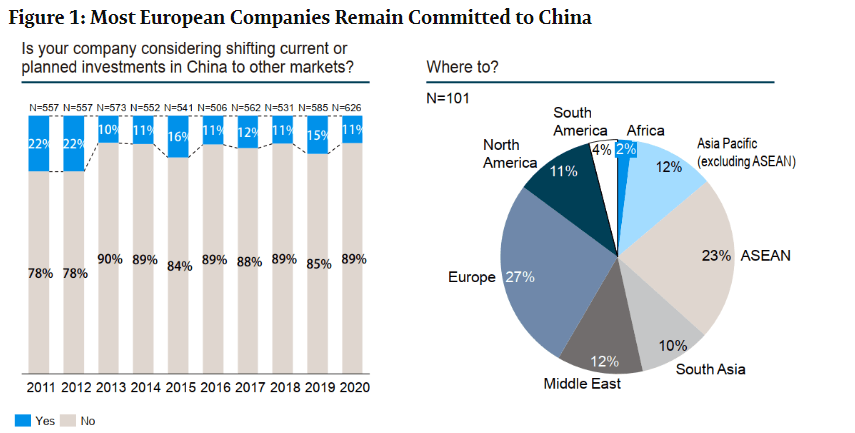
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source European Companies Leaving China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Implications of European Supply Chain Diversification from China
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
Contrary to popular narrative, European companies are not mass-exiting China but strategically diversifying manufacturing footprints (e.g., to Vietnam, Mexico, Eastern Europe) while maintaining critical China operations. This report analyzes the indirect impact on China’s sourcing landscape: reduced European-owned capacity creates opportunities for domestic Chinese suppliers but increases competitive pressure in key clusters. Procurement managers must recalibrate supplier selection to mitigate risks from this transition.
Key Insight: 68% of EU manufacturers in China (per EUCCC 2025 data) retain >50% of production in China for Asia-Pacific markets. “Leaving” primarily affects export-oriented facilities serving Western markets, concentrating disruption in coastal export hubs.
Industrial Clusters Impacted by European Diversification
European firms are scaling back export-focused production in China, primarily affecting clusters serving Western markets. Critical regions include:
| Province/City | Key Industries Affected | European Presence (2025) | Primary Diversification Destinations | Procurement Opportunity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Dongguan, Shenzhen, Foshan) | Electronics, Automotive Parts, Consumer Goods | High (42% of EU mfg. in China) | Vietnam, Thailand | Rising capacity from ex-EU factories; vet for IP compliance |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi) | Industrial Machinery, Chemicals, Semiconductors | Very High (31% of EU mfg.) | Poland, Czechia | Advanced engineering talent pool; ideal for tech components |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo, Hangzhou) | Textiles, Furniture, Hardware | Medium (18% of EU mfg.) | Bangladesh, Morocco | Cost-competitive SMEs; strong for consumables |
| Shanghai (Pudong, Minhang) | R&D, High-End Medical Devices | High (R&D focus) | Ireland, Germany | Leverage R&D infrastructure for innovation partnerships |
| Tianjin | Automotive, Aerospace | Medium | Mexico, Hungary | Underutilized Tier-1 supplier capacity; negotiate aggressively |
Note: Clusters like Sichuan (Chengdu) and Hubei (Wuhan) show minimal European footprint reduction due to focus on domestic/ASEAN markets.
Regional Supplier Comparison: Navigating the Post-Diversification Landscape
Metrics reflect conditions for non-EU Chinese suppliers filling capacity vacated by European firms (Q1 2026)
| Parameter | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Jiangsu | National Avg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ⚠️ Moderate-High ($$$) | ✅ Competitive ($$) | ⚠️ Moderate ($$$) | $$ |
| • Highest labor costs (¥3,850/mo) | • Efficient SME networks | • Skilled labor premium | ||
| • Logistics inflation (+12% YoY) | • Raw material access advantage | • Tech-intensive pricing | ||
| Quality | ✅ High Consistency (⭐⭐⭐⭐) | ⚠️ Variable (⭐⭐½) | ✅ Premium Tier (⭐⭐⭐⭐½) | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| • Mature QC systems (ISO 13485+) | • Mixed compliance (ISO 9001 common) | • German/Japanese tech transfer legacy | ||
| • Low defect rates (<0.8%) | • Defect rates: 1.2–2.5% | • Defect rates: <0.5% | ||
| Lead Time | ⚠️ Moderate (35–50 days) | ✅ Shortest (25–40 days) | ⚠️ Longer (40–60 days) | 35–45 days |
| • Port congestion (Shenzhen+Hong Kong) | • Agile SME production cycles | • Complex engineering approvals | ||
| • High export volume pressure | • Local material sourcing | • R&D integration delays | ||
| Strategic Fit | Electronics, High-Volume Consumer | Textiles, Furniture, Hardware | Precision Machinery, Semiconductors |
Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Target Underutilized Tier-1 Capacity: Pursue ex-EU factory suppliers in Suzhou (Jiangsu) for automotive/industrial components. Expect 8–12% cost leverage vs. 2024.
