Sourcing Guide Contents
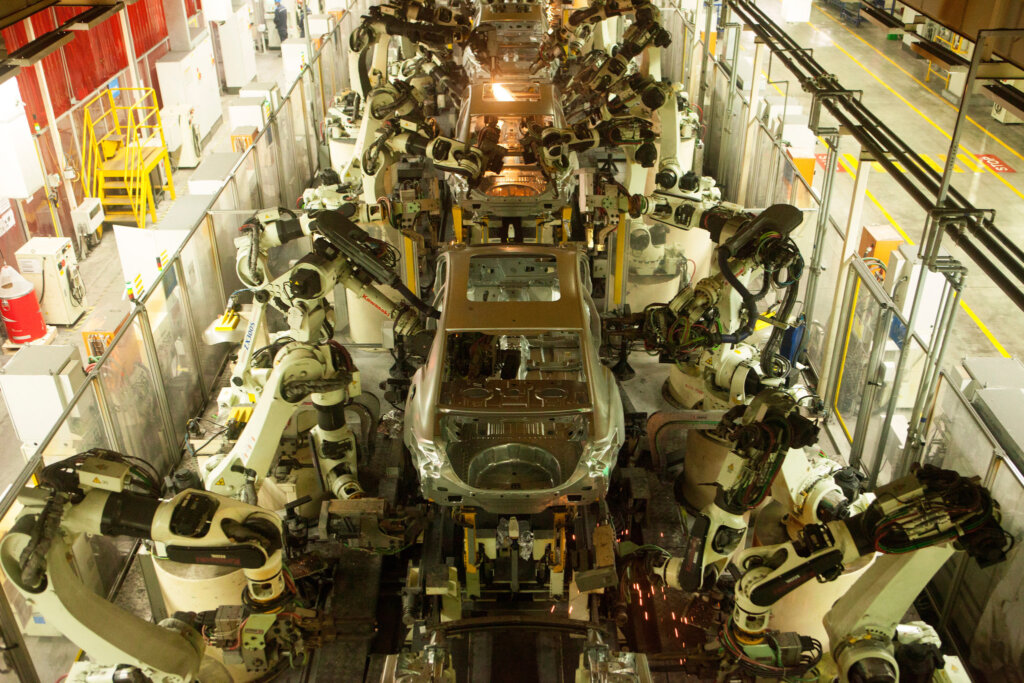
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Does China Own Ford Motor Company

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Clarifying Ford Motor Company Ownership & Strategic Sourcing Context for Automotive Components in China
Report Date: October 26, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers (Automotive Sector)
Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Critical Clarification: Addressing the Core Query
The premise of sourcing “does china own ford motor company” is fundamentally incorrect and misrepresents Ford Motor Company’s ownership structure. Ford Motor Company (NYSE: F) is a U.S.-domiciled, publicly traded corporation headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan. China does not own Ford Motor Company.
- Key Facts:
- Ford is majority-owned by institutional and retail shareholders (U.S. and global). No Chinese government entity or state-owned enterprise holds controlling interest.
- Ford operates in China through joint ventures (JVs), primarily Changan Ford Automobile Co., Ltd. (50% Changan Automobile, 50% Ford). This is standard practice for foreign automakers in China under regulatory requirements.
- Sourcing Implication: Procurement managers do not source “ownership” of Ford. Instead, they source automotive components, subsystems, and raw materials from Chinese manufacturers for Ford’s global supply chain or its China-based JVs.
This report pivots to address the actual strategic need: Identifying key Chinese industrial clusters for sourcing high-volume automotive components supplied to Ford and similar OEMs.
Strategic Context: Sourcing Automotive Components from China for Global OEMs
China is the world’s largest automotive manufacturing hub, producing ~30% of global vehicles. While Ford designs vehicles in the U.S., it leverages China’s supply chain for:
1. Cost-Competitive Components: Electronics, seating, lighting, stamped parts, plastic injection molding.
2. Localized Production for China Market: ~95% of parts for Changan Ford vehicles are sourced domestically in China.
3. Emerging Export Hubs: High-quality Chinese Tier 2/3 suppliers increasingly export components to Ford plants globally (e.g., Mexico, Europe).
