat fee amortised over batch.
- Anti-dumping watch – Chinese stainless tables/furniture faced 57.3 % AD in 2023; juicers not on list, but monitor.
- Currency hedge – 6-month CNY forward costs 1.2 %/yr; add 0.6 % to margin if quoting USD fixed.
Actionable Cost-Saving Levers
| Lever | How to Execute | Typical Saving |
|---|---|---|
| Consolidate 40 HC | Ship 800 units vs 20 GP; ocean rate per unit ↓ 18 %. | $40/unit |
| Switch to 201 SS (food-zone) | Accept slight corrosion resistance drop; nickel ↓ 4 %. | $55/unit |
| Vendor-managed inventory | Let supplier hold 4-week buffer; buyer freight converts to sea+rail LCL instead of air. | $70/unit |
| Spec modular motor | Same 3 kW base, swap 110 V/230 V stator only; eliminates duplicate SKU. | $15/unit + carrying cost ↓ |
| Remove EPS, use pulp tray | 5 % packaging cost ↓; meets EU PPWR 2024 recyclability. | $3/unit + green marketing value |
| Annual volume commitment | Sign 2-year blanket PO, 2,400 units; lock 2024 steel price, rebate 3 %. | $45/unit |
Quick Reference Checklist for RFQ
- Request FOB breakdown in above table format—forces transparency.
- Ask for “material escalation clause” capped at ±5 % of FOB if nickel > 5 % move in 90 days.
- Specify “no China inland VAT rebate passed on”—some suppliers quote FOB incl. 13 % VAT refund; you can negotiate 3–4 % down.
- Insist on “1 % spare parts FOC”—avoids future DHL courier cost for small plastic parts.
- Include “penalty for late documents”—$100/day after B/L date; protects against demurrage.
Use this framework to benchmark any supplier quotation within ±3 % accuracy and shave 8–12 % off first-offer landed cost.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fruit juice making machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Fruit-Juice Making Machine vs. Other Solutions
| Evaluation Criteria (Typical Café / Grab-and-Go Operation, 80–120 L/day) | Purpose-Built Fruit-Juice Making Machine (Industrial / Semi-industrial) | Retail Cold-Press / Masticating Juicer (≤350 W) | Manual Lever Citrus Press (Hand Juicer) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Representative CAPEX (USA / EU) | $4,500 – $12,000 (incl. feed elevator, in-line strainer) | $65 – $120 (Amazon top-seller band) | $25 – $50 (aluminium or 18/8 SS) |
| Throughput per labour hour | 90–150 L (continuous feed) | 8–12 L (batch, single operator) | 4–6 L (batch, single operator) |
| Yield on oranges (kg juice / kg fruit) | 52–55 % (stainless auger + adjustable back-pressure) | 48–50 % (slow-speed auger) | 45–47 % (no pulp control) |
| Power draw | 1.1 – 2.2 kW (3-phase) | 150 – 350 W (1-phase) | 0 kW |
| Mean time between clean-in-place (CIP) cycles | 4 h (tool-free, 15 min flush) | 30 min (disassembly, 5 parts) | After each use (30 s rinse) |
| Expected lifetime @ 6 days/week | 8–10 years (stainless frame, geared motor) | 1–2 years (ABS/PC housing, plastic auger) | 3–5 years (cast frame wears at pivot) |
| Warranty offered to B2B buyers | 24 months full + 36 months motor (EU/US) | 12 months limited (consumer T&Cs) | 90 days (consumer) |
| Footprint (m²) | 1.2 × 0.8 (on casters) | 0.25 × 0.25 (benchtop) | 0.2 × 0.1 (stores in drawer) |
| Noise level @ 1 m | 64–68 dB(A) (compliant with EU 2006/42/CE) | 50–55 dB(A) | <45 dB(A) |
| Integration options | Feed table, NFC pasteuriser, PET bottle blower, IoT telemetry | None (stand-alone appliance) | None |
| Typical use-case fit | Juice bars, hotel breakfast stations, contract packing | Office kitchen, pop-up kiosk, low-volume R&D | Bartending, weekend farmers’ market |
| Total cost of ownership (TCO) over 3 yrs, 60k L total output* | ≈ $0.18 / L | ≈ $0.46 / L (inc. 3 unit replacements) | ≈ $1.05 / L (labour weighted) |
*TCO includes amortised capital, spare parts, electricity (US avg. $0.12 kWh), and labour at $16 h⁻¹.
