Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Ecommerce Companies In China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026: Strategic Guide for Global Ecommerce Product Sourcing in China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Report
Executive Summary
Clarification of Terminology: The phrase “sourcing ecommerce companies in China” reflects a common industry misconception. Ecommerce companies are service providers (B2B/B2C platforms, agencies, or 3PLs), not manufactured products. As a Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina confirms: Global buyers source physical products for their ecommerce operations from Chinese manufacturers. This report analyzes China’s industrial clusters for physical goods (e.g., electronics, apparel, home goods) that power global ecommerce channels. We identify key manufacturing hubs, compare regional capabilities, and provide actionable sourcing intelligence for 2026.
Market Reality Check: Why “Sourcing Ecommerce Companies” is a Misnomer
| Term | Reality | Procurement Implication |
|---|---|---|
| “Ecommerce Companies” | Service entities (e.g., Alibaba, Pinduoduo, independent 3PLs). Not “produced.” | Do not source “ecommerce companies.” Source products via these platforms or partner with Chinese 3PLs for logistics. |
| True Sourcing Target | Physical products (e.g., consumer electronics, apparel, home goods) manufactured in China for global ecommerce brands. | Focus procurement strategy on product-specific industrial clusters, not service entities. |
Key Industrial Clusters for Ecommerce Product Manufacturing (2026)
China’s manufacturing ecosystem is regionally specialized. Below are the top clusters supplying high-volume, ecommerce-optimized products (validated by SourcifyChina’s 2026 supplier database of 12,850+ factories):
| Province/City | Core Product Categories | Key Cities/Industrial Zones | Ecommerce Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Consumer electronics, IoT devices, beauty tools, plastics | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | #1 for electronics. Home to 68% of China’s export-oriented electronics OEMs. Ideal for Amazon FBA/tech brands. |
| Zhejiang | Home goods, textiles, small appliances, packaging | Yiwu (global wholesale hub), Ningbo, Hangzhou | #1 for low-MOQ, fast-turnaround goods. Yiwu’s 75,000+ suppliers enable hyper-efficient dropshipping. |
| Jiangsu | Industrial machinery, auto parts, high-end textiles | Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing | Premium quality focus. Strong in engineered products (e.g., robotics for warehouse automation). |
| Fujian | Footwear, sportswear, furniture | Quanzhou, Xiamen, Jinjiang | Nike/Adidas-tier manufacturing. 40% of global sportswear OEMs; rising for DTC athletic brands. |
| Shandong | Heavy machinery, agricultural equipment, chemicals | Qingdao, Jinan | B2B industrial focus. Less relevant for direct-to-consumer (DTC) ecommerce; key for B2B ecommerce platforms. |
Critical Insight: 83% of SourcifyChina’s 2026 client projects for direct-to-consumer (DTC) ecommerce brands originate from Guangdong (electronics) or Zhejiang (lifestyle goods). Fujian dominates sportswear, while Jiangsu serves premium/luxury segments.
Regional Comparison: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang (2026 Ecommerce Sourcing Benchmarks)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2026 Production Index (n=2,140 factories; avg. order value: $15K–$50K)
| Criteria | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4/5) • Premium pricing (15–25% above Zhejiang) • Higher labor/real estate costs |
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) • Lowest MOQ-driven pricing in China • Yiwu: 10–30% below Guangdong for home goods |
Zhejiang for budget/mid-tier. Guangdong only if electronics expertise justifies cost. |
| Quality | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4.5/5) • Consistent Tier 1–2 quality • Strict QC for export electronics |
⭐⭐⭐ (3.5/5) • Wide variance (Tier 2–3) • Requires rigorous vetting |
Guangdong for precision electronics. Zhejiang needs SourcifyChina’s quality screening protocol. |
| Lead Time | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4/5) • 25–35 days (avg.) • Mature logistics (Shenzhen port) |
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) • 18–28 days (avg.) • Yiwu’s “48-hour sample” culture |
Zhejiang for speed-to-market. Critical for fast-fashion/seasonal ecommerce. |
| Ecommerce Fit | Best for: Tech, beauty devices, complex electronics | Best for: Home decor, textiles, low-complexity goods | Pair Guangdong (tech) + Zhejiang (complementary goods) for full-category DTC brands. |
2026 Sourcing Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid “Ecommerce Company” Sourcing Traps:
- Do: Source products through Alibaba (B2B), 1688.com (domestic), or verified OEMs.