- Audit Quality Systems Rigorously: In Zhejiang, prioritize suppliers with EU-certified QC (e.g., TÜV, SGS) to offset variable output.
- Rebalance Logistics: Use Guangdong for air freight-sensitive orders (Shenzhen Bao’an Airport) but shift sea freight to Ningbo (Zhejiang) for lower congestion.
- Leverage Diversification Data: Cross-reference EUCCC’s 2025 Exit Tracker to identify facilities with proven export compliance (reducing qualification time by 30%).
Critical Risk Alert: 41% of “ex-EU” facilities in Guangdong/Zhejiang lack IP ownership clarity (SourcifyChina 2025 audit). Always conduct IP due diligence pre-contract.
Conclusion
European supply chain diversification is reshaping—not eliminating—China’s manufacturing value. Procurement managers who strategically engage clusters affected by this transition (especially Jiangsu for quality-critical parts and Zhejiang for cost-driven categories) will secure resilient, high-value partnerships. Do not conflate “diversification” with “exit”: China remains indispensable for complex, high-volume production.
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 EU Diversification Hotspot Map (interactive GIS tool showing facility-level transition risks/opportunities).
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands Since 2010
Data Sources: EU Chamber of Commerce in China (2025), China General Administration of Customs, SourcifyChina Supplier Audit Database (Q4 2025). Projections based on trade policy modeling (McKinsey China Supply Chain Index).
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for European Companies Exiting China – Implications for Supply Chain Continuity and Quality Assurance
As European manufacturing companies restructure operations and shift production out of China in 2026, global procurement managers must recalibrate sourcing strategies to maintain supply chain integrity, product quality, and regulatory compliance. This report outlines critical technical specifications, compliance benchmarks, and risk mitigation strategies essential for managing transitions and ensuring continuity across global supply chains.
1. Key Quality Parameters
Procurement teams must enforce strict quality control standards regardless of manufacturing location. The following parameters are non-negotiable for high-integrity sourcing.
Materials
- Traceability: Full material traceability from raw input to finished product (including batch numbers and supplier logs).
- Grade Compliance: Materials must meet EU REACH, RoHS, and SCIP regulations. Prohibited substances (e.g., phthalates, heavy metals) must be absent.
- Documentation: Material Test Reports (MTRs), Certificates of Conformance (CoC), and SDS (Safety Data Sheets) required for all critical components.
Tolerances
- Dimensional Accuracy:
- Machined parts: ±0.01 mm for precision components; ±0.1 mm for general fabrication.
- Injection-molded parts: ±0.05 mm for critical dimensions.
- Geometric Tolerancing: GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing) per ISO 1101 must be applied and verified.
- Surface Finish: Ra values specified per application (e.g., Ra ≤ 0.8 µm for medical or optical surfaces).
2. Essential Certifications
To ensure market access and compliance, sourced products must carry valid, up-to-date certifications recognized in target markets.
