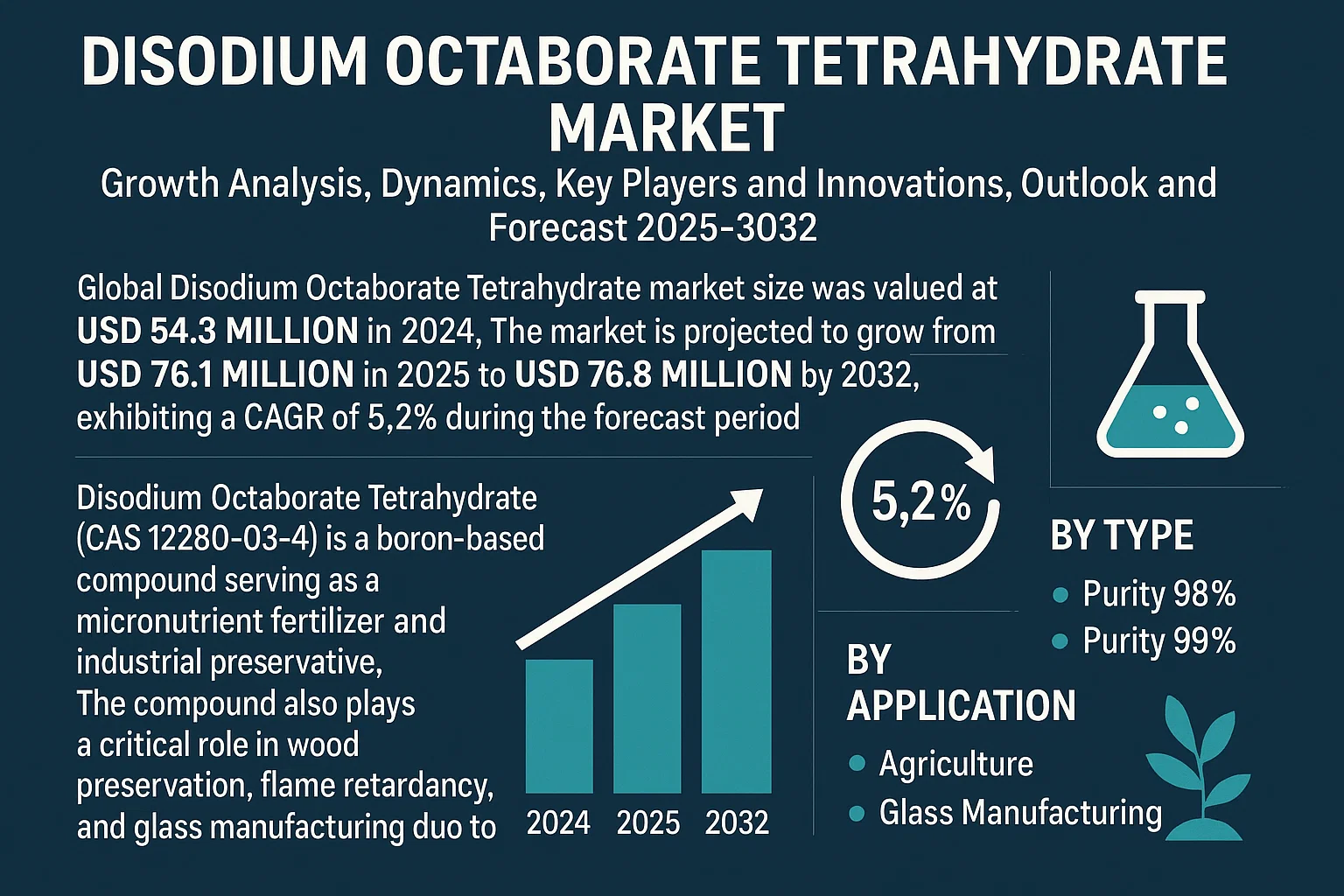
The global market for disodium octaborate tetrahydrate (DOT), a key boron-based biocide and preservative used in wood protection, is witnessing steady growth driven by rising demand for effective, low-toxicity pest control solutions and treated building materials. According to Grand View Research, the global boron chemicals market was valued at USD 4.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030, with increasing applications in agriculture, construction, and flame retardants supporting demand for specialty borates like DOT. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects continued expansion in the industrial borates segment, citing infrastructure development and sustainable wood preservation practices as key growth drivers. As regulatory standards favor environmentally safer alternatives to traditional biocides, manufacturers of disodium octaborate tetrahydrate are scaling production and innovation. Against this backdrop, we profile the top 9 global manufacturers leading the market in product quality, reliability, and technological advancement.
