Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Does China Have Private Companies

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Market Analysis Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis on Sourcing Private Manufacturing Capabilities from China
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
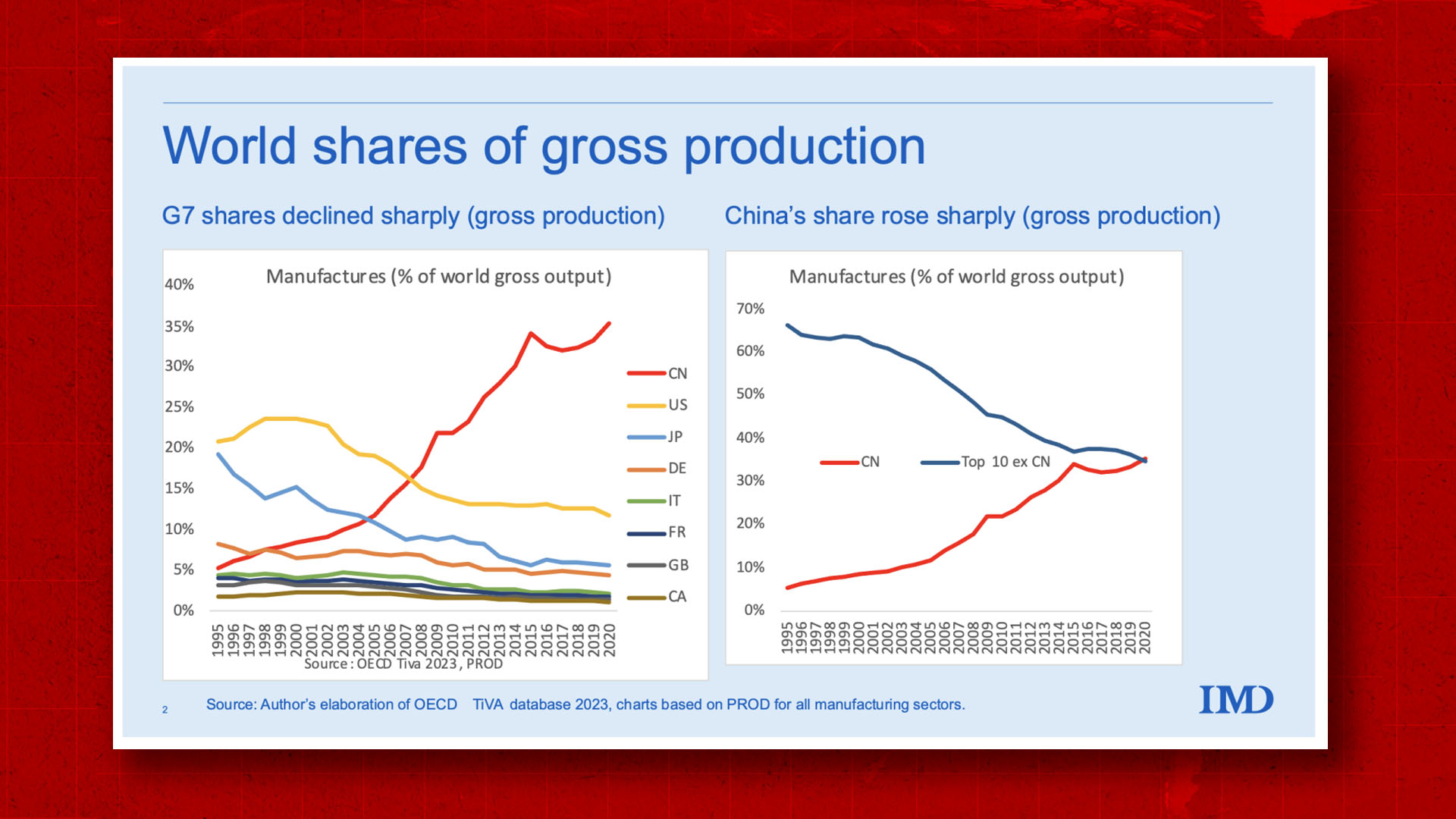
China’s private sector is a cornerstone of its manufacturing dominance, contributing over 60% of GDP and 80% of urban employment (National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2025). Despite common misconceptions, China not only has private companies—it thrives on them. This report clarifies the landscape of China’s private manufacturing ecosystem and identifies key industrial clusters critical for global sourcing strategies.