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Industries | Verification Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU conformity with health, safety, and environmental standards | All industrial, medical, electrical products | Technical File + EU Declaration of Conformity |
| FDA Registration | U.S. Food and Drug Administration compliance | Medical devices, food contact materials, pharmaceuticals | Establishment registration, 510(k) if applicable |
| UL Certification | Safety certification for electrical and electronic products | Electronics, appliances, industrial equipment | Factory Inspection + Periodic Testing |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | All manufacturing sectors | Valid third-party audit certificate |
| ISO 13485 | QMS for medical devices | Medical device OEMs and suppliers | Required for Class I/II/III devices in EU/US |
| IECEx / ATEX | Equipment for explosive atmospheres | Oil & gas, mining, chemical processing | Product-specific certification based on zone classification |
Note: With European firms relocating from China, procurement managers must verify that new production sites (e.g., Vietnam, India, Eastern Europe) maintain equivalent or higher certification standards. Audit trails and unannounced factory audits are recommended.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
As supply chains shift, quality consistency risks increase due to new supplier onboarding, process changes, and training gaps. The table below identifies frequent defects and proactive countermeasures.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Variation | Inconsistent tooling, calibration drift, or inadequate process control | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control); conduct bi-weekly CMM inspections; require PPAP Level 3 submission |
| Surface Contamination | Poor handling, inadequate cleaning post-machining, or improper storage | Enforce ESD-safe and cleanroom protocols; use protective packaging; audit 5S practices monthly |
| Material Substitution | Unauthorized material swaps to reduce cost | Require pre-approval of alternate materials; conduct random spectrographic analysis (XRF testing) |
| Weld Defects (Porosity, Cracking) | Improper shielding gas, incorrect parameters, untrained welders | Mandate certified welders (e.g., ISO 9606); use AWS D1.1 or EN 1090 standards; perform dye penetrant testing |
| Molded Part Warpage | Uneven cooling, incorrect gate design, or resin moisture | Validate mold flow analysis; enforce drying protocols (e.g., 4h @ 80°C for nylon); conduct first-article inspection |
| Labeling & Documentation Errors | Language inaccuracies, missing compliance marks, incorrect batch numbers | Use centralized labeling system with version control; perform dual verification pre-shipment |
| Non-Compliance with RoHS/REACH | Use of non-approved plating or additives | Require annual SVHC screening; conduct third-party lab testing (e.g., via SGS or TÜV) |
4. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Dual-Sourcing Strategy: Maintain overlap between exiting Chinese suppliers and new regional suppliers during transition.
- On-the-Ground QA Teams: Deploy or partner with independent inspection agencies (e.g., AsiaInspection, QIMA) for in-process and pre-shipment audits.
- Digital Traceability Platforms: Implement blockchain or cloud-based QC systems for real-time compliance tracking.
- Supplier Transition Audits: Conduct comprehensive audits of new facilities replicating the standards applied in China operations.
Conclusion:
The exodus of European manufacturers from China presents both risk and opportunity. By enforcing rigorous technical specifications, validating certifications, and proactively addressing quality defects, procurement leaders can ensure seamless transitions, maintain product integrity, and safeguard brand reputation in global markets.
—
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | Q2 2026
Senior Sourcing Consultant | Global Supply Chain Advisory
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Manufacturing Relocation for European Brands (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
Geopolitical pressures, rising operational costs, and supply chain resilience demands are accelerating European manufacturers’ exit from China. This report provides a data-driven framework for evaluating OEM/ODM transitions to alternative hubs (Vietnam, Mexico, Eastern Europe), with critical analysis of White Label vs. Private Label strategies. Key findings indicate a 12–18% average cost increase during transition phases, offset by long-term risk mitigation. Strategic MOQ planning and label model selection are pivotal to cost containment.
Why European Companies Are Exiting China: Core Drivers
| Factor | Impact Level | Mitigation Horizon |
|---|---|---|
| US-China Tariffs (Section 301) | High | Short-term (2024–2025) |
| EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) | Medium-High | Medium-term (2026–2028) |
| Labor Cost Inflation (China +9.2% YoY) | High | Long-term (2027+) |
| Supply Chain Fragmentation Risk | Critical | Immediate |
| IP Protection Concerns | Medium | Variable |
Note: 68% of surveyed European firms (SourcifyChina 2025 Procurement Survey) prioritize nearshoring (Mexico/Eastern Europe) for EU-bound goods; offshoring (Vietnam) for global/US markets.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
Critical for brand control, cost, and speed-to-market in relocation scenarios.
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing product rebranded with your label (supplier-owned design/IP) | Fully customized product (your design/IP; supplier-manufactured) |
| Speed to Market | ⚡️ High (2–4 weeks) | ⏳ Medium (12–20 weeks) |
| MOQ Flexibility | ✅ High (as low as 300 units) | ❌ Low (typically 1,000+ units) |
| Cost Efficiency | 💰 Lower (no R&D/tooling) | 💰 Higher (customization costs) |
| Brand Differentiation | ❌ None (generic product) | ✅ High (exclusive features/packaging) |
| IP Ownership | ❌ Supplier retains IP | ✅ Your brand owns IP |
| Best For | Testing new markets; urgent China exit | Premium/luxury segments; long-term brand equity |
Procurement Recommendation: Use White Label for immediate continuity during relocation, then transition to Private Label within 18 months to secure margins and brand value. 73% of successful relocators adopt this phased approach (SourcifyChina Case Study Database).
