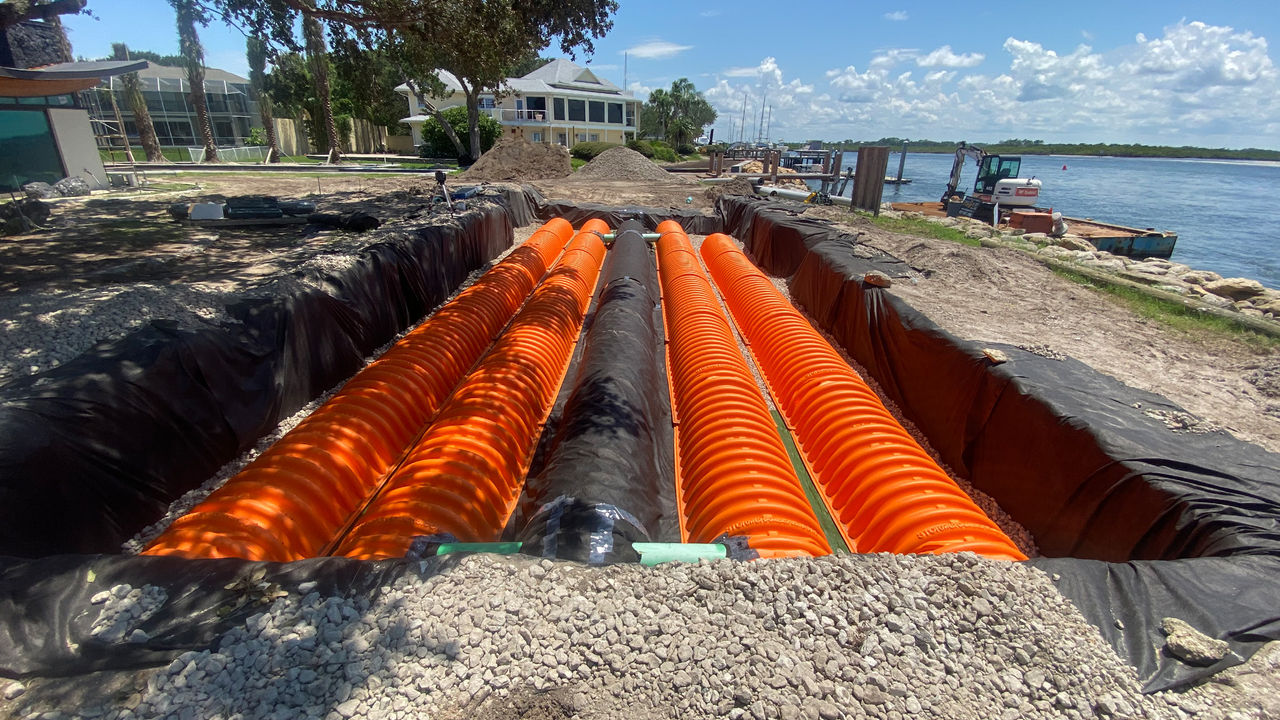
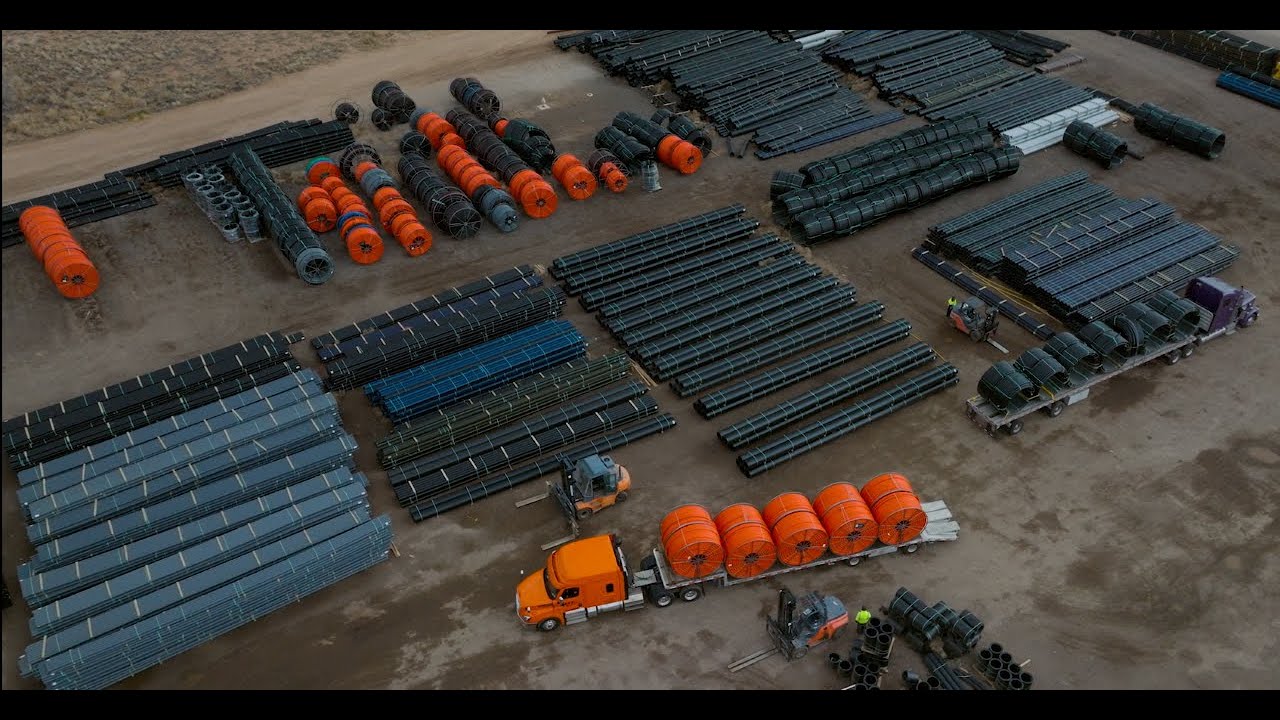
The global discharge pipe market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand across industries such as water and wastewater treatment, oil & gas, power generation, and chemical processing. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the industrial pipe and tube market—of which discharge pipes are a critical segment—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by rising infrastructure development, stricter environmental regulations requiring efficient fluid handling systems, and the ongoing modernization of aging industrial facilities. Additionally, Grand View Research estimates that the global industrial piping systems market was valued at USD 78.4 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand further, supported by advancements in corrosion-resistant materials and increased investments in sustainable water management. As demand intensifies, selecting reliable discharge pipe manufacturers has become crucial for ensuring system longevity, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Top 10 Discharge Pipe Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1934
Website: lane-enterprises.com