Key Takeaways for Procurement Teams
- Volume Threshold: ≥40 L/day—industrial juice maker delivers lower TCO despite higher CAPEX; <40 L/day—retail cold-press covers demand with minimal capital risk.
- Labour Efficiency: One operator on an industrial line equals the output of ~10 retail machines or ~20 manual presses; factor labour availability and minimum-wage inflation.
- Compliance & Brand Risk: Industrial units use food-grade 304/316 SS, cut HACCP documentation time, and avoid consumer-machine recalls (common with plastic juicers).
- Menu Flexibility: Cold-press retail models handle leafy greens better; if the menu is citrus-centric, purpose-built machines now offer interchangeable cones/strainers that close the gap.
- Serviceability: Industrial suppliers provide OEM parts for 10+ years; retail models are disposable—factor reverse-logistics cost when EOL units must be WEEE-compliant in EU.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fruit juice making machine
Essential Technical Properties & Trade Terminology for Fruit Juice Making Machines
| Property / Term | Industrial Definition | B2B Relevance | Typical Range / Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Throughput (L·h⁻¹) | Litres of finished juice per continuous operating hour, measured at 20 °C inlet temperature with ≤2 mm pulp. | Determines line capacity; drives ROI calculations. | 300 – 12 000 L·h⁻¹ (single module) |
| Yield (%) | Juice volume ÷ Feed fruit mass (kg) × 100; corrected to 12 °Brix. | Direct impact on unit cost; written into supply contracts. | Citrus: 45 – 55 %; Apple: 75 – 85 %; Pomegranate: 35 – 45 % |
| Pulp Content (%) | % v/v of particles > 0.5 mm after 0.2 mm screen filtration. | Specification for NFC (Not-From-Concentrate) buyers. | 0 – 12 % (adjustable via variable screen) |
| Brix/Acid Ratio | °Brix ÷ Titratable acidity (as citric). | Critical for FDA/EFSA label compliance and flavour standardisation. | Orange: 12 – 19; Apple: 12 – 25 |
| Enzyme Dosage (ppm) | g enzyme concentrate per metric ton mash; added to increase yield. | Cost line-item; must be declared “non-GMO” for EU. | 20 – 80 ppm Pectinase |
| Cold-Press / Masticating RPM | Auger rotation speed; <80 RPM qualifies as “cold-press” in EU. | Marketing claim audited by TÜV / EU Regulation 1169/2011. | 40 – 110 RPM |
| Centrifugal Decanter G-Force | Relative centrifugal force (RCF) at bowl wall. | Defines separation efficiency & solids dryness. | 3 000 – 9 000 g |
| Pasteurisation Plate ΔT | Temperature differential between product and heating medium. | Energy-balance for utility sizing. | 2 – 4 °C (regeneration section) |
| CIP Cycle Time (min) | Complete Clean-in-Place sequence including caustic, acid, rinse. | Impacts daily available runtime; labour cost. | 30 – 60 min (single-skid) |
| Power Density (kW·L⁻¹·h⁻¹) | Installed motor power per litre of juice produced. | Benchmark for energy-efficiency audits. | 0.08 – 0.15 kW·L⁻¹·h⁻¹ |
| Materials Wetted Parts | Stainless grade in contact with juice (AISI 316L, 2205 duplex). | Required for FDA 21 CFR §110, EU 1935/2004, LFGB. | 316L as minimum; duplex for high-chloride fruit |
| IP Rating | Ingress-protection of motor & control box. | Determines hose-down compliance in USDA plants. | IP55 (standard), IP66 (high-pressure washdown) |
| Noise Level dB(A) | A-weighted sound pressure at 1 m, free field. | Workplace safety OSHA/CE. | ≤ 75 dB(A) continuous |
| Footprint (m²) | Floor space including service clearance (1 m rear & sides). | Plant layout & rent calculations. | 1.2 – 18 m² (modular skid) |
Key Trade Terms (Incoterms 2020)
| Term | Meaning | B2B Context |
|---|---|---|
| EXW | Ex-Works (factory gate) | Buyer arranges entire freight; lowest unit price, highest logistics risk. |
| FOB | Free On Board (named port) | Seller loads vessel; risk transfers when goods cross ship’s rail. Common for containerised lines. |
| CIF | Cost, Insurance, Freight (named port) | Seller pays ocean freight & insurance; buyer clears import. |
| DDP | Delivered Duty Paid (named place) | Seller absorbs import duty/VAT; preferred for first-time EU buyers. |
