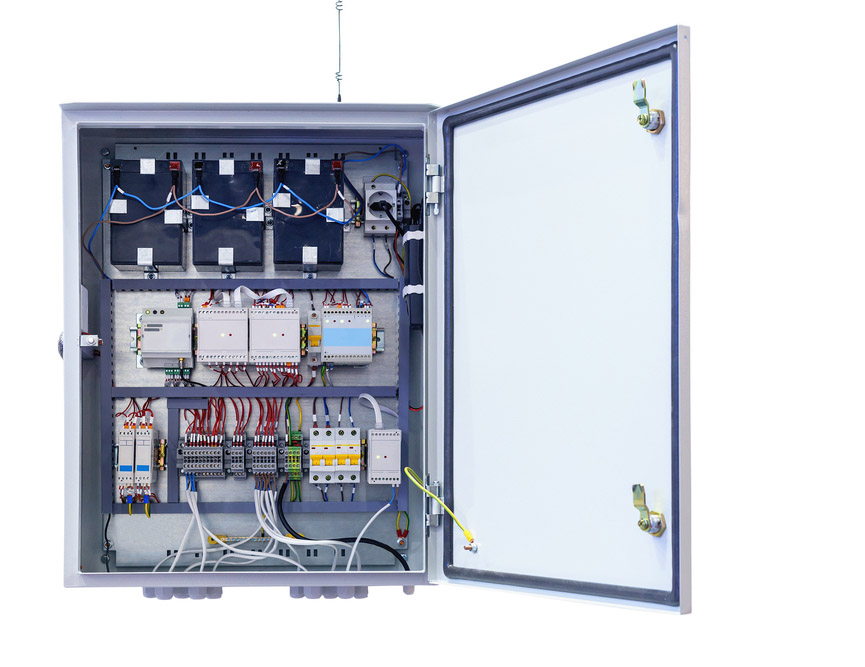
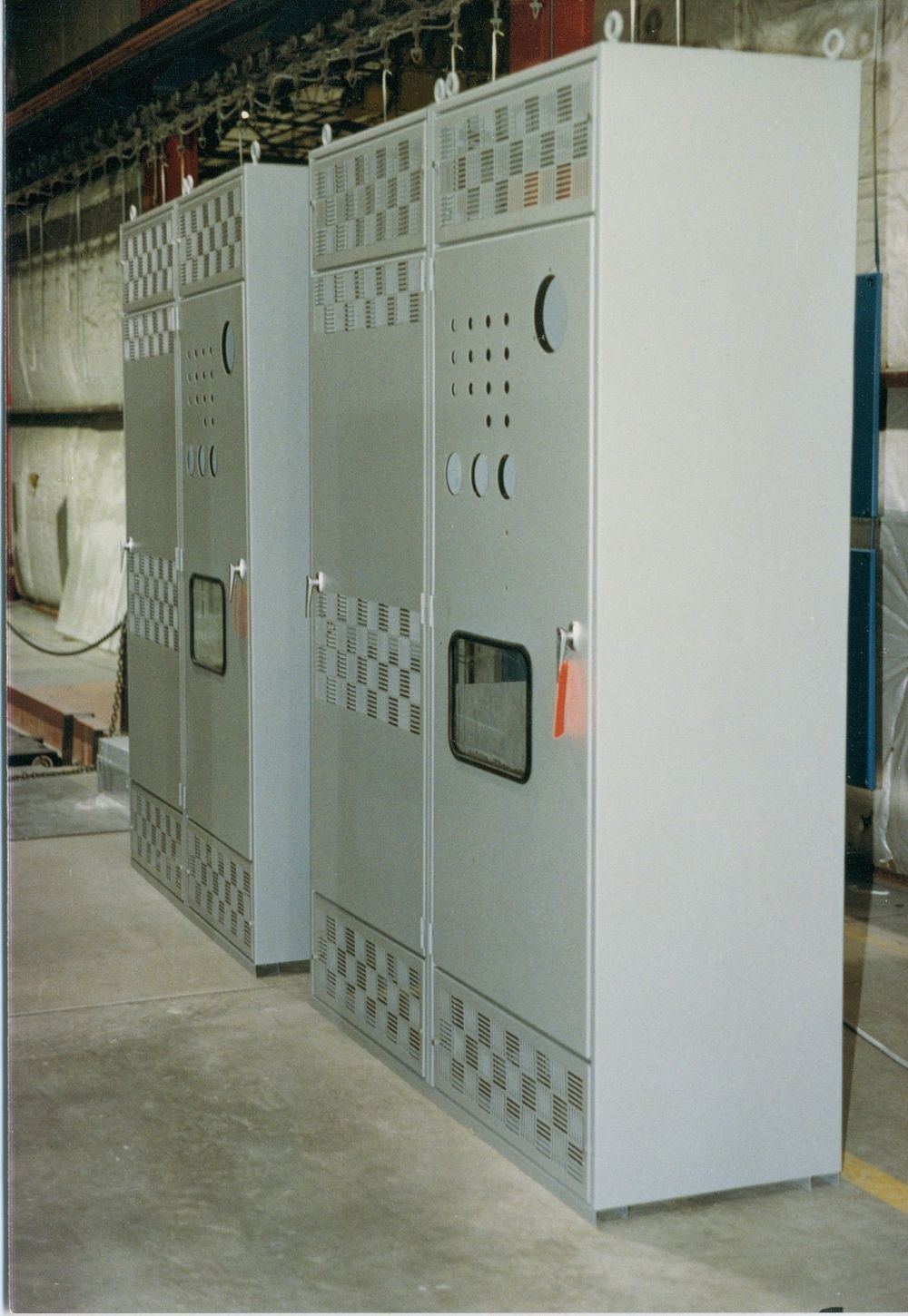
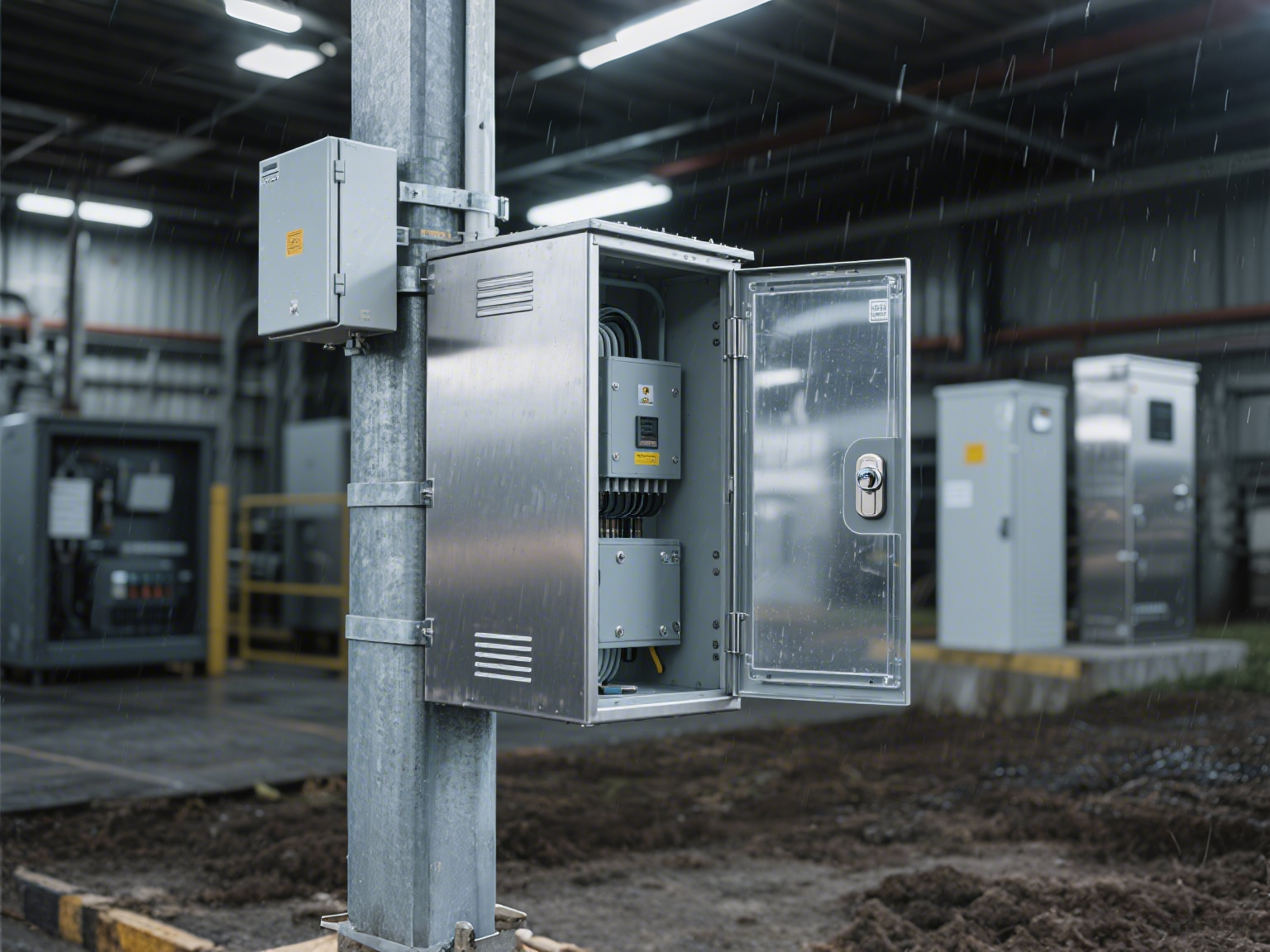
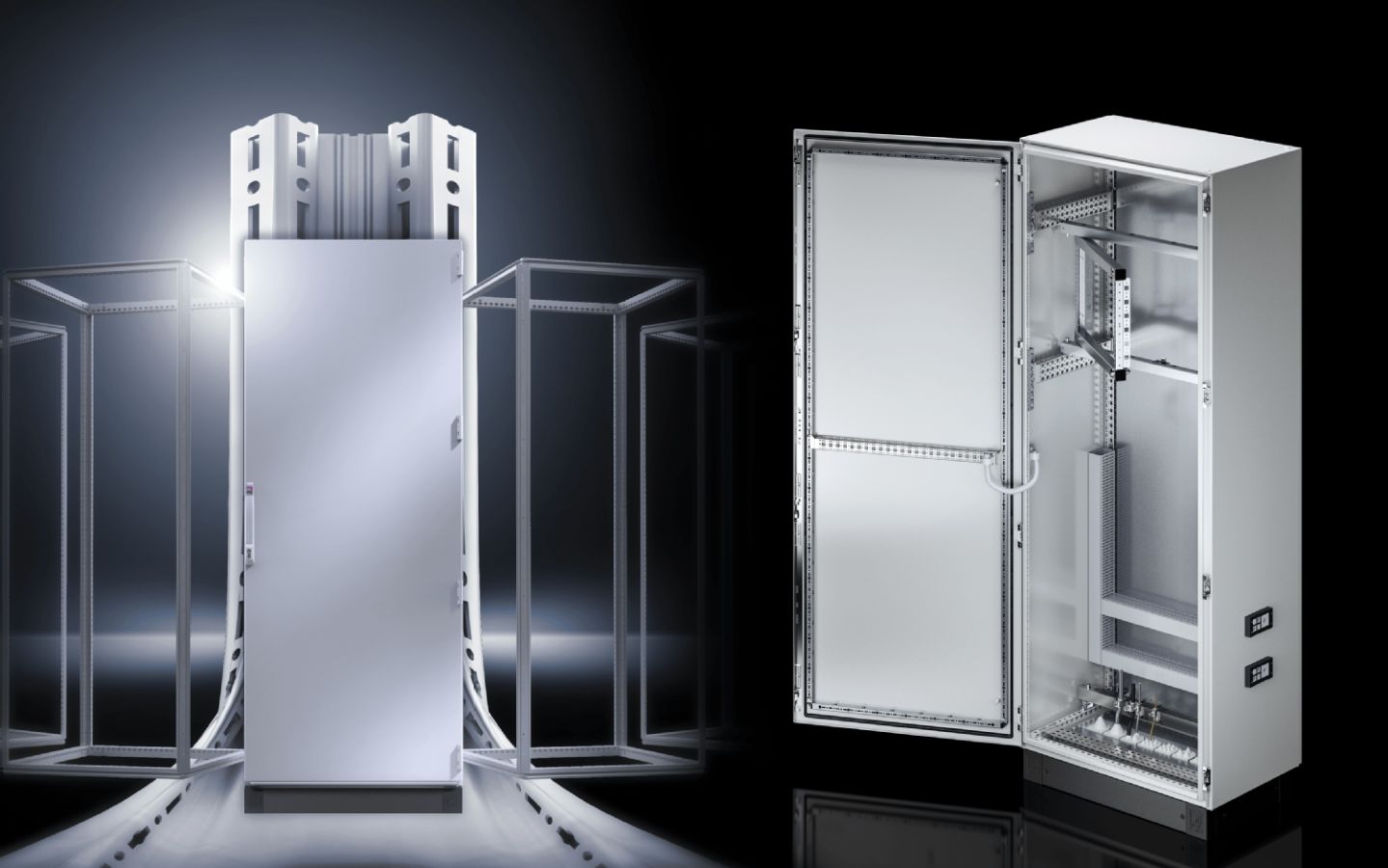
The global electrical enclosures market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industrial automation, energy, telecommunications, and infrastructure sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 14.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. Increasing investments in smart manufacturing, coupled with the need for durable protection of sensitive electrical components, are key catalysts for this growth. Additionally, stringent safety regulations and the proliferation of IoT-enabled devices are escalating the need for robust, application-specific