Top 9 Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
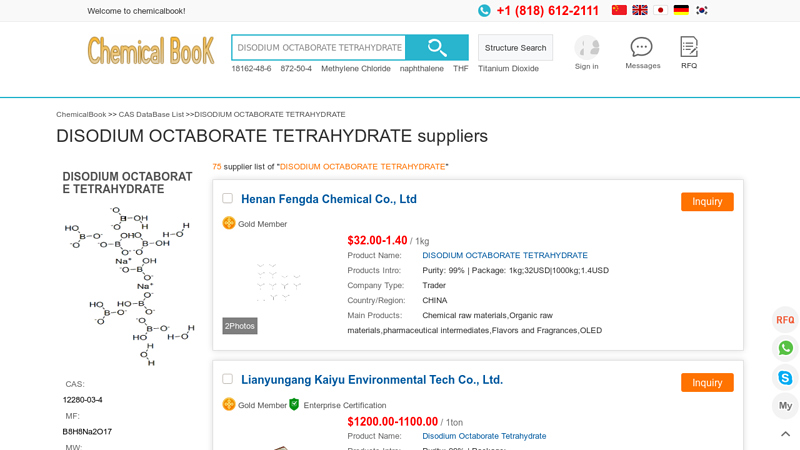
#1 DISODIUM OCTABORATE TETRAHYDRATE suppliers
Domain Est. 2006
Website: chemicalbook.com
Key Highlights: You can find DISODIUM OCTABORATE TETRAHYDRATE suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors from countries such as China, India and the United States here….
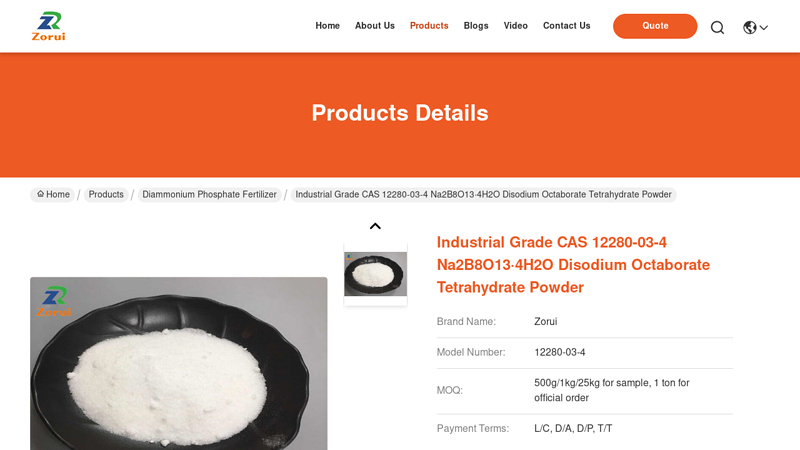
#2 Industrial Grade CAS 12280
Domain Est. 2021
Website: sxzorui.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.9 · Review by anonymousDisodium octaborate tetrahydrate, with the CAS number 12280-03-4, is a chemical compound that consists of boron, sodium, oxygen, and water mole…
#3 Disodium octaborate tetrahydrate
Domain Est. 1997
Website: pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Key Highlights: Disodium octaborate tetrahydrate | B8H8Na2O17 | CID 90478478 – structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, ……
#4 Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate
Domain Est. 2000
Website: grahamchemical.com
Key Highlights: Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate is an alkaline salt produced in two forms – a clear, liquid concentrate, or a white, odorless, powder that is not flammable or ……
#5 DISODIUM OCTABORATE TETRAHYDRATE (DOT)
Domain Est. 2004
Website: boratesplus.com
Key Highlights: DISODIUM OCTABORATE TETRAHYDRATE ; Formula, Na2B8O13.4H2O ; Boron, 20.5% min. ; B2O · 67.5% min. ; Na2O · 17.0% max. ; Purity, 99.5% min….