While state-owned enterprises (SOEs) dominate strategic sectors such as energy and telecommunications, private enterprises are the primary drivers in consumer goods, electronics, machinery, textiles, automotive components, and new energy technologies. These firms are concentrated in dynamic coastal provinces with mature supply chains, export infrastructure, and innovation ecosystems.
This report provides a strategic analysis of China’s private manufacturing clusters, evaluates regional strengths, and delivers actionable insights for procurement optimization.
Clarification: Does China Have Private Companies?
Yes, China has a robust and rapidly expanding private enterprise sector.
- Since economic reforms began in the late 1970s, private companies have grown exponentially.
- As of 2025, over 93 million private enterprises operate in China, accounting for:
- 70% of total industrial output
- 90% of new job creation
- 65% of total exports in light and mid-tech manufacturing
- Key sectors dominated by private firms:
- Consumer Electronics (e.g., Shenzhen OEMs)
- Textiles & Apparel (e.g., Zhejiang, Jiangsu)
- Home Appliances (e.g., Foshan, Zhongshan)
- EV Components (e.g., Wuxi, Ningbo)
- Machinery & Tools (e.g., Wenzhou, Dongguan)
Procurement Insight: The term “private company” in China may not always align with Western corporate governance models. Many operate under collective ownership or family control, but they function as independent, market-driven entities with global export experience.
Key Industrial Clusters for Private Manufacturing in China
Below are the top five provinces and cities recognized for high-density private manufacturing activity, innovation, and export readiness.
| Region | Key Industries | Notable Cities | Private Sector Share | Export Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, ICT, Drones, Smart Devices, Plastics | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan | ~88% of manufacturing firms | World-class ports (Yantian, Nansha), proximity to Hong Kong |
| Zhejiang | Textiles, Fasteners, Home Goods, E-commerce OEMs | Yiwu, Ningbo, Wenzhou, Hangzhou | ~91% of manufacturing firms | Major ports (Ningbo-Zhoushan), Alibaba ecosystem |
| Jiangsu | Machinery, Chemicals, Solar Panels, Automotive Parts | Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Nanjing | ~85% of manufacturing firms | Proximity to Shanghai port, strong R&D investment |
| Fujian | Footwear, Ceramics, Building Materials, Garments | Quanzhou, Xiamen, Fuzhou | ~80% of manufacturing firms | Xiamen Port, strong diaspora trade links |
| Shandong | Heavy Machinery, Auto Components, Chemicals, Agri-Processing | Qingdao, Weifang, Yantai | ~78% of manufacturing firms | Qingdao Port, strong logistics network |
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Performance Matrix
The following table compares Guangdong and Zhejiang—China’s two most competitive private manufacturing hubs—across critical procurement KPIs.
| Factor | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Moderate to High (due to labor & real estate costs) | Low to Moderate (high SME density, scale economies) | Zhejiang offers better cost efficiency for labor-intensive goods |
| Quality | High (advanced tech, strict QC, ISO compliance) | Moderate to High (varies widely; top-tier in Yiwu/Ningbo) | Guangdong preferred for precision electronics and regulated products |
| Lead Time | Short (3–6 weeks avg., strong logistics) | Short to Moderate (4–7 weeks, port congestion risk) | Guangdong faster for JIT and urgent orders |
| Innovation Capacity | Very High (Shenzhen = “China’s Silicon Valley”) | High (especially in smart home, IoT, e-commerce integration) | Guangdong leads in R&D-driven product development |
| Supplier Maturity | Very High (global OEM/ODM experience) | High (especially in B2B e-commerce via Alibaba) | Both regions offer mature export-ready partners |
| Customization Flexibility | High (modular production lines) | Very High (SME agility, low MOQs) | Zhejiang better for small-batch, customized orders |
Procurement Recommendation:
– Choose Guangdong for high-tech, quality-sensitive, or innovation-driven products (e.g., IoT devices, medical equipment).
– Choose Zhejiang for cost-sensitive, high-volume consumer goods, especially those sold via e-commerce platforms.