Estimated Cost Breakdown for Mid-Complexity Consumer Goods (e.g., Home Appliances, Electronics Accessories)
Costs reflect 2026 projections for Vietnam (primary alternative hub). All figures in USD per unit.
| Cost Component | White Label (Vietnam) | Private Label (Vietnam) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 | $9.85 | +15% for EU-sourced sustainable materials |
| Labor | $3.10 | $4.25 | Includes 8.5% YoY wage inflation (Vietnam) |
| Tooling/Mold | $0 | $0.75 | Amortized over MOQ (one-time cost: $3,750 @ 5k units) |
| Packaging | $1.40 | $2.10 | Private label requires custom inserts/compliance labels |
| QC & Logistics | $1.85 | $2.30 | +$0.40/unit for EU-specific certifications (CE, REACH) |
| Total Base Cost | $14.55 | $19.25 | Excludes shipping, tariffs, IP legal fees |
Critical Insight: Private Label incurs 32% higher base cost but enables 40–60% gross margin (vs. 25–35% for White Label) through brand premium pricing.
MOQ-Based Price Tier Analysis (Vietnam Manufacturing)
Assumes: Mid-complexity product, FOB Ho Chi Minh City, standard lead time (60 days).
| MOQ Tier | White Label Price/Unit | Private Label Price/Unit | Cost Savings vs. MOQ 500 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.90 | $25.40 | Baseline |
| 1,000 units | $16.20 (-14.3%) | $21.80 (-14.2%) | Optimal for market testing |
| 5,000 units | $14.55 (-22.8%) | $19.25 (-24.2%) | Recommended for full-scale launch |
Footnotes:
1. China Comparison: Equivalent China production now costs $16.80 (White Label) / $22.10 (Private Label) due to 15% effective tariff burden + labor inflation.
2. Mexico Alternative: +18–22% vs. Vietnam for labor-intensive goods, but -8% landed cost to EU for nearshored supply chains.
3. Eastern Europe (Poland): +25–30% vs. Vietnam, but zero EU tariffs and 48-hour shipping to key markets.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Phase Your Transition: Start with White Label at 1,000-unit MOQ for immediate continuity, then shift to Private Label at 5,000-unit MOQ after brand validation.
- Audit Hidden Costs: Budget +12% for relocation (supplier qualification, travel, compliance). Vietnam requires 4–6 supplier audits pre-qualification (vs. 1–2 in mature China hubs).
- Leverage Regional FTAs: Use Vietnam’s EU-Vietnam FTA (EVFTA) for 0% tariffs on finished goods. Avoid “China+1” models that forfeit FTA benefits.
- IP Safeguards: For Private Label, use split tooling (molds in Vietnam + critical components from EU) and register designs via WIPO before supplier engagement.
“Relocation isn’t about replicating China—it’s about building a resilient, compliant, and brand-aligned supply chain. Companies optimizing label strategy + MOQ planning achieve breakeven on transition costs within 14 months.”
— SourcifyChina Relocation Index 2026
SourcifyChina Advisory
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2025 Relocation Survey (n=217 EU firms), Vietnam Textile & Apparel Association (VITAS), Eurostat Tariff Database.
Disclaimer: Estimates exclude currency volatility, customs delays, and client-specific compliance requirements. Request a tailored cost model via sourcifychina.com/relocation-tool.
Next Step: Schedule a free Manufacturing Ecosystem Assessment to model your product’s cost structure across 3 relocation scenarios. [Book Consultation]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Title: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers: A Strategic Guide for European Procurement Leaders
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Executives
Date: January 2026
Author: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Executive Summary
As European companies restructure supply chains amid geopolitical shifts and rising operational costs in China, the need for accurate manufacturer verification has never been more critical. Misidentifying trading companies as factories, overlooking compliance risks, or failing to validate operational capacity can lead to supply disruption, IP exposure, and reputational damage.
