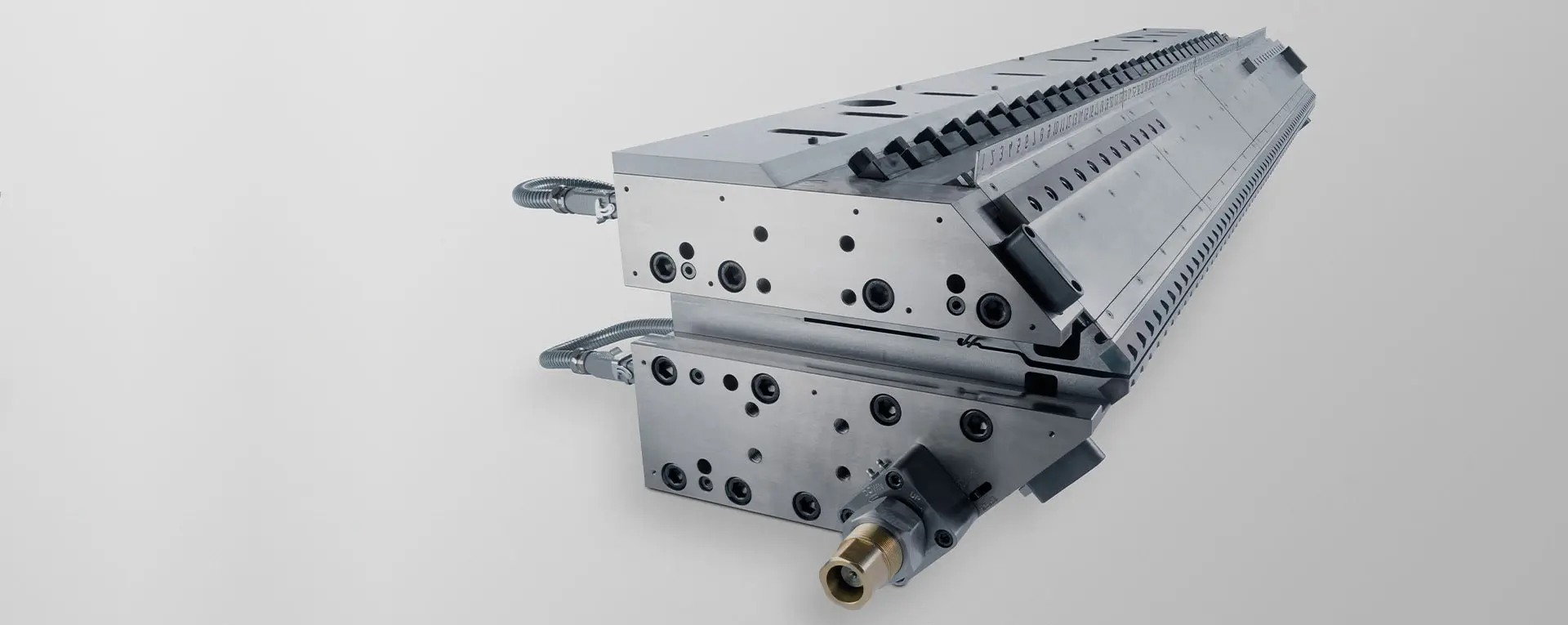
The global extrusion dies market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as automotive, construction, packaging, and consumer goods. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the extrusion dies market was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by advancements in die technology, increasing material efficiency, and the growing adoption of lightweight materials in automotive manufacturing. Meanwhile, Grand View Research highlights the steady rise in plastic and aluminum extrusion applications, particularly in emerging economies, as a key driver for die manufacturing innovation. As competition intensifies and customers demand higher precision and customized solutions, a handful of manufacturers have emerged as industry leaders, setting benchmarks in quality, R&D investment, and global reach. In this analysis, we identify the top 10 extrusion dies manufacturers shaping the future of the industry through technological excellence and market responsiveness.
Top 10 Extrusion Dies Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Guill Tool & Engineering Co. Inc.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: guill.com
Key Highlights: Guill is the leading Extrusion Tooling Designer & Manufacturer with nearly 60 years of experience. Our engineers specialize in plastic extrusion tooling design….
#2 GMA Machinery
Domain Est. 2015 | Founded: 1989
Website: gmatw.com
Key Highlights: As the best extrusion die manufacturer in Taiwan, GMA has been providing high-quality extrusion die products, technology, and services since 1989….