Key Highlights: As a leading drainage pipe manufacturer since 1934, Lane is uniquely positioned to meet the drainage demands for a variety of land developments and applications ……
#2 Sioux Chief: Rough Plumbing Products
Domain Est. 1997
Website: siouxchief.com
Key Highlights: We are an American manufacturer. Sioux Chief believes in making our products right here in America. American manufacturing is important….
#3 Cresline Plastic Pipe Co.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cresline.com
Key Highlights: As one of the largest full-line pipe manufacturers, Cresline’s family of companies offers industry leading coast-to-coast service….
#4 JM Eagle™
Domain Est. 2007
Website: jmeagle.com
Key Highlights: JM Eagle · Delivering life’s essentials through the most eco-friendly plastic pipe products on the market. · Express Service Trucks (ESTs) Deliver within 24 hours ……
#5 U.S. Pipe
Domain Est. 1995
Website: uspipe.com
Key Highlights: US Pipe, a Quikrete company, offers a complete range of Ductile Iron Pipe, Restrained Joint Pipe, Fabrication, Gaskets, and Fittings….
#6 NDS Stormwater Drainage Systems & Irrigation Solutions
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ndspro.com
Key Highlights: Shop NDS irrigation, stormwater, and drainage solutions. Engineered for lasting performance in home landscapes, commercial spaces, and large job sites….