enclosures. As industries prioritize reliability and compliance, the demand for innovative enclosure solutions has elevated the prominence of manufacturers specializing in tailored electrical protection systems. This evolving landscape underscores the importance of identifying the top players who are shaping the future of electrical enclosure applications worldwide.
Top 10 Electrical Enclosure Applications Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 NEMA Enclosures
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nemaenclosures.com
Key Highlights: Nema Enclosures manufactures industrial NEMA enclosures with powder-coated carbon steel, 304 stainless steel, 316 stainless steel, or 5052 aluminum….
#2 Wiegmann
Domain Est. 1995
Website: hubbell.com
Key Highlights: Wiegmann manufactures innovative customizable steel and nonmetallic electrical enclosures for OEM, commercial and MRO markets. This historic brand is part ……
#3 Custom Electrical Enclosure
Domain Est. 1998
Website: dalsinind.com
Key Highlights: Dalsin Industries is an ISO 9001:2015- and 14001:2015-certified manufacturer of electrical enclosures or cabinets for demanding applications….
#4 Electrical Enclosures
Domain Est. 2001
Website: nvent.com
Key Highlights: nVent HOFFMAN is a leading designer and manufacturer of systems to safely and reliably protect the electronic controls and mission critical electrical systems….
#5 EXM Manufacturing
Domain Est. 2007
Website: exmweb.com
Key Highlights: EXM Manufacturing Ltd, based in Canada, USA, and China, is a top-tier electrical enclosures manufacturer: Wallmount, Free standing, Pull Box….
#6 Rittal
Website: rittal.com
Key Highlights: Innovative solutions for industrial applications and IT infrastructure, from versatile electrical enclosures and server racks to climate control, ……
#7 Enclosures
Domain Est. 1994
Website: nema.org
Key Highlights: An electrical enclosure is a cabinet or box that protects electrical or electronic equipment and prevents electrical shock….
#8 AdaletEnclosures
Domain Est. 1996
Website: adalet.com
Key Highlights: Celebrating almost 100 years in business, Adalet has been an industry leader in the development and manufacturing of enclosure systems and cable accessories….
