The global automotive diagnostic scanner market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising vehicle complexity, increasing demand for preventive maintenance, and widespread adoption of smart repair technologies. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.6% through 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates a CAGR of 7.4% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by the rise in electric and connected vehicles requiring advanced diagnostics. As demand surges, a handful of manufacturers have emerged as industry leaders, delivering reliable, feature-rich Fcar (fully compatible automotive repair) scanners that support broad vehicle coverage, real-time data streaming, and over-the-air updates. These top players are leveraging AI integration, cloud-based analytics, and user-centric design to capture growing market share and meet evolving needs across professional repair shops and DIY enthusiasts alike.
Top 4 Fcar Scanner Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
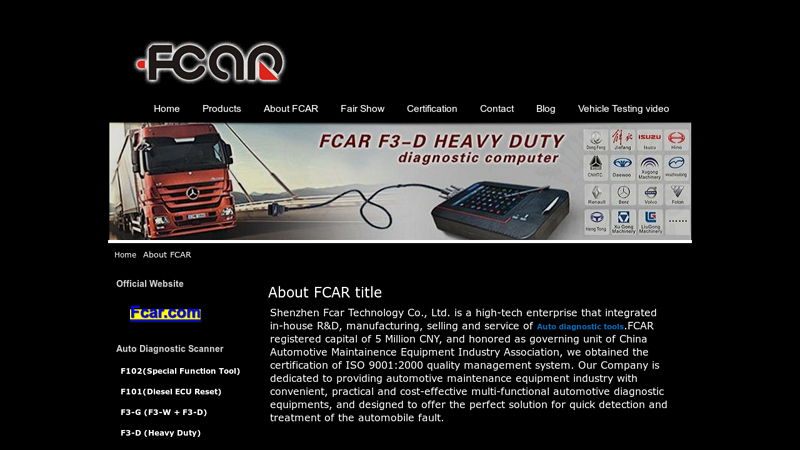
#1 About FCAR Introduce
Website: fcardiagnostictools.com
Key Highlights: Shenzhen Fcar Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise that integrated in-house R&D, manufacturing, selling and service of Auto diagnostic tools….
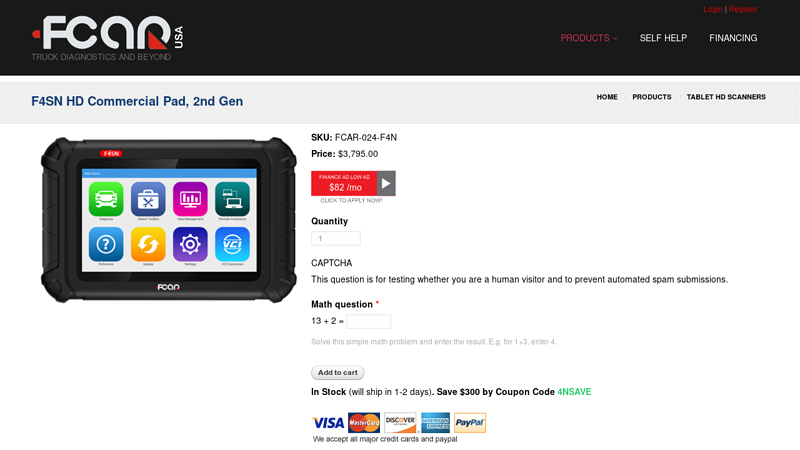
#2 F4SN HD Commercial Pad, 2nd Gen
Domain Est. 2011
Website: fcarusa.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsThis compact scan tool is capable of scanning and diagnosing Class 1-9 engines, transmissions, brakes, and body control units….
#3 Fcar
Domain Est. 2016
Website: vxdas.com
Key Highlights: Fcar-F3-D is newest version of multi-functional intelligentzed automotive scanner which is specialized to design for the diagnosis of diesel engine ……
#4 Professional Automotive Scanners & Vehicle Calibration Tools
Domain Est. 2016
Website: airprodiagnostics.com
Key Highlights: Empower your automotive repair shop with AirPro’s professional scanners and vehicle calibration solutions. Leverage our remote diagnostics Brand-Specialists ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Fcar Scanner
2026 Market Trends for Fcar Scanner
The automotive diagnostic tool market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, changing vehicle architectures, and shifting consumer and professional demands. As a player in this space, Fcar Scanner will need to adapt strategically to these emerging trends to maintain competitiveness and capture market share.
1. Dominance of Connected and Cloud-Based Diagnostics
By 2026, seamless cloud integration will no longer be a differentiator but a baseline expectation. Fcar Scanner tools will be expected to offer real-time data synchronization, over-the-air (OTA) software updates, and remote diagnostics capabilities. Technicians and workshops will increasingly rely on cloud platforms to access vehicle history, share diagnostic reports, and collaborate on complex repairs. Fcar’s ability to provide robust, secure, and scalable cloud infrastructure will be critical for user retention and enterprise adoption.
