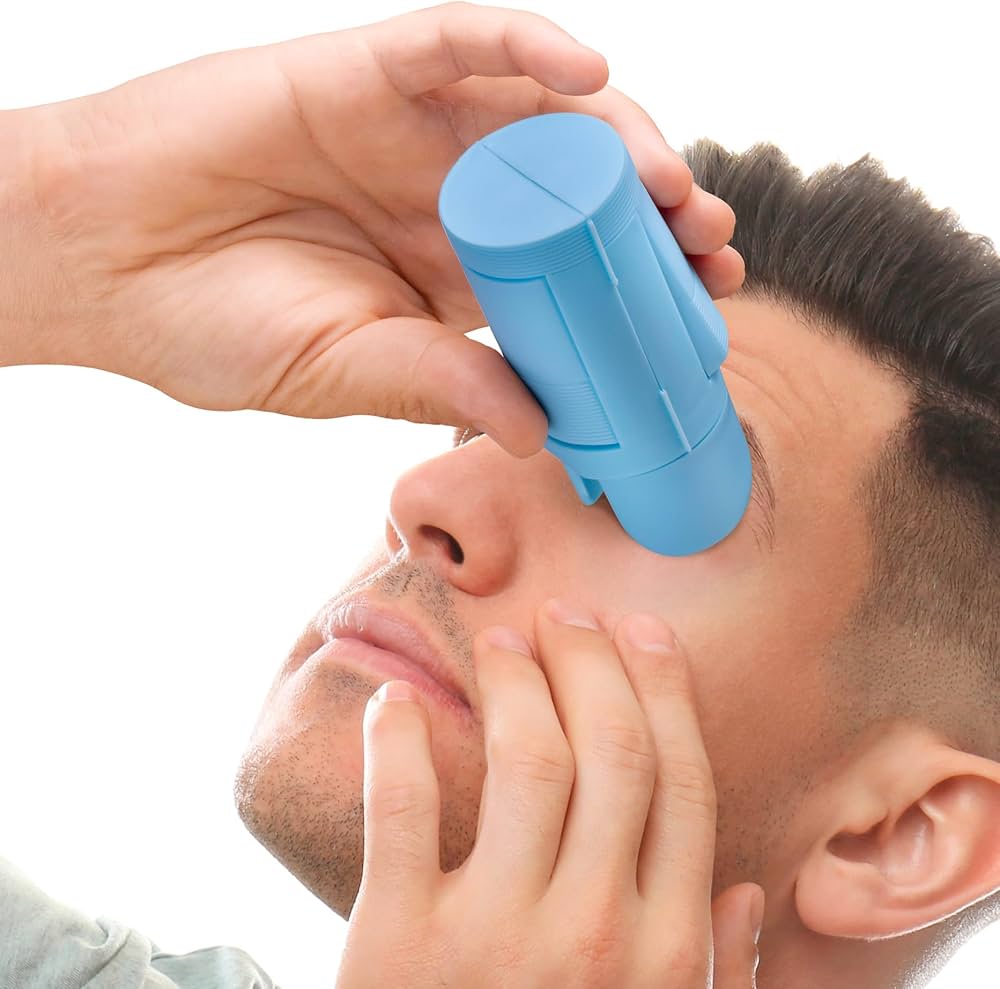
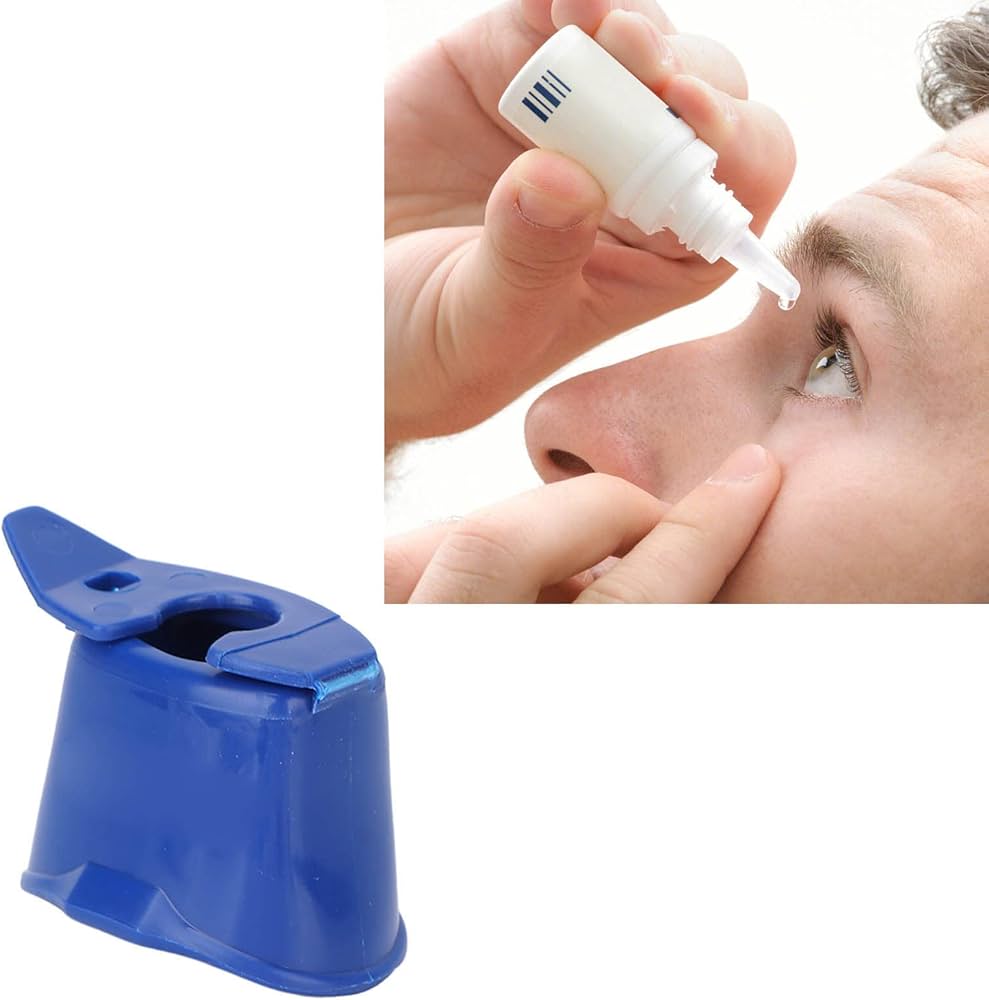
The global eye care devices market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising prevalence of ocular disorders, an aging population, and increasing awareness of eye health. According to Mordor Intelligence, the eye care devices market was valued at USD 36.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. Within this expanding landscape, assistive tools such as eye dropper helpers—designed to improve medication adherence and accuracy in self-administration—have emerged as critical solutions, particularly for patients with limited dexterity or vision impairment. As