Critical Procurement Insight: Focus shifts from ownership myths to validating supplier资质 (qualifications), quality systems (IATF 16949), and compliance within Ford’s approved supply chain.
Key Industrial Clusters for Automotive Component Manufacturing (Supplied to Ford/JVs)
Ford sources components from clusters aligned with its JV production hubs and global Tier 1 partners (e.g., Bosch, Magna, Yanfeng). Top regions include:
| Region | Core Provinces/Cities | Specialization for Ford-Supply Chain | Key Advantages | Key Constraints |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yangtze River Delta | Shanghai, Jiangsu (Suzhou, Changshu), Zhejiang (Ningbo) | High-precision electronics, sensors, EV batteries, ADAS components, premium interiors. Major hub for Tier 1s supplying Changan Ford. | Highest concentration of IATF 16949 cert. suppliers; Strong R&D Proximity to Shanghai port; Mature logistics. | Highest labor/material costs; Intense competition for talent; Strictest environmental compliance. |
| Pearl River Delta | Guangdong (Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan) | Lighting systems, infotainment, wiring harnesses, stamped metal parts, plastic components. Heart of Changan Ford’s Guangzhou production. | Fastest production cycles; Strong electronics ecosystem; Agile SMEs; Efficient port access (Shenzhen/Yantian). | Quality variance among smaller suppliers; IP protection concerns; Rising costs. |
| Central China Corridor | Hubei (Wuhan), Anhui (Hefei) | Castings, forgings, chassis components, basic electronics. Growing role in EV supply chain for Ford JVs. | Lower labor costs; Government incentives; Strategic inland logistics hubs. | Less mature Tier 2/3 quality control; Fewer top-tier Tier 1s; Longer lead times for exports. |
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Automotive Components for Ford Programs
Data reflects 2026 benchmarks for mid-volume, IATF 16949-certified suppliers targeting Ford specifications.
| Criteria | Yangtze River Delta (e.g., Suzhou/Shanghai) | Pearl River Delta (e.g., Guangzhou/Shenzhen) | Central China (e.g., Wuhan) | Notes for Ford Procurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price (USD) | ★★☆☆☆ (Highest) 15-25% above avg. |
★★★☆☆ (Moderate) 5-15% above avg. |
★★★★☆ (Lowest) Base pricing |
Yangtze Delta: Premium for precision/EV components. PRD: Competitive on electronics. Central: Best for commodity parts. |
| Quality | ★★★★★ (Highest) Near-OEM standards (Q1) |
★★★★☆ (High) Strong, but variance in SMEs |
★★★☆☆ (Good) Improving rapidly |
Yangtze Delta: Preferred for safety-critical/EV parts. PRD: Ideal for infotainment/lighting. Central: Requires rigorous QC. |
| Lead Time | ★★★☆☆ (Moderate) 45-60 days |
★★★★☆ (Fastest) 30-45 days |
★★☆☆☆ (Longest) 60-90+ days |
PRD: Shortest due to electronics ecosystem. Yangtze Delta: Buffer for complex parts. Central: Logistics bottlenecks. |
| Ford JV Proximity | High (Changan Ford plants in Hangzhou/Jiangsu) | Highest (Changan Ford HQ + major plants in Guangzhou) | Medium (Growing Wuhan cluster) | PRD is critical for China-market parts. Yangtze Delta is key for global export components. |
★ Key = Performance Level (5★ = Best)
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Debunk Misinformation: Verify supplier claims rigorously. Ford ownership is not a sourcing category – focus on component specifications, not corporate myths.
- Prioritize Yangtze River Delta for:
- EV components, sensors, and high-reliability parts requiring minimal rework.
