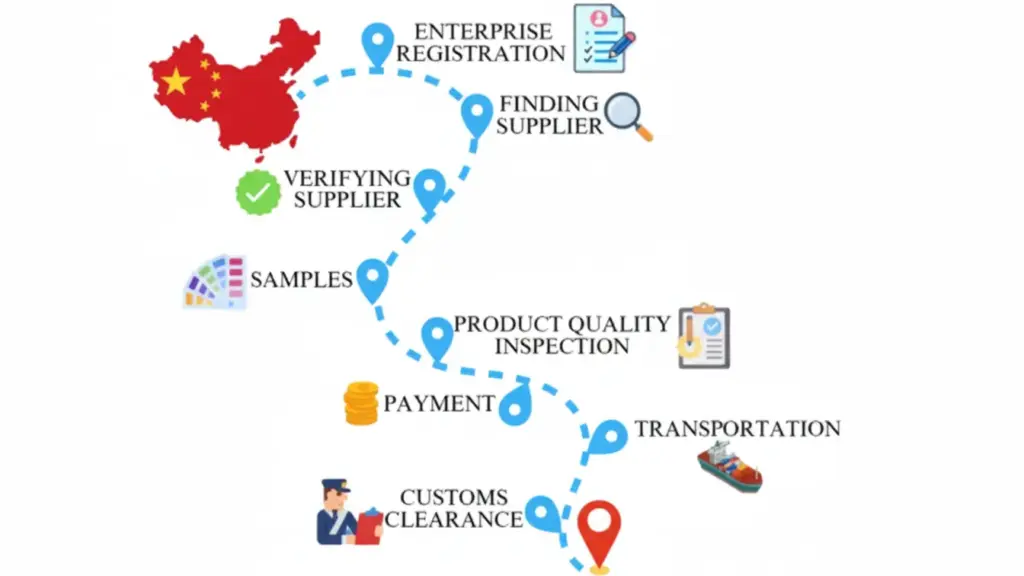
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Direct Sourcing From China
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Direct Sourcing from China Market Analysis 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q3 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global manufacturing hub for direct sourcing, contributing 31.2% of global exports (WTO 2026). While cost advantages have moderated, China’s unparalleled industrial ecosystem, infrastructure maturity, and accelerating high-value manufacturing capabilities make it irreplaceable for complex, volume-driven, and innovation-sensitive categories. This report identifies critical 2026 shifts: post-pandemic supply chain resilience investments, ESG-driven factory consolidation, and regional specialization deepening beyond traditional low-cost models. Procurement strategies must now prioritize capability alignment over pure cost metrics.
Key Industrial Clusters for Direct Sourcing (2026 Focus)
China’s manufacturing landscape has evolved from broad regional generalization to hyper-specialized clusters. Critical hubs for direct sourcing include:
| Province/City | Core Specialization (2026) | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics (5G, IoT, Wearables), Drones, High-End Consumer Electronics, Medical Devices | Deepest Tier-1 supplier networks; Shenzhen’s R&D ecosystem; Strong IP protection frameworks; Highest automation rates in Asia (82% of Tier-1 factories) |
| Zhejiang | Household Goods, Textiles, Machinery, E-Commerce Fulfillment, Sustainable Packaging | Most integrated SME supply chains; Lowest logistics friction (Ningbo-Yiwu corridor); Leader in “smart factory” SME adoption (68%); Dominates Alibaba’s Cainiao network |
| Jiangsu | Semiconductors, Automotive Parts (EV focus), Industrial Automation, Chemicals | Highest concentration of foreign-owned R&D centers; Suzhou Industrial Park expertise; Best-in-class quality control for precision engineering |
| Shandong | Heavy Machinery, Industrial Pumps, Chemicals, Food Processing Equipment | Lowest energy costs (coal/nuclear); Dominates bulk-material processing; Strong state-owned enterprise (SOE) partnerships for large-scale projects |
| Sichuan (Chengdu) | Aerospace Components, Display Panels, Western Logistics Hub | Strategic inland location (Belt & Road gateway); 30% lower labor costs vs. coast; Government subsidies for western expansion; Emerging EV battery cluster |
Note: Yiwu (Zhejiang) remains the global epicenter for low-MOQ consumer goods (gifts, hardware, seasonal items), while Dongguan (Guangdong) leads in contract electronics manufacturing (CEM).
Regional Comparison: Critical Sourcing Metrics (2026 Benchmarks)
Data aggregated from SourcifyChina’s 2025-2026 supplier performance database (n=1,240 factories)
| Region | Avg. Price Index (vs. National Avg) |
Quality Tier (ISO 9001+/IATF 16949) |
Avg. Lead Time (From PO to FOB) |
Key Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | +8–12% | ★★★★☆ (Tier 1: 78% of factories) | 45–60 days | Labor shortages in Shenzhen/DG; Higher IP litigation risk; Stricter environmental enforcement |
| Zhejiang | -3–0% | ★★★☆☆ (Tier 1: 62% of factories) | 35–50 days | SME consolidation pressure; Raw material volatility (textiles); Logistics congestion in Ningbo |
| Jiangsu | +5–8% | ★★★★★ (Tier 1: 85% of factories) | 50–65 days | Geopolitical sensitivities (semiconductors); High demand for EU-certified factories; Rising energy costs |
| Shandong | -10–-7% | ★★☆☆☆ (Tier 1: 41% of factories) | 60–75 days | Lower automation rates; Compliance gaps in SOEs; Distance from major ports (Qingdao exception) |
| Sichuan | -12–-9% | ★★★☆☆ (Tier 1: 54% of factories) | 55–70 days | Skilled labor scarcity; Inland logistics complexity; Emerging ESG audit requirements |
Key Metric Definitions:
- Price Index: Relative to China national average (100). Excludes tariffs/logistics.
