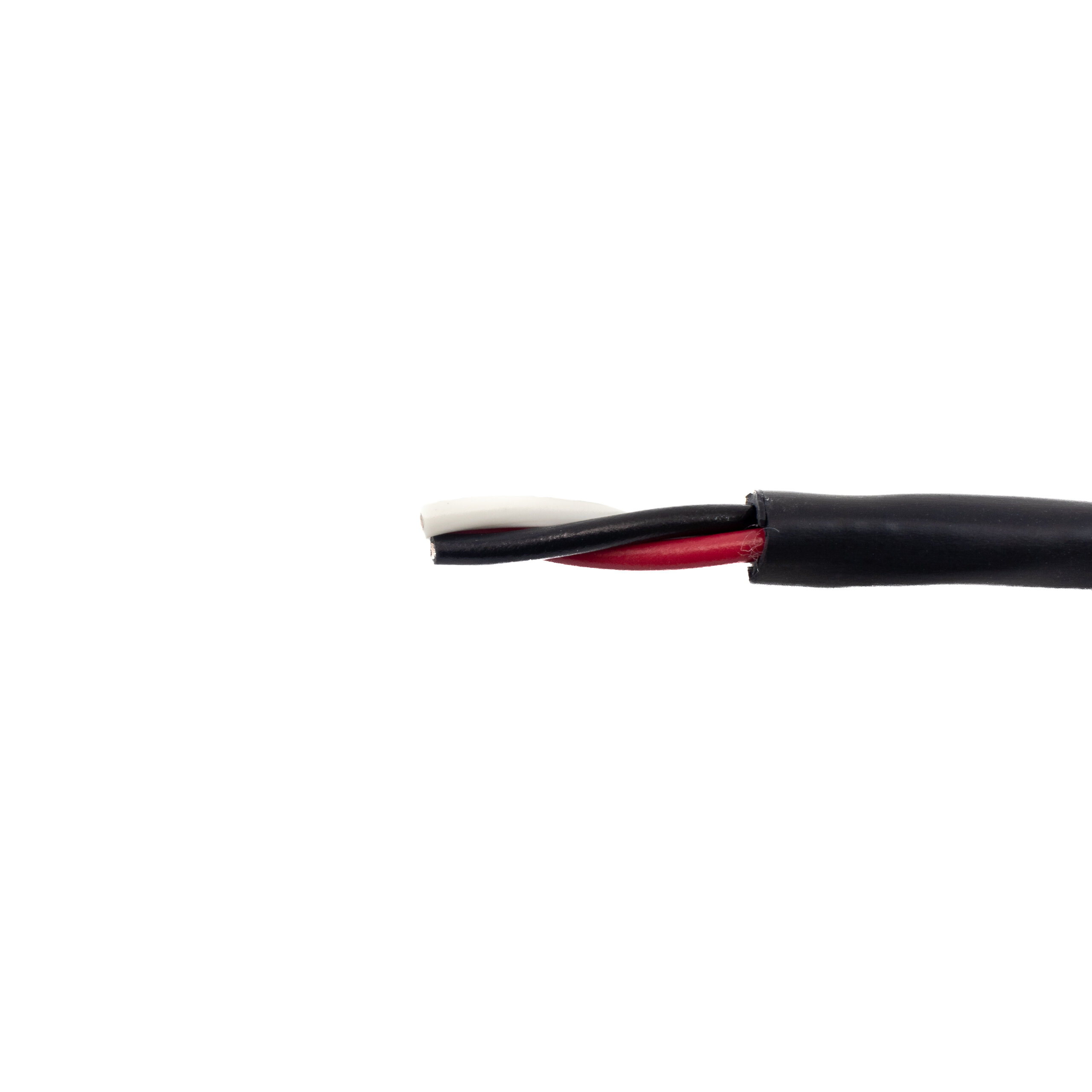
The global electric cable market is witnessing robust expansion, driven by increasing infrastructure development, rising urbanization, and growing demand for reliable power transmission across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global electrical cables market was valued at USD 167.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is further amplified by initiatives in renewable energy integration and smart grid deployment, creating sustained demand for high-quality power cables, including red and black insulated variants used extensively for live and neutral wiring in electrical systems. With Asia-Pacific emerging as the largest consumer due to rapid industrialization and government-led electrification programs, manufacturers specializing in red and black electric cables are scaling production and innovation to meet stringent safety and performance standards. In this competitive landscape, nine key players have distinguished themselves through consistent quality, certifications, and global supply capabilities—setting the benchmark in the low-voltage cable segment.