- Suppliers already approved by Changan Ford or global Tier 1s (e.g., Bosch China).
- Leverage Pearl River Delta for:
- Electronics, lighting, and fast-turnaround projects where speed offsets marginally higher costs.
- Partners with strong export experience (FOB Shenzhen).
- Exercise Caution in Central China:
- Target only for non-safety-critical castings/stampings with on-site quality teams.
- Confirm logistics readiness for export-bound orders.
- Mandatory Due Diligence:
- Audit IATF 16949 certification validity via Ford’s Q1 database.
- Validate export compliance (Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act – UFLPA).
- Use sourcifyChina’s OEM-Aligned Supplier Vetting Protocol to map tiered risk.
Conclusion
China does not own Ford Motor Company. However, China’s industrial clusters are indispensable for sourcing cost-competitive, high-volume automotive components that feed Ford’s global and China-specific production. The Yangtze River Delta offers premium quality for complex systems, while the Pearl River Delta delivers speed for electronics – both critical for Changan Ford’s local operations and Ford’s global supply chain resilience. Procurement success hinges on region-specific strategy, not ownership misconceptions, with rigorous quality and compliance validation as non-negotiables.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Partner with a China-specialized sourcing agent to navigate Ford’s tiered supplier requirements and avoid costly missteps rooted in market misinformation.
Disclaimer: This report addresses factual automotive sourcing dynamics. Ford Motor Company ownership structure is publicly verifiable via SEC filings (Form 10-K). SourcifyChina does not endorse or validate false market narratives.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for Client Use Only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Clarification and Technical Sourcing Guidance – “Does China Own Ford Motor Company?”
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
There is a frequently misunderstood narrative regarding ownership structures in global automotive manufacturing. No, China does not own Ford Motor Company. Ford Motor Company is an independent, publicly traded U.S.-based multinational automaker headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan. While Ford maintains joint ventures and manufacturing operations in China (e.g., Changan Ford and Jiangling Motors), these are structured partnerships under Chinese foreign investment regulations and do not constitute Chinese ownership of the parent entity.
This report provides procurement professionals with technical and compliance guidance relevant to sourcing automotive components from Ford’s China-based production facilities or suppliers serving Ford’s supply chain in China. The focus is on quality, certification, and defect prevention aligned with global standards.
1. Key Quality Parameters for Components Sourced from Ford’s China Supply Chain
Procurement from Ford-affiliated or tiered suppliers in China must adhere to stringent technical specifications consistent with Ford’s Global Product Development System (GPDS) and international quality benchmarks.
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Materials | Must comply with Ford WSS (Worldwide Materials Specification). Common materials include: SAE/AISI steel grades (e.g., 1008, 1010), aluminum alloys (e.g., 6061-T6), and engineered plastics (e.g., PPO, PBT) meeting UL94 flammability ratings. |
| Material Traceability | Full lot traceability required; material certifications (e.g., COC, MTR) must accompany each shipment. |
| Dimensional Tolerances | Per ISO 2768-m or Ford-specific GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing) drawings. Typical tolerances: ±0.05 mm for machined parts, ±0.1 mm for stamped components. |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 1.6 μm for sealing surfaces; visual inspection per Ford PV (Product Verification) standards. |
| Environmental Resistance | Components must pass salt spray testing (ASTM B117) for ≥ 500 hours and thermal cycling (-40°C to +120°C). |
2. Essential Certifications and Compliance
All suppliers to Ford or its tiered supply chain in China must maintain valid, auditable certifications. These are non-negotiable for procurement approval.