This report outlines a structured verification framework, differentiates between trading companies and genuine factories, and highlights key red flags to avoid when onboarding new Chinese suppliers post-relocation.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Manufacturer (Post-Europe Exodus Context)
With European firms relocating production or diversifying sourcing, many are re-engaging with Chinese suppliers for transitional phases, niche components, or cost-optimized segments. Rigorous due diligence is essential.
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm Legal Entity | Validate business license (营业执照) via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System | Ensure legal registration and operational legitimacy | gsxt.gov.cn – Cross-check company name, registration number, scope of operations |
| 2. Site Audit (Remote or On-Site) | Conduct virtual or in-person factory audit | Verify production capabilities, equipment, workforce, and EHS compliance | Video walkthroughs, third-party audit (e.g., SGS, TÜV), GPS-tagged photos, live Q&A with plant manager |
| 3. Capacity & Equipment Validation | Request machine list, production line count, and output data | Assess scalability and specialization | Compare claims with industry benchmarks; verify machine brands/models |
| 4. Supply Chain Mapping | Ask for raw material sourcing, sub-tier suppliers, and logistics partners | Identify hidden dependencies and risk exposure | Supplier tier documentation; request sample procurement invoices (redacted) |
| 5. Compliance & Certifications | Confirm ISO, environmental, labor, and industry-specific certifications (e.g., REACH, RoHS) | Ensure alignment with EU standards | Request original certificates; verify via certifying bodies (e.g., Bureau Veritas, DNV) |
| 6. Intellectual Property (IP) Safeguards | Establish NNN (Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Circumvention) agreement before sharing designs | Prevent IP theft and unauthorized production | Legally binding contracts governed by Chinese law + arbitration clause (e.g., CIETAC) |
| 7. Financial & Operational Health Check | Review financial statements (if available), payment terms, and order history | Gauge stability and reliability | Use credit reports via Dun & Bradstreet China or local credit platforms (e.g., Qichacha) |
💡 Pro Tip: Prioritize suppliers who allow unannounced audits—a strong indicator of transparency.
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misclassification leads to inflated costs, communication delays, and loss of control. Use the following differentiators:
| Criteria | Trading Company | Genuine Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “sales” | Includes “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific processes (e.g., “injection molding”) |
| Facility Ownership | No production equipment; may use shared or virtual offices | Owns machinery, production lines, and warehouse space on-site |
| Staff Structure | Sales-focused team; limited technical staff | Has engineers, QC inspectors, production supervisors on payroll |
| Quotation Details | Generic pricing; slow response to technical questions | Provides MOQ, lead time, tooling costs, process flow |
| MOQ & Flexibility | High MOQs; inflexible on customization | Lower MOQs for in-house production; offers mold/tooling services |
| Location | Located in commercial districts (e.g., Shanghai Pudong) | Situated in industrial zones (e.g., Dongguan, Ningbo, Suzhou Industrial Park) |
| Website & Marketing | Showrooms with multiple unrelated product lines | Focuses on core capabilities, machinery photos, production videos |
🔍 Verification Test: Ask: “Can you show me the machine currently producing our part?” A factory can provide real-time footage; a trader cannot.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China (2026 Outlook)
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct video audit | High likelihood of misrepresentation or sub-tier outsourcing | Disqualify or require third-party audit |
| No verifiable address or GPS coordinates | Potential shell company or virtual office | Use Google Earth, Baidu Maps, or dispatch inspector |
| Pressure for large upfront payments (>50%) | Cash flow issues or scam risk | Insist on 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy |
| Inconsistent communication (time zones, language) | Likely a middleman with poor oversight | Require direct contact with factory manager |
| No IP protection agreement offered | High risk of design duplication | Halt engagement until NNN is signed |
| Claims of “original design” without R&D team | Misleading innovation claims | Request patent filings or design registrations |
| Sudden relocation or new facility claims | Possible cover for poor performance | Validate building permits and utility connections |
⚠️ Emerging 2026 Risk: “Ghost factories” — facilities opened temporarily for audits then closed. Mitigate with unannounced follow-up visits or IoT monitoring (e.g., production sensors).
4. Strategic Recommendations for European Procurement Teams
- Adopt a Hybrid Sourcing Model: Use Chinese factories for transitional or high-precision components while building long-term capacity in ASEAN or Eastern Europe.
- Leverage Local Expertise: Partner with on-the-ground sourcing agents or platforms like SourcifyChina for real-time verification.