#7 Advanced Drainage Systems
Domain Est. 2000
Website: adspipe.com
Key Highlights: Advanced Drainage Systems provides high-performing, durable pipe and innovative stormwater management solutions. Discover our industry-leading products ……
#8 Drainage, Erosion Control & Geosynthetic Products
Domain Est. 2004
Website: drainagesolutionsinc.com
Key Highlights: Drainage Solutions specializes in a variety of drainage products and brands, including pipe, valves and fittings, plus catch basins, grates, channel drains and ……
#9 United Poly Systems
Domain Est. 2011
Website: unitedpolysystems.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture custom HDPE pipe in the USA for the water and sewer, power & communications and oil & gas markets. Contact us for a quote now!…
#10 Contech Engineered Solutions
Domain Est. 2012
Website: conteches.com
Key Highlights: MANUFACTURING AMERICA’S INFRASTRUCTURE ; PIPE. Pipe materials for drainage systems, culverts, and sanitary sewer applications. ; STORMWATER MANAGEMENT….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Discharge Pipe
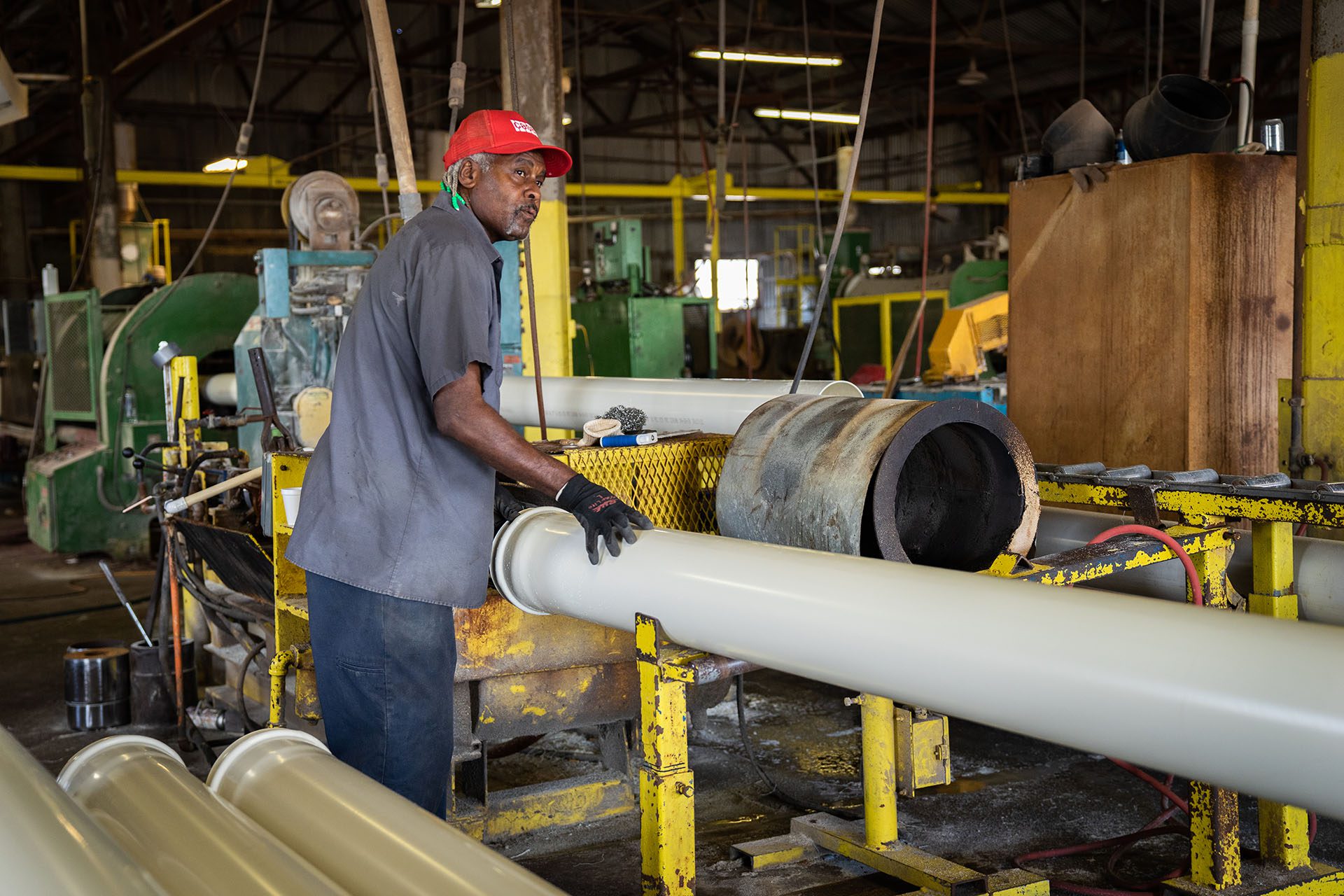

H2: Projected Market Trends for Discharge Pipes in 2026
The global discharge pipe market is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by evolving industrial demands, infrastructure development, and technological advancements. Several key trends are expected to shape the market landscape in the coming years.
-
Increased Demand from Water and Wastewater Treatment Sectors
With growing urbanization and stricter environmental regulations, the need for efficient water and wastewater management systems is rising. Discharge pipes play a critical role in transporting treated and untreated water from treatment plants to disposal or reuse points. Governments worldwide are investing heavily in upgrading aging water infrastructure, which will significantly boost demand for durable and corrosion-resistant discharge pipes, especially in emerging economies. -
Shift Toward Sustainable and High-Performance Materials
There is a clear trend toward the adoption of advanced materials such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP), and lined steel pipes. These materials offer superior resistance to corrosion, abrasion, and chemical exposure—critical in harsh discharge environments. By 2026, eco-friendly and recyclable piping solutions are expected to gain market share, aligning with global sustainability goals and circular economy principles. -
Growth in Industrial and Energy Applications