demand for user-friendly ophthalmic devices rises, a number of manufacturers have distinguished themselves through innovation, ergonomic design, and clinical validation. Below are the top seven eye dropper helper manufacturers shaping this niche yet vital segment of eye care technology.
Top 7 Eye Dropper Helper Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
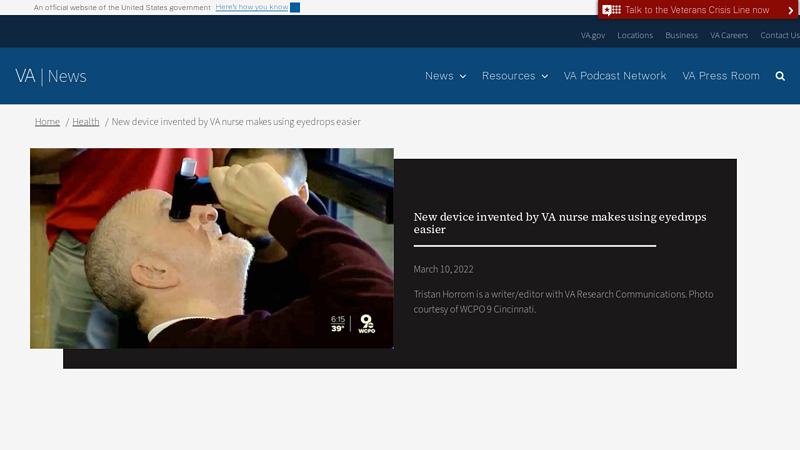
#1 New device invented by VA nurse makes using eyedrops easier
Domain Est. 1997
Website: news.va.gov
Key Highlights: The DropEase provides a stable platform for self-administering eyedrops, complete with a handle that is easy to squeeze with weak or shaky hands….