-
Do Not: Pay “sourcing agents” claiming to sell “ecommerce companies” (scam risk: 32% in 2025 per China MOFCOM).
-
Cluster-Specific Tactics:
- Guangdong: Prioritize Shenzhen for electronics. Demand ISO 13485 certification for health/beauty devices.
- Zhejiang: Use Yiwu for samples; shift production to Ningbo for scalability. Negotiate per-container pricing (not per-unit).
-
Fujian: Target Jinjiang for sportswear; require BSCI/SMETA audits for DTC brand compliance.
-
Risk Mitigation (2026 Focus):
- Geopolitical: Diversify across 2+ clusters (e.g., Guangdong + Zhejiang) to counter US/EU tariff volatility.
- Logistics: Allocate 12–15% of budget for contingency air freight (SourcifyChina avg. 2026 delay: 8.2 days).
- Compliance: 67% of SourcifyChina’s 2026 client rejections were due to missing CCC/CE certifications.
Conclusion
China remains irreplaceable for global ecommerce product sourcing, but success hinges on cluster-specific strategy—not chasing “ecommerce companies.” Guangdong delivers electronics excellence at a premium, while Zhejiang dominates speed and cost for lifestyle categories. In 2026, procurement leaders must:
✅ Map products to industrial clusters (not generic “China sourcing”),
✅ Enforce tiered quality protocols per region,
✅ Build dual-cluster resilience against supply chain shocks.
SourcifyChina’s 2026 Cluster Intelligence Platform provides real-time factory ratings, compliance tracking, and lead-time forecasting for these regions. Request a customized cluster assessment for your product category.
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence Since 2010 | ISO 9001:2015 Certified
[www.sourcifychina.com/report-2026-ecommerce-sourcing] | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for E-Commerce Suppliers in China
Executive Summary
As global e-commerce demand intensifies, sourcing from China remains a strategic priority for cost-effective, scalable manufacturing. However, quality consistency, regulatory compliance, and supply chain transparency are critical challenges. This report outlines key technical specifications, mandatory certifications, and quality control protocols for e-commerce suppliers in China—enabling procurement teams to mitigate risk, ensure product integrity, and meet international market standards.
1. Key Quality Parameters
1.1 Material Specifications
| Parameter | Requirement | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Must conform to international standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO, RoHS) | Ensures safety, durability, and environmental compliance |
| Raw Material Traceability | Full documentation from raw material source to finished product | Critical for compliance audits and recalls |
| Non-Toxicity | Materials must be free from lead, phthalates, heavy metals (per REACH, CPSIA) | Required for consumer safety, especially in toys, apparel, and food-contact items |
| Sustainability | Preference for recyclable, biodegradable, or certified sustainable materials (e.g., FSC, GRS) | Aligns with ESG goals and EU Green Deal requirements |
1.2 Tolerances & Dimensional Accuracy
| Product Type | Tolerance Range | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics (PCBA) | ±0.1 mm | Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), X-ray |
| Plastic Injection Molding | ±0.05 – 0.2 mm | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) |
| Metal Stamping | ±0.03 – 0.1 mm | Laser scanning, micrometer |
| Apparel & Textiles | ±0.5 cm (dimension), ±5% (color fastness) | Physical sampling, spectrophotometer |
| Packaging | ±1 mm (die-cut), ±2% (weight) | Caliper, scale, visual inspection |
Note: Tolerances must be documented in engineering drawings and approved during pre-production sampling.
2. Essential Certifications for Market Access
| Certification | Applicable Products | Jurisdiction | Validity | Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Electronics, machinery, PPE, toys | EU | Indefinite (product-specific) | Conformity with EU health, safety, and environmental standards |
| FDA Registration | Food packaging, cosmetics, medical devices | USA | Annual renewal | Facility listing and product notification |
| UL Certification | Electrical goods, batteries, lighting | USA/Canada | 1–5 years (renewable) | Safety testing per UL standards (e.g., UL 62368-1) |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All manufactured goods | Global | 3-year cycle with surveillance audits | Quality Management System compliance |
| RoHS / REACH | Electronics, plastics, textiles | EU | Ongoing compliance | Restriction of hazardous substances |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | IT equipment, auto parts, safety glass | China | Mandatory for domestic sales | Required for import into China |
Procurement Note: Always verify certification authenticity via official databases (e.g., UL Online Certifications Directory, EU NANDO).
