The global electric supercharger and turbocharger market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by the automotive industry’s shift toward electrification and stricter emissions regulations. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global turbocharger market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated value of USD 36.2 billion by the end of the forecast period. This growth is further amplified by advancements in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and the increasing adoption of electric superchargers to enhance engine efficiency and reduce turbo lag. Grand View Research reinforces this trend, noting that the rising demand for fuel-efficient vehicles and integration of forced induction systems in downsized engines are key market accelerants. As innovation intensifies, a select group of manufacturers are leading the charge in developing high-performance electric supercharger and turbocharger solutions. Here are the top 10 manufacturers shaping the future of forced induction technology.
Top 10 Electric Supercharger Turbocharger Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Turbochargers
Domain Est. 1990
Website: cummins.com
Key Highlights: Learn more about turbochargers from Cummins, experts in medium- and heavy-duty diesel engine turbochargers for increased engine performance….
#2 turbo & supercharging
Domain Est. 1998
Website: calnetix.com
Key Highlights: Calnetix Magnaforce motor generator technology is used in turbocharger applications, supercharger applications, and compounder applications….
#3 IHI Turbo America
Domain Est. 1998
Website: ihi-turbo.com
Key Highlights: We are one of the world’s largest turbocharger manufacturers as well as the only company in the world that mass-produces screw superchargers….
#4 Award
Domain Est. 2018
Website: garrettmotion.com
Key Highlights: Garrett is pioneering E-Turbo technology to deliver superior performance, fuel economy, and emissions, by integrating state-of-the-art, ultra-high-speed ……
#5 Precision Engineered Turbochargers & Turbo Parts
Domain Est. 1999
Website: melett.com
Key Highlights: Supplier of turbochargers, Core Assemblies, turbo parts and repair kits. Our range allows turbo reconditioning, remanufacturing and repair of turbo models….
#6 Whipple Superchargers
Domain Est. 1999 | Founded: 1987
Website: whipplesuperchargers.com
Key Highlights: Explore the legacy of Whipple Superchargers, a family-owned and operated powerhouse since 1987. Founded by the innovative Art Whipple in Fresno, CA, ……
#7 Electric Boosting Technologies
Domain Est. 2002
Website: borgwarner.com
Key Highlights: Equipped with high-performance electric motors, the company’s cutting-edge solutions developed for 12V, 48V and high-voltage vehicles offer fast time-to-torque….
#8 Rotrex
Domain Est. 2003
Website: rotrex.com
Key Highlights: Superchargers with superior combination of compactness, efficiency, reliability and low noise. The inventor of the traction drive supercharger….
#9 Duryea Electric Supercharger
Domain Est. 2015
Website: duryeatechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Duryea’s 12V Electric Supercharger can be installed in all types of vehicles, from ATVs, motorcycles, 4×4 sport utility vehicles, diesel trucks, to most types ……
#10 Electric Supercharger
Domain Est. 2015
Website: torqamp.com
Key Highlights: Bypass Valve. 235,00 € Add to cart · Control Box. 129,00 € Add to cart · TorqAmp Kit. 2.749,00 € Add to cart · TorqAmp Kit Lite. 2.199,00 € Add to cart….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Electric Supercharger Turbocharger
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Electric Supercharger and Turbocharger Systems
The global market for electric superchargers and turbochargers is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by tightening emissions regulations, the rise of hybrid powertrains, and advancements in electrified forced induction technologies. As automakers accelerate their transition toward sustainable mobility, electric superchargers and advanced turbochargers are emerging as critical enablers of improved engine efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced performance in both internal combustion engines (ICEs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs).
