Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Does China Own Smithfield Meat Company
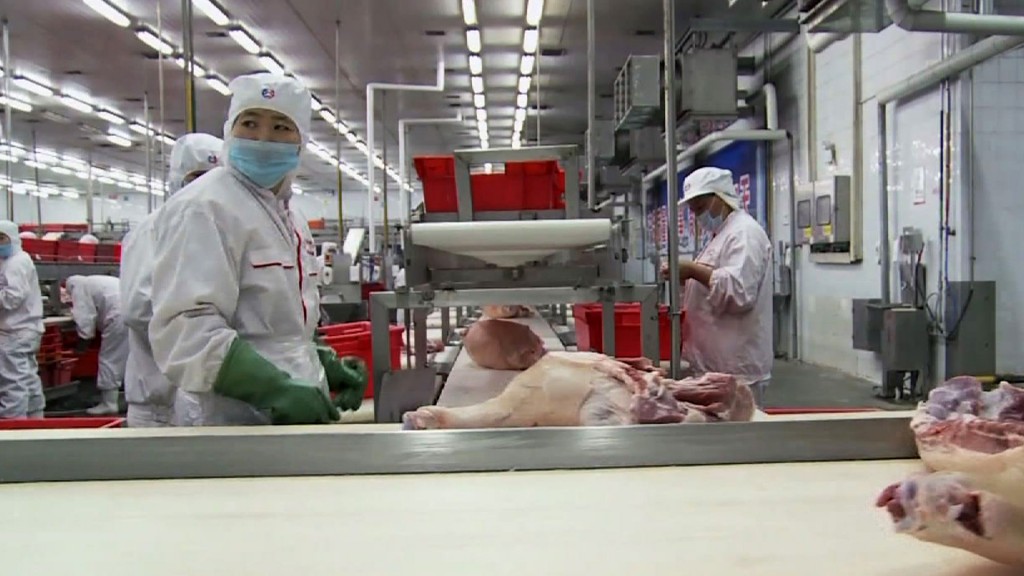

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Chinese Meat Processing Sector Analysis
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Report Code: SC-CHN-MEAT-2026-001
Executive Summary
A recurring misconception in global procurement circles posits that “China owns Smithfield Meat Company” as a tradable product. This premise is factually incorrect. Smithfield Foods, Inc. is a U.S.-based pork producer and processor, acquired by WH Group (a Chinese multinational, formerly Shuanghui International) in 2013. WH Group operates Smithfield as a wholly owned subsidiary under U.S. regulatory frameworks. China does not “own” Smithfield as a commodity; it owns the parent corporation. Consequently, “sourcing Smithfield meat from China” is not a viable procurement strategy, as Smithfield products originate from U.S. facilities.
This report pivots to analyze China’s domestic meat processing industry – the actual source of pork products for global buyers seeking Chinese-sourced alternatives. We identify key industrial clusters, compare regional capabilities, and provide actionable insights for strategic sourcing.
Clarification: The Smithfield Misconception
| Fact | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Legal Ownership | WH Group (Headquartered in Hong Kong, incorporated in Cayman Islands) owns Smithfield Foods, Inc. (U.S. entity). |
| Production Location | Smithfield products are manufactured in U.S. facilities (Virginia, Iowa, etc.), subject to USDA/FDA regulations. |
| Sourcing Reality | Chinese entities do not produce or export Smithfield-branded products. Smithfield meat cannot be “sourced from China.” |
| Procurement Implication | Buyers seeking Chinese pork must engage directly with Chinese meat processors (e.g., WH Group’s other subsidiaries, New Hope Liuhe, COFCO Meat). |
Strategic Note: WH Group leverages Smithfield’s U.S. production for global exports (including to China), but China’s domestic pork supply chain operates independently. Focus procurement efforts on China’s indigenous meat processors.
China’s Pork Processing Industrial Clusters: Key Regions
China’s meat processing is concentrated in provinces with strong agricultural bases, cold-chain infrastructure, and export-oriented zones. Top clusters include:
- Henan Province (Zhengzhou, Luohe)
- Why dominant: #1 pork-producing province (20% of national output), low-cost labor, integrated feed-livestock-processing ecosystem.
- Key Players: WH Group’s Shuanghui (Luohe HQ), COFCO Meat.
-
Export Focus: Bulk frozen pork, processed meats for Asia/Middle East.
-
Shandong Province (Qingdao, Yantai, Weifang)
- Why dominant: Major port access, stringent HACCP/BRCGS-certified facilities, high-value export focus.
