The global epoxy resin market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across industrial manufacturing, construction, and automotive sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global epoxy resin market size was valued at USD 9.93 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the increasing need for high-performance, durable repair materials—particularly epoxy putties capable of bonding, sealing, and restoring metal components under extreme conditions. As industries prioritize longevity and cost-efficiency, demand for advanced epoxy putties tailored for metal repair has surged. From industrial machinery to marine applications, manufacturers are turning to specialized formulations that offer resistance to corrosion, temperature extremes, and mechanical stress. Against this backdrop, identifying the top-performing epoxy putty manufacturers becomes critical for professionals seeking reliable, data-backed solutions in a rapidly evolving market.
Top 7 Epoxy Putty For Metal Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
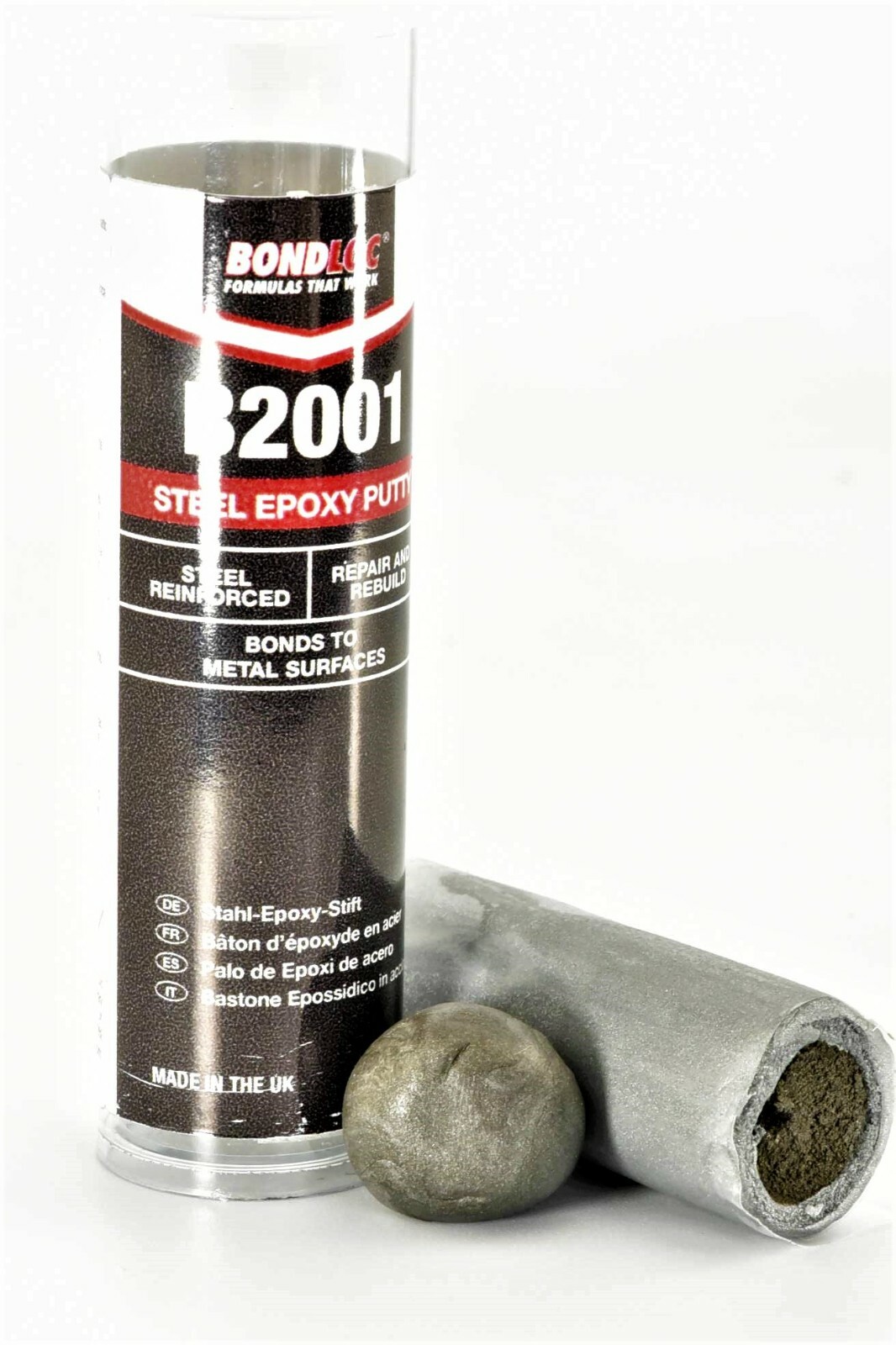
#1 Epoxy Putty Sticks
Domain Est. 2011
Website: unitedresin.com
Key Highlights: United Resin offers fast-setting, high-strength epoxy putty sticks for all materials. NSN-listed, RoHS compliant, and water/oil resistant….