#3 Extrusion Dies
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cloeren.com
Key Highlights: Cloeren offers the most advanced extrusion die technology available. Our extrusion dies are available in a multitude of shapes and sizes to ……
#4 Standard and Custom Extrusion Dies Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2012
Website: daextrusion.com
Key Highlights: Diamond America offers custom designed extrusion dies for any application. Highest grade materials. Best die tooling in the industry. Experts in metallurgy….
#5 Extrusion Dies
Domain Est. 1993
Website: wefa.com
Key Highlights: We achieve outstanding results using high-quality steels in combination with our excellent design know-how and modern precision manufacturing facilities….
#6 EDI® Extrusion Dies and Coextrusion Dies for Polymer Processing
Domain Est. 1993
Website: nordson.com
Key Highlights: Explore our extrusion and coextrusion dies, including biaxially oriented film dies, cast film dies, extrusion coating & laminating dies, and sheet dies….
#7 Aluminum Extrusion Dies & Tooling
Domain Est. 1995
Website: aec.org
Key Highlights: Aluminum extrusion dies can be made to form a limitless array of shapes and sizes. View aluminum extrusion die cost comparisons and download our extrusion ……
#8 Reifenhäuser Extrusion Systems
Domain Est. 1996
Website: reifenhauser.com
Key Highlights: Reifenhäuser Extrusion Systems develops and manufactures tailor-made melt-guiding and forming components for extrusion and injection molding….
#9 Aluminum Extrusion Tooling
Domain Est. 1999
Website: geminigroup.net
Key Highlights: We offer complete die stacks, press tooling components, and die shop equipment backed by 50+ years of tool and die manufacturing experience….
#10 Youngstown
Domain Est. 2000
Website: youngstowntool.com
Key Highlights: Youngstown-Phoenix Aluminum Extrusion Dies is a company devoted to producing custom designed aluminum extrusion dies meeting strict quality requirements….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Extrusion Dies

H2: Extrusion Dies Market Trends in 2026
The extrusion dies market in 2026 is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving material demands, and shifting industrial priorities. Here’s a breakdown of the key trends shaping the landscape:
1. Accelerated Adoption of Smart & Connected Dies (Industry 4.0 Integration):
* Trend: Extrusion dies are becoming “smart,” integrating embedded sensors (pressure, temperature, flow) and IoT connectivity.
* Impact in 2026: Real-time monitoring of die performance, predictive maintenance alerts, and automatic process optimization will become standard for high-value or complex profiles. This reduces downtime, improves quality consistency, and enables data-driven decision-making. Cloud-based platforms for remote die performance analysis will gain traction.
2. Dominance of Advanced Materials & Multi-Material Processing:
* Trend: Rising demand for lightweight, high-performance, and sustainable materials necessitates dies capable of handling challenging polymers and composites.
* Impact in 2026: Dies will be specifically engineered for:
* High-Performance Polymers: PEEK, PEI, PPS, LCP requiring precise thermal control and wear resistance.
* Recycled & Bio-based Materials: Dies designed to handle the variable rheology and potential contaminants in post-consumer recycled (PCR) plastics and bioplastics (e.g., PLA, PHA).
* Multi-Layer & Co-Extrusion: Increased complexity in dies for multi-layer films (barrier packaging), wood-plastic composites (WPC), and multi-material profiles (e.g., rigid/soft combinations) will be critical.
3. Focus on Sustainability: Energy Efficiency & Circular Economy:
* Trend: Regulatory pressure and corporate ESG goals push the entire plastics value chain towards sustainability.
* Impact in 2026:
* Energy-Efficient Die Designs: Dies optimized for lower pressure drops and reduced melt temperature requirements, directly cutting energy consumption in extrusion lines.
* Design for Recyclability: Dies enabling easier production of mono-material structures or facilitating the use of higher PCR content.
* Longer Lifespan & Repairability: Emphasis on durable, easily maintainable dies to reduce waste and resource consumption. Advanced surface coatings (e.g., specialized ceramics, diamond-like carbon) will be standard for wear and corrosion resistance.
* Additive Manufacturing (AM) for Sustainability: AM used not just for prototypes, but for producing lightweight die components with internal cooling channels impossible via traditional methods, improving efficiency.
4. Proliferation of Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) for Die Components:
* Trend: Metal AM (especially DED and PBF) moves beyond prototyping into functional die part production.
* Impact in 2026:
* Conformal Cooling Channels: AM enables intricate internal cooling channels that follow the die profile, enabling faster, more uniform cooling, reducing cycle times, improving part quality, and allowing processing of heat-sensitive materials.