-
Growth in Hybrid and Mild-Hybrid Vehicle Adoption
A key driver for the electric supercharger and turbocharger market is the increasing global penetration of 48V mild-hybrid systems. By 2026, it is projected that over 30% of new light-duty vehicles in Europe and North America will feature mild-hybrid technology, which often incorporates electric superchargers to eliminate turbo lag and improve low-end torque. OEMs such as Audi, Mercedes-Benz, and Volvo have already integrated electric superchargers (e.g., Valeo’s 48V e-Booster) into their engine lineups, and this trend is expected to broaden across mass-market brands. -
Electrification of Forced Induction Systems
Electric superchargers—compact, motor-driven compressors that provide immediate boost pressure—are gaining traction as a solution to maintain performance in downsized engines. Unlike traditional turbochargers that rely on exhaust gas flow, electric superchargers deliver instant response, making them ideal for transient driving conditions. By 2026, the integration of electric superchargers with conventional turbochargers in “e-turbo” or “twin-boost” configurations is expected to become mainstream, especially in performance and premium SUV segments. -
Technological Convergence: e-Turbo Systems
A major innovation shaping the 2026 landscape is the emergence of electrically assisted turbochargers (e-turbos). These systems combine a conventional turbocharger with an electric motor/generator mounted on the shaft, allowing for active control of turbine speed. Companies like Garrett Motion and BorgWarner are leading the development of e-turbo technology, which enables faster spool-up, energy recovery via regenerative braking, and improved thermal efficiency. The e-turbo market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 18% from 2022 to 2026, particularly in high-performance and commercial vehicle applications. -
Regulatory Pressures and Emission Standards
Stringent emissions standards—such as Euro 7 in Europe and China 6b—are compelling automakers to adopt technologies that reduce real-world CO₂ and NOx emissions. Electric superchargers and e-turbos help meet these targets by enabling smaller, more efficient engines without sacrificing drivability. In addition, these systems support lean-burn combustion strategies and improve cold-start emissions, further enhancing compliance. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Europe remains the largest market for electric supercharging and advanced turbocharging technologies due to aggressive decarbonization policies and high diesel and gasoline engine efficiency requirements. China is rapidly catching up, driven by its dual-credit policy and growing HEV market. North America is expected to see moderate growth, primarily led by pickup trucks and SUVs adopting e-turbo systems for performance and towing applications. -
Supply Chain and Manufacturing Trends
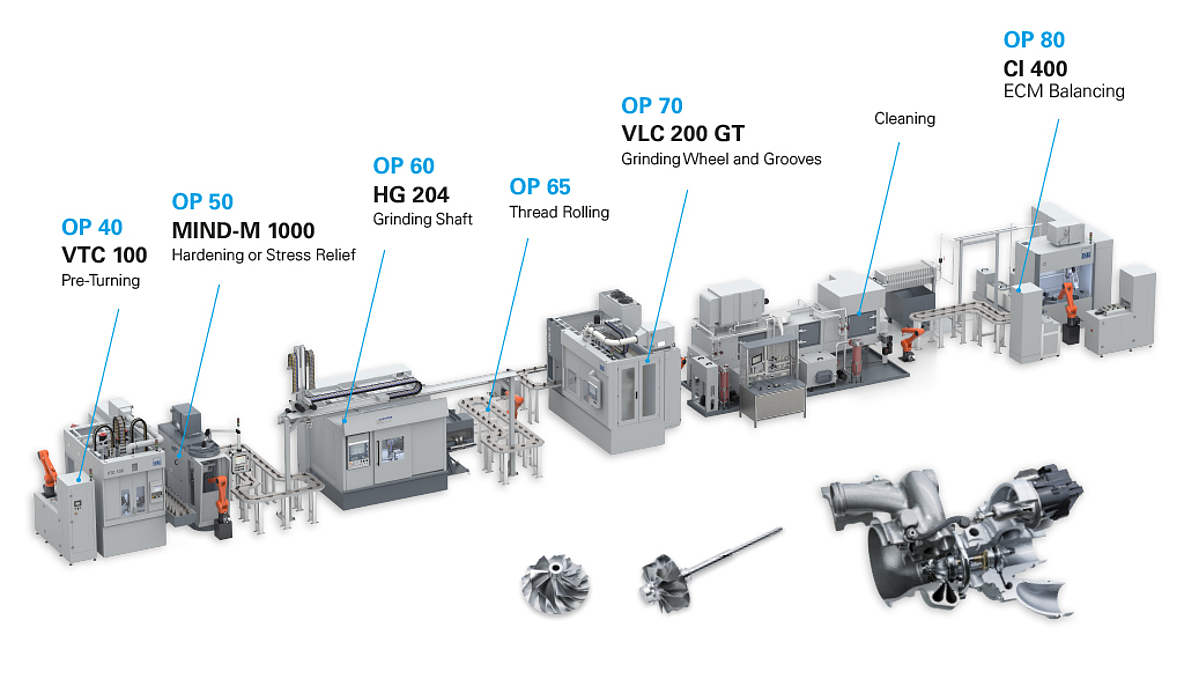
By 2026, key suppliers are expected to scale up production of electric superchargers and e-turbos through localized manufacturing and strategic partnerships with OEMs. Investment in power electronics, thermal management, and compact motor design will be critical to reducing system cost and improving durability. Increased adoption of silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors in control units will further enhance efficiency and power density. -
Competitive Landscape
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with established players like BorgWarner, Garrett Motion, and MAHLE vying with newcomers and tech firms to offer integrated electrified boosting solutions. Consolidation and joint ventures are likely as companies seek to combine expertise in turbocharging, electric motors, and vehicle electrification systems.