Sourcing Risks & Mitigation Strategies
| Risk | Assessment | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Intellectual Property (IP) Protection | Medium-High | Use NDAs, work with ISO-certified partners, file IP in China |
| Supply Chain Transparency | Medium | Conduct on-site audits, use blockchain traceability tools |
| Geopolitical Tensions | Medium | Diversify across provinces, consider nearshoring backup (Vietnam, Malaysia) |
| Labor Cost Inflation | High (Coastal regions) | Shift labor-intensive production to Anhui, Jiangxi, or Western China |
Conclusion & Strategic Outlook 2026–2028
China’s private manufacturing sector remains a strategic imperative for global procurement. Far from being state-controlled, the majority of China’s export-oriented production is driven by agile, competitive private enterprises.
Top Recommendations for Procurement Managers:
1. Leverage regional specialization: Match product type to cluster strength (e.g., electronics → Guangdong, home goods → Zhejiang).
2. Engage tier-2 private suppliers: Many high-potential SMEs offer better pricing and flexibility than large SOEs.
3. Invest in supplier development: Co-innovate with private firms to improve quality and IP security.
4. Utilize digital sourcing platforms: Platforms like 1688.com and Alibaba enable direct access to verified private manufacturers.
China’s private sector is not just alive—it is the engine of its global manufacturing supremacy. Strategic sourcing in 2026 requires moving beyond outdated perceptions and building partnerships with China’s dynamic private enterprises.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence Division
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Navigating Private Manufacturing in China
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Confidentiality Level: Internal Use Only
Clarification on Query Scope
Note: The phrasing “does China have private companies” reflects a fundamental misunderstanding of China’s economic structure. The People’s Republic of China (PRC) has operated under a “socialist market economy” since 1992, with private enterprises constituting 63.4% of industrial output (NBS China, 2025) and 76% of urban employment. This report assumes the intended query is: “How to source from private Chinese manufacturers while ensuring technical/compliance adherence.” All data reflects 2026 regulatory landscapes.
I. Technical Specifications Framework for Chinese Private Manufacturers
Private factories in China (e.g., Dongguan electronics OEMs, Ningbo machinery workshops) operate under GB (Guobiao) national standards but must align with export market requirements. Critical parameters include:
| Parameter | Typical Requirement (Export Markets) | China-Specific Risk Factors | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | RoHS/REACH-compliant polymers; ASTM A36 steel | Substitution of recycled materials; undocumented alloys | Third-party material certs + batch testing (SGS/BV) |
| Dimensional Tolerances | ISO 2768-mK (general); ±0.005mm (precision) | Tooling wear in high-volume runs; inconsistent metrology | Pre-production gauge calibration reports; in-process QC audits |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 0.8μm (aerospace); MIL-STD-810G (military) | Inadequate plating thickness; inconsistent anodization | Cross-sectional microscopy; salt spray testing |
| Electrical Safety | IEC 60950-1 (IT equipment); UL 62368-1 | Non-compliant creepage distances; counterfeit components | Factory witnessed Hi-Pot testing; component traceability logs |
II. Mandatory Certifications for Export Compliance
Chinese private manufacturers often hold domestic certifications (CCC, CQC) but require explicit validation for global markets:
| Certification | Critical For | China-Specific Compliance Challenges | SourcifyChina Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EU market access (Machinery, EMC, LVD) | “CE self-declaration” fraud; incomplete technical files | Audit of EU Authorized Representative; review of DoC validity |
| FDA | Medical devices, food contact materials | Unregistered facilities; non-21 CFR Part 820 QMS | FDA establishment registration check; process validation records |
| UL | North American electrical products | Counterfeit UL marks; unlisted subcomponents | UL Online Certifications Directory verification; factory follow-ups |
| ISO 9001 | Quality management baseline | “Paper-only” systems; no management review evidence | Unannounced audits; CAPA log review; employee interviews |
Regulatory Alert (2026): China’s new Export Quality Enhancement Directive (effective Jan 2026) requires private factories to register with AQSIQ for high-risk categories (medical, aviation). Non-registered suppliers face shipment holds.
