The global electric magnetic brake market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision motion control across industrial automation, material handling, and electric vehicle sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global electromagnetic clutch and brake market was valued at USD 4.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 6.5% during the forecast period 2024–2029, underpinned by advancements in servo-driven systems and rising adoption in renewable energy applications such as wind turbines. As industries prioritize energy efficiency, reliability, and maintenance-free operation, electric magnetic brakes have become critical components in modern mechanical systems. This growing demand has intensified competition among manufacturers, leading to rapid innovation in design, materials, and performance. In this landscape, eight key players have emerged as leaders, combining technological expertise, global reach, and consistent product quality to dominate the market.
Top 8 Electric Magnetic Brake Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Electromagnetic Brakes / Electric Motor Brakes
Domain Est. 1997
Website: cjmco.com
Key Highlights: As a leading electric motor brake manufacturer, our brakes are available in torque ranges from less than 10 lb. ft. to greater than 6000 lb. ft….
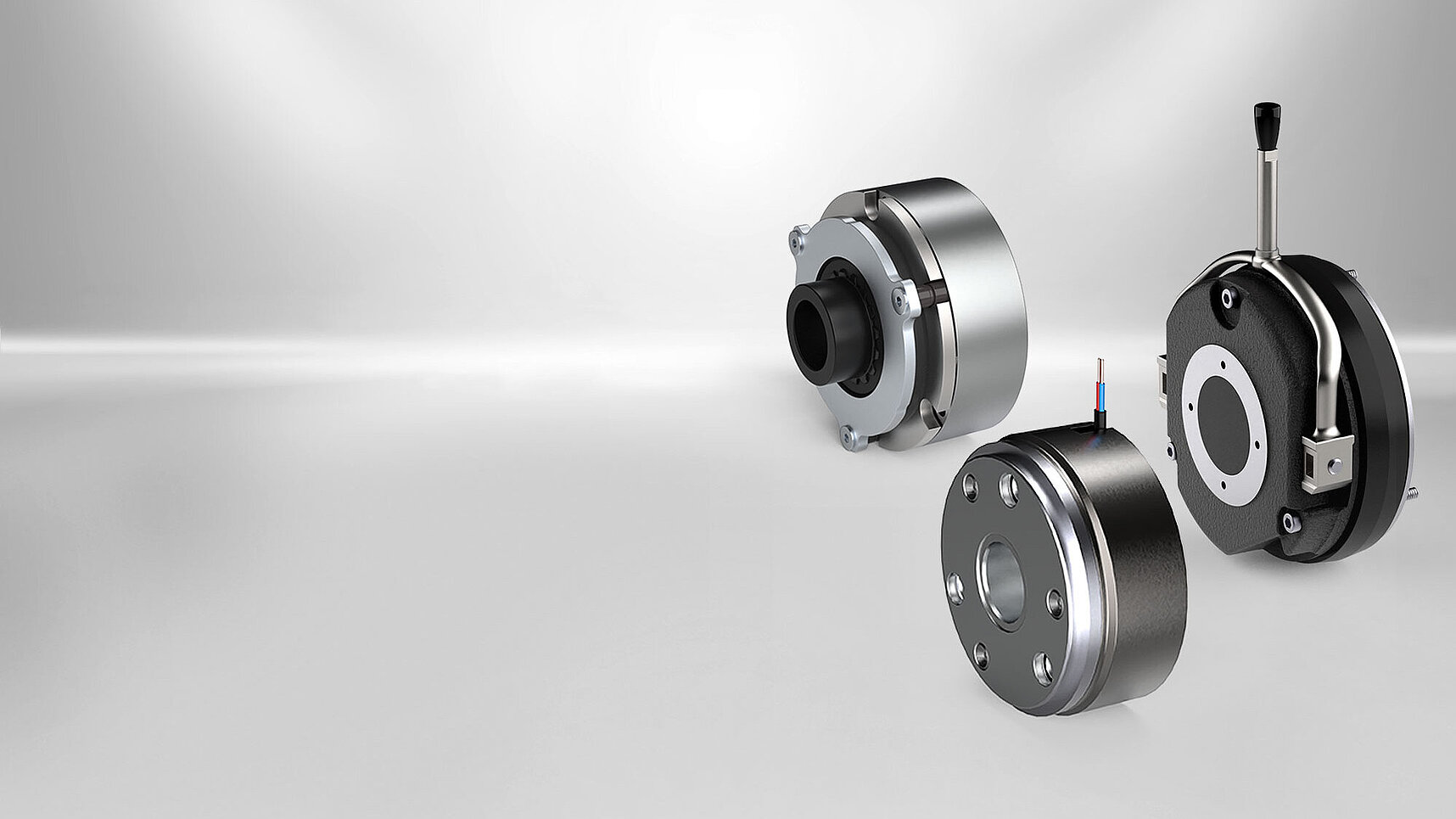
#2 Electromagnetic Brakes
Domain Est. 1998
Website: warnerelectric.com
Key Highlights: Select Product Type. Electromagnetic Brakes. Electromagnetic Brakes. Power Release. Power Apply. Spring Applied. Tooth Technology. Permanent Magnet….