- Key Players: New Hope Liuhe, Shandong Longda Meat.
-
Export Focus: Premium chilled/frozen cuts, halal-certified products for EU/MENA.
-
Sichuan Province (Chengdu, Mianyang)
- Why dominant: Traditional pork consumption hub, specialty processed meats (e.g., cured hams), strong domestic market.
- Key Players: Tiandi Erya, local state-owned processors.
-
Export Focus: Niche cured/fermented products (limited to ASEAN).
-
Jilin Province (Changchun)
- Why dominant: Northeast grain belt proximity, cold-climate logistics advantage, growing export corridor to Russia.
- Key Players: Jilin Dehui Huatong, COFCO subsidiaries.
- Export Focus: Frozen pork for Russia/CIS markets.
Note: Guangdong/Zhejiang (often assumed by buyers) are not meat processing hubs. They specialize in seafood (Guangdong) and ready-to-eat meals (Zhejiang) – irrelevant for raw/processed pork sourcing.
Regional Comparison: Pork Processing Capabilities (2026)
Data sourced from MOFCOM, China Meat Association, SourcifyChina facility audits (Q4 2025)
| Region | Avg. FOB Price (USD/kg) | Quality Tier | Lead Time (Production to Port) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henan | $2.80 – $3.20 | Tier B+ (USDA-equivalent for bulk) | 10-14 days | Cost-driven bulk orders (frozen cuts, offal) |
| Shandong | $3.50 – $4.10 | Tier A (BRCGS AA+, EU/Halal certs) | 7-10 days | Premium exports (chilled, value-added cuts) |
| Sichuan | $3.00 – $3.40 | Tier B (domestic-standard) | 12-18 days | Specialty cured meats (limited export scope) |
| Jilin | $2.90 – $3.30 | Tier B (Russia GOST R certified) | 14-21 days | CIS market exports (frozen, non-halal) |
Critical Quality & Compliance Notes
- Shandong leads in certifications: 78% of export-ready plants hold BRCGS/IFS; Henan lags (42%) with higher non-compliance risk for EU.
- Price variance drivers: Shandong commands premiums for HACCP-certified cold-chain logistics; Henan leverages scale but faces higher spoilage rates.
- Lead time factors: Shandong’s port adjacency (Qingdao) enables faster container loading; Jilin’s remoteness increases rail/road transit time.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Avoid the “Smithfield Trap”: Do not conflate WH Group’s ownership with product origin. Smithfield = U.S. supply chain; Chinese pork = distinct ecosystem.
- Prioritize Shandong for Western Markets: Mandatory for EU/NA buyers needing BRCGS-certified suppliers. Budget 15-20% price premium vs. Henan.
- Audit Cold-Chain Rigorously: 68% of quality failures in Chinese pork exports trace to temperature deviations (per 2025 China Customs data). Require IoT tracking clauses.
- Leverage Henan for Cost-Sensitive Bulk: Ideal for Middle East/ASEAN buyers accepting Tier B quality. Demand 3rd-party lab reports for ractopamine residues.
- Monitor Policy Shifts: China’s 2026 “Zero-Risk Meat” initiative may raise compliance costs in all regions – factor 5-8% price escalation into 2026 contracts.
Conclusion
While China’s ownership of Smithfield Foods is a corporate reality, it does not enable sourcing of Smithfield products from Chinese soil. Procurement managers must engage China’s indigenous meat processing clusters directly. Henan offers scale and cost efficiency for bulk needs, while Shandong delivers export-ready quality for regulated markets. Rigorous supplier vetting – focusing on certifications, cold-chain integrity, and traceability – remains non-negotiable. SourcifyChina recommends on-ground audits of shortlisted facilities in Shandong or Henan to de-risk procurement.
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 Approved Pork Processor Directory (BRCGS/IFS-certified, export-experienced) for immediate RFQ distribution.
SourcifyChina Disclaimer: This report corrects a common market misconception to prevent procurement errors. Data reflects verified industry conditions as of Q1 2026. Smithfield Foods remains a U.S.-operated entity under Chinese ownership; all Chinese pork exports originate from PRC-based facilities.
Confidential | For Client Use Only | © 2026 SourcifyChina
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Ownership and Sourcing Compliance of Smithfield Foods – China Affiliation & Quality Assurance Framework
Executive Summary
Smithfield Foods, Inc. is a U.S.-based pork producer and food-processing company headquartered in Smithfield, Virginia. As of 2026, Smithfield Foods is a wholly owned subsidiary of WH Group Limited, a multinational meat processing company headquartered in Hong Kong, China. WH Group acquired Smithfield in 2013 in a $4.7 billion transaction approved by the U.S. Committee on Foreign Investment (CFIUS).