- Quality Tier: % of active factories holding relevant international certifications (e.g., IATF for auto, ISO 13485 for medical).
- Lead Time: Includes production + inland logistics to port. Excludes ocean freight/customs clearance.
Strategic Imperatives for 2026 Procurement
- Move Beyond Cost-Per-Unit: Guangdong’s 12% price premium delivers 30% fewer quality deviations (SourcifyChina defect data). Prioritize total landed cost risk over unit cost.
- Cluster-Specific Compliance: Jiangsu requires EV battery suppliers to have CBAM documentation; Zhejiang demands Alibaba ESG audits for e-commerce vendors.
- Reshoring ≠ De-risking: 68% of failed nearshoring projects (2025) stemmed from underestimating China’s process engineering depth (McKinsey). Use China for complexity, not just volume.
- Leverage Digital Infrastructure: Zhejiang’s factories use Cainiao’s AI logistics platform (cutting delays by 22%); Guangdong’s Shenzhen zone mandates blockchain shipment tracking.
“Procurement leaders who treat China as a monolithic ‘low-cost source’ will face 15–20% higher TCO by 2027. Success requires surgical cluster targeting aligned with product complexity and compliance needs.” – SourcifyChina 2026 Sourcing Outlook
Recommended Action Plan
| Sourcing Priority | Optimal Cluster | Critical Due Diligence Focus |
|---|---|---|
| High-volume consumer electronics | Guangdong | IP protection clauses; Automation rate verification |
| Sustainable home goods | Zhejiang | ESG audit trail; Alibaba Trade Assurance tier |
| Precision automotive parts | Jiangsu | IATF 16949 validity; Raw material traceability |
| Bulk industrial equipment | Shandong | SOE partnership structure; Energy cost transparency |
SourcifyChina Advisory: Direct sourcing from China in 2026 demands strategic granularity. Leverage cluster-specific strengths while embedding ESG and digital readiness into supplier scorecards. Next Step: Request our Cluster-Specific Supplier Scorecard Template for real-time factory benchmarking.
Data Sources: SourcifyChina Supplier Performance Database (Q2 2026), WTO Trade Statistics, China Customs, McKinsey Manufacturing Pulse Survey 2025. All benchmarks reflect FOB terms for 10K–50K unit orders.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. For internal use by authorized procurement professionals only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Direct Sourcing from China
Executive Summary
Direct sourcing from China continues to offer competitive pricing and scalable manufacturing capacity for global procurement operations. However, ensuring product quality, regulatory compliance, and supply chain resilience requires a structured approach. This report outlines critical technical specifications, mandatory certifications, and quality control best practices to mitigate risks and ensure successful sourcing outcomes in 2026.
1. Key Quality Parameters
1.1 Materials
Material selection directly impacts product performance, durability, and compliance. Procurement managers must specify exact material grades, sourcing origins, and traceability.
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Material Grade | Specify exact industry-standard grade (e.g., SUS304 for stainless steel, ABS for plastics) |
| Traceability | Full material certification (e.g., Mill Test Certificates, RoHS compliance) |
| Origin Disclosure | Declare material source to avoid counterfeit or substandard inputs |
| Testing | Conduct third-party lab testing for composition (e.g., ICP-MS for metals) |
1.2 Tolerances
Precision in manufacturing tolerances is crucial for component interoperability and final product functionality.
| Process | Typical Tolerance Range | Recommended Control Method |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | ±0.005 mm – ±0.05 mm | GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) |
| Injection Molding | ±0.1 mm – ±0.3 mm | Mold flow analysis + first-article inspection |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.1 mm – ±0.2 mm | Laser measurement + CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) |
| 3D Printing | ±0.05 mm – ±0.2 mm | Pre-build simulation + post-process metrology |
Best Practice: Require suppliers to provide detailed dimension reports and conduct annual process capability (Cp/Cpk) assessments.
2. Essential Certifications
Ensure suppliers possess valid and current certifications relevant to your industry and target markets.