#3 Kendrion & INTORQ Industrial Brakes Engineered for your needs
Domain Est. 1999
Website: kendrion.com
Key Highlights: Kendrion designs electromagnetic brakes for industrial and medical applications ✓ Explore our expert solutions for braking ✓ holding ✓ and securing loads….
#4 Magnetic Brake, Clutch, Coupling
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1984
Website: magnetictech.com
Key Highlights: Since 1984, we have designed and manufactured magnetic products, including magnetic brakes and clutches, magnetic couplings, and electromagnetic brakes….
#5 Brake Motors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: reuland.com
Key Highlights: Reuland offers top-of-line Brakes motors with braking capacities ranging from 1.5 to 1000 ft-lb. These motors are designed for frequent start/stop cycles….
#6 Electromagnetic Brake Calipers from RINGSPANN
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ringspann.com
Key Highlights: Please find our wide selection of electromagnetic clutches and brakes, spring-actuated or electromagnetically actuated….
#7 Magnetic Brake Systems
Domain Est. 2011
Website: magbrakesystems.com
Key Highlights: Magnetic Brake Systems manufactures and sells. magnetic contactless brakes and dynamometers. Our brakes offer high power dissipation, linear torque output ……
#8 Electromagnetic Brakes
Domain Est. 2016
Website: electric-brake.com
Key Highlights: Electromagnetic brakes operate electrically but transmit torque mechanically. This is why they used to be referred to as Electro Mechanical clutches and brakes….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Electric Magnetic Brake

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Electric Magnetic Brakes
The global market for electric magnetic brakes is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in industrial automation, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), and increasing demand for energy-efficient motion control systems. Electric magnetic brakes—valued for their contactless operation, low maintenance, and high reliability—are becoming integral components across multiple industries.
One key trend shaping the 2026 landscape is the rapid adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies. Smart manufacturing environments require precise and responsive braking systems that can integrate seamlessly with IoT-enabled devices and digital control systems. As a result, electric magnetic brakes equipped with real-time diagnostics, predictive maintenance capabilities, and communication interfaces (such as CAN bus or Ethernet) are expected to dominate new installations in robotics, CNC machinery, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
Another major driver is the continued expansion of the electric vehicle and e-mobility sector. In EVs, electric magnetic brakes are increasingly used in regenerative braking systems and auxiliary safety mechanisms. By 2026, stricter global emissions standards and government incentives for sustainable transportation are projected to boost demand for these brakes in automotive applications, particularly in commercial electric buses and last-mile delivery vehicles.
Moreover, growth in renewable energy infrastructure—especially wind turbines—will support market expansion. Electric magnetic brakes play a critical role in yaw and pitch control systems, where reliability under extreme conditions is paramount. The push for cleaner energy sources is expected to increase wind farm installations, especially in emerging economies, further stimulating demand.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific is anticipated to lead market growth due to industrial modernization in countries like China, India, and South Korea. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will maintain strong demand, driven by high automation rates and stringent safety regulations in industrial and transportation sectors.
In terms of innovation, manufacturers are focusing on miniaturization, improved thermal management, and the use of advanced materials (e.g., rare-earth magnets and composite friction linings) to enhance performance and durability. Customization for application-specific needs—such as food-grade brakes for packaging machinery or explosion-proof designs for hazardous environments—will also be a competitive differentiator by 2026.
Overall, the electric magnetic brake market is expected to experience steady CAGR growth through 2026, underpinned by technological innovation, regulatory support for energy efficiency, and expanding applications in high-growth sectors. Companies that invest in smart, sustainable, and scalable braking solutions will be best positioned to capture emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Electric Magnetic Brakes (Quality, IP)
Sourcing electric magnetic brakes involves navigating several potential pitfalls, particularly concerning quality consistency and accurate Ingress Protection (IP) ratings. Overlooking these aspects can lead to premature failures, safety hazards, and increased maintenance costs. Below are key issues to watch for:
Inconsistent Component Quality
Suppliers may use substandard materials or inconsistent manufacturing processes, especially with critical components like coil windings, friction materials, and bearings. Low-quality coils can overheat or fail prematurely, while inferior friction linings wear out faster or produce excessive dust. Always verify material certifications and request sample testing to ensure durability and performance under expected loads and temperatures.
Misrepresented or Unverified IP Ratings
Many suppliers claim high IP ratings (e.g., IP65, IP67) without third-party certification or actual testing. Brakes exposed to dust or moisture without proper sealing can suffer from coil corrosion, short circuits, or mechanical failure. Ensure the supplier provides test reports from accredited laboratories and confirm that the IP rating applies to the assembled unit under real-world operating conditions—not just individual parts.