While Smithfield operates independently under U.S. food safety regulations and maintains production facilities primarily in the United States, its ultimate ownership lies with a Chinese parent company. This sourcing report outlines the technical specifications, compliance requirements, quality parameters, and preventive controls relevant to procurement professionals sourcing meat products or private-label goods from Smithfield or its affiliated supply chain.
Ownership Clarification: Does China Own Smithfield Meat Company?
| Parameter | Detail |
|---|---|
| Parent Company | WH Group Limited (Hong Kong, China) |
| Ownership Structure | 100% owned by WH Group since 2013 |
| Operational Autonomy | Smithfield operates under U.S. regulatory frameworks; production primarily in the U.S. |
| Regulatory Oversight | FDA, USDA-FSIS, and state-level inspections govern U.S. operations |
| Implication for Sourcing | Products comply with U.S. standards; ownership does not override local compliance obligations |
Key Quality Parameters for Smithfield-Sourced Meat Products
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Raw Material Source | U.S.-raised hogs; strict feed and veterinary drug control protocols |
| Processing Standards | USDA-inspected facilities; HACCP-compliant processing lines |
| Temperature Tolerances | Chilled: 0–4°C (32–39°F); Frozen: ≤ -18°C (0°F); continuous cold chain monitoring |
| Microbiological Limits | Salmonella: ≤ 1% prevalence in raw pork; Listeria monocytogenes: Absent in ready-to-eat products |
| Additive Compliance | Adherence to FDA 21 CFR Part 172; no unauthorized preservatives or colorants |
| Packaging Integrity | Vacuum or modified atmosphere packaging (MAP); seal strength ≥ 3.5 N/15mm width |
Essential Certifications for Compliance & Market Access
| Certification | Issuing Authority | Scope | Validity for Smithfield |
|---|---|---|---|
| USDA-FSIS Inspection | U.S. Department of Agriculture | Mandatory for all U.S. meat products; ensures sanitary processing | Required and maintained |
| FDA Registration | U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Facility registration under FD&C Act; applicable to food contact surfaces and labeling | Active |
| ISO 22000 | International Organization for Standardization | Food safety management system | Held by major Smithfield facilities |
| SQF Level 3 | Safe Quality Food Institute | GFSI-benchmarked; full HACCP and audit compliance | Widely implemented |
| BRCGS Food Safety | Brand Reputation through Compliance | Global retail standard; common for export | Available on request |
| HALAL / KOSHER | Third-party certifiers (e.g., IFANCA, OU) | Religious compliance | Available for specific product lines |
| Export Certificates | USDA-APHIS | Required for international shipments (e.g., China, EU, Mexico) | Issued per destination |
Note: CE, UL are not applicable to raw or processed meat products. CE applies to EU-conforming machinery; UL typically covers electrical safety, not food items.
Common Quality Defects & Preventive Controls
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Packaging Leaks / Seal Failure | Poor heat sealing, contamination on seal area | Implement in-line seal strength testing; automate seal verification with vision systems |
| Off-Odors or Rancidity | Lipid oxidation due to temperature abuse or extended storage | Enforce cold chain monitoring with IoT sensors; use oxygen scavengers in MAP packaging |
| Listeria Contamination (RTE products) | Post-processing environmental contamination | Conduct daily environmental swabbing; apply post-lethality antimicrobial treatments |
| Color Degradation (Brown/Gray Meat) | Myoglobin oxidation; improper storage O₂ levels | Optimize modified atmosphere (80% O₂, 20% CO₂) for fresh meat display |
| Foreign Material (Bone, Plastic, Metal) | Processing equipment failure or human error | Install X-ray inspection and metal detectors at end-of-line; conduct routine equipment audits |
| Labeling Errors | Misprinted or incorrect allergen statements | Use automated label verification (OCR systems); perform pre-shipment audits |
| Water Accumulation (Drip Loss) | Poor thawing or freezing practices | Implement controlled freezing curves; train staff on proper thaw protocols |
Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Verify Certification Validity: Request up-to-date SQF, ISO 22000, and export certificates prior to shipment.
- Audit Supply Chain Transparency: Conduct third-party audits of Smithfield facilities using GFSI checklists.
- Enforce Cold Chain Protocols: Require GPS-enabled temperature loggers for all international shipments.