Top 9 Electric Cable Red Black Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Electrical Cords and Cables
Domain Est. 1997
Website: centurywire.com
Key Highlights: Century Wire & Cable is the leading manufacturer of electrical wire and cable products. … Red, Yellow, Orange, Black, White, Pink, Purple, Grey, Navy Blue….
#2 Wire & Cable
Domain Est. 1994
Website: southwire.com
Key Highlights: Choose a Product Category: Wire & Cable, Tools & Equipment, Power Management, Temporary Lighting, Electrical Components, Lamps & Luminaires.Missing: red black…
#3 Wiring devices and connectivity
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: Wiring devices & connectivity. Innovative NEC and IEC electrical connectivity and control solutions that provide reliable, efficient and safe power management ……
#4 Alpha Wire
Domain Est. 1997
Website: alphawire.com
Key Highlights: Cable · Wire · Accessories · Custom · Markets · Aerospace and Defense · Automated … We use necessary cookies to make our site work. By clicking “accept all” you …Missing: red …
#5 Wire, Cable and Electrical Products Provider
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1965
Website: milspecind.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1965, Milspec Industries is one of the world’s leading providers of wire and cable as well as related electrical products and accessories….
#6 Polar Wire Products®
Domain Est. 1999
Website: polarwire.com
Key Highlights: Our Wire. Battery connector cables with red and black polarity. Custom Assembly Services. We specialize in manufacturing high-quality custom cable assemblies ……
#7 Powerwerx
Domain Est. 1999
Website: powerwerx.com
Key Highlights: 10–21 day delivery · 30-day returnsCustom DC Power Cables · Adapter & Extension Cables · Wire & Cable Reels Red/Black Zip Cord, Hookup Wire, PTFE, Silicone, Welding Cable · Termin…
#8 Remington Industries
Domain Est. 2000
Website: remingtonindustries.com
Key Highlights: Remington Industries is a trusted wire distributor. Trust us for electrical wire, raw metals, wire processing, coil winding, and 3D printing. Shop now….
#9 Machine Tool Wire
Domain Est. 2000
Website: atlaswirecorp.com
Key Highlights: Atlas Wire, LLC manufactures PVC, XLPE, and Nylon insulated electrical lead wires to UL, Automotive, Military and Customer specifications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Electric Cable Red Black

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Red and Black Electric Cables
The global market for red and black electric cables—commonly used for DC power distribution, automotive applications, solar installations, and low-voltage systems—is expected to experience notable growth and transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and rising demand across key industries.
1. Increased Demand from Renewable Energy Sectors
The expansion of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems worldwide is a primary driver for red (positive) and black (negative) cable demand. As countries intensify efforts to meet climate targets under agreements like the Paris Accord, solar farm installations are accelerating. Red and black cables are integral to DC wiring in solar arrays, and the International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts a 50% increase in solar capacity by 2026, directly boosting cable consumption.
2. Growth in Electric Vehicle (EV) and EV Charging Infrastructure
The EV revolution is significantly influencing cable demand. Red and black cables are standard in EV battery systems, onboard electronics, and DC fast-charging stations. With EV adoption projected to rise above 40% of new car sales in major markets (e.g., EU, China, U.S.) by 2026, the need for reliable, high-performance DC cabling will surge. Additionally, governments are investing in public EV charging networks, further driving demand for standardized color-coded cables.
3. Standardization and Safety Regulations
Regulatory emphasis on electrical safety and color-coding standards (such as NEC and IEC 60446) will reinforce the use of red and black cables for DC polarity identification. By 2026, stricter enforcement of these standards in construction, industrial, and renewable sectors will ensure consistent demand and reduce the risk of miswiring, especially in DIY and residential solar markets.