#9 Saginaw Control and Engineering
Domain Est. 1997
Website: saginawcontrol.com
Key Highlights: Saginaw Control & Engineering now offers vortex cooling for your enclosure cooling needs! A vortex cooler uses compressed air to increase your cooling capacity ……
#10 Hoffman
Website: hoffman-enclosures.com
Key Highlights: Explore Hoffman Electrical Enclosures for high-quality, customizable solutions designed to safeguard your electrical equipment in any setting….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Electrical Enclosure Applications

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Electrical Enclosure Applications
The global electrical enclosure market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving industry standards, and increasing demand across key end-use sectors. Electrical enclosures—critical components that protect sensitive electrical equipment from environmental factors and ensure operational safety—are adapting to meet the needs of smarter, more connected, and sustainable infrastructure. Below are the major market trends shaping electrical enclosure applications in 2026:
-
Growth in Smart Infrastructure and Industrial Automation
The expansion of smart cities, Industry 4.0, and IoT-enabled manufacturing is fueling demand for intelligent electrical enclosures. By 2026, enclosures are increasingly integrated with sensors, remote monitoring systems, and thermal management solutions to support real-time data analytics and predictive maintenance. This trend is particularly evident in sectors such as manufacturing, energy, and transportation, where uptime and operational efficiency are paramount. -
Rising Adoption of Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Materials
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt recyclable and low-carbon materials in enclosure production. Polycarbonate, recycled aluminum, and bio-based composites are gaining traction as alternatives to traditional materials. Enclosures designed for energy efficiency—such as those with enhanced thermal insulation and passive cooling—are also becoming standard, especially in data centers and renewable energy installations. -
Expansion in Renewable Energy and EV Charging Infrastructure
The global shift toward clean energy is significantly impacting enclosure demand. Solar farms, wind turbines, and electric vehicle (EV) charging stations require rugged, weather-resistant enclosures capable of withstanding harsh environments. By 2026, the EV charging market alone is expected to be a major growth driver, with enclosures needed for both public and private charging stations. These enclosures must meet stringent safety standards while supporting fast-charging capabilities and network connectivity. -
Increased Focus on Cybersecurity and Physical Protection
As electrical systems become more connected, the risk of cyber-physical threats grows. In response, electrical enclosures in 2026 are being designed with enhanced security features, including tamper-proof locks, intrusion detection, and electromagnetic shielding. This trend is especially critical in critical infrastructure sectors such as utilities, defense, and telecommunications. -
Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Localization
Asia-Pacific remains the fastest-growing region for electrical enclosures, led by industrialization in India, Vietnam, and Indonesia. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are focusing on retrofitting aging infrastructure and adopting modular, pre-fabricated enclosure solutions. Geopolitical factors and supply chain resilience concerns are also encouraging localization of production, reducing dependency on global supply chains and shortening delivery times. -
Advancements in Customization and Modular Design
End users increasingly demand customizable enclosure solutions that can be quickly adapted for specific applications. Modular enclosures allow for scalability and easier upgrades, particularly in dynamic environments like data centers and smart grids. 3D printing and digital design tools are enabling faster prototyping and cost-effective customization, accelerating time-to-market. -
Regulatory Compliance and Standardization
Stringent safety and environmental regulations—such as IEC 61439, NEMA, and IP ratings—are shaping product development. By 2026, compliance with global standards is not only a legal requirement but also a competitive advantage. Manufacturers are investing in testing and certification to ensure their enclosures meet diverse regional requirements.
In conclusion, the 2026 landscape for electrical enclosure applications reflects a convergence of digitalization, sustainability, and resilience. As industries continue to evolve, electrical enclosures are transitioning from passive protective housings to active components of intelligent, secure, and efficient electrical systems. Companies that embrace innovation, agility, and sustainability will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this dynamic market.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Electrical Enclosure Applications (Quality, IP)
Inadequate IP Rating Verification
One of the most frequent mistakes is assuming an enclosure’s stated IP (Ingress Protection) rating without verification. Suppliers may overstate ratings or provide enclosures tested under ideal conditions that don’t reflect real-world environments. Sourcing enclosures without third-party certification or test reports can lead to failures in dust or moisture resistance, compromising equipment safety and reliability.
Poor Material Quality and Thickness
Low-cost enclosures often use substandard materials—such as thin-gauge steel, low-grade plastics, or insufficient corrosion protection. This compromises structural integrity, electromagnetic shielding, and long-term durability, especially in harsh environments. Buyers may overlook material specifications, leading to premature degradation, warping, or failure under thermal or mechanical stress.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances
Enclosures with poor dimensional accuracy can cause misalignment of doors, gaskets, and mounting hardware. This directly impacts the IP rating, as gaps or uneven seals allow dust and water ingress. Sourcing from manufacturers without strict quality control often results in inconsistent units, even within the same batch.