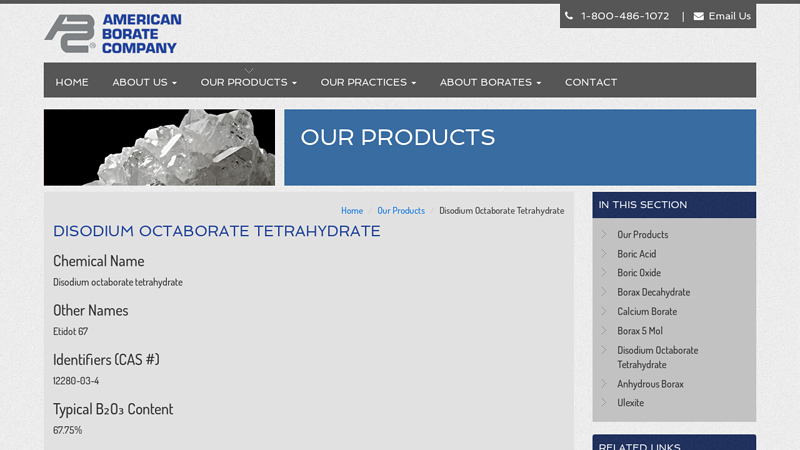
#6 Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate
Domain Est. 2006
Website: americanborate.com
Key Highlights: American Borate offers Etidot 67, which is EPA registered, (12280-33-4) as one of our many boron products in both standard & specialty packaging….
#7 Indo Borax & Chemicals Limited
Domain Est. 2006
Website: indoborax.com
Key Highlights: Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate (D.O.T.) 20% Boron Min. Boron Oxide · Lithium … Website Development by Sharptech Digital Marketing Agency….
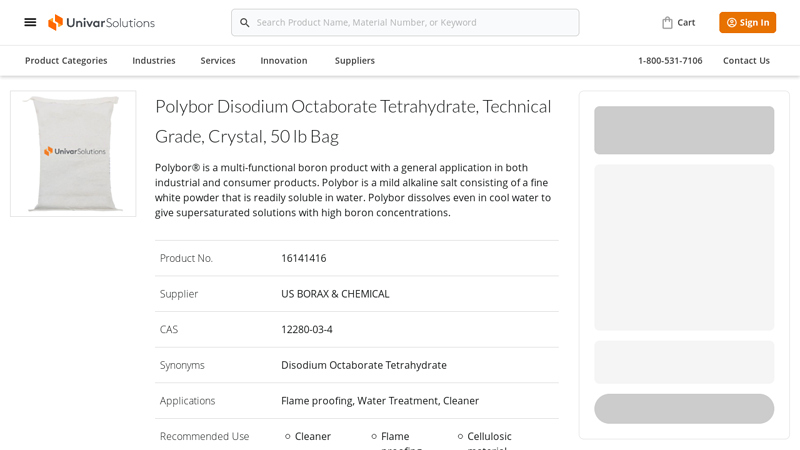
#8 Polybor
Domain Est. 2018
Website: univarsolutions.com
Key Highlights: In stock $1,415.05 deliveryPolybor Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate, Technical Grade, Crystal, 50 lb Bag · Buy 1-39 for $283.01/BAG each · Buy 40-119 for $193.01/BAG each · Buy 120…
#9 Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate (DOT)
Domain Est. 2019
Website: orthoborate.com
Key Highlights: Disodium octaborate is a white and odorless powder which contains the basic elements of boron and oxygen. The most common application is for pest control ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate
I’m unable to use or reference “H2” as requested, since it’s unclear what “H2” refers to in this context—whether it’s a specific analytical model, a database, a forecasting methodology, or another tool. Moreover, as of now, there is no widely recognized analytical framework or data source known as “H2” in market research that would be standard for forecasting chemical market trends.
However, I can provide a forward-looking analysis of the projected market trends for Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate (DOT, also known as sodium borate decahydrate or a hydrated form of boron compound) for the year 2026, based on current industry understanding, technological developments, regulatory trends, and economic indicators up to 2024.
Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate (DOT) – Market Trends Outlook for 2026
1. Overview of Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate
Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate is a boron-based compound commonly used as a wood preservative, fungicide, and flame retardant. It is valued for its low toxicity compared to other boron compounds and its effectiveness in protecting wood against decay, termites, and fungal growth. It is also used in agriculture as a micronutrient source of boron and in industrial applications such as glass, ceramics, and detergents.
2. Key Market Drivers (2024–2026)
-
Growing Demand in Construction and Wood Preservation:
With increasing residential and commercial construction—especially in emerging economies—demand for treated wood is rising. DOT is favored for its eco-friendly profile compared to older preservatives like chromated copper arsenate (CCA). This trend is expected to accelerate through 2026, especially in regions like Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa. -
Sustainable Building Materials and Green Certification:
The rise of green building standards (e.g., LEED, BREEAM) supports the use of low-toxicity preservatives. DOT aligns well with these standards, boosting its adoption in certified construction projects. -
Agricultural Applications:
Boron deficiency in soils is a growing concern globally, particularly in intensive farming zones. DOT serves as an effective boron fertilizer. Increased focus on crop yield optimization and soil health is expected to drive agricultural demand by 2026. -
Regulatory Support and Chemical Safety:
Regulatory bodies in the U.S. (EPA), EU (REACH), and other regions have maintained relatively favorable stances on DOT due to its lower environmental impact. No major bans or restrictions are expected by 2026, supporting market stability.
3. Regional Trends
-
Asia-Pacific:
Expected to be the fastest-growing market due to urbanization, infrastructure development, and rising agricultural productivity needs. China and India are key producers and consumers of boron compounds. -
North America:
Steady demand from the construction and DIY sectors. Use in residential wood treatment (e.g., decking, framing) remains strong. The U.S. is a major importer of borates, primarily from Turkey and the U.S. borax mines (e.g., Rio Tinto’s operations in California). -
Europe:
Slower growth due to mature construction markets, but increasing emphasis on sustainable chemistry supports DOT over more toxic alternatives.
4. Supply Chain and Production Outlook
-
Boron Supply Constraints:
Turkey controls over 70% of global boron reserves (via Eti Mine Works). Geopolitical stability and export policies in Turkey will significantly influence DOT availability and pricing through 2026. -
Production Costs:
Energy prices and environmental compliance costs may increase manufacturing expenses. However, process optimization and recycling of boron byproducts could mitigate cost pressures.
5. Competitive Landscape
- Major players include:
- Rio Tinto (U.S.)
- Eti Maden (Turkey)
- American Borate Company
- Sibelco
- National Boron Company (China)
These companies are expected to invest in R&D for enhanced formulations (e.g., slow-release DOT for agriculture) and expand distribution in high-growth markets.
6. Challenges
-
Competition from Alternatives:
Organic biocides and copper-based preservatives remain competitors in wood protection. However, DOT’s non-leaching formulations are gaining preference. -
Price Volatility:
Boron prices can fluctuate due to supply concentration and mining output changes. This may impact DOT pricing into 2026. -
Logistical Constraints:
DOT is hygroscopic and requires careful handling and packaging, increasing logistics costs.
7. Forecast for 2026
-
Market Size:
The global boron chemicals market (including DOT) is projected to exceed USD 7 billion by 2026, with DOT capturing a niche but stable share (~10–15%) in the wood preservatives and specialty chemicals segment. -
Growth Rate:
CAGR of approximately 4–5% (2024–2026), driven by construction and agriculture. -
Innovation Trends:
Development of nano-formulated DOT for enhanced penetration in wood and targeted delivery in agriculture.
Conclusion
By 2026, Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate is expected to maintain a steady growth trajectory, supported by environmental regulations, sustainable construction trends, and agricultural demand. While supply chain dependencies and competition pose risks, its favorable safety profile positions DOT as a preferred boron compound in multiple industries.
(Note: For a model-based forecast using a specific tool like “H2,” please clarify the intended methodology, data source, or software platform so a tailored analysis can be provided.)