Lack of Compliance with Industry Standards
Some electric magnetic brakes fail to meet essential international standards such as ISO, IEC, or specific regional safety regulations. Non-compliant units may not integrate safely into machinery or meet regulatory requirements in your market. Always require documentation proving compliance with relevant standards and verify certifications are current and applicable to the exact model being supplied.
Inadequate Thermal Management Design
Poorly designed brakes may lack sufficient heat dissipation, leading to thermal runaway, reduced torque, or permanent damage during frequent cycling. Verify that the brake’s duty cycle and thermal class (e.g., Class F, Class H insulation) match your application’s demands. Request thermal test data or field performance records to assess real-world reliability.
Hidden Costs from Poor Reliability
While some suppliers offer low initial prices, unreliable brakes result in higher total cost of ownership due to downtime, replacement parts, and labor. Evaluate total lifecycle costs rather than upfront price alone. Ask for mean time between failures (MTBF) data and customer references to assess long-term reliability.
Insufficient Documentation and Traceability
A lack of detailed technical documentation, serial number traceability, or batch records complicates maintenance, quality audits, and root cause analysis during failures. Ensure the supplier provides comprehensive manuals, performance curves, and full traceability for every unit delivered.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality brakes require maintenance and occasional replacement parts. Sourcing from suppliers with limited support networks or long lead times for spares can disrupt operations. Confirm spare parts availability, warranty terms, and technical support responsiveness before finalizing procurement.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Electric Magnetic Brake
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the handling, transportation, import/export, and installation of Electric Magnetic Brakes. Adherence to these guidelines ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and optimal product performance.
Product Classification & Documentation
Ensure accurate classification of the Electric Magnetic Brake for customs and regulatory purposes. Typically classified under HS Code 8537.10 (Electrical apparatus for switching/distributing electrical circuits), though verification with local authorities is recommended. Required documentation includes:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Certificate of Conformity (CE, RoHS, etc.)
– Technical Datasheet
– Safety Data Sheet (if applicable)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
Packaging & Handling
Use manufacturer-approved packaging to prevent damage during transit. Brakes should be:
– Securely mounted in shock-absorbent material
– Protected from moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures
– Clearly labeled with orientation indicators (e.g., “This Side Up”)
Handle with care—avoid dropping or impact. Use appropriate lifting equipment for heavy units. Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment prior to installation.
Transportation Requirements
Transport via standard freight methods (air, sea, or ground) depending on urgency and volume. Comply with International Air Transport Association (IATA) or International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations if shipping hazardous components (e.g., batteries or magnets). Confirm that packaging meets ISTA 3A or equivalent standards for vibration and drop resistance.
Import/Export Compliance
Verify country-specific import regulations. Key compliance areas include:
– CE Marking (mandatory for EU market): Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
– RoHS Compliance: Restriction of Hazardous Substances (lead, mercury, cadmium, etc.)—required in EU, UK, and several other regions.
– REACH: Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals—applicable if brake contains regulated substances.
– UKCA Marking: Required for sale in Great Britain (England, Scotland, Wales).
– FCC Certification: May be needed if the brake includes electronic controls emitting radio frequency energy (U.S. market).
– EAC Certification: Required for sale in Eurasian Economic Union (EEU) countries.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Electric Magnetic Brakes must comply with EMC directives (e.g., EU Directive 2014/30/EU) to ensure they do not interfere with other equipment and are immune to external interference. Shielded cables and proper grounding are essential during installation.
Installation & Safety Compliance
Install in accordance with manufacturer instructions and local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC 60204-1 internationally). Key safety considerations:
– Ensure proper grounding to prevent electric shock
– Verify voltage compatibility with power supply
– Implement lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance
– Comply with machinery safety standards (e.g., ISO 13849 for safety-related parts of control systems)
Environmental & Disposal Regulations
Dispose of end-of-life units in compliance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive in the EU and similar regulations elsewhere. Recycle metals and electronic components through authorized treatment facilities. Avoid landfill disposal.
Regulatory Updates & Traceability
Maintain records of batch numbers, compliance certifications, and shipping documentation for traceability. Monitor regulatory updates in target markets and ensure ongoing compliance with evolving standards.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance management for Electric Magnetic Brakes ensures legal conformity, operational safety, and environmental responsibility. Partner with certified suppliers and logistics providers familiar with industrial electrical components to streamline global distribution.
Conclusion for Sourcing an Electromagnetic Brake:
In conclusion, sourcing the right electromagnetic brake requires a thorough evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, quality standards, and supplier reliability. It is essential to select a brake that not only meets the performance needs—such as torque capacity, response time, duty cycle, and environmental resistance—but also ensures long-term durability and safety. Cost-effectiveness should be balanced with quality, favoring suppliers with proven industry experience, certification compliance (e.g., ISO, CE), and responsive technical support. By conducting a comprehensive supplier assessment and validating product performance through testing or references, organizations can ensure a reliable, efficient, and sustainable sourcing decision. Ultimately, the right electromagnetic brake enhances system performance, reduces maintenance costs, and contributes to the overall operational efficiency of the machinery.