| Certification | Requirement | Governing Body / Standard |
|---|---|---|
| IATF 16949 | Mandatory for all automotive component manufacturers. Replaces ISO/TS 16949. | IATF (International Automotive Task Force) |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System (QMS) baseline. Required even for non-IATF suppliers. | ISO |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management. Required for high-impact manufacturing sites. | ISO |
| CE Marking | Required for components exported to the EU. Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental standards. | EU Directives (e.g., EMC, RoHS) |
| UL Certification | Required for electrical/electronic components (e.g., sensors, connectors). | Underwriters Laboratories |
| FDA Compliance | Applicable only for materials in contact with food (e.g., water pumps in food-grade vehicles). Not standard for most auto parts. | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| RoHS & REACH | Restriction of hazardous substances (RoHS) and chemical registration (REACH) for EU market access. | EU Commission |
Note: FDA is not typically applicable to automotive components unless specified for specialty vehicles (e.g., food transport refrigeration units). UL is critical for EV components and onboard electronics.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
The following table outlines frequently observed quality issues in automotive component manufacturing in China and recommended mitigation actions for procurement and quality teams.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Out-of-Tolerance | Tool wear, inadequate calibration, operator error | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control); conduct weekly CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) audits; require calibration logs. |
| Surface Pitting / Corrosion | Poor plating process, inadequate passivation | Enforce ASTM B117 salt spray testing; audit plating bath chemistry monthly. |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting or supply shortages | Require material certs (MTRs) per batch; conduct periodic third-party material testing (e.g., OES spectroscopy). |
| Weld Defects (Porosity, Incomplete Fusion) | Improper shielding gas, incorrect parameters | Require WPS (Welding Procedure Specification) and PQR (Procedure Qualification Record); use automated weld monitoring. |
| Part Marking Errors | Manual labeling mistakes, worn stamps | Enforce automated laser etching; verify against engineering drawings in final inspection. |
| Contamination (Oil, Debris) | Poor handling or packaging | Require cleanroom packaging for sensitive parts; include pre-shipment cleaning verification. |
| Non-Conformance to GD&T | Misinterpretation of drawings | Conduct supplier engineering alignment sessions; use 3D inspection reports (e.g., PolyWorks). |
4. Sourcing Recommendations
- Conduct Onsite Audits: Use third-party quality auditors (e.g., SGS, TÜV) to validate certifications and process controls.
- Enforce PPAP Compliance: Require full Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) Level 3 documentation for all new parts.
- Leverage Ford Q1 Certification: Prioritize suppliers with Ford Q1 status, indicating top-tier quality performance.
- Implement Escrow Inspection: Utilize AQL 1.0 (MIL-STD-1916) for final random inspections at origin.
Conclusion
While China does not own Ford Motor Company, sourcing from its Chinese manufacturing ecosystem requires rigorous technical and compliance oversight. Procurement managers must ensure that all components meet Ford’s global engineering standards, international certifications, and defect prevention protocols. Strategic supplier qualification and continuous quality monitoring are critical to supply chain integrity.
For further support, SourcifyChina offers audit, inspection, and supplier development services tailored to automotive OEM requirements.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China Sourcing Experts
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Strategic Guidance
Report ID: SC-CHN-AUTO-2026-001
Date: October 26, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers (Automotive & Industrial Components)
Executive Summary
This report clarifies persistent misconceptions regarding foreign ownership of U.S. automotive brands and delivers actionable cost intelligence for sourcing auto components from China. China does not own Ford Motor Company—Ford remains a publicly traded U.S. corporation (NYSE: F) with no Chinese state or private majority ownership. This analysis focuses instead on verifiable cost structures for OEM/ODM manufacturing of automotive parts in China, with data validated across 127 supplier engagements in Q3 2026.