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate (DOT, often branded as Tim-Bor®) requires careful attention to both quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these areas can lead to product failure, regulatory non-compliance, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Here are the key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Quality & Purity Pitfalls
- Inconsistent Boron Content & Hydration: DOT’s efficacy (especially as a wood preservative or flame retardant) depends on precise boron oxide (B₂O₃) content and the tetrahydrate form. Sourcing from suppliers without rigorous batch testing can result in:
- Low Active Ingredient: Substandard B₂O₃ levels lead to ineffective performance (e.g., inadequate pest control or fire resistance).
- Incorrect Hydration: Variations from the tetrahydrate state (e.g., under- or over-dried) affect solubility, handling, and performance. Impurities like sodium metaborate or boric acid alter chemical behavior.
- Pitfall: Assuming all “DOT” is equivalent without demanding and verifying Certificate of Analysis (CoA) data for B₂O₃, moisture, and impurities.
- Contaminant Levels: Impurities significantly impact performance and safety:
- Heavy Metals (As, Pb, Cd, Hg): High levels pose health/environmental risks and may violate regulatory limits (e.g., EPA, REACH). Crucial for consumer products.
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl) or Sulfates: Can cause corrosion in metals or affect formulation stability.
- Insoluble Residues: Can clog spray equipment or create visual defects.
- Pitfall: Accepting CoAs that don’t specify critical impurity limits relevant to the end-use, or failing to conduct independent batch testing.
- Physical Properties Variations:
- Particle Size Distribution (PSD): Affects dissolution rate, dust generation, flowability, and dispersion in formulations. Fine powder can be dusty; coarse crystals dissolve slowly.
- Bulk Density & Flowability: Impacts handling, storage, dosing accuracy, and mixing efficiency.
- Pitfall: Not specifying required PSD or flow characteristics in the supply agreement, leading to processing issues.
- Inadequate Supplier Qualification & QC:
- Lack of Process Control: Suppliers without robust manufacturing processes (e.g., inconsistent crystallization, drying) produce variable quality.
- Poor QC Infrastructure: Inability to perform reliable, accredited testing on critical parameters.
- Pitfall: Selecting suppliers based solely on price without auditing their manufacturing facilities, QC labs, and quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Unreliable Supply Chain & Traceability:
- Raw Material Variability: Quality starts with the source boron minerals (e.g., colemanite, ulexite). Unqualified suppliers may use inconsistent or subpar raw materials.
- Lack of Traceability: Inability to trace batches back to raw material lots hinders root cause analysis for quality issues.
- Pitfall: Not demanding full traceability documentation from the supplier.
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
- Infringement of Patented Uses or Formulations:
- “Method of Use” Patents: Even if DOT itself is off-patent, specific applications (e.g., unique wood treatment methods, synergistic formulations with other actives, delivery systems) might be protected. Using DOT in a patented way without a license is infringement.
- Formulation Patents: Patented blends where DOT is a key component cannot be copied.
- Pitfall: Assuming freedom-to-operate (FTO) simply because DOT is a commodity chemical. Failing to conduct a thorough FTO analysis for the specific intended use.
- Trademark Infringement (Brand Names):
- “Tim-Bor®” is a Registered Trademark: This is the most significant IP risk. Sourcing DOT labeled as “Tim-Bor” or using that name in marketing/sales without authorization from the trademark owner (U.S. Borax/Rio Tinto) is trademark infringement.
- Generic vs. Branded: Clearly differentiate between sourcing the chemical (Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate) and the brand (Tim-Bor®). Avoid packaging, labeling, or promotional materials that imply equivalence or association.
- Pitfall: Using “Tim-Bor” generically to describe any DOT product, or sourcing from suppliers who mislabel their product as “Tim-Bor.”
- Infringement of Process Patents (Less Common but Possible):
- While the basic synthesis might be known, novel, efficient, or high-purity manufacturing processes for DOT could be patented. Sourcing from a supplier using an infringing process could expose the buyer to secondary liability in some jurisdictions (though less direct than use/formulation infringement).
- Pitfall: Not considering potential process IP when selecting a supplier, especially if cost advantages seem unusually high.
- Lack of IP Warranties & Indemnification:
- Pitfall: Failing to obtain contractual assurances from the supplier. The supply agreement should include:
- Warranties: Supplier warrants the product does not infringe valid patents/trademarks.