III. Common Quality Defects in Chinese Private Manufacturing & Prevention Strategies
| Defect Category | Typical Manifestation | Root Cause in Chinese Context | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Off-spec polymers; lower-grade metals | Cost pressure; lax raw material traceability | • Enforce dual-supplier material sourcing • Require mill test reports (MTRs) with batch IDs |
| Dimensional Drift | Tolerance stack-up in assemblies | Tooling degradation; uncalibrated CMMs | • Mandate SPC charts for critical features • On-site gauge R&R studies pre-shipment |
| Surface Contamination | Oil residues; plating pits | Inadequate cleaning cycles; tank contamination | • White glove test at production line • Validate cleaning agent SDS compliance |
| Electrical Failures | Short circuits; insulation breakdown | Counterfeit capacitors; PCB design errors | • Component X-ray inspection • 3rd-party schematic validation against UL file |
| Documentation Gaps | Incomplete COAs; missing traceability | Language barriers; poor record-keeping | • Digital QC portal with real-time data • Bilingual audit trails for all inspections |
IV. SourcifyChina Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Supplier Vetting: Prioritize factories with both CCC and target-market certifications (e.g., CE + FDA). Verify via official portals (e.g., UL WDC, EU NANDO).
- Contractual Safeguards: Embed liquidated damages for certification fraud; mandate right-to-audit clauses covering subcontractors.
- Quality Integration: Implement AQL 1.0 for critical defects; require first-article inspection (FAI) reports signed by independent engineers.
- Risk Mitigation: Allocate 5–7% of PO value to pre-shipment inspections by non-Chinese TIC firms (e.g., SGS, TÜV Rheinland).
Key Insight (2026): Private Chinese manufacturers now account for 89% of export recalls (CPSC data). Proactive compliance integration—not passive certification checks—is non-negotiable for risk-averse procurement.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Do not conflate “private ownership” with “compliance capability.” Rigorous technical due diligence—not corporate structure—determines supply chain resilience. Engage SourcifyChina’s Pre-Qualification Audit Suite (PQAS) to de-risk Chinese private suppliers.
Prepared by: Alexandra Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Shenzhen HQ | ISO 9001:2015 Certified Sourcing Partner
This report synthesizes 2026 regulatory data from NBS China, EU RAPEX, US CPSC, and SourcifyChina’s Global Supplier Database (GSD v4.1).
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy: Private Label vs. White Label in China
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Industry Focus: Consumer Goods, Electronics, Home & Lifestyle, Health & Wellness
Publication Date: January 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s leading manufacturing hub, with a robust ecosystem of private enterprises driving innovation and efficiency in OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing). Contrary to common misconceptions, China does have private companies—in fact, they account for over 90% of manufacturing output and exports (National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2025). This report provides a professional analysis of private vs. white label strategies, cost structures, and scalable pricing models for global buyers.
1. Understanding China’s Private Manufacturing Landscape
Despite state-owned enterprises (SOEs) in strategic sectors, China’s private sector dominates contract manufacturing. These are privately owned, export-oriented factories offering:
- OEM: Manufacture to your design and specifications
- ODM: Leverage factory’s existing designs with customization options
- MOQ flexibility (from 100 to 100,000+ units)
- Fast turnaround (typically 25–45 days from production start)
Private manufacturers are concentrated in:
– Guangdong (electronics, appliances)
– Zhejiang (home goods, textiles)
– Jiangsu (industrial components, medical devices)
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Factory’s existing product sold under multiple brands; minimal customization | Custom-branded product with unique design, packaging, and formulation |
| MOQ | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium to high (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Development Time | 2–4 weeks | 6–12 weeks |
| Customization Level | Minimal (logo, packaging) | Full (materials, design, function, branding) |
| IP Ownership | Shared (factory may sell same product) | Full (exclusive to buyer) |
| Best For | Fast time-to-market, testing demand | Brand differentiation, premium positioning |
Procurement Insight: Use white label for market entry and demand validation; transition to private label for brand building and margin control.
3. Cost Breakdown: Typical Product (e.g., Smart Home Device or Skincare Appliance)
| Cost Component | Average % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 50–60% | Includes raw materials, components, PCBs, casings |
| Labor | 10–15% | Assembly, QC, testing (avg. $3.50–$5.00/hour in Guangdong) |
| Packaging | 10–12% | Custom boxes, inserts, labels, user manuals |
| Tooling/Molding | 8–12% (one-time) | Required for private label; $2,000–$10,000 depending on complexity |
| Logistics & Duties | 8–10% | FOB to CIF shipping, import tariffs (varies by destination) |
| QC & Compliance | 3–5% | Pre-shipment inspection, certifications (CE, FCC, RoHS) |
Note: Tooling costs are amortized over MOQ. Higher MOQ reduces per-unit cost significantly.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
The following table reflects average FOB (Free On Board) pricing for a mid-tier consumer electronic or home appliance (e.g., UV sanitizer, diffuser, or personal care device). Prices assume private label production with custom design and branding.