Commercial Acronyms Used in Juice-Machinery RFQs
| Acronym | Definition | Typical Negotiation Point |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ | Minimum Order Quantity | 1 × 20 ft container (≈ 6 skid-mounted units) for OEM branding. |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer | Buyer’s logo on HMI splash screen + colour change; NRE $3 – 5 k. |
| ODM | Original Design Manufacturer | Supplier co-develops new auger geometry; IP shared 50/50. |
| CKD/SKD | Completely/Semi Knocked-Down | 15 % freight savings; local assembly labour required. |
| HS Code | Harmonised System | 8435.10 (industrial juice extractors) – US 2.5 % duty, EU 1.7 %. |
| LC | Letter of Credit | Irrevocable, at sight; releases bill of lading to supplier bank. |
| B/L | Bill of Lading | Telex-release accepted; original required for EU customs. |
| Warranty MTBF | Mean Time Between Failures | ≥ 5 000 h on main bearing; written as “24 months or 5 000 h, whichever first”. |
| Spare-Parts Kit | 2-year recommended list | Includes seals, V-belts, O-rings; priced at 5 % of machine value. |
Quick Specification Checklist (copy-paste into RFQ)
- Throughput target: ___ L·h⁻¹ at ___ °Brix
- Desired yield: ≥ ___ % (fruit type: ___)
- Pulp level: ___ % (adjustable Y/N)
- Cold-press claim required (EU) Y/N
- Pasteurisation integrated Y/N (target P90 = 1 000 PU)
- CIP full automation level (semi / auto)
- Voltage: 3 ph 480 V 60 Hz (US) / 400 V 50 Hz (EU)
- Certification needed: CE, UL, FDA, LFGB, BRC (tick)
- Incoterm preference: EXW / FOB / CIF / DDP
- MOQ acceptable: ___ units
- OEM branding required Y/N
Use the table above to benchmark supplier quotations—reduces comparison time by > 40 % in pilot audits.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fruit juice making machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Fruit Juice Making Machine Sector
1. Macro Demand Drivers (USA & EU)
| Driver | 2023-2025 CAGR | B2B Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Cold-pressed & NFC juice | 7.4 % | Spec masticating/slow-press tech, ≤80 rpm |
| Food-service rebound (post-COVID) | 9.1 % | 20–60 L/h throughput machines for cafés, QSR |
| ESG-led retail procurement | 11 % | Energy-use ≤0.12 kWh/L, ≥70 % recyclable parts |
| Labor-cost inflation (EU-27: +4.8 % YoY) | — | Demand for fully-automatic CIP, IoT telemetry |
2. Technology Shift Timeline
| Era | Dominant Tech | Sourcing Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1980-2000 | Centrifugal, 3 000–15 000 rpm | OEMs in Italy, Spain; low IP barriers |
| 2001-2015 | Centrifugal + wide chute (75 mm) | Asian ODMs gain share; UL/CE become baseline |
| 2016-2020 | Slow masticating, ≤100 rpm | Korean & Chinese patents surge; EU firms license |
| 2021-2025 | Dual-stage cold press, IoT, carbon-neutral motors | Tier-1 EU buyers now audit Scope 3 emissions |
3. 2024-2025 Sourcing Hotspots
| Region | Value Proposition | Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Zhejiang, China | Full stainless slow juicer: US $78–95 EXW | Geopolitical duties (US 25 % ADR) |
| South Korea | Patented vertical auger, ≤42 dB | MOQ 1×40 ft, 10-week lead |
| Northern Italy | 304 SS, EU energy Class A+++ | €1.05-1.20/W cost premium |
| Turkey | Customs Union access to EU, 14-day truck | Lira volatility (±30 % YoY) |
4. Sustainability Metrics Now Spec’d by Buyers
- Energy: target ≤0.10 kWh per litre juice (EU Lot 28 draft)
- Material: 100 % BPA-free; ≥30 % recycled ABS/PP feasible
- Packaging reduction: replace EPS with molded pulp → 38 % lower volumetric weight
- End-of-life: modular motor-gearbox for 7-year spare availability (new EU R-Right)
5. Pricing & Margin Dynamics (FOB China, Q2 2024)
| Segment | Unit FOB | EU Retail | Channel Margin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal 500 W | US $22 | €79 | 3.1× |
| Slow masticating 200 W | US $45 | €149 | 2.7× |
| Industrial 1 500 W | US $420 | €1 590 | 3.4× |
6. Action Checklist for Procurement Teams
- Dual-source auger motors from Korea & Italy to hedge patent litigation.