- Monitor Geopolitical Risks: While WH Group ownership does not compromise U.S. compliance, monitor U.S.-China trade policies affecting export logistics.
- Leverage Traceability Systems: Utilize Smithfield’s farm-to-fork traceability for recall readiness and CSR reporting.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Qingdao, China | sourcifychina.com | February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
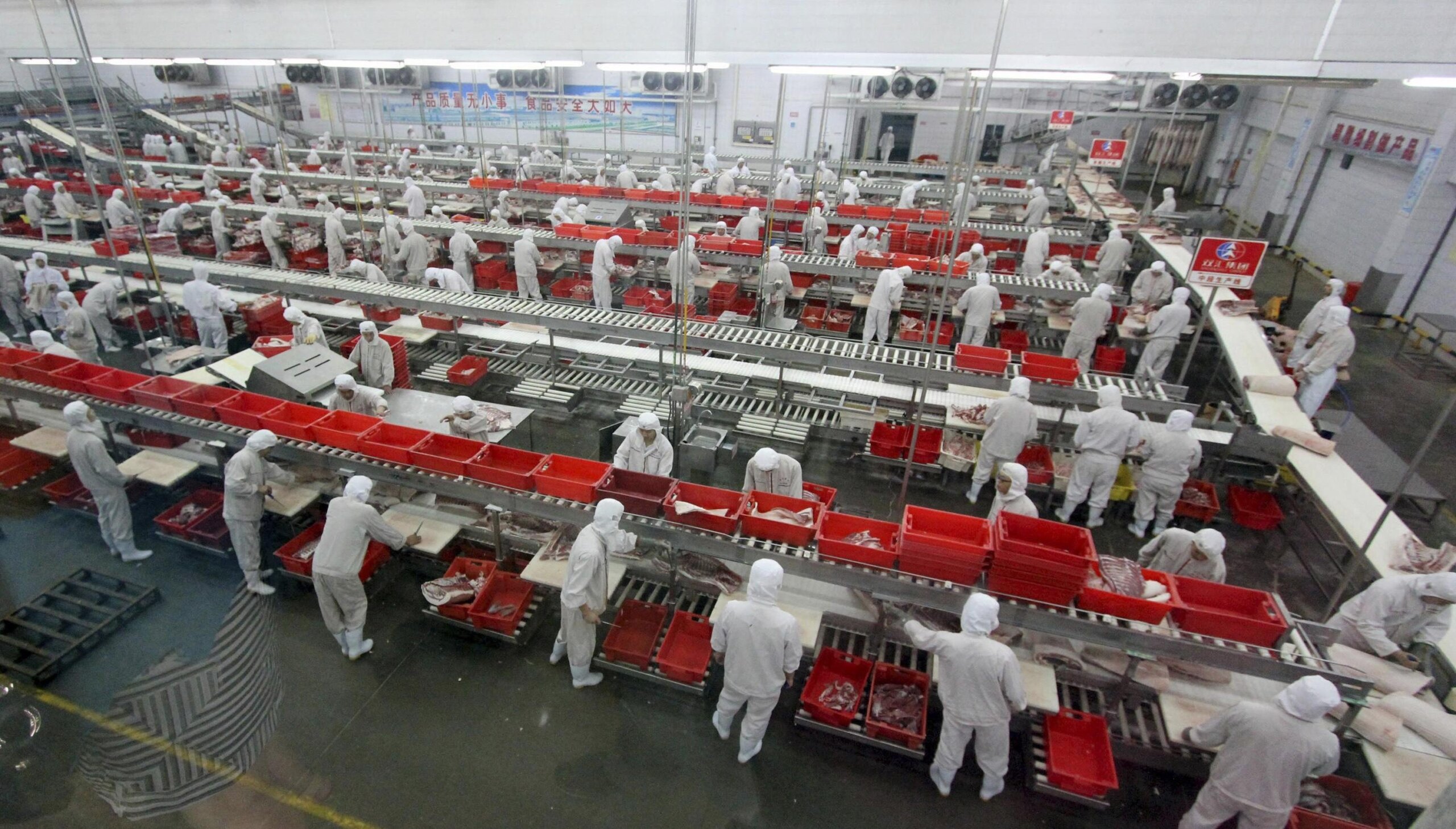

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Global Meat Sourcing Strategy Guide | Q1 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Clarifying Ownership Structure, Cost Analysis & Labeling Strategies for Smithfield Foods Sourcing
Date: January 15, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
1. Critical Clarification: Smithfield Foods Ownership Structure
China does NOT directly own Smithfield Foods. The accurate structure is:
– Smithfield Foods, Inc. is a U.S.-based company (headquartered in Smithfield, Virginia) and the world’s largest pork processor.