2. Expansion of EV and ADAS Support
Electric vehicles (EVs) and Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) will dominate automotive innovation, and diagnostic tools must keep pace. Fcar Scanner will need to offer comprehensive EV-specific diagnostics—such as battery health analysis, regenerative braking system checks, and high-voltage component safety protocols. Similarly, support for ADAS calibration (e.g., radar, LiDAR, camera alignment) will be essential. Tools lacking these features will become obsolete in professional repair environments.
3. Integration with AI-Powered Diagnostics and Predictive Analytics
Artificial intelligence will play a central role in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. By 2026, Fcar Scanner could leverage AI to analyze vast datasets from vehicle ECUs, identify failure patterns, and offer predictive maintenance recommendations. This shift from reactive to proactive diagnostics will appeal to fleet operators and service centers aiming to reduce downtime and improve customer satisfaction.
4. Growth of Mobile and Tablet-Based Solutions
The trend toward mobile diagnostic platforms will accelerate, with mechanics favoring lightweight, portable solutions over bulky standalone scan tools. Fcar’s compatibility with Android and iOS devices—alongside intuitive apps—will enhance accessibility and user experience. Enhanced user interfaces, voice commands, and AR-assisted repair guidance may further differentiate Fcar’s mobile offerings.
5. Emphasis on Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
As vehicles become more connected, so do the risks of cyberattacks. Diagnostic tools that interface with vehicle networks must prioritize cybersecurity. By 2026, Fcar Scanner will need to implement end-to-end encryption, secure boot processes, and rigorous authentication protocols to protect both vehicle systems and user data, meeting increasingly stringent global regulations.
6. Rise of Subscription-Based Service Models
The market is shifting from one-time purchases to subscription-based models that include software updates, technical support, and cloud services. Fcar can capitalize on this by offering tiered subscriptions—basic, pro, and enterprise—with scalable features. This recurring revenue model improves customer lifetime value and ensures users always have access to the latest diagnostic capabilities.
7. Increased Demand from Independent Repair Shops and DIY Users
While OEM tools remain expensive, independent repair facilities and skilled DIYers will continue seeking cost-effective yet powerful alternatives. Fcar Scanner can target this growing segment with competitively priced tools that offer broad vehicle coverage, multilingual support, and user-friendly interfaces, particularly in emerging markets.
Conclusion
By 2026, the Fcar Scanner ecosystem must evolve beyond traditional OBD2 scanning to become a smart, connected, and AI-enhanced platform. Success will depend on embracing cloud integration, supporting next-gen vehicles, adopting AI and mobile-first design, ensuring cybersecurity, and offering flexible business models. Companies that anticipate and respond to these trends will lead the future of automotive diagnostics.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Fcar Scanners (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Fcar diagnostic scanners—especially from third-party or OEM-adjacent suppliers—can present several challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Awareness of these pitfalls is crucial for businesses aiming to maintain reliability, compliance, and brand reputation.
Quality Inconsistencies
One of the most prevalent issues when sourcing Fcar scanners is inconsistent product quality. Many suppliers, particularly in competitive or less-regulated markets, may offer scanners that appear identical but vary significantly in performance and durability.
- Inferior Hardware Components: Low-cost manufacturers may use substandard circuitry, screens, or connectors, leading to frequent malfunctions, inaccurate diagnostics, or shortened product lifespan.
- Firmware Instability: Poorly maintained or outdated firmware can result in missed vehicle compatibility, erroneous code readings, or failure to update, reducing the scanner’s usefulness over time.
- Lack of Calibration and Testing: Reputable suppliers perform rigorous testing across vehicle models. Some sourced units may skip these steps, resulting in unreliable real-world performance.
To mitigate this, always demand sample testing, request third-party quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), and verify supplier track records through customer references or industry reviews.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Fcar scanners often rely on proprietary software, diagnostic protocols, and branding, making IP a critical concern when sourcing.
- Unauthorized Replicas or Clones: Some suppliers may offer “compatible” scanners that actually reverse-engineer or copy Fcar’s software without licensing, exposing buyers to legal liability.
- Software Licensing Violations: Using unlicensed firmware or diagnostic databases (e.g., OEM scan protocols) can breach copyright or end-user license agreements (EULAs), leading to legal action or blocked updates.
- Brand Infringement: Scanners that mimic Fcar’s branding, logos, or packaging may constitute trademark violations, especially if marketed as “original” or “genuine.”
To protect against IP issues:
– Verify that the supplier holds proper distribution or licensing rights from Fcar or authorized partners.
– Request documentation of software licenses and compliance with regional IP laws.
– Avoid suppliers offering suspiciously low prices—this often signals counterfeit or pirated software.
Conclusion
Sourcing Fcar scanners requires due diligence beyond cost and delivery. Prioritizing verified quality standards and ensuring full IP compliance protects your business from operational failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Always conduct thorough supplier audits and consider partnering with officially authorized distributors whenever possible.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for FCAR Scanner
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the distribution, handling, and use of the FCAR Scanner, a vehicle diagnostic tool designed for automotive repair and maintenance professionals.