The oil & gas, power generation, and chemical processing industries require reliable discharge systems for effluent and cooling water. As these sectors expand—particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific and the Middle East—the demand for high-pressure and thermally stable discharge pipes will rise. Offshore and onshore drilling activities, along with the commissioning of new power plants, will further fuel market growth. -
Technological Integration and Smart Monitoring
The integration of IoT-enabled sensors and smart monitoring systems in discharge pipe networks is an emerging trend. By 2026, predictive maintenance and real-time flow monitoring are expected to become standard in large-scale installations, reducing downtime and preventing leaks or failures. This digital transformation will drive demand for “smart” discharge systems with embedded diagnostics and remote control capabilities. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is projected to dominate the discharge pipe market by 2026, led by rapid industrialization and infrastructure projects in China, India, and Southeast Asia. North America and Europe will see steady growth due to regulatory mandates and replacement cycles in aging municipal systems. Meanwhile, the Middle East and Africa will experience increased demand driven by desalination projects and oil & gas developments. -
Regulatory and Environmental Pressures
Stricter environmental regulations concerning effluent discharge and pollution control are compelling industries to upgrade their piping infrastructure. Compliance with standards such as ISO 14001 and local environmental codes will necessitate the use of leak-proof, high-integrity discharge systems, pushing innovation and adoption of higher-grade materials.
In conclusion, the 2026 discharge pipe market will be shaped by sustainability, digitalization, and infrastructure modernization. Manufacturers and stakeholders who adapt to these trends—by innovating materials, embracing smart technologies, and aligning with regulatory frameworks—are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Discharge Pipe (Quality, IP)
When sourcing discharge pipes—critical components in pumping systems for wastewater, industrial processes, or drainage—overlooking key quality and Ingress Protection (IP) factors can lead to premature failure, safety hazards, and costly downtime. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Material Quality and Compatibility
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting discharge pipes made from substandard or incompatible materials. Pipes exposed to corrosive fluids, abrasive slurries, or extreme temperatures require specific material properties. Using generic PVC or carbon steel in aggressive environments leads to rapid degradation, leaks, and system failure. Always verify material certifications (e.g., ASTM, ISO) and ensure chemical resistance aligns with the intended application.