#2 J
Domain Est. 1995
Website: jbweld.com
Key Highlights: Epoxy Putty – 1 oz. View Product. Compare. KwikWood™ Quick Look. KwikWood™ Epoxy Putty – 2 oz. View Product. Compare. WaterWeld™ Quick Look. WaterWeld™ Epoxy ……
#3 Epoxy Putty
Domain Est. 1996
Website: oatey.com
Key Highlights: Oatey and Hercules epoxy putties tackle a wide range of repair tasks with ease and precision, molding like putty and hardening like steel….
#4 Metal Epoxy Putty
Domain Est. 1997
Website: uccoatings.com
Key Highlights: Metal epoxy putty is ideal for repairing or filling metal components, castings, tanks, and magnetic fixtures. This steel-filled epoxy adhesive is preferred ……
#5 Loctite Epoxy Putty
Domain Est. 1999
Website: loctiteproducts.com
Key Highlights: This two-part adhesive putty combines to produce a hard, tough, permanent and waterproof bond and seal that is potable water safe. Quick and easy to use, the ……
#6 NuMetal
Domain Est. 2005
Website: kbs-coatings.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 (72) NuMetal Epoxy Putty is an easy-to-use, two-part putty ……
#7 Devcon® Plastic Steel® Putty (A)
Domain Est. 2017
Website: itwperformancepolymers.com
Key Highlights: Plastic Steel is the original metal-filled epoxy putty used for hundreds of routine maintenance, production, and tooling applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Epoxy Putty For Metal

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Epoxy Putty for Metal
The global market for epoxy putty for metal is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by expanding industrial applications, technological advancements, and increased demand across repair and maintenance sectors. Several key trends are expected to shape the market landscape in the coming years.
-
Rising Demand in Industrial Maintenance and Repair
Epoxy putty for metal continues to gain traction as a go-to solution for rapid, durable repairs in industrial settings. By 2026, growing emphasis on minimizing equipment downtime in manufacturing, oil & gas, and marine industries will boost demand. Its ability to bond with metal surfaces, resist water, chemicals, and high temperatures makes it ideal for sealing, filling, and structural repairs without requiring welding or specialized tools. -
Growth in DIY and Consumer Applications
The do-it-yourself (DIY) trend is expanding globally, especially in North America and Europe. Homeowners and hobbyists increasingly use epoxy putty for metal in plumbing fixes, automotive repairs, and household maintenance. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to launch user-friendly, pre-measured, and color-coded putties tailored for non-professionals, further accelerating consumer adoption. -
Technological Innovations and Product Differentiation
Advancements in epoxy formulations—such as faster curing times, improved adhesion to difficult substrates, and enhanced temperature resistance—are key drivers. By 2026, we anticipate greater market segmentation with specialty putties for extreme environments (e.g., underwater curing, cryogenic applications). Additionally, environmentally friendly, low-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations will gain preference amid tightening environmental regulations. -
Expansion in Automotive and Marine Sectors
The automotive aftermarket is a major consumer of epoxy putty for metal, particularly for rust repair, dent filling, and custom fabrication. Similarly, the marine industry relies heavily on waterproof and corrosion-resistant putties for hull and engine repairs. As both sectors grow, especially in emerging economies, demand for high-performance metal epoxy putty will rise significantly by 2026. -
Regional Market Developments
Asia-Pacific, led by China, India, and Southeast Asia, is expected to register the highest growth due to rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and a burgeoning automotive sector. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand, supported by mature industrial bases and regulatory support for sustainable repair solutions. Latin America and the Middle East will also see moderate growth, driven by oil & gas and construction activities. -
Competitive Landscape and Brand Positioning
By 2026, competition among key players such as Loctite, J-B Weld, Devcon, and ITW Performance Polymers is expected to intensify. Companies will focus on product innovation, distribution expansion, and strategic partnerships with hardware retailers and e-commerce platforms. Private label and generic brands may also gain market share, especially in price-sensitive regions.
In conclusion, the epoxy putty for metal market in 2026 will be characterized by innovation, diversification, and increasing accessibility across both industrial and consumer segments. As sustainability and performance become central to purchasing decisions, manufacturers who invest in advanced, eco-conscious formulations are likely to lead the market.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Epoxy Putty for Metal (Quality & IP)
Sourcing the right epoxy putty for metal applications requires careful consideration to ensure performance, longevity, and legal compliance. Overlooking key factors can lead to product failure, safety risks, or intellectual property (IP) issues. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Cost Over Performance Specifications
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting epoxy putty based solely on price. Low-cost options often use inferior resins or fillers, leading to:
- Poor adhesion to metal substrates
- Reduced tensile and shear strength
- Inadequate resistance to temperature, moisture, or chemicals
- Premature cracking or delamination
Always verify technical data sheets (TDS) and ensure the product meets required standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) for your specific use case—especially in industrial, marine, or structural applications.