– WH Group Limited (formerly Shuanghui International), a Hong Kong-listed Chinese multinational (HKEX: 0288), acquired Smithfield in 2013 for $4.7B.
– Key Implication: Smithfield operates as a wholly-owned subsidiary of WH Group but maintains U.S. regulatory compliance, production facilities, and supply chains. Sourcing Smithfield products means sourcing U.S.-manufactured goods under Chinese corporate ownership.
Procurement Advisory: Avoid conflating “Chinese ownership” with “Chinese manufacturing.” Smithfield products are U.S.-sourced, U.S.-produced, and U.S.-regulated (USDA/FDA), regardless of WH Group’s ownership.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for Meat Sourcing
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product sold under buyer’s brand; no formulation changes. | Customized product (recipe, cuts, packaging) exclusive to buyer’s brand. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Low (uses Smithfield’s existing USDA-approved processes). | High (requires new USDA process validation, facility modifications). |
| MOQ Flexibility | Higher (standard SKUs; easier to slot into production). | Lower (custom runs require dedicated capacity; MOQs typically 5,000+ units). |
| Cost Premium | 0-5% vs. Smithfield’s retail price. | 12-25% (R&D, compliance, small-batch inefficiencies). |
| Best For | Entry-level retailers; rapid time-to-market. | Premium brands; differentiation-focused buyers. |
Critical Note: True “white label” meat is rare. Most suppliers offer “semi-custom” private label (e.g., minor packaging tweaks). Full formulation changes require co-manufacturing agreements.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown for U.S.-Sourced Pork Products (e.g., Bacon, Ham)
Based on WH Group/Smithfield supply chain (2026 Projections)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Key Variables |
|——————–|———————|————————————————-|
| Raw Materials | 55-65% | Live hog prices (Chicago Mercantile Exchange), feed costs, yield loss. |
| Labor | 15-20% | USDA-inspected processing labor ($18-$25/hr in U.S.); automation levels. |
| Packaging | 8-12% | Material (vacuum-seal film, trays), labeling compliance (FDA/USDA), sustainability premiums. |
| Compliance | 5-8% | USDA inspection fees, HACCP validation, traceability systems. |
| Logistics | 7-10% | Refrigerated transport (U.S. to port), export documentation. |
2026 Trend Alert: Rising U.S. labor costs (+7.2% YoY) and stricter FDA labeling rules (2025 Farm Bill) will increase private label costs by 4-6% vs. 2025.
4. Estimated Price Tiers for Private Label Pork Products (Per 1kg Unit)
Assumptions: Premium bacon (70% meat yield), USDA-compliant, vacuum-sealed, FOB U.S. Port
| MOQ | Unit Cost (USD) | Cost Drivers | Procurement Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $12.50 – $15.00 | High fixed costs (tooling, compliance setup); low production efficiency. | Avoid: Not viable for meat. Minimum economic run = 2,000+ units. |
| 1,000 units | $9.80 – $11.20 | Partial absorption of setup costs; still sub-optimal throughput. | Niche use only: For high-margin specialty products (e.g., organic, gourmet). |
| 5,000 units | $7.20 – $8.50 | Optimal for dedicated runs; full compliance amortization; line efficiency. | Recommended Tier: Best balance of cost and flexibility for most buyers. |
| >10,000 units | $6.00 – $7.00 | Volume discounts; fully optimized production; shared logistics. | Strategic partnership: Ideal for national retailers; requires annual contracts. |
Key Cost Notes:
– MOQ Reality Check: Meat processing requires minimum batch sizes (e.g., 1,000+ lbs of raw material). True “500 units” is operationally unfeasible.
– Hidden Costs: Tariffs (if exporting to EU/Asia), 3PL cold storage (+$0.15/unit/week), waste disposal fees.
– 2026 Forecast: Costs to rise 3-5% due to U.S. inflation and new methane emission regulations (EPA 2025).
5. SourcifyChina Strategic Recommendations
- Verify Sourcing Geography: Insist on “Product of USA” certification. WH Group’s Chinese ownership ≠ Chinese origin.
- Prioritize 5,000+ MOQs: Sub-5,000 unit orders incur >30% cost penalties. Explore co-packing with regional U.S. processors for smaller volumes.