Product Classification and Regulatory Compliance
The FCAR Scanner is classified as a portable electronic diagnostic device under international trade regulations. It complies with the following standards:
– CE Marking: Conforms to EU directives, including the Radio Equipment Directive (RED) 2014/53/EU and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive 2014/30/EU.
– FCC Part 15: Complies with U.S. Federal Communications Commission regulations for unintentional radiators, ensuring it does not cause harmful interference.
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Meets EU Directive 2011/65/EU, confirming the absence of lead, mercury, cadmium, and other restricted materials.
– REACH: Complies with EU Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 concerning the registration, evaluation, authorization, and restriction of chemicals.
Ensure all product packaging and documentation include applicable certification marks and regulatory statements.
Import/Export Documentation
Proper documentation is required for international shipments:
– Commercial Invoice: Must include product description, quantity, unit price, total value, HS Code (8543.70.90 – other electronic communication devices), country of origin (China), and Incoterms (e.g., FOB Shenzhen or DDP Los Angeles).
– Packing List: Details package dimensions, weight, and item breakdown.
– Certificate of Origin: Required for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements, if applicable.
– FCC Declaration of Conformity and CE Declaration of Conformity: Must accompany shipments to the U.S. and EU, respectively.
Verify destination-specific import requirements; some countries may require additional local certifications (e.g., KC mark for South Korea or EAC for Russia).
Shipping and Handling
- Packaging: FCAR Scanners must be shipped in manufacturer-sealed retail boxes with protective inner packaging (e.g., foam inserts) to prevent damage during transit.
- Labeling: Each package must display:
- Product name and model number
- Barcodes and serial numbers (if applicable)
- Handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”)
- Regulatory compliance labels (CE, FCC, etc.)
- Storage Conditions: Store in a dry, climate-controlled environment (5°C to 35°C, 20%–80% relative humidity). Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures or direct sunlight.
- Transportation: Use carriers compliant with IATA/IMDG regulations if shipping by air or sea. The device contains lithium-ion batteries (in some models), which may be subject to special handling rules (UN3481, PI 966 Section II).
Customs Clearance
- HS Code: Use 8543.70.90 for classification. This code covers electronic diagnostic tools and similar devices.
- Duties and Taxes: Duty rates vary by country. Example rates:
- USA: 0% (under HTSUS 8543.70.90)
- EU: 0% (autonomous tariff suspension)
- Canada: 0% (under tariff item 8543.70.90)
Always confirm current rates with local customs authorities. - Customs Broker: Engage a licensed customs broker in the destination country to facilitate clearance and ensure compliance with local regulations.
End-User Compliance and Warranty
- User Manuals: All units must include multilingual user manuals with safety instructions, regulatory information, and warranty details.
- Warranty: FCAR Scanners are covered by a standard 12-month limited warranty against defects in materials and workmanship. Proof of purchase is required for warranty claims.
- Software Updates: Users must comply with end-user license agreements (EULA) when downloading firmware or application updates. Unauthorized modifications void the warranty and may violate export control laws.
- Export Controls: The device may contain encryption software subject to U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR). Re-export to embargoed countries (e.g., Iran, North Korea) is prohibited without proper authorization.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
- WEEE (EU): The FCAR Scanner falls under WEEE Category 6 (monitoring and control instruments). Distributors must register with national WEEE authorities and provide take-back options for end-of-life devices.
- Battery Disposal: Lithium-ion batteries must be removed and recycled separately in accordance with local regulations (e.g., EPA guidelines in the U.S. or WEEE in the EU).
- Recycling Symbols: Include the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol on product and packaging to indicate proper disposal requirements.
Summary
Adherence to this logistics and compliance guide ensures smooth international distribution, regulatory conformity, and environmental responsibility for the FCAR Scanner. Always consult local legal and customs experts when entering new markets to confirm up-to-date requirements.
Conclusion on Sourcing an FCAR Scanner
Sourcing an FCAR scanner presents a practical and cost-effective solution for automotive professionals seeking reliable diagnostic capabilities without the high price tag of OEM tools. FCAR scanners are known for their broad vehicle coverage, especially in Asian, European, and American models, and offer a range of features from basic fault code reading to advanced bi-directional controls and ECU programming.
When sourcing an FCAR scanner, it is essential to consider factors such as device model (e.g., FCAR F3, F9, or VCMI), software update policies, technical support availability, warranty, and authenticity to ensure long-term reliability and functionality. Purchasing from authorized distributors or reputable suppliers helps avoid counterfeit products and ensures access to timely updates and customer service.
In conclusion, the FCAR scanner is a strong contender in the professional OBD2 diagnostic tool market. With careful sourcing and due diligence, it offers excellent value, robust performance, and versatility suitable for independent repair shops and mobile technicians aiming to deliver efficient and accurate vehicle diagnostics.