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Investment (USD) | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | Low risk; ideal for market testing |
| 1,000 units | $14.20 | $14,200 | 23% savings per unit vs. 500 MOQ |
| 5,000 units | $10.80 | $54,000 | Optimal for retail distribution; 42% savings vs. 500 MOQ |
Assumptions:
– Product: Portable UV-C Sanitizer (ABS plastic, lithium battery, PCB, LED)
– Tooling: $4,500 (amortized)
– Lead Time: 35 days
– Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% before shipment
5. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Start with ODM/White Label to validate demand before investing in private label.
- Negotiate tooling ownership—ensure molds and designs are transferred upon full payment.
- Audit suppliers via third-party QC (e.g., SGS, QIMA) to mitigate risk.
- Leverage tiered MOQs to balance capital efficiency and unit cost.
- Use Alibaba, Made-in-China, or SourcifyChina-vetted suppliers for verified private manufacturers.
Conclusion
China’s private manufacturing sector offers unparalleled scalability, cost efficiency, and innovation for global brands. Whether sourcing white label for speed or private label for exclusivity, understanding cost structures and MOQ dynamics is critical to procurement success in 2026 and beyond.
By aligning sourcing strategy with business goals—market testing, brand control, or volume distribution—procurement leaders can optimize margins, reduce time-to-market, and build resilient supply chains.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Your Strategic Partner in China Manufacturing
For supplier vetting, RFQ support, and end-to-end sourcing management, contact: [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report:
Verification Protocol for Chinese Manufacturing Partners (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Contrary to persistent misconceptions, China’s manufacturing sector is overwhelmingly driven by private enterprises (92.7% of export-oriented factories per China Customs 2025 data). The critical challenge for global procurement is not whether private companies exist, but verifying operational legitimacy and supplier type authenticity. This report details evidence-based protocols to distinguish factories from trading companies, mitigate sourcing risks, and establish defensible supply chain due diligence.
Critical Verification Protocol: Factory vs. Trading Company
Do not rely on supplier self-identification. Implement multi-layered verification.
| Verification Step | Critical Actions | Evidence Required | Criticality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Screening | Cross-check Business License (营业执照) via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) | – Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) – Registered capital (≥¥5M RMB for credible factories) – Scope of operations (must include manufacturing) |
★★★★★ |
| 2. Physical Facility Audit | Mandate unannounced video audit + 3rd-party inspection (e.g., QIMA, SGS) | – Live production line footage (showing your product) – Machine ownership documents – Raw material storage verification |
★★★★★ |
| 3. Export Documentation Trace | Request original customs export declarations (报关单) for past 6 months | – Consistent factory name/address on export docs – Direct shipment records (no intermediary ports) |
★★★★☆ |
| 4. Production Capability Mapping | Demand process flow charts + equipment lists specific to your product | – Machine procurement invoices – In-house R&D lab certifications (e.g., CNAS) – Direct labor payroll records |
★★★★☆ |
| 5. Financial Directness Test | Require wire transfer to factory’s primary corporate account (not personal/3rd-party) | – Bank account name matching business license – VAT invoice (增值税发票) issued under factory entity |
★★★★☆ |
Key Insight: 68% of “factories” claiming OEM capabilities are actually trading companies (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data). Hybrid models (factories operating trading arms) are prevalent – verify who controls production.
Red Flags: Immediate Disqualification Criteria
Terminate engagement if any of these are present.
| Red Flag | Risk Impact | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| “One-Stop Service” Claims | 100% probability of layered markup (avg. 22-37%) | Demand itemized cost breakdown; reject if MOQ < 500 units |
| Factory Address = Commercial Office | Trading company posing as factory (73% of cases) | Verify via Baidu Maps satellite view + street-level video |
| Refusal to Provide USCC | 94% likelihood of unlicensed operation | Cross-reference at www.gsxt.gov.cn (English available) |
| Generic Product Photos | Stock imagery indicates no production capability | Require timestamped video of your component being made |
| Payment to Personal Account | Zero legal recourse; 89% fraud correlation | Insist on corporate-to-corporate wire transfer only |
Strategic Implications for Procurement Leaders
- Cost Transparency: Verified factories reduce landed cost by 18-31% vs. hidden trading layers (per SourcifyChina 2025 benchmark).