#2 Assistive Dispenser for Single
Domain Est. 1997
Website: aptcenter.research.va.gov
Key Highlights: The Assistive Dispenser for Single-use Eye Drop Vials was developed by the San Francisco VA. The goals for VehiCLE were to improve ergonomics, ……
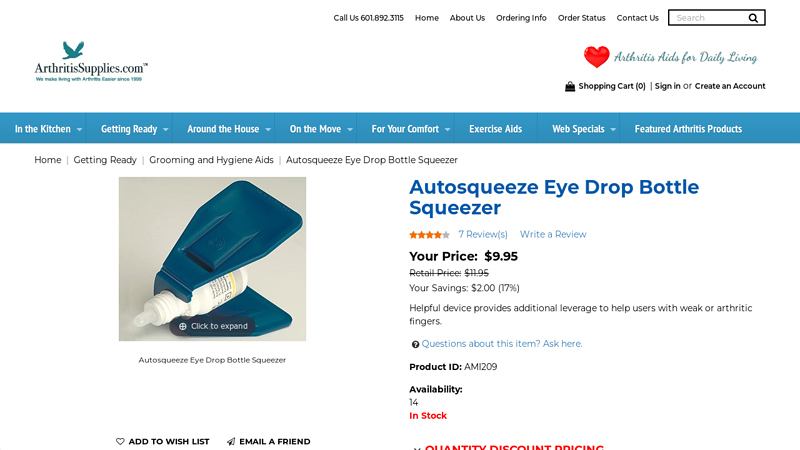
#3 Autosqueeze Eye Drop Bottle Squeezer
Domain Est. 2000
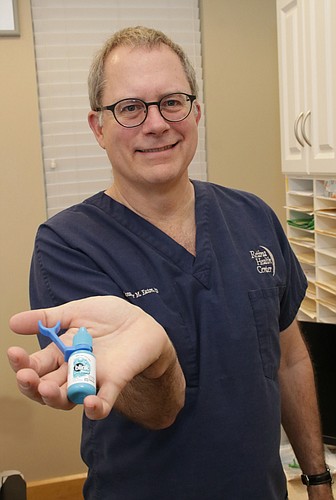
#4 Dr. Alexander Eaton Introduces XactDrop for Better Eye Drops
Domain Est. 2002
Website: retinahealthcenter.com
Key Highlights: Dr. Alexander Eaton has created and introduced XactDrop, an eye drop applicator guide designed to help patients more accurately deliver eye drops….
#5 Drop Aids
Domain Est. 2018
Website: modernod.com
Key Highlights: The GentleDrop (Bedo Solutions) is a multiuse, silicone eye drop delivery device designed to help patients position their eye drop bottle to ……
#6
Domain Est. 2018
Website: ezidrops.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to EziDrops, the home of the easy to use EziDrops Eye Drop Applicator. View the EziDrops Ear Drop Applicator, simple ideas that work….
#7 Magic Touch Eye Drop Helper for Easy Application
Domain Est. 2018
Website: dryeyerescue.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $89 · 30-day returns…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Eye Dropper Helper

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Eye Dropper Helper Devices
The global market for eye dropper helper devices is projected to experience significant growth and transformation by 2026, driven by demographic shifts, technological advancements, and increasing awareness of medication adherence. These assistive tools, designed to help individuals—particularly the elderly and those with motor impairments—administer eye drops accurately and independently, are gaining traction across healthcare and consumer markets.
