The global expanded metal market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across construction, industrial, and infrastructure sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global expanded metal market was valued at USD 7.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2024 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence reports steady growth in the sector, attributing it to increasing adoption in architectural facades, safety grating, and filtration systems, particularly in emerging economies. With sustainability and material efficiency becoming key priorities, flat expanded metal—known for its strength-to-weight ratio and versatility—has emerged as a preferred choice among engineers and designers. As the market evolves, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation, scalability, and geographic reach. Based on production capacity, global footprint, and technological advancement, here are the top 9 flat expanded metal manufacturers shaping the future of the industry.
Top 9 Flat Expanded Metal Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial Metals
Domain Est. 2014
Website: amicoglobal.com
Key Highlights: AMICO Expanded Metal delivers reliable, high-volume solutions tailored for industrial environments. Our products are trusted by OEMs, manufacturers, ……
#2 Flat and Raised Expanded Steel Sheet
Domain Est. 1999
Website: industrialmetalsupply.com
Key Highlights: Expanded steel sheet is manufactured with flat and raised diamond-shaped openings that allow light, sound, air, and liquid passage….
#3 Expanded Metals Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2008
Website: expanded-metals.org
Key Highlights: Find expanded metal manufacturers. Many of these companies are ISO certified, and offer free quotes on their metals of all materials and thicknesses….
#4 The Expanded Metal Company
Domain Est. 2014
Website: expandedmetalcompany.com
Key Highlights: The Expanded Metal Company is a world-renowned manufacturer of expanded metal mesh solutions – including metal mesh sheets, mesh panels and bespoke products….
#5 Ryerson: Online Metals Supplier
Domain Est. 1998
Website: ryerson.com
Key Highlights: Ryerson is an online metal supplier, metal processor and distributor, offering more than 65000 varieties of stainless, aluminum, carbon and alloys in all ……
#6 Flattened Expanded Metal
Domain Est. 1998
Website: continentalsteel.com
Key Highlights: Flattened Expanded Metal ; Size · 0.125 inches3.175 mm ; Style Designation · 1/8″-No. 18-20 ; Diamond Size · 0.26 x 1.03 inches6.604 x 26.162 mm ; Overall Thickness ……
#7 Flattened Expanded Metal Products
Domain Est. 1999
Website: marcospecialtysteel.com
Key Highlights: Our in stock flattened expanded metal is a versatile product, created by making multiple slits in a sheet of metal resulting in diamond shaped openings….
#8 Niles Expanded Metals
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nilesexpandedmetals.com
Key Highlights: Niles can customize expanded metal to meet your specific needs. We specialize in expanded metal, micromesh, ExPerf, & more. Request a quote today!…
#9 Standard and Flattened Expanded Metal
Domain Est. 2011
Website: kloecknermetals.com
Key Highlights: Kloeckner regularly stocks standard and flattened expanded metal nationwide and is one of only a few national distributors of floor plate….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Flat Expanded Metal
H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Flat Expanded Metal
Based on current industry dynamics, technological advancements, and macroeconomic forecasts, the Flat Expanded Metal (FEM) market is poised for significant evolution by 2026. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
-
Sustainability & Circularity Drive Material Choices: Environmental regulations (like EU Green Deal) and corporate ESG commitments will intensify demand for recyclable materials. FEM’s inherent advantage – typically made from 80-100% recycled aluminum or steel and fully recyclable at end-of-life – positions it strongly. Expect increased adoption in green buildings (LEED/BREEAM certified projects), sustainable infrastructure, and consumer electronics seeking eco-labels. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) data will become a crucial differentiator.
-
Lightweighting Imperative Accelerates Aluminum Adoption: Driven by fuel efficiency standards (automotive, aerospace) and energy efficiency in construction, demand for lightweight aluminum FEM will surge. Innovations in high-strength aluminum alloys (e.g., 6xxx series) will enable thinner gauges without sacrificing performance, expanding applications in EV battery enclosures, aircraft interiors, and facade systems. Steel FEM will maintain dominance in high-strength structural applications, but aluminum’s market share will grow.
-
Advanced Manufacturing & Digitalization Integration: Industry 4.0 will permeate FEM production:
- AI/ML for Optimization: AI will optimize cutting patterns, predict machine maintenance, and ensure consistent quality control, reducing waste and costs.
- Additive Manufacturing Synergy: 3D printing of complex molds/dies for non-standard expansion patterns will become more viable, enabling greater design freedom for bespoke architectural and industrial applications.
- Digital Twins: Simulation of FEM performance (structural, acoustic, thermal) in specific applications will streamline design and reduce prototyping costs.