* Complex Geometries & Lightweighting: Production of dies with previously impossible internal structures or significantly reduced weight.
* Faster Prototyping & Low-Volume Customization: Dramatically reduced lead times for custom or complex die designs, making small-batch production more economical.
5. Increased Demand for Precision, Miniaturization, and Complexity:
* Trend: End markets (especially medical, electronics, automotive) demand smaller, more intricate, and highly precise extruded parts.
* Impact in 2026: Dies will feature:
* Micro-Extrusion Capabilities: Dies for producing extremely small profiles (<1mm) with high dimensional accuracy for medical tubing, optical fibers, and micro-fluidics.
* Advanced Flow Simulation & Modeling: CFD and FEA will be indispensable tools for designing dies for complex profiles (e.g., multi-lobed tubing, intricate window profiles) to ensure uniform flow and eliminate defects.
* Tighter Tolerances & Surface Finishes: Higher precision machining and polishing techniques will be standard.
6. Regional Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience:
* Trend: Geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions post-pandemic drive localization and nearshoring.
* Impact in 2026:
* Growth in Asia-Pacific: Continued strong demand, particularly in China, India, and Southeast Asia, driven by infrastructure, automotive, and packaging growth. Local die manufacturing capabilities will expand.
* Reshoring/Nearshoring in Americas & Europe: Increased investment in die manufacturing closer to end-users to mitigate risks, supported by automation to offset higher labor costs. Focus on high-value, complex dies.
* Supplier Consolidation & Partnerships: Increased strategic partnerships between die makers, material suppliers, and extrusion equipment manufacturers to offer integrated solutions.
Conclusion for 2026:
The extrusion dies market in 2026 will be characterized by intelligence, sustainability, and sophistication. Success will depend on die manufacturers’ ability to leverage digital technologies (IoT, AM, simulation), master advanced and sustainable materials, and deliver highly precise, efficient solutions tailored to specific high-growth applications. The focus will shift from merely shaping material to optimizing the entire extrusion process for performance, quality, and environmental impact.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Extrusion Dies: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing extrusion dies from external suppliers, especially overseas or from unfamiliar vendors, can introduce significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to production delays, compromised product performance, increased costs, and long-term competitive disadvantages.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances
Extrusion dies require extremely tight tolerances to ensure uniform material flow and consistent product dimensions. Suppliers with inadequate machining capabilities or lax quality control may deliver dies that deviate from specifications, resulting in defects such as uneven wall thickness, warping, or poor surface finish. Without proper inspection protocols—such as CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) verification—these inconsistencies may go undetected until production begins.
Substandard Material Selection and Heat Treatment
The performance and lifespan of an extrusion die depend heavily on the choice of tool steel and proper heat treatment. Some suppliers may use lower-grade materials or skip critical post-machining processes like stress relieving and tempering to cut costs. Dies made from improper materials are prone to premature wear, cracking, or deformation under high pressure and temperature, leading to frequent replacements and downtime.
Lack of Design Validation and Testing
Reputable die manufacturers typically conduct flow simulations and produce trial runs to validate die performance before final delivery. However, many suppliers skip this step, providing dies based solely on dimensional accuracy without functional testing. This increases the risk of unexpected flow imbalances, die lines, or startup issues that can disrupt production schedules and require costly modifications.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Unauthorized Replication or Reverse Engineering
When sharing detailed CAD files and die designs with a supplier, there is a risk that the design could be copied and sold to competitors—especially in regions with weak IP enforcement. Without strict contractual safeguards, suppliers may reverse-engineer your proprietary die geometry and offer similar profiles to other customers, eroding your product differentiation and market advantage.
Inadequate Legal Protections and Jurisdictional Challenges
Many die suppliers operate in countries where IP laws are difficult to enforce. Even with a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) in place, pursuing legal action against IP theft can be costly, time-consuming, and ineffective across international borders. Contracts may lack clear clauses on IP ownership, usage rights, and penalties for infringement, leaving the buyer exposed.
Lack of Design Traceability and Control
Relying on third parties to store and manage design files increases the risk of unauthorized access or distribution. Without a documented chain of custody and secure data protocols, it becomes difficult to prove original ownership of a design in case of disputes. Suppliers may also make undocumented modifications, leading to inconsistencies and potential infringement issues.