2. Ignoring Cure Time and Working Window
Not all epoxy putties cure at the same rate. Choosing a product without considering environmental conditions (temperature, humidity) or application complexity can result in:
- Incomplete curing in cold environments
- Insufficient working time for proper shaping or mixing
- Thermal stress from exothermic reactions in large repairs
Ensure the putty’s stated cure profile aligns with your operational timeline and ambient conditions.
3. Overlooking Environmental and Chemical Resistance
Epoxy putties vary widely in resistance to:
- Water and salt spray (critical for marine or outdoor use)
- UV exposure (some formulations degrade or discolor)
- Oils, solvents, acids, or alkalis
Using a general-purpose putty in a chemically aggressive environment leads to rapid degradation. Confirm compatibility with the specific substances the repair will encounter.
4. Assuming All “Metal-Filled” Putties Are Equal
Many epoxy putties are labeled as “metal-repair” or “metal-filled,” but the type and percentage of metal content (e.g., steel, aluminum, bronze) affect:
- Electrical conductivity
- Thermal expansion matching
- Machinability and sandability
- Appearance post-cure
Verify the filler composition and its relevance to your application—especially if conductivity or matching thermal properties is essential.
5. Neglecting Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Some industrial or consumer applications require compliance with regulations such as:
- REACH, RoHS (especially in EU markets)
- FDA approval for food-contact surfaces
- Non-toxic formulations for potable water systems
Failure to meet these can result in product recalls or legal liability. Always request compliance documentation from suppliers.
6. Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
When sourcing epoxy putty formulations—especially for private labeling, reverse engineering, or OEM integration—be cautious of:
- Patent infringement: Many high-performance formulations are protected by patents (e.g., on resin chemistry, hardener systems, or filler blends)
- Trademark violations: Repackaging or rebranding without authorization
- Trade secret exposure: Sharing proprietary formulations with untrusted suppliers
Conduct a patent landscape search and work with legal counsel to ensure your sourcing strategy doesn’t expose your business to IP litigation.
7. Relying on Unverified Supplier Claims
Some suppliers exaggerate performance claims or provide inconsistent batch quality. Pitfalls include:
- Inconsistent mix ratios or cure behavior across batches
- Misleading strength or temperature resistance data
- Lack of traceability or quality control certifications (e.g., ISO 9001)
Always request samples, conduct in-house testing, and prioritize suppliers with transparent quality assurance practices.
8. Failing to Consider Long-Term Availability and Supply Chain Stability
Even a high-quality putty is useless if the supplier discontinues it or faces supply disruptions. Assess:
- Supplier reliability and production capacity
- Shelf life and storage requirements
- Availability of technical support and batch traceability
Choose partners with a stable track record, especially for mission-critical or long-term maintenance programs.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively, you can ensure the epoxy putty you source delivers reliable performance on metal substrates while minimizing legal and operational risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Epoxy Putty for Metal
Product Overview
Epoxy Putty for Metal is a two-part adhesive compound composed of a resin and hardener, typically supplied in a dual-barrel cartridge or as pre-measured sticks. When mixed, it forms a durable, high-strength bond suitable for sealing, repairing, and rebuilding metal surfaces. It cures at room temperature and offers resistance to water, chemicals, and temperature extremes.
Regulatory Classification
Hazard Classification (GHS)
Epoxy Putty for Metal is generally classified under the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) as:
– Skin Irritation (Category 2) – May cause skin irritation.
– Serious Eye Damage/Eye Irritation (Category 2A) – May cause serious eye irritation.
– Skin Sensitization (Category 1) – May cause an allergic skin reaction.
– Hazardous to the Aquatic Environment (Acute, Category 3) – Toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effects.
Note: Specific classifications may vary by formulation. Always refer to the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) provided by the manufacturer.
UN Number and Transport Classification
- UN Number: UN 3082 (if classified as environmentally hazardous)
- Proper Shipping Name: ENVIRONMENTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, LIQUID, N.O.S. (Non-Other-Specified)
- Hazard Class: 9 (Miscellaneous Dangerous Substances and Articles)
- Packing Group: III (Low danger)
- Marine Pollutant: Yes (typically marked on packaging)
Note: Some epoxy putties may not require UN classification if they are non-liquid and not classified as hazardous; confirm with SDS and local regulations.
Safety Data Sheet (SDS) Requirements
- Maintain a current SDS (in compliance with local regulations such as OSHA HazCom in the U.S., CLP in the EU).
