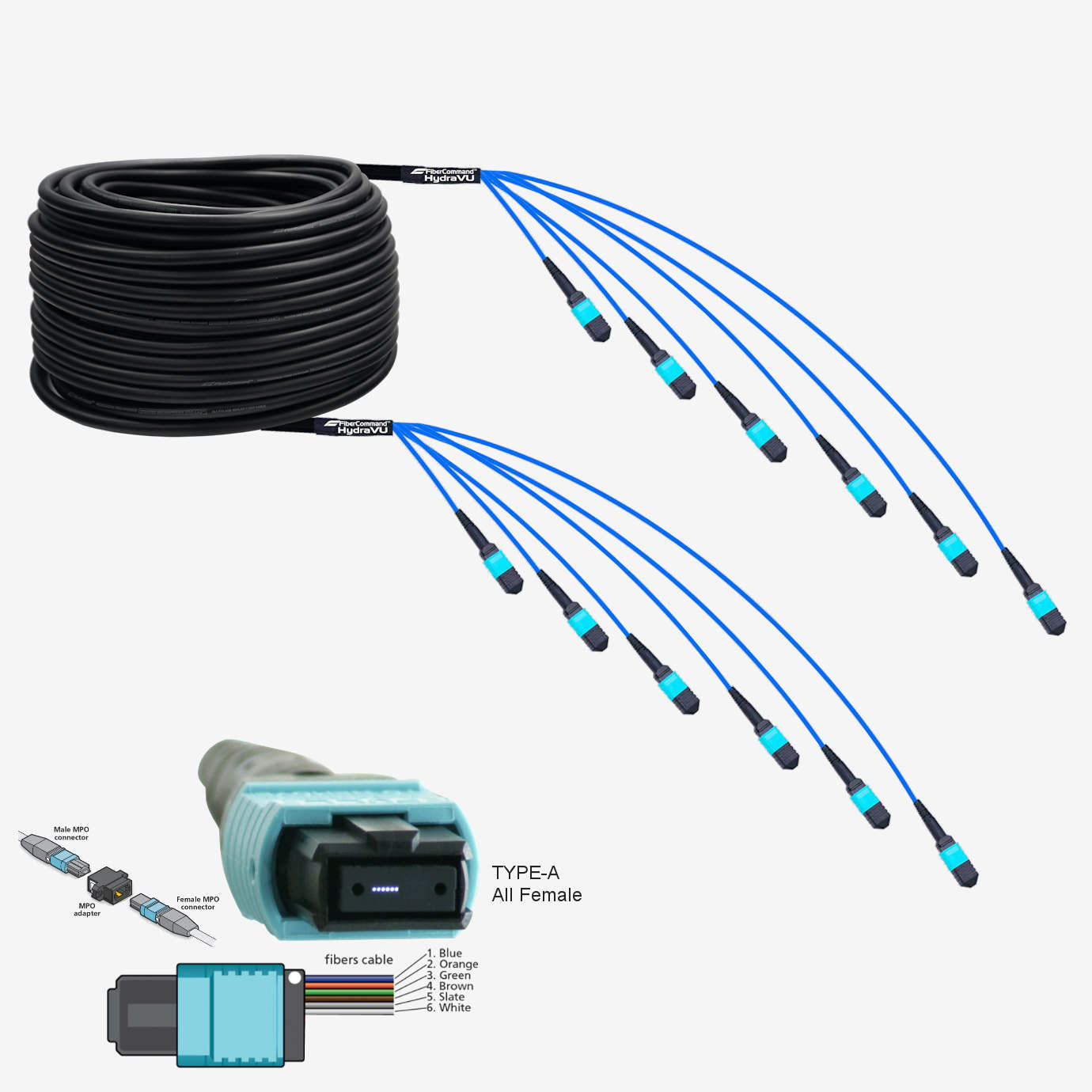
The global fiber optic cable market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for high-speed internet, the proliferation of 5G networks, and increased investment in broadband infrastructure. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 10.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 8.5% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates the market size exceeded USD 11 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 8.9% through 2030, fueled by digital transformation initiatives and government-led connectivity programs worldwide. As demand for reliable and scalable fiber connectivity intensifies, manufacturers specializing in fiber cable extensions—essential for bridging network segments in FTTH, enterprise, and data center applications—are playing a pivotal role in enabling seamless data transmission. The following list highlights the top 10 fiber cable extension manufacturers leading innovation, quality, and scalability in this dynamic and growing sector.