To mitigate these risks, it is essential to conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers, enforce robust legal agreements, specify strict quality requirements, and consider working with trusted partners who offer IP protection guarantees and proven quality management systems.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Extrusion Dies
Overview
Extrusion dies are precision tooling components used in manufacturing processes such as plastics, rubber, and aluminum extrusion. Due to their specialized nature, international shipping, import/export, and regulatory compliance require careful planning. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and legal transportation of extrusion dies.
Classification & HS Codes
Proper classification under the Harmonized System (HS) is critical for customs clearance and tariff determination. Extrusion dies are typically classified under:
– HS Code 8480.71: Dies for extruding metal (e.g., aluminum or steel dies).
– HS Code 8480.79: Other dies, including those for plastics or rubber extrusion.
Note: Exact codes may vary by country and material. Always verify with local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker.
Export Controls & Licensing
Certain extrusion dies may be subject to export controls if they are dual-use (civilian and military applications) or involve advanced technology:
– EAR (Export Administration Regulations – U.S.): Check Commerce Control List (CCL) for any license requirements. Most standard dies fall under EAR99 (low concern), but high-precision or proprietary designs may require review.
– ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations): Generally not applicable unless dies are designed for defense-related applications.
– Wassenaar Arrangement: Monitor for advanced tooling technologies that may be controlled for export.
Documentation Requirements
Ensure accurate and complete documentation for smooth customs processing:
– Commercial Invoice (with full description, value, and HS code)
– Packing List (detailing weight, dimensions, and quantity)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (if claiming preferential tariffs under trade agreements)
– Export Declaration (e.g., AES filing in the U.S. for shipments over $2,500)
Packaging & Handling
Extrusion dies are sensitive to shock, moisture, and corrosion:
– Use wooden crates with internal foam or custom fittings to prevent movement.
– Apply rust-inhibiting coatings or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper for metal dies.
– Clearly label packages as “Fragile,” “Handle with Care,” and “Do Not Stack.”
– Include orientation arrows to ensure proper positioning during transit.
Transportation Modes
Choose the appropriate shipping method based on urgency, cost, and destination:
– Air Freight: Recommended for high-value or time-sensitive dies. Faster but more expensive.
– Ocean Freight: Cost-effective for heavy or large dies. Use FCL (Full Container Load) to minimize handling risks.
– Ground Transport (Domestic/Regional): Ideal for local or cross-border shipments within regions like North America or the EU.
Import Duties & Taxes
Understand the destination country’s import regulations:
– Duty rates vary by HS code and country of import.
– VAT, GST, or other consumption taxes may apply.
– Some countries offer reduced tariffs for industrial tooling under specific conditions (e.g., temporary importation for repair).
Compliance with International Standards
Ensure dies meet relevant technical and safety standards where applicable:
– ISO 9001 (Quality Management) – recommended for manufacturers.
– CE Marking – required if dies are sold as part of machinery in the European Economic Area.
– Regional safety standards (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., Machinery Directive in the EU) for integrated systems.
Special Considerations
- Used Dies: May require additional documentation or face import restrictions in some countries.
- Intellectual Property (IP): Protect proprietary designs; consider non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) with logistics partners if dies contain sensitive technology.
- Insurance: Secure all-risk cargo insurance to cover loss or damage during transit.
Recommended Best Practices
- Partner with experienced freight forwarders familiar with industrial tooling.
- Conduct pre-shipment compliance reviews.
- Maintain a compliance checklist for every shipment.
- Stay updated on trade regulations through government resources (e.g., U.S. Census Bureau, EU TARIC, or local customs agencies).
By following this guide, companies can ensure efficient logistics and full compliance when shipping extrusion dies globally.
Conclusion for Sourcing Extrusion Dies
Sourcing extrusion dies is a critical step in ensuring the efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness of the extrusion process. The success of a manufacturing operation depends heavily on selecting the right die supplier who can deliver high-quality, durable, and accurately engineered dies tailored to specific material and profile requirements. Key considerations include the supplier’s technical expertise, use of advanced materials and manufacturing technologies, quality control processes, lead times, and after-sales support.
Investing in high-performance dies from reputable suppliers may involve higher initial costs but results in long-term savings through improved productivity, reduced downtime, consistent product quality, and extended die life. Additionally, maintaining strong collaboration with suppliers enables quick troubleshooting, design optimization, and innovation in response to evolving production demands.
In conclusion, a strategic and well-informed approach to sourcing extrusion dies—focused on quality, reliability, and partnership—directly contributes to operational excellence and competitive advantage in the extrusion industry.