Substandard Sealing Components
The gasket or sealing system is critical to maintaining IP integrity. However, many sourced enclosures use low-quality rubber or foam seals that degrade quickly due to UV exposure, temperature fluctuations, or chemical contact. Overlooking seal material compatibility and longevity undermines the enclosure’s environmental protection.
Lack of Compliance Documentation
Sourcing enclosures without proper certification (e.g., UL, CE, IEC) or traceability documentation increases regulatory and safety risks. Non-compliant enclosures may fail safety inspections or void insurance, especially in industrial or outdoor applications requiring adherence to international standards.
Insufficient UV and Corrosion Resistance
For outdoor use, enclosures must resist UV radiation and corrosion. Sourcing unpainted or poorly coated metal enclosures—or non-UV-stabilized plastics—leads to cracking, fading, and rust, compromising both function and appearance. This is often overlooked in cost-driven procurement decisions.
Overlooking Internal Component Compatibility
The enclosure must accommodate internal components with proper mounting options, ventilation, and cable entry points. Sourcing enclosures without considering internal layout or heat dissipation needs can result in overcrowding, overheating, or difficult maintenance access.
Failure to Validate Real-World Performance
Lab-tested IP ratings don’t always reflect field conditions. Enclosures may pass static tests but fail under dynamic conditions like water spray, vibration, or thermal cycling. Sourcing without pilot testing or field validation increases the risk of in-service failures.
Ignoring Supplier Reliability and Support
Choosing suppliers based solely on price without assessing their track record, technical support, or scalability can backfire. Poor after-sales service, long lead times, or inconsistent quality disrupt project timelines and increase total cost of ownership.
Incomplete Customization Oversight
Custom enclosures (e.g., special cutouts, finishes, or labeling) require precise specifications. Miscommunication or lack of detailed drawings during sourcing leads to incorrect modifications, rework, or non-functional units upon delivery.
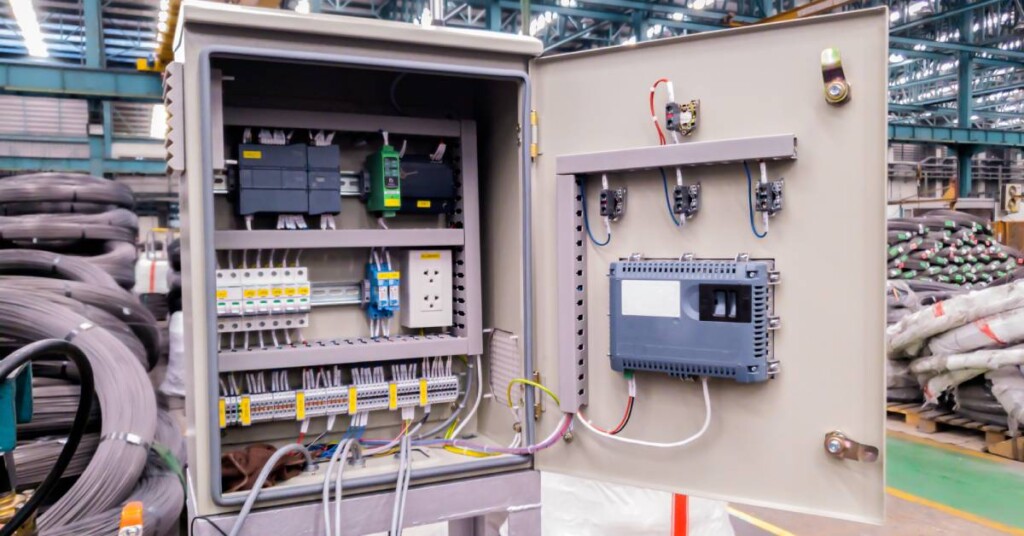

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Electrical Enclosure Applications
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the specification, procurement, installation, and maintenance of electrical enclosures. Adhering to these standards ensures safety, reliability, and regulatory acceptance across global markets.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Electrical enclosures must comply with a range of international and regional standards depending on their application and location. Key certifications include:
- UL 50/50E (USA): Standard for Enclosures for Electrical Equipment, covering non-hazardous environments.
- NEMA Enclosure Types (North America): Defines protection against environmental conditions (e.g., NEMA 4X for watertight, corrosion-resistant enclosures).