Conclusion
By 2026, the electric supercharger and turbocharger market will be defined by the convergence of electrification, performance, and sustainability. While fully electric vehicles continue to grow, the continued relevance of internal combustion and hybrid powertrains ensures strong demand for advanced forced induction technologies. Electric superchargers and e-turbos will play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between efficiency and performance, positioning them as essential components in the next generation of automotive propulsion systems.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Electric Supercharger & Turbocharger Components (Quality & IP Risks)
Sourcing electric superchargers and turbochargers—especially for high-performance or emerging applications like hybrid and electric vehicles—presents unique challenges. While these components offer significant efficiency and performance benefits, procurement efforts can quickly run into serious issues related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Below are the most common pitfalls to watch for.
1. Inadequate Quality Control and Material Standards
One of the primary risks in sourcing electric superchargers and turbochargers is inconsistent product quality, particularly when working with new or low-cost manufacturers.
- Substandard Materials: Suppliers may use inferior alloys or composites in turbine wheels, housings, or motor components to cut costs. This compromises durability, heat resistance, and efficiency, increasing the risk of premature failure.
- Lack of Certification: Failure to verify compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO/TS 16949, AS9100 for aerospace applications, or ISO 1940 for balance) can result in unreliable components.
- Inconsistent Manufacturing Processes: Variability in precision machining, balancing, or motor winding processes can lead to vibration, noise, or reduced efficiency.
Mitigation: Require detailed quality documentation, conduct on-site audits, and enforce rigorous incoming inspection protocols—including third-party testing for material composition and performance.
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement and Reverse Engineering
Electric supercharger and turbocharger designs often incorporate proprietary technologies, especially in motor integration, control algorithms, and aerodynamic profiling.
- Design Copying: Some suppliers may reverse-engineer branded components and offer “compatible” versions that infringe on patents or trade secrets.
- Unlicensed Technology Use: Suppliers might integrate third-party IP (e.g., motor controllers or software) without proper licensing, exposing buyers to legal liability.
- Lack of IP Clarity in Contracts: Agreements that fail to clearly assign ownership of custom designs or modifications can lead to disputes.
Mitigation: Conduct thorough IP due diligence, require suppliers to warrant non-infringement, and include strong IP clauses in contracts specifying ownership, confidentiality, and permitted use.
3. Overreliance on Unverified “Copy” or Generic Parts
In cost-driven sourcing, buyers may opt for generic or aftermarket versions of established OEM parts.
- Performance Gaps: These components often fail to meet OEM specifications for flow rate, pressure ratio, response time, or efficiency, undermining system performance.
- Hidden Defects: Lack of traceability and testing increases the risk of latent defects that emerge under thermal or mechanical stress.
- Voided Warranties: Using non-OEM or uncertified parts can void warranties on the final product or vehicle system.
Mitigation: Limit sourcing to authorized distributors or OEM-approved partners. Require performance validation data and conduct side-by-side benchmarking when evaluating alternatives.
4. Inadequate Supplier Technical Capability and R&D Transparency
Electric superchargers integrate mechanical, electrical, and control systems, requiring multidisciplinary expertise.
- Limited In-House Engineering: Some suppliers outsource core design work or lack in-house R&D, reducing their ability to customize or troubleshoot.
- Opaque Development Processes: Suppliers may be unwilling to share design schematics, simulation data, or test results, making it difficult to assess innovation or reliability.
Mitigation: Evaluate supplier technical depth during qualification. Require access to engineering documentation and insist on collaborative development processes for custom designs.
5. Weak Contractual Protections and Compliance Gaps
Procurement agreements that neglect key clauses can leave buyers exposed.
- Absence of Warranty and Recall Provisions: Poorly defined liability terms make it difficult to enforce recalls or claim compensation for defective batches.
- Non-Compliance with Export Controls: High-performance turbo components may be subject to export regulations (e.g., ITAR, EAR), especially if used in defense or aerospace applications.
- Data Rights and Software Licensing: Embedded firmware or control software may have restrictive licenses that limit integration or updates.
Mitigation: Work with legal and compliance teams to ensure contracts cover warranties, liability, export classification, and software rights. Include audit rights for quality and IP compliance.
Conclusion
Sourcing electric superchargers and turbochargers demands a strategic approach that balances cost, performance, and risk. Prioritizing quality assurance, protecting intellectual property, and selecting technically capable partners are essential to avoid costly failures and legal exposure. Due diligence, clear contractual terms, and ongoing supplier management are critical to long-term success.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Electric Supercharger Turbocharger
Overview
This guide provides essential information for the safe, efficient, and compliant logistics and handling of Electric Supercharger Turbochargers throughout the supply chain—from manufacturing to final delivery. These advanced components combine traditional turbocharger technology with electric motor assistance and require special attention due to their sensitive electronics, mechanical precision, and regulatory considerations.
Packaging Requirements
Ensure Electric Supercharger Turbochargers are packaged to prevent damage from shock, vibration, moisture, and electrostatic discharge (ESD):
- Inner Packaging: Use anti-static foam or ESD-safe bubble wrap to protect electronic control units and sensors.
- Outer Packaging: Utilize double-walled corrugated cardboard or reusable plastic containers with impact-resistant lining.