4. Shift Toward High-Performance and Fire-Safe Materials
Market trends indicate a growing preference for cables with enhanced durability, UV resistance, and flame-retardant properties—especially in outdoor and high-temperature environments. Manufacturers are increasingly using cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) and low-smoke zero-halogen (LSZH) insulation for red and black cables, aligning with safety regulations and customer expectations for long-term reliability.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China and India, will dominate demand due to rapid urbanization, government-backed renewable projects, and manufacturing growth. North America and Europe will see steady growth, supported by green energy incentives and infrastructure modernization. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America will also contribute, particularly through off-grid solar solutions that rely heavily on simple, color-coded cabling.
6. Supply Chain and Sustainability Pressures
Copper price volatility and sustainability concerns are pushing innovation in cable design, including the use of aluminum conductors in non-critical applications. Recycling programs and eco-labeling are expected to gain traction, with manufacturers highlighting environmentally responsible production to meet ESG goals.
Conclusion
By 2026, the market for red and black electric cables will be shaped by the convergence of energy transition, electrification, and safety compliance. Companies that invest in high-quality, code-compliant, and sustainably produced cables will be best positioned to capitalize on expanding opportunities in solar, EVs, and smart infrastructure.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Electric Cable Red Black (Quality, IP)
Sourcing electric cables, particularly common types like red and black insulated cables, involves more than just color and price. Overlooking critical quality and Ingress Protection (IP) factors can lead to safety hazards, system failures, and costly downtime. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Assuming Color Indicates Performance or Polarity
One of the most frequent mistakes is assuming that red and black colors denote specific electrical functions (e.g., red = live, black = neutral) across all applications or regions. In reality:
– Color coding varies by country and standard (e.g., IEC vs. NEC).
– Some cables use red/black for DC polarity, while others use them for phase identification.
– Relying solely on color without verifying specifications can result in incorrect installations and safety risks.
2. Ignoring Cable Construction and Material Quality
Low-cost cables often cut corners on materials, leading to:
– Use of recycled or substandard copper, increasing resistance and overheating risk.
– Thin or inconsistent insulation, compromising dielectric strength and durability.
– Poor jacketing that cracks under UV exposure, temperature swings, or mechanical stress.
Always verify conductor material (e.g., bare copper vs. tinned), insulation type (e.g., PVC, XLPE), and compliance with standards like UL, IEC, or BS.
3. Overlooking Voltage and Current Ratings
Sourcing cables without verifying voltage (e.g., 300/500V, 600V) and current-carrying capacity for the intended application can lead to:
– Overheating and fire hazards.
– Premature cable degradation.
– Non-compliance with electrical codes.
Ensure the cable’s rating exceeds the expected operational load, including ambient temperature derating factors.
4. Misunderstanding IP Ratings for Cable Assemblies
The IP (Ingress Protection) rating applies to enclosures and terminations, not the cable itself. A common pitfall is assuming a cable has an IP rating:
– Individual cables typically do not carry IP ratings; the rating applies to the entire installation (connectors, glands, enclosures).
– Poor terminations can negate any protection, allowing dust or moisture ingress even with high-quality cable.
Always assess the full system’s IP compliance, not just the cable.
5. Neglecting Environmental and Mechanical Durability
Cables used in harsh environments (industrial, outdoor, automotive) require specific features:
– UV resistance for outdoor use.
– Oil, chemical, or abrasion resistance in industrial settings.
– Flexibility and tensile strength for moving applications (e.g., robotics).
Standard red/black PVC cables may fail quickly if these factors are ignored.
6. Failing to Verify Certifications and Traceability
Unverified suppliers may provide counterfeit or non-compliant cables. Pitfalls include:
– Missing or fake certification marks (e.g., UL, CE, RoHS).
– Lack of traceability (batch numbers, test reports).
– No access to datasheets or test results.
Always source from reputable suppliers and request documentation.
7. Not Considering Installation Conditions
Installation practices impact cable performance:
– Bending radius violations can damage conductors or insulation.
– Improper support or routing leads to stress and wear.
– Running cables near heat sources without thermal protection.
Ensure the cable is suitable for the installation method (conduit, tray, direct burial) and environment.
By addressing these common pitfalls, you can ensure the reliable, safe, and compliant use of red and black electric cables in your applications.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Red and Black Electric Cables
Product Overview
Red and black electric cables are commonly used in electrical installations for power distribution, control circuits, and grounding. Typically, red signifies the live (positive/hot) conductor, while black may indicate neutral or a secondary live conductor depending on regional codes. These cables are available in various insulation types (e.g., PVC, XLPE), conductor materials (copper or aluminum), and voltage ratings.