Top 10 Fiber Cable Extension Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Broadcast Fiber Optic Cable Solutions and Accessories
Domain Est. 1997
Website: camplex.com
Key Highlights: Welcome To Camplex. A leading US manufacturer and provider of fiber optic cable solutions and accessories for the Broadcast, Pro-Audio, and Pro-AV markets….
#2 Our Technology
Domain Est. 2022
Website: cleerline.com
Key Highlights: Cleerline offers industry-leading fiber optic solutions, including cables, tools, and accessories. Discover innovative products and expert resources for ……
#3 Fiber Optic Cables
Domain Est. 1991
Website: corning.com
Key Highlights: Corning has fiber optic cables for outdoor, indoor/outdoor, and indoor environments in a variety of types and applications….
#4 Fiber Optic Cables
Domain Est. 1994
Website: commscope.com
Key Highlights: CommScope designs and manufactures a comprehensive line of fiber optic cables—from outside plant to indoor/outdoor and fire-rated indoor fiber ……
#5 Fiber Optic Cables, Adaptors, & Accessories
Domain Est. 1994
Website: panduit.com
Key Highlights: Our extensive offering of fiber optic cables, connectors, cassettes, enclosures, patch cords, cable assemblies, cable distribution products and accessories…
#6 Fiber Optic Extenders
Domain Est. 1995
Website: extron.com
Key Highlights: Extron Fiber Optic Extenders enable long haul transmission of AV and RS-232 control signals or USB over fiber optic cable at extreme distances….
#7 Fiber Optic Cables, Adapters, Couplers, Connectors & Other …
Domain Est. 1996
Website: l-com.com
Key Highlights: 3-day delivery · 30-day returnsOur range of products includes bulk fiber optic cable, assemblies, connectors, attenuators, couplers, splitters, termination enclosures and transcei…
#8 Fiber Optic Cable Solutions
Domain Est. 2008
Website: aflglobal.com
Key Highlights: AFL Fiber Optic Cable offers a complete solution for all of your needs, from aerial to underground to indoor to outdoor. We have a wide variety of fiber ……
#9 Fiber Optic Cables – Single-Mode & Multimode
Domain Est. 2013
Website: enetusa.com
Key Highlights: ENET Fiber Optic cables offer low-latency, optimized performance and increased reliability between network devices. Precision manufacturing ……
#10 Elfcam
Domain Est. 2018
Expert Sourcing Insights for Fiber Cable Extension

2026 Market Trends for Fiber Cable Extension
The global fiber cable extension market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by surging demand for high-speed connectivity, the rollout of 5G networks, and increasing investments in digital infrastructure. As industries and consumers alike rely more heavily on data-intensive applications, fiber optic technology remains the backbone of modern communication systems. This analysis explores the key trends expected to shape the fiber cable extension market in 2026 under the H2 (second half) outlook.
Accelerated 5G Network Deployments
One of the most influential drivers of fiber cable extension in 2026 will be the continued expansion of 5G networks. 5G requires dense fiber backhaul and fronthaul infrastructure to support low latency and high bandwidth. Telecommunications providers are increasingly extending fiber cables to cell towers, small cells, and edge data centers to ensure seamless 5G performance. By H2 2026, widespread urban and suburban 5G coverage will necessitate additional fiber extension projects, particularly in emerging markets where 5G adoption is accelerating.
Government Broadband Initiatives and Subsidies
Governments worldwide are prioritizing universal broadband access, with major funding programs supporting rural and underserved area connectivity. In the U.S., the BEAD (Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment) Program will continue to fuel fiber extension projects through 2026. Similarly, the European Union’s Digital Decade targets and India’s BharatNet initiative are expected to drive large-scale fiber deployments. These public investments will significantly boost demand for fiber cable extension services, especially in H2 2026 as project timelines align with funding disbursement schedules.