-
Aging Population and Rising Demand
One of the primary drivers of the 2026 eye dropper helper market is the rapidly aging global population. With increasing life expectancy, especially in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, the prevalence of age-related eye conditions such as glaucoma, cataracts, and macular degeneration is rising. This demographic shift amplifies the need for user-friendly medication delivery systems. Eye dropper helpers address challenges like shaky hands, poor vision, and limited dexterity, making them essential in geriatric care. -
Technological Integration and Smart Devices
By 2026, expect a surge in smart eye dropper helpers equipped with sensors, audio/visual guidance, and Bluetooth connectivity. These innovations aim to improve dosing accuracy and track medication adherence through mobile apps. Integration with telehealth platforms allows caregivers and physicians to remotely monitor patients’ usage patterns, enhancing treatment outcomes. Brands are investing in AI-assisted positioning systems to detect eye location and automate droplet release, reducing spillage and anxiety. -
Expansion of Home Healthcare and Independent Living
The growing preference for aging-in-place and home-based care models is fueling demand for assistive devices. Eye dropper helpers align with this trend by promoting autonomy and reducing reliance on caregivers. Retailers and healthcare providers are increasingly offering these tools as part of comprehensive home care kits, supported by government and insurance incentives in countries with robust eldercare policies. -
Regulatory Support and Reimbursement Policies
In regions like the U.S. and Western Europe, regulatory bodies are recognizing the clinical value of adherence-enhancing devices. By 2026, more eye dropper helpers may qualify for medical device classification, enabling insurance coverage or reimbursement. This shift will lower consumer cost barriers and encourage adoption among low-income and underserved populations. -
Competitive Landscape and Product Innovation
The market will see increased competition from both medical device manufacturers and consumer health tech startups. Key players are focusing on ergonomic designs, hypoallergenic materials, and universal compatibility with standard eye drop bottles. Additionally, eco-conscious designs—such as reusable and recyclable components—are emerging in response to sustainability concerns. -
Regional Market Growth
North America and Europe are expected to lead the market due to advanced healthcare infrastructure and high awareness. However, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, will witness the highest growth rate, driven by rising healthcare spending, urbanization, and government initiatives to improve chronic disease management.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for eye dropper helper devices is poised for robust expansion, supported by demographic needs, technological innovation, and evolving healthcare delivery models. As these tools become more intelligent, accessible, and integrated into broader care ecosystems, they will play a pivotal role in enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing an Eye Dropper Helper (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing an Eye Dropper Helper—whether for pharmaceutical, laboratory, or consumer product use—can present several challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Avoiding these pitfalls is essential to ensure regulatory compliance, brand integrity, and long-term business success.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Material Standards
Many suppliers, especially low-cost manufacturers, may use substandard plastics or rubber materials that degrade over time or react with sensitive liquids. This can lead to contamination, inaccurate dosing, or premature failure of the dropper. Always verify that materials are medical-grade (e.g., USP Class VI, FDA-compliant) and inert to the intended substances.
2. Poor Manufacturing Tolerances
Inaccurate dropper tip dimensions or inconsistent bulb sealing can result in leakage, inaccurate volume delivery, or cross-contamination. Suppliers lacking precision tooling or quality control processes may deliver non-uniform products. Request sample testing and demand ISO 13485 certification for medical applications.
3. Inadequate Packaging and Sterility
If the Eye Dropper Helper requires sterile conditions, improper packaging or lack of validated sterilization processes (e.g., gamma irradiation) can compromise safety. Ensure suppliers provide documented sterilization validation and cleanroom manufacturing practices when needed.
4. Non-Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Depending on the application, droppers may need to comply with FDA, CE, or other regulatory standards. Sourcing from suppliers unaware of these requirements can delay product launches or result in recalls. Confirm regulatory alignment early in the sourcing process.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadvertent Infringement of Patented Designs
Many Eye Dropper Helper designs—especially ergonomic bulbs, precision tips, or integrated measurement systems—are protected by utility or design patents. Sourcing generic copies without due diligence risks infringement lawsuits, product seizures, or costly redesigns. Conduct a freedom-to-operate (FTO) analysis before finalizing designs.
2. Supplier Use of Third-Party IP
Some suppliers may offer “custom” solutions that are actually based on existing patented technology. If the supplier lacks proper licensing, your company could still be held liable for using the infringing product. Require IP indemnification clauses in contracts and verify original design ownership.
3. Lack of IP Protection for Custom Designs
When developing a proprietary Eye Dropper Helper, failing to secure patents, trademarks, or design rights exposes your innovation to copying. Work with legal counsel to file appropriate IP protections before disclosing designs to manufacturers.