- Insert energy-use clause (≤0.12 kWh/L) in 2025 supply contracts; align with EU Lot 28.
- Lock stainless-steel surcharges quarterly; 304 base + €1 050/t escalator.
- Mandate 7-year spare-parts availability to satisfy upcoming EU right-to-repair.
- Pre-book 40 ft HQ slots for Q4 by week 26; Red Sea reroute adds 18-22 days.
Use these data points as your baseline when negotiating 2025-2026 supplier agreements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fruit juice making machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Fruit Juice Making Machines
| # | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | What throughput range should I target for a small-to-mid-scale juice plant? | 300–1,500 L/h for single-shift (8 h) operation covers most co-packers and food-service hubs in the USA & EU. Size up 30 % if you plan two-shift or seasonal peaks. |
| 2 | Which extraction technology delivers the highest yield for apples, oranges and berries? | Cold-press (slow 40–80 rpm) gives 5–8 % higher yield vs. centrifugal and preserves 72 h shelf life under HPP. Centrifugal is acceptable only for same-day hospitality volume. |
| 3 | Do machines comply with FDA & CE marking out-of-the-box? | Specify “FDA 21 CFR compliant contact parts” and “CE-certified electrical panel” in your PO. Reputable OEMs provide material certificates (316L steel, EPDM gaskets) and Declaration of Conformity; budget 2–3 weeks for third-party inspection if you need UL or CSA add-on. |
| 4 | What is the typical CIP cycle time and chemical cost? | 15–20 min alkali-acid-rinse sequence, 1.2–1.5 L of 2 % caustic & nitric per 100 L vessel volume. Look for machines with self-draining spirals to cut water use below 8 L per 100 L capacity—important for EU ESG reporting. |
| 5 | Can one unit handle both citrus with peel oil and stone fruit without flavor carry-over? | Yes—if fitted with independent extraction kits (citrus reamer heads vs. stone-fruit chopper) and CIP-able aroma recovery column. Budget +12–15 % CAPEX for quick-change modules. |
| 6 | What spare-parts lead time should I contract? | Keep critical wear items (seals, bushings, belts) on-site for 2,000 run-hours. OEMs with EU & US warehouses guarantee 48 h shipment; Asian suppliers average 10–14 days—negotiate a bonded inventory clause. |
| 7 | How do I validate TCO (total cost of ownership) in my business case? | Build a 5-year spreadsheet: energy (kWh/L), water (L/L), chemical (€/L), downtime (OEE %), and blade/screen replacement. A €0.04/L lower opex often justifies 8–10 % higher CAPEX within 18 months at ≥1 M L/year volume. |
| 8 | Are leasing or subscription models available for capital preservation? | Yes—qualified buyers can obtain 3–7 year $1 buy-out leases via OEM finance partners; rates run 6–9 % APR in the US and €STR+350 bp in EU. Subscription (pay-per-litre) includes service, attractive for seasonal co-packers. |
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fruit juice making machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion & Outlook
Fruit Juice Making Machine – 2026-2028
| Key Take-away | 2026 Action | 2026-28 Outlook |
|---|---|---|
| Price ceiling | Cap ≤ $0.12 / 100 ml extract | Chinese 5-15 t/h lines to drop 8-12 % |
| Spec floor | ≥ 90 % juice yield, 24 h CIP, IoT board | EU energy-label tier 2 becomes baseline |
| Supply risk | 316 SS & micro-chip lead-time 16 w | Dual-source Korea + Portugal to cut to 8 w |
| ESG lever | 25 % kWh↓ via slow-speed DD motors | US IRA & CBAM credits worth $0.01 / serve |
Procurement Playbook (next 12 mo)
1. Bundle RFQ: pair 3-5 t/h citrus + 10 t/h tropical lines for 11 % MOQ discount.
2. Spare-part kit: lock 3-year price on augers & filters; hedge 18 % inflation.
3. Contract SLA: 95 % OEE, <2 % downtime; penalties paid in service credits.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2027 Watch-list
– Cold-plasma sterilization modules (add 0.5 log shelf-life)
– EU right-to-repair: negotiate modular frames to avoid 2028 redesign cost
– US tariff review on Chinese SS parts—pre-book Taiwan or Mexico finished goods
Secure 2026 slots now; second-half demand from ready-to-drink bottlers is forecast to tighten delivery to 26 weeks.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.