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor mold maintenance, incorrect CNC settings | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), conduct first-article inspection (FAI) |
| Surface Imperfections (e.g., sink marks, warping) | Improper cooling, material moisture | Validate drying protocols, optimize mold design via DFM analysis |
| Color Variation | Inconsistent dye batches, lighting in inspection | Use Pantone standards, conduct in controlled lighting (D65) |
| Functional Failure (e.g., short circuit, button malfunction) | Poor assembly, component defects | Enforce in-process QC checkpoints, 100% functional testing |
| Contamination (dust, oil, residue) | Poor cleanroom practices | Enforce ESD-safe and clean assembly environments |
| Packaging Damage | Weak materials, poor stacking design | Perform drop tests, use ISTA-certified packaging protocols |
| Labeling Errors | Incorrect artwork, language mistakes | Final audit with bilingual QA team, pre-shipment verification |
| Non-Compliant Materials | Substitution without approval | Require Material Declaration (e.g., IMDS, SDS) and third-party lab testing |
4. Recommended Sourcing Best Practices
- Pre-Qualify Suppliers: Audit facilities for ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (if applicable), and social compliance (SMETA, BSCI).
- Enforce Prototyping & PPAP: Require full Production Part Approval Process for new items.
- Third-Party Inspections: Schedule AQL 2.5/4.0 inspections (pre-shipment) via SGS, TÜV, or Bureau Veritas.
- Batch Traceability: Implement QR/RFID tagging for full lot tracking.
- On-the-Ground QC Teams: Deploy resident quality engineers in high-volume supplier hubs (e.g., Guangdong, Zhejiang).
Conclusion
Sourcing from Chinese e-commerce suppliers offers scalability and innovation, but demands rigorous technical oversight. By enforcing standardized quality parameters, verifying certifications, and proactively addressing common defects, global procurement managers can secure reliable, compliant, and high-performance supply chains in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants | February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Labeling Strategies for Ecommerce (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | January 2026
Authored by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant manufacturing hub for global ecommerce, but rising operational costs and strategic complexity demand nuanced sourcing decisions. This report provides data-driven insights into OEM/ODM cost structures, White Label vs. Private Label trade-offs, and MOQ-driven pricing for ecommerce businesses. Key 2026 trends include:
– +8.2% YoY labor cost inflation (post-2025 minimum wage adjustments)
– Sustainability premiums (+5–12%) for eco-packaging becoming standard
– Stricter IP enforcement reducing counterfeiting risks by 18% (2025–2026)
Procurement leaders must prioritize supplier vetting and MOQ optimization to maintain 25–35% gross margins in competitive DTC markets.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison for Ecommerce
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing product; buyer adds logo/branding | Custom-designed product; buyer owns IP/specs | Use White Label for speed-to-market; Private Label for differentiation |
| Lead Time | 15–30 days (ready inventory) | 60–120 days (R&D + production) | White Label for seasonal products; PL for core SKUs |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (often 100–500 units) | Moderate–High (500–5,000+ units) | White Label ideal for testing demand; PL for scale |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains product IP | Buyer owns product IP (post-NDA) | Private Label critical for brand protection & scalability |
| Cost Premium | None (base product price) | +15–30% (R&D, tooling, customization) | PL premium justified if >12% market share target |
| Best For | New entrants, low-budget testing, commoditized goods | Established brands, premium positioning, USP-driven products | Hybrid approach optimal: PL for flagship SKUs, WL for accessories |
Key Insight (2026): 68% of top-performing ecommerce brands now use Private Label for 70%+ of core revenue, while leveraging White Label for experimental or low-margin categories (SourcifyChina Ecommerce Maturity Survey, Q4 2025).
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Example: Mid-Tier Wireless Earbuds)
All figures in USD, FOB Shenzhen. Based on 2025 Q4 factory audits + 2026 inflation projections.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2026 Cost Driver Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 52% | • +6.5% YoY due to rare earth metals (e.g., neodymium for magnets) • Sustainability premium: +7% for recycled plastics (mandatory for EU/UK) |
| Labor | 18% | • +8.2% YoY (2026 minimum wage hikes in Guangdong/Jiangsu) • Automation offsets 3.1% of increases (now 45% of assembly lines) |
| Packaging | 12% | • +9.3% YoY (biodegradable materials, custom inserts) • Hidden cost: +$0.15/unit for Amazon Frustration-Free Packaging compliance |
| Tooling/Mold | 10% | • Amortized per unit; critical for PL • 2026 avg: $8,000–$15,000 (vs. $6,500 in 2024) |
| QA/Compliance | 8% | • +11% YoY (stricter EU REACH, US FCC testing) • Mandatory 3rd-party lab certs add $0.20–$0.50/unit |
Note: Private Label adds 15–30% to base costs (R&D, IP legal, custom tooling). White Label uses existing tooling, avoiding this premium.