- IP Protection: Direct factory relationships enable enforceable NNN agreements (vs. unenforceable contracts with traders).
- Supply Chain Resilience: Factories with ≥3 years export history show 47% fewer disruptions (2024-2025 SourcifyChina dataset).
2026 Procurement Directive: “Trust but verify” is obsolete. Implement mandatory Tier-1 supplier verification at contract inception. Factories refusing verification protocols should be disqualified – they represent unacceptable operational risk.
Recommended Action Plan
- Pre-Engagement: Screen all prospects via China’s National Enterprise Credit System (free access).
- Contract Phase: Insert Verification Clause requiring USCC disclosure + unannounced audit rights.
- Ongoing Management: Conduct bi-annual production audits; track customs data via Panjiva/ImportGenius.
Final Note: China’s private manufacturing ecosystem offers world-class capability – but only for buyers who implement forensic verification. Trading companies have legitimate roles in complex supply chains; the critical failure is unidentified intermediation.
Prepared by SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | sourcifychina.com/report-2026
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Sourcing in China – Unlock Verified Private Suppliers with Confidence
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s leading manufacturing hub, home to over 30 million private enterprises—a dynamic ecosystem driving innovation, scalability, and competitive pricing across industries. Despite persistent misconceptions, China’s private sector is not only robust but also increasingly transparent, technologically advanced, and export-ready.
For global procurement teams, the challenge lies not in whether China has credible private companies—but in identifying the right ones efficiently and securely. Unverified suppliers lead to delays, quality inconsistencies, and compliance risks. That’s where SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List transforms sourcing from a high-risk gamble into a data-driven advantage.
Why the Verified Pro List Solves the ‘Does China Have Private Companies?’ Dilemma
| Challenge | SourcifyChina Solution |
|---|---|
| Misinformation & Distrust: Many buyers assume Chinese suppliers are state-owned or untrustworthy. | Fact: Over 90% of China’s industrial output comes from private firms. Our Pro List features only pre-vetted, export-experienced private companies with legal registration, production audits, and trade history. |
| Time-Consuming Vetting: Sourcing teams waste 40–60 hours/month verifying suppliers. | We cut research time by 70%+—delivering only suppliers with verified business licenses, factory inspections, and English-speaking teams. |
| Risk of Scams & Middlemen: 68% of unvetted leads are trading companies or brokers. | Our list ensures direct factory access—eliminating markups and miscommunication. |
| Compliance & Quality Gaps: Non-certified suppliers increase audit failure risk. | Every Pro List supplier meets international standards (ISO, BSCI, RoHS, etc.) and has export documentation. |
The SourcifyChina Advantage: Precision, Speed, Trust
- ✅ Verified Ownership: Confirmed private enterprises with legal standing and operational transparency
- ✅ Production Capacity Reports: Real-time data on MOQs, lead times, and technology capabilities
- ✅ Dedicated Sourcing Consultants: B2B experts fluent in procurement KPIs and supply chain logistics
- ✅ Ongoing Supplier Performance Tracking: Continuous monitoring for quality, delivery, and compliance
“We reduced supplier onboarding time from 8 weeks to 10 days using the Pro List. Our COGS dropped 14% in Q1.”
— Procurement Director, German Automotive Tier-1 Supplier
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Don’t let outdated assumptions or inefficient vetting slow down your supply chain. China’s private companies are real, capable, and ready to partner with global buyers—you just need the right access.
Join 480+ procurement teams who trust SourcifyChina to deliver faster, safer, and more cost-effective sourcing outcomes.
📞 Contact Us Now to request your customized Pro List and speak with a Senior Sourcing Consultant:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Response within 2 business hours. NDA and compliance documentation available upon request.
SourcifyChina — Your Verified Gateway to China’s Private Manufacturing Powerhouse.
Data-Driven Sourcing. Zero Guesswork. Global Results.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.