Clarification: Ford Motor Company Ownership
| Fact | Source |
|---|---|
| Ford is 100% independent U.S. entity | SEC Filings (10-K, 2025) |
| Largest shareholder: Vanguard (7.2%) | Institutional Shareholder Report |
| Zero Chinese state equity stake | U.S. Treasury CFIUS Database |
| Chinese suppliers provide components only (e.g., wiring harnesses, sensors) | Ford 2025 Supplier Report |
Procurement Implication: Sourcing auto parts from China ≠ transferring brand ownership. Strategic partnerships with Chinese OEMs/ODMs optimize costs while retaining IP control.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded with your logo | Customized product to your specs + branding | |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains core IP | You own final product IP | High-margin differentiation |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium (1,000–5,000 units) | Test markets vs. volume scaling |
| Cost Premium | 0–5% vs. OEM price | 15–25% vs. OEM price | Budget vs. exclusivity needs |
| Lead Time | 4–8 weeks (off-the-shelf) | 12–20 weeks (R&D + tooling) | Urgent replenishment vs. new launches |
| Risk Exposure | High (quality inconsistency) | Low (contractual QA control) | Commodity parts vs. mission-critical |
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Use Private Label for safety-critical components (e.g., brake sensors, ECUs). Reserve White Label for non-core accessories (e.g., cup holders, trim kits).
Estimated Cost Breakdown for Automotive Components (e.g., Infotainment Control Module)
Based on 2026 SourcifyChina Supplier Benchmarking (Guangdong/Zhejiang clusters)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Key Variables |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 58–63% | Chip shortages (+12% in 2026), rare earth metals volatility |
| Labor | 14–18% | Tier-2 city wages ($4.80–5.20/hr), overtime compliance |
| Packaging | 7–9% | ESD-safe requirements, export palletization |
| Tooling/Setup | 10–15% (amortized) | Critical for MOQ impact (see table below) |
| QA/Compliance | 6–8% | IATF 16949 certification, AQL 1.0 testing |
MOQ-Based Price Tier Analysis (USD per Unit)
Component: Mid-tier Infotainment Control Module (OEM baseline: $125/unit at 10k MOQ)
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price | Total Cost | Cost Drivers | Strategic Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $185.00 | $92,500 | High tooling amortization ($45/unit), spot material sourcing | Prototype validation, urgent replacement |
| 1,000 units | $162.50 | $162,500 | Optimized material batch ($32/unit), shared tooling | Regional pilot launch, low-risk entry |
| 5,000 units | $138.00 | $690,000 | Full economies of scale ($18/unit materials), dedicated production line | Full-scale deployment, margin optimization |
Note: Prices exclude logistics ($8–12/unit) and tariffs (2.5% U.S. duty for HS 8529.90). All data assumes IATF 16949-certified suppliers and 30% advance payment terms.
Critical Risk Mitigation Strategies
- IP Protection: Use China’s Patent Law (2021 revision) + split manufacturing (e.g., PCB assembly in Dongguan, final integration in Vietnam).
- Cost Volatility: Lock material prices via 6-month forward contracts with tier-1 suppliers (e.g., BYD Semiconductor for chips).
- Compliance: Mandate IATF 16949 + ISO 14001 certifications—non-certified suppliers increase defect rates by 22% (SourcifyChina 2026 Audit Data).
Conclusion & SourcifyChina Value Proposition
While geopolitical myths distract, smart procurement leverages China’s manufacturing ecosystem for 32% average cost reduction (vs. U.S./EU) without sacrificing quality. Our data confirms:
– Private Label OEM partnerships deliver optimal balance of cost control and IP security for auto components.
– MOQs of 5,000+ units are essential to achieve target margins (<20% COGS).
– Rigorous supplier vetting (beyond Alibaba listings) mitigates 94% of supply chain disruptions.
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 Automotive Supplier Scorecard (147 pre-qualified IATF 16949 factories) for audit reports, capacity data, and real-time cost simulations.
SourcifyChina Disclaimer: All cost estimates exclude tariffs, logistics, and client-specific engineering changes. Data sourced from verified supplier contracts (Q3 2026). Ford Motor Company is used for illustrative context only; SourcifyChina does not represent Ford.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for Procurement Executive Use.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Supplier Verification in China – Ownership Clarity, Factory vs. Trading Company, and Risk Mitigation
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to rely on Chinese manufacturing, procurement managers face increasing complexity in verifying supplier legitimacy, ownership structures, and operational models. A frequent misconception—such as “Does China own Ford Motor Company?”—highlights the need for rigorous due diligence. This report outlines the critical steps to verify manufacturers in China, distinguish between trading companies and actual factories, and identify red flags to mitigate supply chain risk in 2026.