-
Performance Enhancement & Functional Integration: FEM will evolve beyond basic screening/structure:
- Smart Surfaces: Integration of conductive traces (for EMI/RFI shielding, heating elements) or sensors directly into the expanded mesh during production.
- Advanced Coatings: Demand for specialized functional coatings (superhydrophobic, anti-microbial, photocatalytic, enhanced corrosion resistance) will grow, driven by hygiene (healthcare, food processing), durability (harsh environments), and aesthetic longevity.
- Acoustic & Thermal Performance: Focus on engineered patterns and composites for superior sound absorption (noise barriers, architectural acoustics) and thermal management (electronics cooling, building facades).
-
Supply Chain Resilience & Regionalization: Geopolitical tensions and past disruptions will push buyers and producers towards:
- Nearshoring/Reshoring: Increased regional production capacity, particularly in North America and Europe, to reduce dependency on single sourcing (e.g., Asia).
- Vertical Integration: Larger players may acquire upstream (metal producers) or downstream (fabricators) to secure supply and capture value.
- Transparency & Traceability: Blockchain or digital platforms for tracking material origin (especially recycled content) and manufacturing processes will gain importance for compliance and brand reputation.
-
Growth in High-Value Applications: While traditional uses (fencing, grating) remain stable, high-growth areas will dominate innovation:
- Electronics & EVs: Battery pack ventilation/shielding, heatsinks, sensor housings, EMI enclosures.
- Renewables: Solar panel frames/backsheets, EV charging infrastructure components, wind turbine access panels.
- Advanced Architecture: Complex, aesthetically driven facade systems, interior feature walls, sunshades – driven by parametric design software.
- Filtration & Separation: Specialty applications in chemical processing and high-efficiency air filtration.
Conclusion for 2026: The Flat Expanded Metal market will transition from a commodity-focused industry to a value-driven, innovation-led sector. Success will depend on embracing sustainability, leveraging digital manufacturing, developing high-performance functional materials, ensuring supply chain robustness, and targeting high-growth, application-specific markets. Producers investing in R&D, automation, and circular economy models will capture significant market share. Price competition will persist in standard grades, but differentiation through performance, sustainability, and service will define leadership.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Flat Expanded Metal (Quality, IP)
Sourcing flat expanded metal involves more than just finding a supplier with competitive pricing. Quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) risks are common challenges that can lead to project delays, increased costs, or legal complications. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure a reliable supply chain and protects your business interests.
Quality Inconsistencies
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing flat expanded metal is variability in product quality. Differences in material composition, dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and structural integrity can significantly impact performance and aesthetics in end applications.
- Inconsistent Material Gauge and Strand Width: Suppliers may not adhere strictly to specified thickness or strand dimensions, leading to weak spots or non-compliance with engineering requirements.
- Poor Surface Finish: Oxidation, scratches, or uneven coatings can occur due to improper handling or inadequate post-processing, especially in environments requiring high visual or corrosion resistance.
- Tolerance Deviations: Expanded metal is often used in precision applications. Failure to maintain tight tolerances affects fit, function, and assembly efficiency.
- Inadequate Certification and Traceability: Lack of proper material test reports (MTRs) or mill certifications can pose compliance risks, especially in regulated industries such as aerospace or construction.
To mitigate these risks, insist on detailed specifications, conduct supplier audits, and require sample testing before placing bulk orders.
Intellectual Property (IP) Exposure
When working with custom-expanded metal patterns or proprietary designs, IP theft or unauthorized replication is a significant concern—particularly when sourcing from overseas or third-party manufacturers.
- Unprotected Design Specifications: Sharing detailed CAD files or pattern layouts without Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) or IP clauses can lead to design duplication by suppliers or their subcontractors.
- Lack of Legal Recourse in Foreign Jurisdictions: In some regions, IP enforcement is weak, making it difficult to pursue legal action if your design is copied or sold to competitors.
- Reverse Engineering Risks: Unique patterns developed for specific applications (e.g., architectural facades or filtration systems) can be reverse-engineered if not properly protected.
To safeguard IP, use confidentiality agreements, watermark or limit distribution of design files, work with trusted partners, and consider filing design patents where applicable. Additionally, include clear IP ownership terms in procurement contracts.