Growth in Data Center Interconnectivity
The proliferation of cloud computing, AI, and hyperscale data centers is intensifying the need for high-capacity interconnects. Fiber cable extensions are critical for linking geographically dispersed data centers to ensure redundancy, load balancing, and low-latency communication. By H2 2026, major cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Google, Microsoft) are expected to expand their inter-data center fiber networks, particularly across regional hubs in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, further stimulating market growth.
Advancements in Fiber Technology and Installation Methods
Innovations in fiber optic technology—such as bend-insensitive fibers, higher fiber count cables, and micro-trenching techniques—are reducing deployment costs and improving scalability. Additionally, the adoption of aerial fiber extension using existing utility poles and underground microduct installation is gaining traction, particularly in congested urban areas. By 2026, these advancements will enable faster and more cost-effective fiber extensions, supporting last-mile connectivity and reducing time-to-market for new services.
Rising Demand from Smart Cities and IoT
Smart city initiatives are integrating IoT devices, intelligent transportation systems, and connected public infrastructure—all of which depend on robust fiber networks. Municipalities are investing in fiber extension to support traffic management, public safety systems, and energy grids. In H2 2026, as more cities enter advanced stages of digital transformation, fiber cable extension will become a critical enabler of urban connectivity and sustainability goals.
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The fiber extension market is witnessing increased competition among telecom operators, infrastructure providers, and specialized contractors. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions are expected to rise in H2 2026 as companies seek to expand geographic reach and service capabilities. Additionally, the entry of non-traditional players—such as tech firms and utility companies—into fiber deployment may reshape the competitive dynamics.
Conclusion
By H2 2026, the fiber cable extension market will be shaped by technological innovation, supportive government policies, and escalating demand for high-speed digital infrastructure. With 5G, smart cities, and data center growth acting as primary catalysts, fiber extension will remain a cornerstone of global connectivity. Companies that invest in scalable solutions, efficient deployment methods, and strategic collaborations are likely to gain a competitive edge in this rapidly evolving market.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Fiber Cable Extensions (Quality, IP)
Sourcing fiber cable extensions requires careful attention to both quality and IP (Ingress Protection) ratings to ensure reliable, long-term performance. Overlooking key factors can lead to network failures, safety hazards, and increased costs. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Cable Quality and Construction
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting fiber cables based on price alone without evaluating build quality. Low-cost cables may use inferior fibers, poor jacket materials, or substandard buffering, leading to high signal loss (attenuation), reduced bandwidth, or physical damage during installation. Always verify compliance with industry standards (e.g., ITU-T G.652.D for single-mode) and check for certifications like UL, ETL, or ISO.
Ignoring IP Rating Requirements
The IP rating indicates the level of protection against dust and moisture. Using cables with insufficient IP ratings in harsh environments—such as outdoor installations, industrial settings, or underground conduits—can result in water ingress, corrosion, and signal degradation. For example, an IP67 or IP68 rating is typically required for direct burial or wet locations, while IP54 may suffice for indoor use. Never assume standard indoor cables are suitable for outdoor or rugged conditions.
Mismatched Fiber Type (Single-Mode vs. Multi-Mode)
Choosing the wrong fiber type can severely limit network performance. Single-mode fiber (SMF) is necessary for long-distance, high-bandwidth applications, while multi-mode fiber (MMF) is suitable for shorter runs. Using MMF beyond its distance limits or SMF in cost-sensitive short-reach applications leads to inefficiencies or failures. Ensure compatibility with existing network equipment and future scalability needs.
Poor Connector Quality and Polish
Low-quality connectors (e.g., LC, SC) or improper polishing increase insertion loss and back reflection, degrading signal integrity. Poorly terminated field-installed connectors are especially prone to failure. Pre-terminated cables with factory-tested connectors offer higher reliability. Look for connectors with UPC (Ultra Physical Contact) or APC (Angled Physical Contact) polish, depending on the application—APC is preferred in high-performance or RFoG networks.
Lack of Mechanical and Environmental Durability
Fiber cables must withstand installation stress and environmental conditions. Pitfalls include using non-armored cables in rodent-prone areas, ignoring temperature ratings, or selecting cables without UV-resistant jackets for outdoor exposure. Armored fiber cables or those with robust outer sheaths (e.g., LSZH or PE) enhance durability and longevity.