- IEC 60529 (International): Ingress Protection (IP) ratings (e.g., IP65, IP66) specifying dust and water resistance.
- ATEX/IECEx (Europe/Global): Required for enclosures used in explosive atmospheres; mandates design, testing, and certification for hazardous locations.
- RoHS and REACH (EU): Restrict hazardous substances in electrical equipment and ensure chemical safety.
- CE Marking: Mandatory for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental standards.
Ensure all enclosures bear appropriate certification marks and are accompanied by technical documentation (e.g., Declaration of Conformity, test reports).
Material Selection and Environmental Suitability
Choose enclosure materials based on the operating environment and required durability:
- Metal Enclosures (Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Carbon Steel): Ideal for industrial settings requiring high mechanical strength and EMI shielding. Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance.
- Polycarbonate and ABS (Plastic): Suitable for indoor or light-duty outdoor use; lightweight and resistant to corrosion but less impact-resistant than metal.
- Fiberglass (GRP): Excellent for corrosive environments (e.g., chemical plants, wastewater treatment) and non-conductive applications.
Match the material to environmental factors such as UV exposure, temperature extremes, humidity, and chemical presence.
Ingress Protection (IP) and NEMA Ratings
Select enclosures with appropriate protection levels:
- IP65: Dust-tight and protected against low-pressure water jets.
- IP66: Dust-tight and protected against powerful water jets.
- IP67/IP68: Suitable for temporary or continuous submersion.
- NEMA 3R: Outdoor use, protects against rain, sleet, and external ice formation.
- NEMA 4X: Watertight and corrosion-resistant, ideal for washdown or coastal areas.
Verify that gaskets, seals, and conduit entries maintain the rated protection throughout the enclosure’s lifecycle.
Thermal Management and Ventilation
Proper thermal design prevents overheating of internal components:
- Calculate heat dissipation based on internal load and ambient conditions.
- Use passive cooling (vents, heat sinks) where ambient conditions allow.
- For high-heat environments, consider active cooling (fans, air conditioners, heat exchangers).
- Ensure ventilation does not compromise the enclosure’s IP or NEMA rating (e.g., use filtered vents or pressurization systems).
Mounting, Installation, and Accessibility
Follow best practices for installation:
- Secure enclosures to stable structures using appropriate hardware to prevent vibration or tampering.
- Maintain recommended clearances for heat dissipation and maintenance access (per NEC, IEC, or local codes).
- Label enclosures clearly with voltage, hazards, and circuit information.
- Ensure doors open fully (typically 120°–180°) and latches are robust and corrosion-resistant.
Supply Chain and Logistics Considerations
Efficient logistics ensure timely and compliant delivery:
- Partner with suppliers who provide certified, traceable products and full documentation.
- Verify packaging standards to prevent damage during transit (e.g., shock-absorbent materials, moisture barriers).
- Consider lead times, especially for custom enclosures or those requiring special certifications.
- Implement inventory management systems to track enclosure specifications, compliance status, and lifecycle data.
Maintenance and Compliance Audits
Regular inspection and documentation support long-term compliance:
- Schedule periodic checks for seal integrity, corrosion, and mechanical damage.
- Update documentation for modifications or retrofits.
- Retain records of inspections, repairs, and certification renewals.
- Conduct compliance audits to ensure ongoing adherence to regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
A comprehensive approach to logistics and compliance in electrical enclosure applications minimizes risk, ensures operational safety, and supports regulatory acceptance. Always consult applicable standards and involve qualified engineers during design and deployment phases.
In conclusion, sourcing electrical enclosures requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, compliance, and reliability. Selecting the right supplier involves evaluating key factors such as material durability, environmental protection ratings (e.g., NEMA or IP ratings), customization capabilities, certifications, and adherence to industry standards. Additionally, considerations like lead times, scalability, technical support, and total cost of ownership play a critical role in long-term success. By partnering with reputable suppliers who demonstrate engineering expertise and consistent quality control, organizations can ensure the safe, efficient, and reliable operation of their electrical systems. Ultimately, effective sourcing of electrical enclosures contributes to enhanced system performance, reduced downtime, and compliance with safety regulations across diverse applications in industrial, commercial, and utility environments.