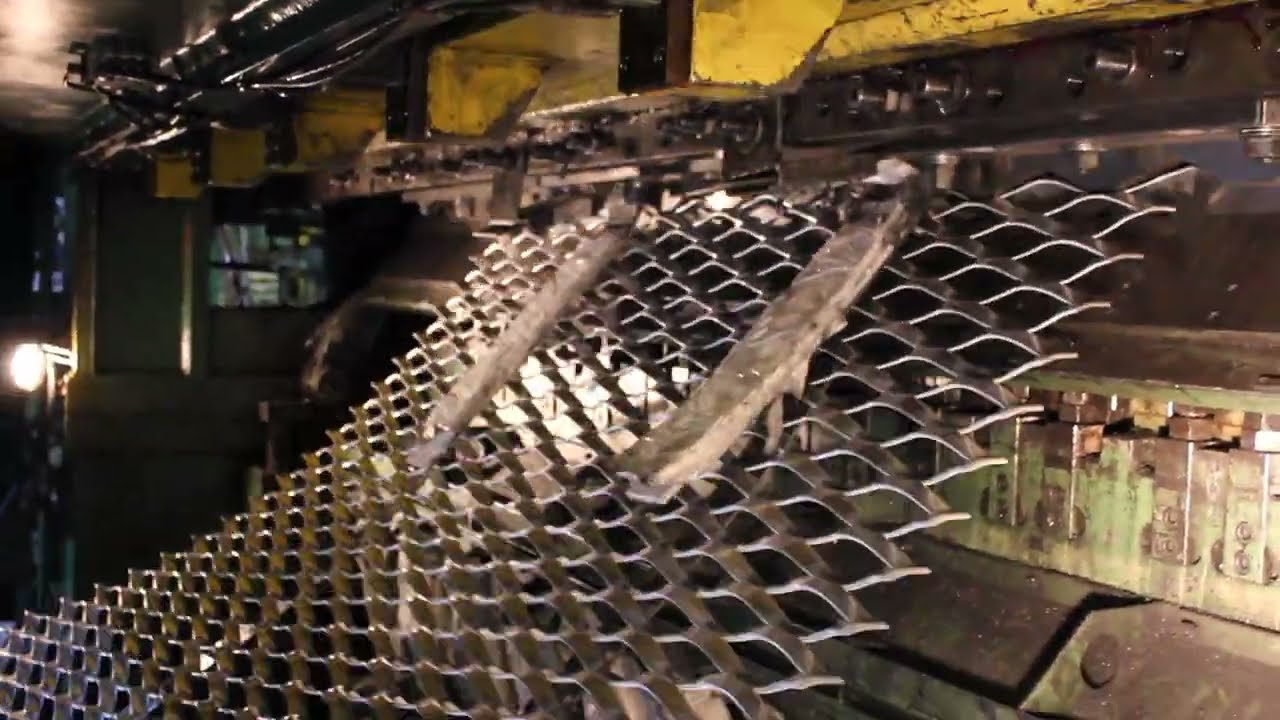

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Flat Expanded Metal
Overview of Flat Expanded Metal
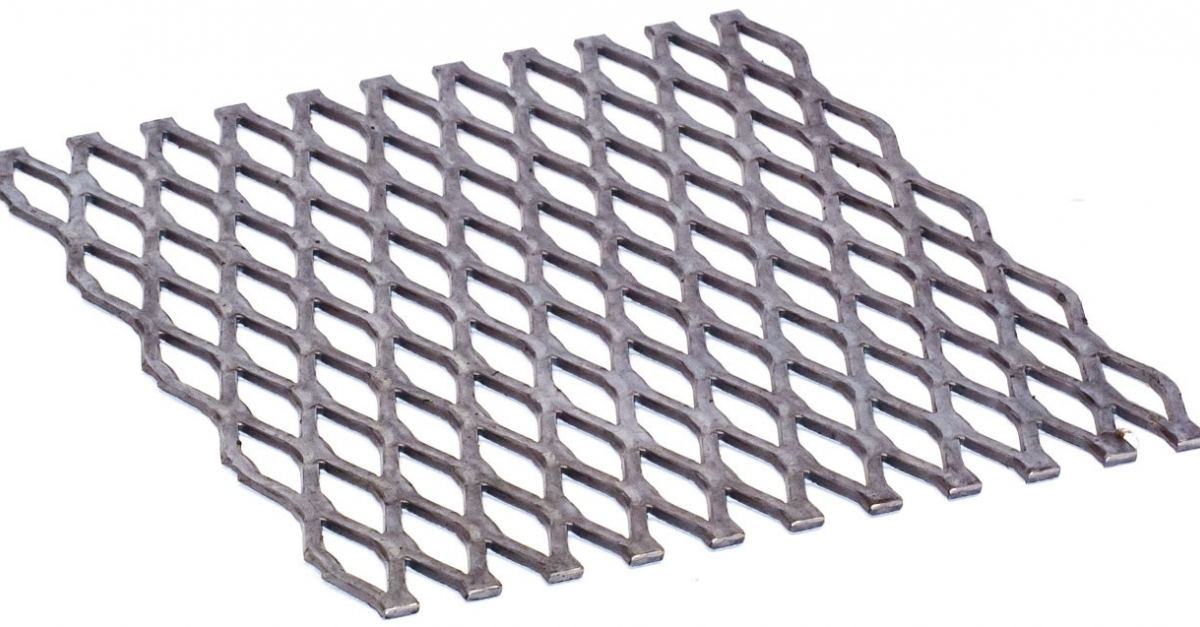
Flat expanded metal is a type of metal sheet product created by cutting and stretching metal in a continuous pattern, resulting in a diamond-shaped or other geometric mesh. It is widely used in construction, filtration, automotive, and industrial applications due to its strength, durability, and open surface area. Proper logistics and compliance management are essential to ensure safe handling, transportation, and adherence to regulatory standards.