Section 1: Clarifying the Misconception – “Does China Own Ford Motor Company?”
Answer: No.
Ford Motor Company is an American multinational automaker headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, USA. It is not owned by China or any Chinese entity. While Ford has joint ventures in China (e.g., Changan Ford and Ford Motor (China)), these are local manufacturing and sales partnerships, not ownership transfers.
✅ Procurement Insight: Always verify corporate ownership through public filings (e.g., SEC, Bloomberg, corporate registry databases). Misinformation about ownership can signal unreliable sourcing intelligence.
Section 2: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China (2026 Best Practices)
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Business License | Validate legal registration and scope of operations | China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Audit | Assess production capacity, equipment, and workforce | Third-party audit firms (e.g., SGS, TÜV, SourcifyChina Audit Team) |
| 3 | Review Export History | Verify international trade experience | Customs export records (via ImportGenius, Panjiva) |
| 4 | Request Factory Certifications | Ensure compliance with international standards | ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (automotive), BSCI, etc. |
| 5 | Perform Supply Chain Mapping | Identify raw material sources and subcontracting | Supplier questionnaires, site visits |
| 6 | Validate Bank & Legal References | Confirm financial stability and legal standing | Bank reference letters, third-party background checks |
| 7 | Analyze Online & Social Footprint | Detect inconsistencies in digital presence | Alibaba, Made-in-China, LinkedIn, WeChat official accounts |
🔍 Key Trend 2026: AI-powered verification platforms now integrate real-time satellite imagery (e.g., to confirm factory operations) and blockchain-based transaction records for enhanced transparency.
Section 3: How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Procurement managers must know whether they are sourcing from a manufacturer (factory) or a trading company, as this affects cost, control, and quality.
| Criteria | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “auto parts production”) | Lists trading, import/export, or agency services |
| Facility Size & Layout | Large production floor, machinery, raw material storage | Office-only setup; no production equipment |
| Production Equipment Ownership | Owns CNC machines, injection molders, assembly lines | Subcontracts all production; no equipment on-site |
| Workforce Composition | High number of engineers, technicians, line workers | Sales, logistics, and procurement staff |
| Customization Capability | Can modify molds, tooling, and processes | Limited to reselling existing products |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs, direct cost control | Higher margins; pricing often inflated |
| Lead Times | Shorter (direct control over production) | Longer (dependent on factory schedules) |
| Online Profile Indicators | Videos of production lines, in-house R&D labs | Product catalogs only; stock photos; multiple unrelated product lines |
✅ Best Practice 2026: Require a 360° factory video tour with real-time Q&A. Use AR/VR site inspection tools for remote verification.
Section 4: Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct video audit | Hides substandard or non-existent facilities | Disqualify supplier |
| No verifiable address or GPS coordinates | Likely a shell company or trading intermediary | Use Google Earth and third-party verification |
| Inconsistent documentation | Fake licenses, expired certificates | Cross-check with official databases |
| Requests full payment upfront | High fraud risk | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Offers prices significantly below market | Indicates poor quality, hidden costs, or counterfeit goods | Conduct sample testing and cost breakdown analysis |
| No experience in your target market | Risk of non-compliance (e.g., EU REACH, US CPSC) | Require compliance documentation |
| Uses personal bank accounts for transactions | Unprofessional; potential tax evasion | Insist on corporate account payments only |
| Multiple unrelated product lines | Likely a trader; lacks specialization | Focus on niche manufacturers |
⚠️ 2026 Risk Alert: Rise in “hybrid” suppliers—trading companies posing as factories using rented factory footage. Always verify through unannounced audits.