Ignoring Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings for Associated Components
While the pipe itself isn’t typically assigned an IP rating, associated components like pump housings, flanges, or control enclosures connected to the discharge line often are. A common pitfall is sourcing pipes without considering the IP requirements of the overall system. For example, installing a discharge pipe in a wet or dusty environment without ensuring connected electrical components meet IP65 or higher can result in water ingress, electrical faults, or motor damage.
Poor Dimensional and Tolerance Compliance
Low-quality discharge pipes may deviate from standard dimensions or have inconsistent wall thicknesses. This leads to misalignment during installation, stress on joints, and potential leaks. Always demand dimensional compliance documentation and conduct visual or physical inspections upon delivery to ensure consistency with project specifications.
Overlooking Hydrostatic and Pressure Ratings
Discharge pipes must withstand system pressure, including surge or water hammer effects. Sourcing pipes with insufficient pressure ratings (e.g., PN10 instead of required PN16) risks bursting or joint failure. Verify the maximum allowable working pressure and include a safety margin for transient events.
Compromising on Joint and Connection Quality
Even high-quality pipe material can fail due to poor joints. Using incompatible gaskets, incorrect flange types, or improper installation techniques compromises system integrity. Ensure compatibility between pipe material and connection methods (e.g., spigot & socket, flanged, threaded), and confirm joint sealing materials meet temperature and chemical resistance needs.
Skipping Third-Party Testing and Certification
Relying solely on supplier claims without third-party validation is risky. Reputable discharge pipes should come with test reports for pressure, leakage, and material composition. Avoid suppliers who cannot provide certifications from recognized bodies, as this increases the likelihood of counterfeit or non-compliant products.
Neglecting Environmental and Installation Conditions
Pipes installed outdoors or underground face UV exposure, soil movement, or freezing temperatures. Sourcing pipes without UV stabilizers, sufficient flexibility, or freeze-thaw resistance leads to cracking and failure. Always match pipe specifications to the installation environment, including burial depth and backfill requirements.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—focusing on material quality, system-level IP considerations, and comprehensive certification—procurement teams can ensure reliable, long-lasting discharge pipe performance.
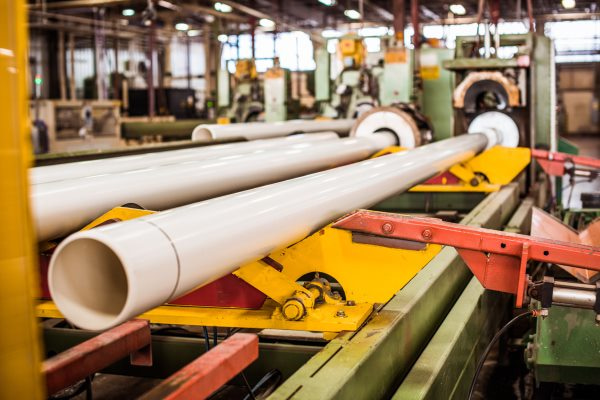

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Discharge Pipe
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, handling, storage, and regulatory adherence related to discharge pipes—critical components in fluid transfer systems used across industries such as marine, industrial processing, wastewater management, and energy.
1. Transportation & Handling
Packaging & Protection
– Discharge pipes must be packaged to prevent physical damage (e.g., dents, scratches, deformation) during transit. Use wooden crates, protective end caps, and internal supports for large or fragile pipes.
– Wrap metallic pipes with anti-corrosion paper or use VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) packaging for long-distance or marine shipments.
– Ensure plastic or composite pipes are shielded from UV exposure and extreme temperatures.
Loading & Securing
– Use appropriate lifting equipment (slings, spreader bars) to avoid stress on pipe ends. Never lift by threaded or flanged ends.