Packaging Requirements
- Cables must be wound on wooden or plastic reels or spools suitable for the cable length and diameter.
- Reels should be secured with protective end caps or covers to prevent damage during transit.
- Bulk packaging must include clear labeling indicating cable type, length, gauge (AWG or mm²), voltage rating, and color coding.
- Moisture-resistant wrapping (e.g., polyethylene film) is required for outdoor storage or maritime transport.
Storage Conditions
- Store in a dry, well-ventilated indoor area with temperatures between 5°C and 40°C.
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, UV radiation, and extreme temperature fluctuations.
- Keep reels upright on flat, stable surfaces to prevent deformation.
- Do not stack reels unless designed for vertical stacking; use appropriate supports if necessary.
Transportation Guidelines
- Secure reels on pallets or in containers using straps or braces to prevent rolling or shifting.
- For international shipping, comply with IATA (air), IMDG (sea), or ADR (road) regulations as applicable.
- Protect from moisture, oil, chemicals, and physical impact during transit.
- Use forklifts or cranes with appropriate attachments when handling heavy spools.
Labeling and Documentation
- Each reel must be labeled with:
- Manufacturer name and logo
- Cable type (e.g., THHN, XLP, PVC)
- Conductor size (e.g., 14 AWG, 2.5 mm²)
- Voltage rating (e.g., 600V)
- Color (Red, Black)
- Length (in feet or meters)
- Batch/lot number and manufacturing date
- Include a Certificate of Conformity (CoC) and Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) with each shipment.
- For export, provide commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading/airway bill.
Regulatory Compliance
- North America (USA/Canada):
- Comply with National Electrical Code (NEC) / Canadian Electrical Code (CEC).
- Ensure UL, CSA, or cULus listing for electrical safety.
-
RoHS and REACH compliance may be required for certain materials.
-
European Union:
- Meet Low Voltage Directive (LVD) 2014/35/EU and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive.
- CE marking required.
-
Comply with RoHS and REACH regulations for hazardous substances.
-
Other Regions:
- Check local standards such as BS (UK), AS/NZS (Australia/New Zealand), or GB (China).
- Some countries require import permits or product certification (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, KC in South Korea).
Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Do not incinerate cable waste; dispose of in accordance with local e-waste regulations.
- Avoid contact with sharp tools during handling to prevent insulation damage.
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety shoes when moving heavy reels.
- Ensure compliance with OSHA (US) or equivalent workplace safety standards.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
- Maintain batch traceability through lot numbers and production records.
- Conduct routine quality checks including insulation resistance, conductor continuity, and tensile strength.
- Retain test reports and compliance certificates for a minimum of 5 years.
Returns and Non-Conformance
- Damaged or non-compliant shipments must be reported within 48 hours of receipt.
- Return authorization (RA) required for all returns; include detailed reason and photos if applicable.
- Non-compliant products must be quarantined and handled per environmental regulations.
Contact Information
For compliance inquiries, logistics support, or documentation requests, contact:
[Your Company Name]
Compliance & Logistics Department
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +1 (555) 123-4567
Conclusion for Sourcing Electric Cables (Red and Black):
In conclusion, sourcing red and black electrical cables requires careful consideration of quality, compliance, and supplier reliability. Red and black cables are commonly used for live (red) and neutral (black) wiring in electrical installations, particularly in older systems or specific regional standards, making it essential to ensure they meet relevant safety certifications such as IEC, BS, or NEC, depending on local regulations.
Sourcing from reputable suppliers with a proven track record in electrical materials guarantees product durability, conductivity, and fire resistance. Factors such as cable gauge (cross-sectional area), insulation type (e.g., PVC or XLPE), and temperature rating must align with the intended application to ensure safety and performance.
Additionally, conducting a cost-benefit analysis, evaluating lead times, and maintaining relationships with multiple suppliers can enhance supply chain resilience. By prioritizing certified products, technical specifications, and reliable procurement practices, organizations can ensure safe, efficient, and compliant electrical installations when using red and black cables.