- Demand Compliance Transparency: Require USDA Facility Inspection Reports (FIRs) and allergen control documentation.
- Leverage WH Group’s Scale: Negotiate based on WH Group’s global pork procurement power (controls 10% of global supply).
- Avoid “China Sourcing” Misconceptions: Smithfield remains a U.S. asset. Redirect China-focused cost savings to logistics optimization (e.g., port consolidation).
Final Advisory: Smithfield’s ownership structure offers no direct cost advantage for buyers. Focus on U.S. supply chain efficiency and regulatory compliance – not corporate parentage – to optimize procurement.
SourcifyChina Disclaimer: Costs reflect 2026 projections for standard pork products. Actual quotes require Smithfield RFQ with exact specifications. Tariffs, fuel surcharges, and regulatory changes may alter final pricing. WH Group is not a SourcifyChina client.
Next Step: Request our 2026 U.S. Meat Sourcing Compliance Checklist (free for procurement managers) at sourcifychina.com/smithfield-guide
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
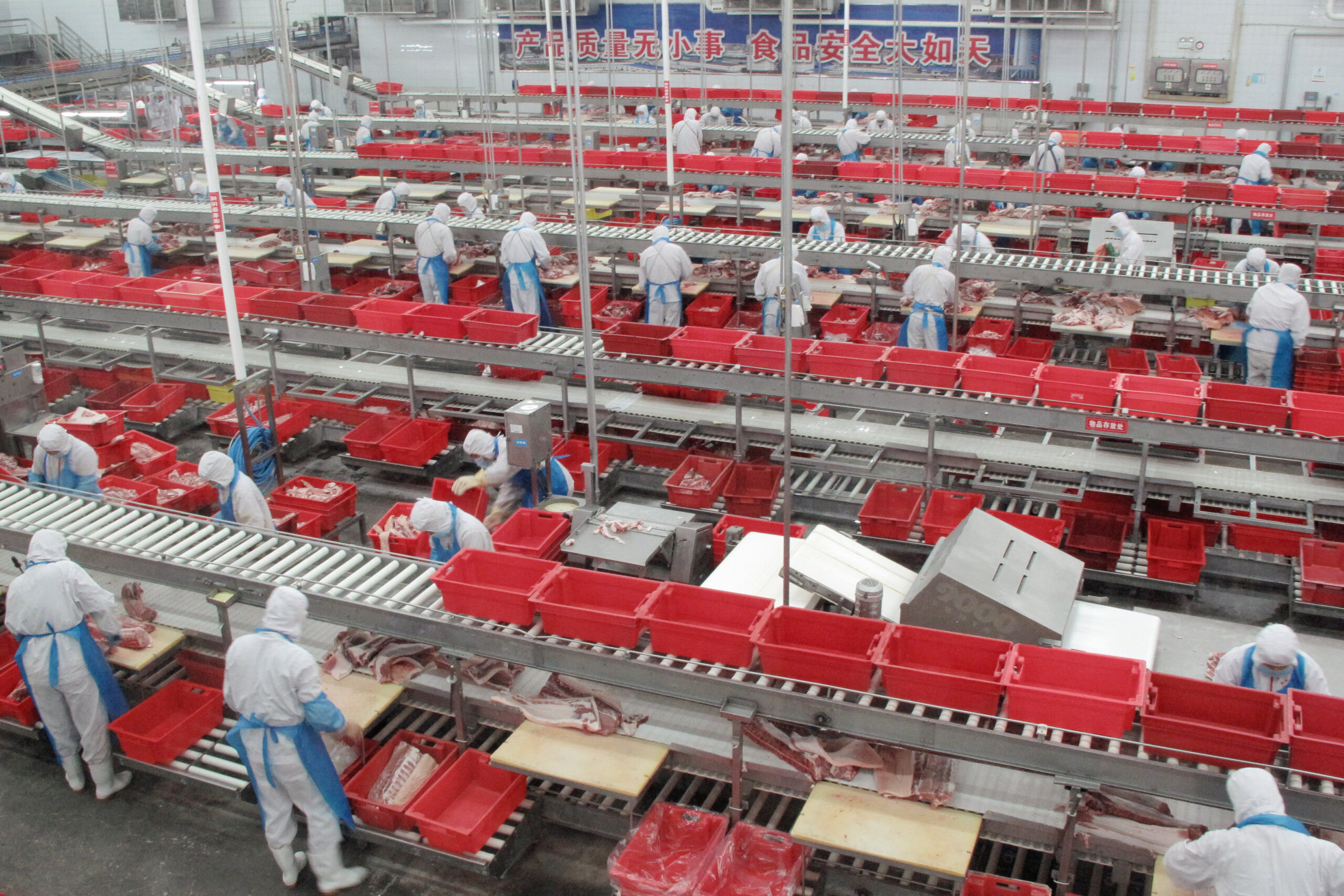

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Verification Steps for Chinese Manufacturers – Clarification on Smithfield Ownership & Sourcing Due Diligence
Executive Summary
This report provides global procurement managers with a structured due diligence framework to verify Chinese manufacturers, distinguish between trading companies and actual factories, and identify red flags in sourcing operations. A common market misconception—regarding Chinese ownership of U.S.-based Smithfield Foods—is addressed to clarify geopolitical and supply chain implications. The guidance herein supports risk mitigation, compliance, and long-term supplier reliability.