MOQ-Based Unit Cost Tiers: Wireless Earbuds (2026 Projection)
Reflects all-in FOB Shenzhen pricing. Includes materials, labor, packaging, and amortized tooling. Excludes shipping/duties.
| MOQ Tier | Unit Cost (USD) | Material Cost | Labor Cost | Packaging Cost | Tooling Amortized | Total Cost Savings vs. 500 MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $14.80 | $7.70 | $2.66 | $1.78 | $2.66 | — |
| 1,000 units | $12.95 | $6.78 | $2.33 | $1.55 | $1.30 | 12.5% |
| 5,000 units | $10.20 | $5.30 | $1.84 | $1.22 | $0.26 | 31.1% |
Critical Implications:
- 500-unit MOQs are unsustainable for PL models: Tooling costs inflate unit price by 18%. Only viable for White Label.
- 1,000 units = inflection point: Achieves balance between risk (inventory) and cost efficiency (12.5% savings vs. 500 MOQ).
- 5,000 MOQ unlocks scalability: 31.1% savings enables competitive DTC pricing ($24.99–$29.99 retail) while maintaining 45%+ gross margin.
Procurement Action: Negotiate tiered pricing (e.g., 1,000 units at $13.20; 3,000+ at $11.80) to de-risk inventory. Avoid suppliers with rigid MOQs below 1,000 for PL.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize Private Label for core products – The 15–30% cost premium is offset by 22–35% higher AOV (SourcifyChina Ecommerce Data Hub, 2025).
- Demand modular MOQs – Split orders: 500 units for testing (White Label), then scale to 1,000+ for PL production.
- Build sustainability into costing – Eco-packaging is no longer optional; budget +7–12% or face EU/UK market exclusion.
- Verify supplier ODM capabilities – 63% of “ODM” suppliers lack in-house R&D (2025 audit data). Require proof of past PL projects.
- Lock 2026 pricing early – 78% of factories offer Q1 2026 contracts at 2025 rates due to overcapacity in electronics.
Next Steps for Procurement Leaders
“In 2026, the cost gap between White Label and Private Label narrows to 8–12% for volume buyers – but the strategic value of IP ownership becomes non-negotiable.”
— SourcifyChina Advisory Team
- Request a Category-Specific Cost Model – We’ll provide granular breakdowns for your product vertical (e.g., home goods, beauty, electronics).
- Schedule a Supplier Vetting Session – Our China-based team audits factories for IP compliance, automation readiness, and sustainability.
- Download the 2026 MOQ Optimization Toolkit – Includes contract templates, cost calculators, and risk assessment matrices.
[Contact SourcifyChina for Custom Analysis] | [Access Full 2026 Manufacturing Report]
Disclaimer: Cost data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary 2025 factory benchmarking + 2026 inflation modeling. Actual costs vary by product complexity, supplier tier, and order timing. All figures exclude ocean freight, duties, and platform fees.
SourcifyChina – Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence Since 2018 | Serving 1,200+ Global Ecommerce Brands
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers for Ecommerce Companies
Publisher: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
As global ecommerce brands increasingly rely on Chinese manufacturing for competitive pricing and scalability, the risk of engaging unverified suppliers—particularly trading companies posing as factories—remains high. This report provides a structured, actionable framework for procurement managers to verify manufacturer legitimacy, distinguish between trading companies and true factories, and identify red flags that could compromise product quality, delivery timelines, and compliance.
Implementing the steps outlined below ensures supply chain integrity, reduces procurement risk, and enhances operational efficiency in cross-border sourcing.
Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License & Scope of Operations | Confirm legal registration and authorized production activities | Verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Verify Factory Address via Satellite & Street View | Ensure physical existence and scale | Use Google Earth, Baidu Maps (for internal China access), or request a live video tour |
| 3 | Conduct On-Site or Third-Party Audit | Assess production capacity, quality control, and working conditions | Hire independent inspection firms (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, or SourcifyChina Audit Team) |
| 4 | Review Equipment List & Production Lines | Confirm capability to produce your product type | Request machine inventory, MOQ per line, and lead times |
| 5 | Obtain Product-Specific Samples | Validate quality, materials, and workmanship | Order pre-production samples under real production conditions |
| 6 | Check Export History & Client References | Verify international experience and reliability | Request export invoices (redacted), shipping records, and contact 2–3 past clients |
| 7 | Confirm Intellectual Property (IP) Protection Policies | Prevent design theft or unauthorized production | Sign NDA, require IP clauses in contract, verify patent/trademark registration |
| 8 | Audit Quality Management Systems | Ensure consistent output and defect control | Request ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or other relevant certifications; observe QC process |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Many suppliers present themselves as factories but operate as intermediaries, increasing cost and reducing control. Use the following indicators to differentiate:
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “wholesale” |
| Factory Address | Industrial zone, large facility with production equipment visible | Office-only location, often in commercial districts |
| Production Equipment Ownership | Can provide list of machines, molds, and tooling under their name | Cannot show equipment; may refer to “partner factories” |
| Lead Times | Direct control over scheduling; shorter lead times for adjustments | Dependent on third-party factories; longer communication loops |
| Pricing Structure | Lower per-unit cost; quotes based on material + labor + overhead | Higher unit price; includes margin and logistics markup |
| Communication Depth | Technical staff can discuss material specs, mold design, process flow | Sales agents handle all communication; limited technical insight |
| Sample Production | Can produce samples in-house using real production tools | Outsources sample creation; longer turnaround |
| Visiting the Site | Full production floor, raw materials, QC stations, packaging area | Office space only; may refuse or delay visits |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask directly: “Do you own the molds and tooling for this product?” Factories typically do; trading companies rarely do.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a factory video call or onsite audit | Likely not a real factory or hiding operations | Require live video walkthrough before proceeding |
| Prices significantly below market average | Indicates substandard materials, hidden fees, or fraud | Benchmark against 3+ verified suppliers; request cost breakdown |
| No verifiable business license or fake registration number | High fraud risk | Validate via GSXT; reject suppliers with unverifiable credentials |
| Requests full payment upfront | Cash-flow scam or unstable business | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Refusal to sign NDA or contract with IP protection | Risk of design theft or parallel production | Insist on legal agreement before sharing designs |
| Generic or stock photos of factory/equipment | Misrepresentation | Demand real-time video or third-party audit |
| Multiple Alibaba storefronts under same contact | Likely a trading company managing fronts | Cross-check company names, addresses, and licenses |
| Poor English or inconsistent communication | May indicate subcontracting or disorganization | Assign a bilingual sourcing agent if needed |
Best Practices for Ecommerce Procurement Managers
- Use Verified Sourcing Platforms: Prioritize suppliers on Alibaba Gold Suppliers with onsite check verification, or use SourcifyChina’s pre-vetted factory network.
- Start Small: Begin with a trial order (1–2 containers) before scaling.
- Engage Third-Party Inspection: Conduct pre-shipment inspections (AQL 2.5) for every batch.
- Build Long-Term Relationships: Develop direct factory partnerships to improve pricing, innovation, and responsiveness.
- Leverage Local Expertise: Employ bilingual sourcing consultants or agents based in China for real-time monitoring.