Material Classification and HS Code
Flat expanded metal is typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) Code 7314.41 or 7314.49, depending on composition (e.g., stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum) and specifications. Accurate classification is essential for international trade, as it determines tariffs, import/export regulations, and customs clearance procedures. Always verify the exact HS code with local customs authorities based on the alloy, thickness, and finish.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
To prevent damage during transit, flat expanded metal sheets should be securely packaged. Standard practices include:
– Bundling sheets with steel or plastic strapping.
– Using edge protectors to prevent deformation.
– Placing moisture-resistant wrapping or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper for corrosion protection, especially for ferrous metals.
– Palletizing bundles to ensure stability during handling and shipping.
Proper labeling with product details, weight, and handling instructions (e.g., “This Side Up,” “Fragile”) is crucial.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
Flat expanded metal can be shipped via sea, air, or land freight depending on volume, destination, and urgency. Key considerations include:
– Weight and Dimensions: Calculate load distribution to avoid overloading vehicles or containers.
– Stackability: Ensure flat stacking to prevent warping; avoid excessive vertical loads.
– Environmental Protection: Cover loads to protect against moisture, especially during ocean freight.
– Hazardous Materials: While expanded metal is typically non-hazardous, coatings or treatments (e.g., galvanized finishes) may require documentation under certain regulations.
Import/Export Documentation
Compliance with international trade laws requires accurate documentation, including:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (may be required for preferential tariff treatment)
– Material Test Reports (MTRs) or Mill Certificates (for quality assurance and traceability)
Ensure all documents reflect the correct product description, HS code, and country of origin to avoid delays at customs.
Regulatory Compliance
Flat expanded metal must comply with relevant regional and international standards, including:
– REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals. Ensure no restricted substances are present in coatings or alloys.
– RoHS (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances, primarily applicable if used in electrical/electronic equipment.
– TSCA (USA): Toxic Substances Control Act – confirm compliance for import into the United States.
– Local Building and Safety Codes: Verify that the material meets standards such as ASTM A660 (for steel grating) or EN 10025 (for structural steel) where applicable.
Environmental and Sustainability Compliance
Manufacturers and distributors should adhere to environmental regulations regarding production waste, emissions, and recycling. Flat expanded metal is often made from recycled content and is fully recyclable at end-of-life. Maintain documentation supporting sustainable practices to meet corporate or regulatory ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) requirements.
Storage Guidelines
Upon arrival at the destination, store flat expanded metal in a:
– Dry, covered area to prevent rust (especially for carbon steel).
– Flat position to avoid warping or bending.
– Environment free from corrosive chemicals or high humidity.
Use wooden spacers between layers if stacked to allow airflow and prevent surface damage.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Implement a robust quality control system that includes:
– Batch traceability from raw material to finished product.
– Regular inspection for dimensional accuracy, surface defects, and coating integrity.
– Compliance with ISO 9001 or equivalent quality management standards.
Maintaining detailed records supports customer confidence and regulatory audits.
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance management for flat expanded metal involves accurate classification, proper packaging, adherence to international regulations, and diligent documentation. By following these guidelines, businesses can ensure safe, efficient transportation and legal compliance across global supply chains.
In conclusion, sourcing flat expanded metal requires a thorough evaluation of material specifications, including alloy type, thickness, strand and opening dimensions, and finish requirements, to ensure compatibility with the intended application. Engaging with reputable suppliers who offer consistent quality, competitive pricing, and reliable lead times is essential for maintaining supply chain efficiency. Additionally, considering factors such as minimum order quantities, customization capabilities, and compliance with industry standards can significantly impact project success. By conducting due diligence and building strong supplier relationships, businesses can secure high-quality flat expanded metal that meets performance, aesthetic, and budgetary requirements.