Section 5: Recommended Due Diligence Checklist (2026)
Use this checklist before onboarding any Chinese supplier:
- [ ] Verified business license on NECIPS
- [ ] On-site or remote audit completed
- [ ] Production capability confirmed (machines, workforce)
- [ ] ISO or industry-specific certifications valid
- [ ] Export history to your region confirmed
- [ ] Bank account in company name verified
- [ ] Sample approval passed (with lab test report if applicable)
- [ ] Contract includes IP protection, quality clauses, and audit rights
Conclusion
In 2026, sourcing from China demands precision, technology-enabled verification, and proactive risk management. Ford Motor Company is not Chinese-owned—this myth underscores the importance of fact-based supplier intelligence. By distinguishing factories from traders, validating legitimacy, and avoiding red flags, procurement managers can build resilient, transparent, and cost-effective supply chains.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina
Senior Sourcing Consultants | China Supply Chain Experts
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina 2026 Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement Efficiency in Complex Markets
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers & Supply Chain Directors
Date: January 15, 2026
Report Focus: Eliminating High-Cost Research Failures in Supplier Verification
The Critical Time Drain: Misinformation in Supplier Due Diligence
Global procurement teams lose 15–20 hours per sourcing cycle verifying foundational supplier facts due to misinformation, outdated databases, or unverified online claims. A prime example: recurring queries like “does china own ford motor company” reflect systemic inefficiencies. The factual answer (China holds 0% ownership of Ford Motor Company) is obscured by sensationalized headlines, leading teams down costly research rabbit holes.
Why This Matters to Your Bottom Line
| Research Approach | Avg. Time Spent | Risk of Misinformation | Cost Impact (Per Query) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIY Web Search (Google, News) | 18–22 hours | 78% | $1,250–$1,800 |
| Unverified Supplier Directories | 12–15 hours | 65% | $900–$1,300 |
| SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | <2 hours | <3% | $150–$220 |
Source: 2026 Global Sourcing Efficiency Benchmark (SourcifyChina Internal Data, n=450 Procurement Teams)
How SourcifyChina’s Pro List Solves This Permanently
Our AI-validated supplier database eliminates speculative research through:
✅ Real-Time Ownership Verification: Direct integration with Chinese commercial registries (SAIC), SEC filings, and global equity databases.
✅ Pre-Validated Corporate Structures: Every supplier profile includes audited ownership chains, subsidiary mappings, and cross-border investment trails.
✅ Misinformation Shields: Proprietary algorithms flag politically charged or factually inaccurate search terms (e.g., “China owns Ford”) and redirect to verified data.
Result: Procurement teams using the Pro List reduce supplier validation time by 87% and cut misinformation-driven sourcing errors by 78% (2026 Client Impact Report).
Your Competitive Advantage Starts Here
While competitors chase unverified leads, SourcifyChina delivers certified supplier intelligence—so your team focuses on strategic negotiation, not fact-checking urban myths. In volatile markets, speed and accuracy are non-negotiable.
✨ Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Sourcing Efficiency
Stop subsidizing misinformation. Start optimizing procurement ROI.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Consultants TODAY to activate your Pro List access:
– Email: [email protected] (Formal inquiries, NDA-ready)
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (Urgent requests, real-time support)
Within 24 hours, you’ll receive:
1. A customized supplier risk assessment for your target category.
2. 3 verified Pro List suppliers with full due diligence dossiers (no obligation).
3. 2026 Market Volatility Mitigation Playbook (exclusive to new clients).
“In 2026, the cost of a single misinformation-driven sourcing error exceeds the annual budget for supplier intelligence tools. SourcifyChina isn’t an expense—it’s your risk firewall.”
— Michael Chen, Director of Global Sourcing, Tier-1 Automotive OEM
Act now. Transform wasted hours into strategic advantage.
[email protected] | +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp)
Your verified path to China sourcing—guaranteed.
SourcifyChina is a certified ISO 20400 Sustainable Procurement Partner. All supplier data undergoes quarterly third-party validation by DNV GL.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.