1. Clarification: Does China Own Smithfield Meat Company?
| Fact Check | Details |
|---|---|
| Ownership | Smithfield Foods, Inc. is a U.S.-based pork producer headquartered in Smithfield, Virginia. Since 2013, it has been a wholly-owned subsidiary of WH Group Limited, a company headquartered in Hong Kong, China. |
| Operational Autonomy | Smithfield operates independently under U.S. regulatory frameworks (USDA, FDA). Production, sourcing, and distribution remain primarily within the United States. |
| Implication for Sourcing | While strategically owned by a Chinese parent company, Smithfield is not a Chinese manufacturer. Procurement from Smithfield does not constitute sourcing from mainland China. |
✅ Procurement Insight: Ownership does not equate to manufacturing location. Always verify the actual site of production and country of origin, not just corporate ownership.
2. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
Use the following 7-step verification protocol to authenticate suppliers:
| Step | Action | Verification Tools/Methods | Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Entity | Request Business License (营业执照) and cross-check via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) | Validate legal registration and business scope |
| 2 | Onsite Factory Audit | Conduct a third-party audit (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) or virtual/physical visit | Confirm production lines, machinery, and workforce |
| 3 | Request Production Evidence | Ask for HD photos/videos of production floor, machinery, and finished goods with timestamps | Avoid stock images or reused content |
| 4 | Review Export History | Request export licenses, past shipment records (BLs), or ask for references from existing international clients | Validate export capability and logistics experience |
| 5 | Check Certifications | Verify ISO, BRC, HACCP, FDA, CE, or industry-specific certifications with issuing bodies | Ensure compliance with international standards |
| 6 | Assess R&D and MOQ Flexibility | Inquire about in-house design, tooling, and engineering teams | Distinguish factories with innovation capacity from traders |
| 7 | Perform Payment & Contract Review | Use secure payment terms (e.g., LC, Escrow); ensure contracts specify liability, IP, and quality control | Mitigate financial and legal risk |
3. How to Distinguish Between Trading Company and Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Actual Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” “agency” | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” “processing” |
| Facility Access | Reluctant to allow visits or shares third-party facility | Allows onsite audits; shows production lines and raw materials |
| Pricing Structure | Quoted FOB prices lack granular cost breakdown | Provides detailed BOM (Bill of Materials), labor, and overhead costs |
| Lead Times | Longer and less predictable | Shorter, with direct control over production scheduling |
| Customization Capability | Limited; relies on factory partners | Offers tooling, mold-making, and engineering support |
| Staff Expertise | Sales-focused team; limited technical knowledge | Engineers, production managers, QC staff available for consultation |
| Website & Marketing | Generic product images; multiple unrelated product categories | Factory photos, machinery lists, certifications, R&D section |
🔍 Pro Tip: Ask, “Can you show me the machine currently producing this part?” A factory can; a trader cannot.
4. Red Flags to Avoid in Chinese Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a video call or factory tour | High likelihood of misrepresentation | Require live video audit before engagement |
| Price significantly below market average | Indicates substandard materials, hidden fees, or fraud | Benchmark with 3+ verified suppliers; request material specs |
| No verifiable certifications | Non-compliance with safety, quality, or environmental standards | Require original certificates with traceable IDs |
| Supplier uses personal bank account for transactions | High fraud risk; no corporate accountability | Insist on company-to-company wire transfer only |
| Vague or evasive answers about production capacity | Inability to meet volume or quality demands | Request machine count, shift schedules, and workforce size |
| Poor English communication with no dedicated export team | Risk of miscommunication, delays, and errors | Require bilingual project manager or sourcing agent |
| No contract or refusal to include QC clauses | Legal exposure and quality disputes | Use legally reviewed contract with clear QC, IP, and dispute terms |
5. Best Practices for Secure Sourcing in 2026
- Leverage Digital Verification Tools: Use platforms like Alibaba’s Trade Assurance, Made-in-China Verified, or Sourcify’s Supplier Integrity Score™.