– Secure loads on trucks, containers, or vessels to prevent shifting. Use dunnage and lashings compliant with ISO 1496 and national freight safety standards.
– Segregate discharge pipes from hazardous materials unless compatibility is verified.
Transport Modes
– Road: Comply with national weight, dimension, and load securement regulations (e.g., FMCSA in the U.S., ADR in Europe for hazardous zones).
– Sea: Follow IMDG Code guidelines if shipped with hazardous materials. Use moisture-resistant packaging and ensure containers are ventilated if needed.
– Air: Adhere to IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if applicable (e.g., pipes coated with flammable substances). Confirm dimensional and weight limits with carriers.
2. Storage Requirements
Environment
– Store in dry, covered areas away from direct sunlight, moisture, and corrosive atmospheres.
– Maintain stable temperatures; avoid freezing conditions for pipes with coatings or linings.
– Elevate pipes off the ground using racks or wooden beams to prevent soil contact and water pooling.
Stacking
– Stack pipes horizontally with even support at multiple points to prevent bending or ovalization.
– Limit stack height based on pipe diameter, wall thickness, and material (refer to manufacturer guidelines).
– Separate different pipe types, sizes, and materials to avoid cross-contamination or damage.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Material & Safety Standards
– Ensure discharge pipes meet applicable standards such as:
– ASME B31.3 (Process Piping)
– API 5L (Line Pipe for Petroleum)
– ASTM A53/A106 (Steel Pipe)
– ISO 14692 (Glass-Reinforced Plastic Piping)
– Verify compliance with pressure, temperature, and chemical resistance ratings for the intended application.
Environmental Regulations
– For pipes used in waste or effluent discharge, comply with:
– EPA Clean Water Act (U.S.) – Permits for discharge points (e.g., NPDES).
– EU Water Framework Directive – Restrictions on material leaching and discharge quality.
– Local environmental protection laws regarding runoff and contamination.
Customs & Import/Export
– Provide accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes (e.g., 7306 for steel pipes).
– Submit required documentation: Commercial Invoice, Packing List, Certificate of Origin, and Material Test Reports (MTRs).
– Comply with trade restrictions or sanctions; verify if pipes are subject to ITAR, EAR, or other export controls (especially for dual-use or military applications).
Certifications
– Maintain valid certifications such as:
– PED (Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU) for CE marking in Europe.
– CRN (Canadian Registration Number) for use in Canadian provinces.
– NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 for sour service environments.
4. Documentation & Traceability
- Retain Material Test Reports (MTRs), Mill Certificates (e.g., 3.1 or 3.2 per EN 10204), and compliance declarations.
- Implement a traceability system using batch/heat numbers for quality control and recalls.
- Provide operation and maintenance manuals if supplied with valves or fittings.
5. End-of-Life & Disposal
- Follow local and international waste management regulations (e.g., Basel Convention for transboundary movement).
- Recycle metallic pipes through certified scrap processors.
- Dispose of non-recyclable or contaminated pipes (e.g., asbestos-lined) via licensed hazardous waste handlers.
Note: Always consult the pipe manufacturer’s specifications and local regulatory authorities to ensure full compliance. Regular audits and training for logistics personnel are recommended to maintain safety and legal adherence.
Conclusion for Sourcing Discharge Pipe:
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, material specifications, cost-efficiency, and supplier reliability, the optimal sourcing strategy for the discharge pipe has been identified. The selected material—typically corrosion-resistant options such as HDPE, PVC, or stainless steel, depending on the application—ensures durability, minimal maintenance, and long-term performance under expected operational conditions.
Engaging with reputable suppliers offering compliant certifications, timely delivery, and competitive pricing further strengthens project viability. Additionally, considerations for environmental impact, installation feasibility, and future scalability support a sustainable and resilient infrastructure solution.
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of the discharge pipe, based on technical suitability, quality assurance, and lifecycle cost analysis, ensures reliable system operation and aligns with project safety, efficiency, and sustainability goals.