- SDS must include:
- Product identifier and manufacturer details
- Hazard identification
- Composition/information on ingredients
- First-aid and firefighting measures
- Accidental release measures
- Handling and storage instructions
- Exposure controls and PPE recommendations
- Physical and chemical properties
- Stability and reactivity
- Toxicological and ecological information
- Disposal considerations
- Transport information
- Regulatory information
Handling and Storage
Handling
- Use in well-ventilated areas.
- Avoid skin and eye contact; wear nitrile gloves and safety goggles.
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke when using the product.
- Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
Storage
- Store in a cool, dry place between 15°C and 25°C (59°F – 77°F).
- Keep containers tightly closed and protected from moisture.
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight or freezing temperatures.
- Shelf life is typically 12–24 months; check manufacturer’s label for expiration date.
Packaging and Labeling
Primary Packaging
- Dual-compartment cartridges, foil-wrapped sticks, or blister packs.
- Must be leak-proof and protect from moisture and contamination.
Labeling Requirements
- Product name and identifier
- Supplier/contact information
- GHS pictograms (e.g., exclamation mark, environment)
- Signal word: “Warning” or “Danger” as appropriate
- Hazard statements (e.g., H315, H319, H317)
- Precautionary statements (e.g., P261, P280, P305+P351+P338)
- First aid instructions
- “Keep out of reach of children”
- “Environmentally hazardous substance”
Ensure labels comply with local regulations (e.g., OSHA, CLP, WHMIS).
Transportation
Land (Road/Rail)
- Classified under ADR/RID (Europe) or 49 CFR (USA) as Class 9, UN 3082 if environmentally hazardous.
- Use packaging meeting Packing Group III standards.
- Transport documents must include proper shipping name, UN number, hazard class, and quantity.
- Vehicles may require placards if transporting large quantities.
Air
- IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations: Class 9, UN 3082.
- Limited quantity exemptions may apply (e.g., ≤1 L per inner package).
- Packages must pass drop and leak tests.
- Shipper must be trained and certified per IATA requirements.
Sea
- IMDG Code: Class 9, UN 3082, Marine Pollutant.
- Packages must be marked with marine pollutant symbol.
- Stowage and segregation per IMDG guidelines.
Import/Export Compliance
Key Regulatory Frameworks
- USA: EPA TSCA (Toxic Substances Control Act), DOT 49 CFR
- EU: REACH, CLP Regulation, Biocidal Products Regulation (if applicable)
- Canada: WHMIS 2015, TDG Regulations
- UK: UK REACH, CHIP/CLP (post-Brexit)
- Australia: AICIS, ADG Code
Export Documentation
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
- Certificate of Conformity (if required)
- Dangerous Goods Note (for hazardous shipments)
Verify destination country regulations; some may require product registration or labeling in local language.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
Waste Disposal
- Uncured epoxy putty: Treat as hazardous waste due to reactivity and toxicity.
- Cured putty: Generally non-hazardous; dispose of as solid waste according to local regulations.
- Contaminated packaging: Dispose of as hazardous waste.
- Follow local, state, and federal waste disposal regulations (e.g., EPA, EEA).
Spill Response
- Contain spill with absorbent materials (e.g., sand, vermiculite).
- Collect material and place in labeled, sealed container for disposal.
- Avoid washing into drains or waterways.
- PPE must be worn during cleanup.
Worker Safety and Training
Required Training
- GHS hazard communication
- Safe handling and mixing procedures
- Use of PPE
- Spill response and emergency procedures
- Waste disposal protocols
PPE Recommendations
- Nitrile gloves
- Safety goggles or face shield
- Respiratory protection (if ventilation is inadequate)
- Protective clothing (apron, lab coat)
Regulatory Updates and Audits
- Regularly review SDS and product compliance (annually or after formulation changes).
- Monitor changes in regulations (e.g., EPA, ECHA, OSHA).
- Conduct internal audits of labeling, storage, and transport practices.
Summary of Key Compliance Actions
- Obtain and maintain up-to-date SDS.
- Classify product correctly per GHS and transport regulations.
- Label all containers and shipments appropriately.
- Train personnel in safe handling and emergency response.
- Use compliant packaging for transport.
- Maintain proper shipping documentation.
- Dispose of waste in accordance with environmental regulations.
Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications and regulatory experts to ensure full compliance in your region.
In conclusion, sourcing epoxy putty for metal repair and bonding requires careful consideration of factors such as bonding strength, temperature and chemical resistance, cure time, ease of application, and compatibility with the specific metal type. Whether for industrial maintenance, DIY projects, or emergency repairs, selecting a high-quality epoxy putty specifically formulated for metal ensures durable, long-lasting results. It is essential to evaluate reputable suppliers, check product specifications, and prioritize safety and performance standards. By choosing the right epoxy putty from a reliable source, users can achieve strong, waterproof, and corrosion-resistant repairs that extend the life of metal components and reduce downtime or replacement costs.