- Sealing: Securely seal all boxes with tamper-evident tape; label with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack.”
- Moisture Protection: Include desiccant packs in sealed packaging, particularly for ocean freight or high-humidity environments.
Labeling and Documentation
Proper labeling and documentation are critical for traceability and regulatory compliance:
- Product Labeling: Include part number, model, serial number, voltage rating, and CE/FCC/ROHS markings.
- Hazard Labels: Apply labels for “Electrostatic Sensitive Device” and “Handle with Care.”
- Shipping Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Certificate of Conformity (CE, FCC, ISO)
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), if applicable
- Export Declaration (for international shipments)
- Customs Compliance: Accurately classify under HS Code 8414.30 (Turbochargers) or 8501.31 (Electric Motors), depending on primary function.
Transportation Considerations
Choose appropriate transport modes with attention to environmental and handling risks:
- Temperature Control: Maintain storage and transport temperatures between -10°C and 50°C; avoid condensation.
- Vibration & Shock: Use shock-absorbing pallets and avoid rough handling. Do not drop or roll containers.
- Stacking Limits: Observe maximum stacking heights to avoid crushing lower units.
- Mode-Specific Guidelines:
- Air Freight: Comply with IATA regulations; batteries (if integrated) must meet UN 38.3 testing.
- Ocean Freight: Use moisture barriers and marine-grade packaging; ensure proper ventilation in containers.
- Ground Transport: Secure cargo to prevent movement; avoid exposure to dust and extreme weather.
Import/Export Compliance
Ensure adherence to international trade regulations:
- Export Controls: Verify if product contains controlled technology (e.g., under EAR or ITAR). Most electric turbochargers fall under ECCN 9A991.d (Civil aircraft-related).
- Country-Specific Regulations:
- EU: Comply with REACH, RoHS, and CE marking directives.
- USA: FCC Part 15 compliance for electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- China: Obtain CCC certification if applicable; register with MIIT.
- UK: UKCA marking post-Brexit; follow UK REACH.
- Duty Optimization: Leverage Free Trade Agreements (e.g., USMCA, RCEP) where applicable.
Handling and Storage
Proper handling preserves product integrity:
- Receiving & Inspection: Check for shipping damage upon arrival; verify contents against packing list.
- Storage Conditions: Store in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment (15–25°C, 30–60% RH).
- Shelf Life: Monitor for obsolescence; electronic components may degrade after 24 months in storage.
- Handling Tools: Use non-magnetic, ESD-safe tools during unpacking or assembly.
Compliance Certifications
Maintain up-to-date certifications to ensure market access:
- ISO 9001: Quality Management
- ISO 14001: Environmental Management
- IATF 16949: Automotive Quality Standards
- CE Marking: EU conformity (EMC, LVD, RoHS)
- FCC Certification: USA electromagnetic compatibility
- E-Mark (ECE R10): Automotive EMC compliance in Europe
Returns and Reverse Logistics
Establish protocols for returns due to warranty, repair, or recalls:
- Return Authorization (RA): Require prior approval with tracking.
- Packaging: Use original or equivalent protective packaging.
- Data Security: Wipe or disable embedded control unit data if applicable.
- Environmental Disposal: Follow WEEE guidelines for end-of-life units; recycle metals and electronics responsibly.
Conclusion
Electric Supercharger Turbochargers require meticulous logistics planning and strict compliance adherence due to their hybrid mechanical-electrical nature. By following this guide, manufacturers, distributors, and logistics providers can ensure product integrity, regulatory compliance, and customer satisfaction across global markets. Regular audits and training are recommended to maintain standards.
Conclusion: Sourcing Electric Supercharger and Turbocharger
Sourcing electric superchargers and turbochargers presents a strategic opportunity to enhance engine performance, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce emissions in modern automotive and industrial applications. Electric superchargers offer near-instantaneous boost with minimal lag, making them ideal for improving low-end torque and responsiveness, particularly in downsized engines and hybrid powertrains. Turbochargers, especially when paired with electric assist (e-turbos), combine traditional exhaust-driven efficiency with enhanced transient response.
When sourcing these components, it is crucial to evaluate suppliers based on technological expertise, reliability, scalability, and compliance with industry standards. Key considerations include thermal management capabilities, integration with existing engine control units (ECUs), durability under varying load conditions, and total cost of ownership. Leading manufacturers and emerging innovators offer a range of solutions, from off-the-shelf units to fully customized systems tailored to specific performance requirements.
In conclusion, the integration of electric superchargers and advanced turbocharging technologies represents a forward-looking approach to powertrain optimization. A well-structured sourcing strategy—emphasizing technical compatibility, long-term support, and supply chain resilience—will enable organizations to leverage these technologies effectively in the transition toward cleaner, more efficient propulsion systems.