Insufficient Testing and Documentation
Receiving cables without proper test reports (e.g., OTDR traces, insertion loss measurements) makes it difficult to verify performance. Always request certification for each cable run and ensure traceability. Untested cables may appear functional initially but fail prematurely under real-world loads.
Overlooking Installation and Bend Radius Limits
Exceeding the minimum bend radius during installation causes micro-bends or breaks in the fiber, leading to signal loss. Cables with poor flexibility or inadequate design for tight spaces increase the risk. Choose bend-insensitive fiber (e.g., ITU-T G.657.A1/A2) where routing in confined areas is expected.
By addressing these pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable, high-performance fiber cable extensions that meet both current and future network demands. Always partner with reputable suppliers and verify specifications against project requirements.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Fiber Cable Extension
This guide outlines the key logistical considerations and compliance requirements for planning, deploying, and maintaining fiber cable extension projects. Adhering to these guidelines ensures project efficiency, regulatory adherence, and long-term network reliability.
Project Planning and Site Assessment
Conduct thorough site surveys to evaluate terrain, existing infrastructure, and environmental conditions. Identify potential obstacles such as roads, waterways, or protected areas. Confirm property access rights and utility easements. Develop detailed route maps and project timelines, including risk assessments and contingency plans.
Regulatory and Permitting Compliance
Obtain all necessary permits from local, state, and federal authorities before commencing work. This includes rights-of-way permits, excavation permits, environmental clearances (e.g., wetland or wildlife habitat approvals), and compliance with FCC or national telecommunications regulations. Ensure adherence to local building codes and zoning laws.
Environmental and Safety Regulations
Follow environmental protection standards, including erosion control, proper disposal of excavated materials, and minimization of habitat disruption. Comply with OSHA safety standards for trenching, excavation, and working at heights. Use personal protective equipment (PPE) and implement safety protocols for all field personnel.
Right-of-Way and Land Access
Secure written permission from landowners or governing bodies for any private or public right-of-way usage. Maintain accurate records of all agreements and permits. Coordinate with utility companies to avoid interference with existing underground or aerial infrastructure.
Cable Installation Standards
Adhere to industry best practices such as those defined by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Ensure proper cable pulling tension, bending radius, and splice point protection. Document all splice locations and test results.
Testing and Certification
Perform end-to-end optical testing (e.g., OTDR and insertion loss testing) upon installation completion. Certify the fiber link according to project specifications and industry standards. Maintain detailed test reports for compliance audits and future troubleshooting.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Keep comprehensive records including as-built drawings, permit copies, test results, maintenance logs, and compliance certifications. Ensure all documentation is stored securely and accessible for regulatory inspections or future upgrades.
International and Cross-Border Considerations
For cross-border fiber extensions, comply with international telecommunications agreements and customs regulations. Coordinate with relevant national regulatory authorities and ensure adherence to data sovereignty and security requirements.
Ongoing Maintenance and Compliance Audits
Schedule regular inspections and maintenance to ensure network integrity. Conduct periodic compliance audits to verify continued adherence to safety, environmental, and regulatory standards. Update documentation to reflect any network changes.
Conclusion
Successful fiber cable extension projects require meticulous planning, strict compliance with legal and technical standards, and proactive stakeholder coordination. By following this guide, organizations can ensure safe, lawful, and efficient deployment of fiber infrastructure.
Conclusion for Sourcing Fiber Cable Extension:
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, supplier capabilities, cost considerations, and long-term scalability, the sourcing of fiber cable extensions has been strategically aligned with project objectives. Selecting a reliable vendor offering high-quality, standardized fiber optic cables ensures optimal performance, minimal signal loss, and future-ready infrastructure. Emphasis on durability, compatibility with existing systems, and adherence to industry standards (such as ITU-T G.652D or ISO/IEC 11801) guarantees a robust and sustainable network upgrade. Additionally, negotiating favorable lead times, warranty terms, and logistical support enhances operational efficiency. Overall, a well-planned sourcing approach not only meets current connectivity demands but also supports the organization’s long-term growth and technological resilience.