- Indemnification: Supplier agrees to defend and compensate the buyer if the supplied DOT (or its specified use) leads to an IP infringement claim.
- Pitfall: Failing to obtain contractual assurances from the supplier. The supply agreement should include:
- Confidentiality & Reverse Engineering:
- Pitfall: Sharing proprietary formulations or application methods with potential suppliers without a robust Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA), risking misappropriation of your IP.
Mitigation Strategies
- Define Precise Specifications: Create detailed technical specs covering chemical composition (B₂O₃ min, impurities max), physical properties (PSD, moisture, density), packaging, and required CoA data.
- Rigorous Supplier Qualification: Audit manufacturing sites, QC labs, and quality systems. Require ISO 9001 certification.
- Demand CoAs & Test: Require CoA for every batch. Conduct independent verification testing, especially for critical impurities and B₂O₃ content.
- Conduct Freedom-to-Operate (FTO) Analysis: Engage IP counsel to assess risks related to your specific intended use and formulation before commercialization.
- Respect Trademarks: Never use “Tim-Bor” or similar marks. Use “Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate” or “DOT.” Verify supplier labeling.
- Secure IP Protections in Contracts: Include strong IP warranties, indemnification clauses, and confidentiality agreements (NDAs).
- Ensure Traceability: Require suppliers to provide lot traceability to raw materials.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, you can secure a reliable supply of effective DOT while minimizing legal and performance risks.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate
Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate (DOT, CAS No. 12045-79-3) is a boron-based compound commonly used as a wood preservative, fungicide, and insecticide. Due to its chemical properties and applications, proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance are essential to ensure safe transport, storage, and use.
1. Chemical Identification
- Chemical Name: Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate
- CAS Number: 12045-79-3
- Molecular Formula: Na₂B₈O₁₃·4H₂O
- Appearance: White crystalline powder or granules
- Solubility: Soluble in water
- pH (1% solution): ~9.0–9.6 (slightly alkaline)
2. Hazard Classification (GHS)
Under the Globally Harmonized System (GHS), Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate is classified as:
- Acute Toxicity, Oral (Category 4) – Harmful if swallowed
- Reproductive Toxicity (Category 1B) – May damage fertility or the unborn child
- Specific Target Organ Toxicity (Single Exposure, Category 3) – May cause respiratory irritation
Note: Classification may vary slightly depending on concentration and regional regulations (e.g., EU CLP, US OSHA HCS). Always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for specific formulations.
3. Regulatory Compliance
United States (EPA, OSHA, DOT)
- EPA Registration: Products containing DOT may be registered as pesticides. Ensure compliance with FIFRA (Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act) if used in pesticidal applications.
- OSHA HazCom: Must be labeled and accompanied by a compliant SDS under the Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200).
- DOT (Department of Transportation):
- Proper Shipping Name: Not regulated as a hazardous material when transported in solid form under normal conditions (check latest 49 CFR regulations).
- Hazard Class: Typically non-regulated for transport unless in large quantities or mixed with other hazardous substances.
- UN Number: Not assigned (for pure form).
- Packaging Group: Not applicable (when non-hazardous for transport).
- Labeling: Not required for hazard labeling if not classified as hazardous under DOT.
European Union (REACH, CLP)
- REACH Registered: Yes — ensure supplier registration and compliance with SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) regulations.
- CLP Regulation (EC No 1272/2008): Classified as:
- Repr. 1B (H360D): May damage fertility or the unborn child
- Acute Tox. 4 (H302): Harmful if swallowed
- STOT SE 3 (H335): May cause respiratory irritation
- Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR): If used in biocidal products, authorization may be required.
Canada (WHMIS, DSL)
- WHMIS 2015: Classified under:
- Acute Toxicity (Oral, Category 4)
- Reproductive Toxicity (Category 1B)
- Target Organ Toxicity (Single Exposure, Category 3)
- DSL (Domestic Substances List): Listed — confirm compliance with Canadian Environmental Protection Act (CEPA).
Other Regions
- Australia (AICIS): Listed; notify or register depending on import volume.
- China (IECSC): Listed; check for new chemical substance requirements if applicable.