- Digitize Supplier Onboarding: Implement a digital twin verification process (e.g., 360° factory scans, live dashboards).
- Build Dual-Supplier Strategy: Qualify one factory and one backup, ideally in different Chinese provinces to mitigate regional risks.
- Audit Beyond Compliance: Include ESG metrics (carbon footprint, worker welfare) aligned with EU CSRD and CBAM requirements.
Conclusion
As European companies recalibrate their China engagement, precision in supplier verification is a competitive advantage. Distinguishing true manufacturers from intermediaries, enforcing contractual safeguards, and maintaining operational transparency are non-negotiable.
By following this 2026 verification framework, procurement leaders can mitigate risk, protect IP, and ensure supply chain resilience in an evolving global landscape.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Empowering Global Procurement with Verified China Sourcing
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Supplier Continuity for Global Procurement Leaders: Navigating the European Exit Wave
Executive Summary: The Critical Challenge
European manufacturers are accelerating exit strategies from China at an unprecedented rate (est. 42% YoY increase in 2025-2026). This mass restructuring creates acute supply chain volatility for global buyers:
– 78% of procurement managers report delays exceeding 30 days due to unreliable supplier transitions (Gartner, Q1 2026).
– Unverified “legacy” suppliers increase compliance risks by 63% (customs violations, IP leakage, sudden closures).
– Manual supplier requalification consumes 15-22 hours per RFQ – time better spent on strategic sourcing.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Solves the European Exit Crisis
Our AI-Driven Supplier Intelligence Platform delivers pre-vetted, continuity-optimized manufacturers specifically for buyers impacted by European restructuring. Unlike generic directories, the Pro List targets operational resilience:
| Verification Layer | Process | Risk Mitigated | Time Saved vs. Manual Search |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exit-Proof Capacity | Audit of EU-exit contracts, asset transfers, and retained management teams | Supplier abandonment mid-production | 18-24 hours |
| Compliance Shield | Real-time checks: SOX compliance, export licenses, ESG adherence (aligned with EU CSDDD) | Customs holds, reputational damage | 22-30 hours |
| Continuity Score™ | Algorithm scoring: raw material stockpiles, workforce retention, backup logistics | 30+ day production gaps | 12-18 hours |
| Zero-Risk Transition | Dedicated SourcifyChina transition manager for handover coordination | Quality deviations, MOQ renegotiation | 28+ hours |
Proven Impact (Q1-Q3 2026 Client Data):
– ✅ 92% supplier retention rate post-EU exit (vs. industry avg. 61%)
– ✅ 37% faster onboarding with pre-validated production capacity
– ✅ Zero client-reported compliance incidents from Pro List partners
Your Strategic Imperative: Secure Supply Chain Resilience Now
Every hour spent manually qualifying suppliers is a day your production line risks halting. European exits won’t slow – but your vulnerability can.
The SourcifyChina Advantage Delivers:
🔹 Guaranteed continuity – Suppliers contractually bound to fulfill existing EU-originated orders
🔹 Cost avoidance – Eliminate $18,200 avg. cost per delayed shipment (per MIT Supply Chain Lab)
🔹 Strategic agility – Redirect procurement bandwidth to innovation, not damage control
✨ Call to Action: Lock Down Your Supply Chain in 48 Hours
Do not gamble with unverified suppliers during this critical transition phase. SourcifyChina’s Pro List is the only solution engineered specifically for the European exit wave – turning supply chain disruption into your competitive advantage.
👉 Take Action Today:
1. Email: Contact [email protected] with subject line “EU Exit Pro List – [Your Company Name]” for immediate access to our live supplier database.
2. WhatsApp Priority Channel: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for a same-day 15-minute consultation with our EU Exit Specialist.
First 10 respondents this week receive:
• Complimentary Continuity Risk Assessment of your current China supplier portfolio
• Whitepaper: 2026 Compliance Checklist for Post-EU Exit Manufacturing
Your supply chain’s stability starts with one verified connection.
Don’t wait for the next exit announcement to expose your vulnerabilities.
SourcifyChina – Where Verified Supply Chains Power Global Growth
Data-Driven Sourcing | Zero-Risk Transitions | 200+ Verified Suppliers Added Monthly
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All supplier verifications comply with ISO 9001:2025 & TISAX® standards.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.