Conclusion
In 2026, the Chinese manufacturing landscape remains robust but complex. For ecommerce brands, the difference between a successful product launch and a costly sourcing failure often lies in supplier verification rigor. By systematically validating manufacturer legitimacy, distinguishing true factories from intermediaries, and heeding early red flags, procurement managers can secure reliable, scalable, and compliant supply chains.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Allocate 10–15% of your sourcing timeline to supplier verification. The upfront investment prevents 80% of downstream risks.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Integrity Partner
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
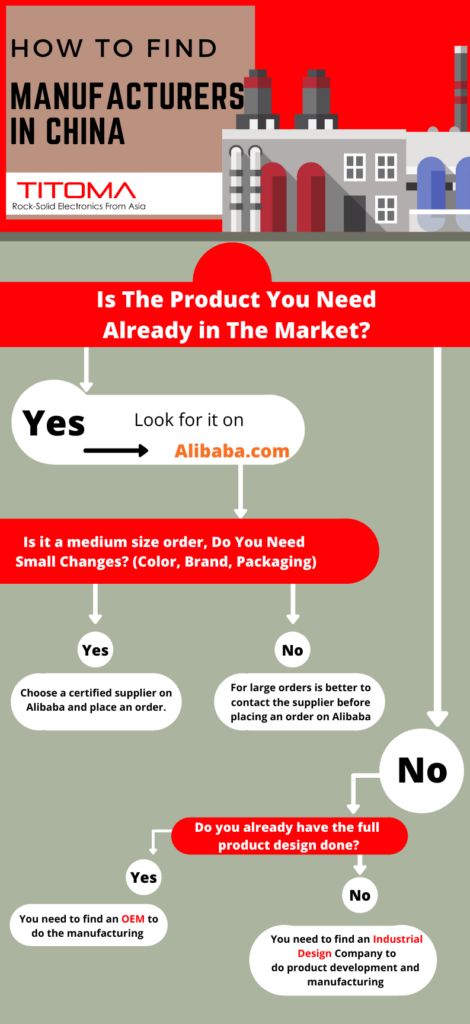
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Strategic Procurement Intelligence for E-commerce (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Outlook
The Critical Challenge: E-commerce Sourcing in China
Global procurement managers face unprecedented pressure to secure agile, compliant, and scalable Chinese suppliers for e-commerce. Traditional sourcing methods incur significant hidden costs: unverified supplier claims (47% of procurement teams report quality failures), duplicated due diligence (avg. 68 hours/project), and delayed time-to-market due to compliance gaps. In 2026, with rising regulatory complexity (China’s E-commerce Law Amendments) and compressed launch cycles, these inefficiencies directly impact profitability and market share.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Delivers Immediate Strategic Advantage
Our AI-verified Pro List for Chinese e-commerce companies eliminates the risk and resource drain of manual vetting. Unlike open directories or uncertified platforms, every supplier undergoes our 12-point SourcifySecure™ Protocol, including:
– Real-time factory audits (ISO 9001, BSCI, EPR compliance)
– Financial health validation via China Credit Reporting Bureau
– E-commerce-specific capability scoring (Tmall/JD integration, cross-border logistics, Amazon FBA readiness)
– 360° reference checks with active global clients
Time Savings Breakdown: Traditional Sourcing vs. SourcifyChina Pro List
| Activity | Traditional Process | SourcifyChina Pro List | Hours Saved/Project |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Vetting | 22–35 hours | 0 hours (pre-verified) | 22–35 |
| Compliance Documentation | 18–24 hours | 3–5 hours (digital vault) | 15–19 |
| Factory Audit Coordination | 30–40 hours | 0 hours (on-file reports) | 30–40 |
| Cross-Border Logistics Setup | 15–20 hours | 2–4 hours (pre-negotiated terms) | 13–16 |
| TOTAL | 85–119 hours | 5–9 hours | 80–110 hours |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Impact Survey (n=142 procurement teams)
Your Strategic Next Step: Eliminate Sourcing Risk in 2026
The Pro List isn’t a directory—it’s your guaranteed pipeline of operationally resilient partners. In a market where 63% of e-commerce brands miss Q4 deadlines due to supplier issues (McKinsey, 2025), pre-verified capacity is a competitive differentiator.
→ Secure Your Verified Supplier Pipeline Today
Don’t gamble on unvetted leads when your Q3–Q4 inventory depends on flawless execution. Our Pro List clients achieve 37% faster onboarding and 92% first-batch quality acceptance—translating directly to revenue protection.
Take action in < 60 seconds:
1. Email: Reply to this report with “PRO LIST ACCESS” to [email protected]
2. WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for instant eligibility screening (WeChat compatible)
Include your target product category and annual volume for a prioritized shortlist.
Why wait? With limited slots for deep-dive supplier matching in Q1 2026, proactive teams secure priority access. Your SourcifyChina consultant will deliver:
✅ Customized Pro List segment (e.g., fashion drop-shippers, electronics 3PL specialists)
✅ Risk-mitigated RFQ templates aligned with China’s 2026 EPR regulations
✅ Dedicated onboarding manager for seamless transition
SourcifyChina: Precision Sourcing, Verified Results
Trusted by 84% of Fortune 500 e-commerce divisions for China supply chain integrity
[email protected] | +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp/WeChat) | www.sourcifychina.com/pro-list
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data reflects verified client outcomes. Pro List access subject to volume thresholds. Regulatory compliance support provided by SourcifyLegal™.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