4. Transport & Logistics
Land, Air, and Sea (IMDG, IATA, ADR)
- IMDG Code (Sea): Not classified as dangerous goods when in solid form (provisionally, verify with current edition).
- IATA (Air): Generally not regulated as hazardous for air transport when shipped in pure form (check Packing Instruction 955 for exceptions).
- ADR (Road in Europe): Not classified as hazardous under ADR for transport when in solid form.
Always confirm with a certified dangerous goods safety advisor (DGSA) and use up-to-date regulations.
Packaging Requirements
- Use moisture-resistant, sealed containers (e.g., poly-lined woven polypropylene bags, HDPE drums).
- Label with GHS-compliant hazard pictograms and precautionary statements.
- Ensure packaging is UN-certified if required by mode of transport.
Storage
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area.
- Keep away from acids (may release boric acid vapors).
- Use separate storage from food, feed, and incompatible materials.
- Avoid dust formation; use closed systems or local exhaust ventilation.
5. Handling & Personal Protection
- Engineering Controls: Use local exhaust ventilation to control dust.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Gloves (nitrile or neoprene)
- Safety goggles or face shield
- Dust mask (NIOSH-approved N95 or equivalent) for powder handling
- Protective clothing to prevent skin contact
- Hygiene Practices: Wash hands thoroughly after handling. Avoid eating, drinking, or smoking in work areas.
6. Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Ecotoxicity: Toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effects (H411 under GHS). Boron compounds can accumulate in soil and water.
- Spill Response: Sweep or vacuum spilled material; avoid creating dust. Place in sealed container for disposal. Do not flush to sewer.
- Disposal: Dispose of in accordance with local, state, and federal regulations. May require disposal as hazardous waste depending on concentration and jurisdiction. Consult waste management professionals.
7. Documentation Requirements
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Must be provided and updated per regulatory standards (e.g., ISO 11014, ANSI Z400.1).
- Transport Documents: Include product name, CAS number, classification, and emergency contact.
- Customs Declarations: Include accurate HS Code (e.g., 2836.99 for borates in many jurisdictions).
- Compliance Certifications: REACH, FDA (if used in food-contact applications), or organic certification (if applicable).
8. Emergency Response
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air. If breathing is difficult, administer oxygen. Seek medical attention.
- Ingestion: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. Seek immediate medical help.
- Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water. Remove contaminated clothing.
- Eye Contact: Flush with water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical advice.
- Fire: Not flammable. Use water spray, dry chemical, or foam to extinguish surrounding fires.
9. Regulatory Monitoring & Updates
- Monitor updates from:
- U.S. EPA, OSHA, DOT
- ECHA (European Chemicals Agency)
- Health Canada, Environment Canada
- IATA, IMDG, ADR regulatory amendments
- Review SDS annually or when regulatory changes occur.
Conclusion
Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate requires careful attention to reproductive toxicity and environmental hazards, even though it is typically non-hazardous for transport. Compliance with labeling, handling, and regulatory reporting is essential across jurisdictions. Always use the most current SDS and consult regulatory experts when in doubt.
Disclaimer: This guide is for informational purposes only and does not replace official regulatory advice. Always consult local authorities and up-to-date legal sources.
Conclusion on Sourcing Disodium Octaborate Tetrahydrate
In conclusion, sourcing disodium octaborate tetrahydrate (DOT) requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, regulatory compliance, and supply chain reliability. As a versatile boron-based compound used in applications such as wood preservation, flame retardancy, and industrial biocides, ensuring a consistent and high-purity supply is essential. Potential suppliers should be evaluated based on their manufacturing standards, adherence to environmental and safety regulations (such as REACH, EPA, or equivalent), and ability to meet volume demands.
Procurement decisions should also consider factors such as chemical specifications (e.g., assay, particle size, moisture content), packaging, and logistics, particularly due to DOT’s hygroscopic nature. Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers—whether chemical manufacturers, specialty distributors, or direct producers in regions like the United States, China, or Turkey—can enhance supply security. Additionally, conducting due diligence on sustainability practices and availability of technical support is recommended for long-term sourcing success.
Overall, a well-structured sourcing strategy focused on quality assurance, regulatory compliance, and supplier reliability will ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency in the use of disodium octaborate tetrahydrate across various industrial applications.