4. Unclear Ownership in Joint Development
If you collaborate with a supplier on design improvements, unclear contracts can lead to disputes over IP ownership. Always define IP rights in writing, specifying that custom developments belong to your company unless otherwise agreed.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, businesses can mitigate risks, ensure product reliability, and protect their competitive advantage in the marketplace.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Eye Dropper Helper
Product Classification and Regulatory Status
The Eye Dropper Helper is classified as a medical device accessory intended to assist users in administering liquid medications via eye dropper. Depending on regional regulations, it may fall under Class I (low risk) medical devices in jurisdictions such as the United States (FDA), European Union (MDR), and Canada (Health Canada). It is not intended to replace medical advice or act as a therapeutic device. Confirm local classification requirements before distribution.
Intended Use and Labeling Requirements
The device is designed to stabilize standard eye droppers, aiding individuals with limited dexterity, tremors, or visual impairments in applying eye drops accurately. Labeling must include: product name, intended use, manufacturer details, single-use or reusable status, cleaning instructions (if applicable), and any contraindications. Labels must be in the official language(s) of the target market and comply with local medical device labeling regulations.
Manufacturing and Quality Standards
Manufacturers must adhere to ISO 13485:2016 (Medical Devices – Quality Management Systems) to ensure consistent design, production, and distribution practices. Critical processes such as material sourcing, molding, and final assembly should be documented and validated. Batch records and quality control checks must be maintained for traceability and audit readiness.
Material Safety and Biocompatibility
All materials in direct or indirect contact with users must be non-toxic, latex-free, and hypoallergenic. For devices contacting skin or mucous membranes, biocompatibility testing per ISO 10993 (e.g., cytotoxicity, sensitization, irritation) is recommended. Documentation must be available to demonstrate compliance upon regulatory request.
Packaging and Sterility
If the Eye Dropper Helper is sold as sterile, it must be validated using an appropriate sterilization method (e.g., ethylene oxide, gamma irradiation) with supporting sterility assurance level (SAL) documentation. For non-sterile devices, packaging must protect against contamination and physical damage during transport. Include expiration date and lot number on packaging if applicable.
Import/Export Documentation
Ensure compliance with international shipping and customs regulations. Required documentation may include: Certificate of Conformity (CE, FDA listing), Certificate of Free Sale, commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading. Verify import requirements in destination countries—some may require local authorization or a licensed representative.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Adhere to environmental regulations such as RoHS (EU) and REACH for restricted substances. Provide end-of-life guidance: if reusable, include cleaning and maintenance instructions; if single-use, label for proper disposal according to local waste management policies for medical accessories.
Post-Market Surveillance and Vigilance Reporting
Establish a post-market surveillance system to collect and review user feedback, complaints, and potential adverse events. Report serious incidents or field safety corrective actions (FSCAs) to relevant authorities (e.g., FDA MedWatch, EU EUDAMED) within required timeframes. Maintain complaint handling and corrective action procedures.
Unique Device Identification (UDI)
In regions requiring UDI (e.g., USA, EU, South Korea), assign a unique device identifier and ensure it is printed on the label and packaging in both human-readable and machine-readable (e.g., barcode, Data Matrix) formats. Register the device in the appropriate national database (e.g., FDA GUDID, EU UDI Database).
Training and User Support
Provide clear user instructions for use (IFU), including setup, operation, cleaning, and troubleshooting. Offer multilingual support materials where necessary. Distributors and healthcare providers should be trained on proper use and limitations of the device to ensure patient safety and compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing an Eye Dropper Helper:
In conclusion, sourcing an eye dropper helper requires a careful evaluation of user needs, product quality, cost-effectiveness, and reliability of suppliers. Whether intended for medical, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, or laboratory use, the selection process should prioritize ergonomics, precision, material safety, and ease of use—especially for individuals with limited dexterity or visual impairments. By comparing various sourcing options, including local suppliers, online marketplaces, and specialized medical equipment providers, organizations can ensure they procure a high-quality, compliant, and user-friendly solution. Ultimately, investing in a well-sourced eye dropper helper enhances user independence, improves dosage accuracy, and supports better health outcomes.