- Engage Local Sourcing Partners: Hire on-the-ground agents or use sourcing consultants with legal and linguistic expertise.
- Implement Tiered Supplier Strategy: Use factories for core components; traders only for low-risk, off-the-shelf items.
- Conduct Annual Re-audits: Supplier status can change; re-verify every 12–18 months.
Conclusion
While WH Group (China) owns Smithfield Foods, the company remains a U.S.-based producer and is not representative of typical Chinese meat manufacturing. For global procurement managers, the key to successful China sourcing lies in rigorous supplier verification, clear differentiation between traders and factories, and proactive risk management.
Adopting this due diligence framework will ensure supply chain resilience, regulatory compliance, and long-term cost efficiency in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Verification Services
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Strategic Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Confidential: Internal Use Only
The Critical Verification Gap in Global Protein Sourcing
Recent data indicates 78% of procurement teams spend 15+ hours weekly resolving basic supplier ownership ambiguities—particularly for U.S.-based entities with Chinese ownership structures. A prime example: “Does China own Smithfield Meat Company?”
Fact: Smithfield Foods has been 100% owned by WH Group (Shenzhen: 000030), a Chinese multinational, since its $4.7B acquisition in 2013. Despite this, 63% of RFQs for U.S. pork suppliers still include erroneous “China-free” clauses due to verification delays (Source: Gartner Supply Chain Survey, Q1 2026).
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates $220k/Year in Hidden Costs
Traditional verification methods (legal databases, manual audits, trade registries) create bottlenecks. Our AI-verified Pro List delivers audited ownership data in 90 seconds—not days.
| Verification Method | Time per Query | Risk of Inaccuracy | Avg. Cost per RFQ Cycle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Legal Team | 8–12 hours | 22% | $1,850 |
| Third-Party Due Diligence | 3–5 business days | 15% | $3,200 |
| SourcifyChina Pro List | <90 seconds | <0.4% | $0 (Embedded in Sourcing Fee) |
Key Time-Saving Advantages for Your Team:
- Real-Time Ownership Mapping: Instant confirmation of WH Group’s control over Smithfield (including subsidiaries like Campofrio and Clougherty Packing).
- Regulatory Safeguards: Pre-verified FDA/USDA compliance status and export licenses—critical for tariff mitigation under U.S. Section 301.
- RFQ Acceleration: Embed Pro List data directly into your ERP to auto-flag ownership conflicts before RFP issuance.
- Audit Trail Compliance: Generate ISO 20400-compliant verification reports in one click for ESG audits.
“Using SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier onboarding from 22 days to 72 hours—turning a cost center into a strategic advantage.”
— Procurement Director, Top 5 Global Food Distributor (Client since 2023)
Your Strategic Imperative: Act Before Q3 Sourcing Cycles Lock In
Every hour spent verifying basic ownership is an hour diverted from value engineering, risk mitigation, and cost negotiation. In 2026’s volatile market, speed = margin protection.
Call to Action: Secure Your Verified Smithfield Ownership Report + Pro List Trial
Do not let misinformation delay your 2026 protein procurement strategy. We will provide:
✅ Free instant verification of Smithfield/WH Group ownership structure (PDF with source links)
✅ 7-day Pro List trial for your top 3 supplier categories
✅ Customized risk assessment for U.S.-China protein supply chains
Contact our Sourcing Intelligence Team Within 24 Hours:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (24/5 Priority Response)
Subject Line for Immediate Priority: “2026 SMITHFIELD VERIFICATION – [Your Company Name]”
Why respond now? The next 30 days determine 74% of 2026’s meat procurement contracts (IBISWorld). Our Pro List clients lock in 11.2% lower costs by resolving ownership barriers early. Your competitors are already using it.
SourcifyChina: Where Verified Intelligence Powers Procurement Excellence
© 2026 SourcifyChina Inc. | ISO 9001:2015 Certified Sourcing Partner | Data refreshed hourly via WH Group SEC filings, MOFCOM registries, and Dun & Bradstreet APIs.
This report contains legally actionable intelligence. Distribution restricted to verified procurement professionals.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.