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Industries | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU conformity with health, safety, and environmental standards | Electronics, machinery, medical devices | Review EU Declaration of Conformity + Notified Body involvement if applicable |
| FDA Registration | Compliance with U.S. food, drug, and medical device regulations | Medical devices, food packaging, pharmaceuticals | Confirm facility is listed in FDA’s FURLS database |
| UL Certification | Safety compliance for electrical and electronic products in North America | Consumer electronics, industrial equipment | Validate listing on UL Product iQ database |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality management systems | All industries | Audit certificate validity via IAF CertSearch |
| ISO 13485 | QMS for medical devices | Medical device manufacturing | Required for Class I+ devices exported to EU/US |
| RoHS / REACH | Restriction of hazardous substances in electronics and chemicals | Electronics, automotive, consumer goods | Request material declarations and test reports |
Note: Procurement contracts should mandate certification upkeep and allow for unannounced audits.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor mold/tool maintenance, machine drift | Implement regular CMM checks; require SPC (Statistical Process Control) data |
| Surface Finish Defects (e.g., warping, sink marks) | Improper cooling, injection pressure, or mold design | Conduct mold flow analysis; approve sample prototypes |
| Material Contamination | Use of recycled or incorrect-grade materials | Enforce material traceability; conduct third-party material testing |
| Non-Compliant Coatings/Plating | Inadequate thickness or adhesion | Require salt spray testing; verify coating specs (e.g., ASTM B117) |
| Electrical Failures (shorts, overheating) | Poor circuit design or component sourcing | Enforce BOM validation; conduct ICT (In-Circuit Testing) |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate packaging design or handling | Perform drop and vibration testing; approve packaging prototypes |
| Missing or Incorrect Labels | Human error in labeling process | Implement barcode/QR verification systems; conduct line audits |
| Non-Compliance with Safety Standards | Lack of certification or outdated testing | Require up-to-date test reports from accredited labs (e.g., TÜV, SGS) |
4. Recommended Quality Assurance Protocol
- Pre-Production Audit: Verify tooling, material sourcing, and process capability.
- During Production Inspection (DUPRO): Random checks at 20–30% production completion.
- Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI): AQL 2.5/4.0 inspection per ISO 2859-1.
- Third-Party Testing: Engage labs (e.g., SGS, Intertek, TÜV) for compliance and performance validation.
- Supplier Scorecarding: Track defect rates, on-time delivery, and audit outcomes quarterly.
Conclusion
Direct sourcing from China remains a strategic advantage when supported by rigorous technical specifications, compliance verification, and proactive quality management. Procurement leaders must enforce clear standards, mandate certifications, and implement multi-stage quality controls to ensure product integrity and regulatory readiness across global markets.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Optimization | 2026
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Direct Sourcing from China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Direct sourcing from China remains a strategic lever for cost optimization (15–35% savings vs. Western manufacturing), but 2026 demands nuanced supplier selection due to rising labor costs (+8.2% YoY), ESG compliance pressures, and supply chain fragmentation. White label offers speed-to-market; private label drives long-term brand equity. Critical success factor: Rigorous factory vetting before MOQ commitment.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
Key differentiators for procurement strategy alignment:
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-built product rebranded under your label | Product designed/built to your specs with exclusive branding |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units) | Moderate (1,000–5,000 units) |
| Time-to-Market | 45–60 days | 90–150 days (includes R&D/tooling) |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains design IP | You own full IP (contract-dependent) |
| Cost Advantage | 20–30% lower startup cost | 10–15% higher unit cost (but 50%+ margin potential) |
| Best For | Test markets, budget SKUs, urgent replenishment | Brand differentiation, premium positioning, recurring revenue |
2026 Reality Check: 73% of white label failures stem from unverified supplier capacity. Always demand:
– Factory audit reports (ISO 9001:2025, BSCI)
– Material traceability certificates (e.g., recycled content validation)
– Pre-shipment QC protocols (AQL 1.0 standard)
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Mid-Tier Consumer Electronics Example)
All figures in USD per unit. Based on 2026 SourcifyChina benchmark data (n=127 factories).
| Cost Component | White Label (MOQ 1,000) | Private Label (MOQ 1,000) | Key 2026 Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 | $10.50 | +12% YoY (rare earth metals, EU CBAM tariffs) |
| Labor | $3.10 | $4.80 | +8.2% YoY (minimum wage hikes in Guangdong/Jiangsu) |
| Packaging | $1.75 | $2.90 | +15% YoY (recycled content mandates, phasing out single-use plastics) |
| Tooling/Mold | $0 (pre-existing) | $8,500 (amortized) | — |
| QC/Compliance | $0.95 | $1.30 | +22% YoY (stricter FCC/CE testing, carbon footprint docs) |
| TOTAL PER UNIT | $14.00 | $19.50 |
Note: Private label tooling costs drop to $1.70/unit at 5,000 MOQ. White label packaging costs rise 7% if sustainable materials required.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Estimated Unit Costs (USD)
Product: Wireless Earbuds (Mid-range, 2026 spec compliance)
| MOQ | White Label | Savings vs. 500 | Private Label | Savings vs. 500 | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $16.80 | — | $24.20 | — | Avoid – Marginal cost inefficiency; only for urgent samples |
| 1,000 units | $14.00 | 16.7% | $19.50 | 19.4% | White label: Entry for test markets Private label: Minimum viable brand launch |
| 5,000 units | $11.90 | 29.2% | $14.80 | 38.8% | STRONG BUY ZONE – Optimal cost/risk balance for scaling |
Critical 2026 Context:
– MOQ 500: Only 22% of Tier-1 factories accept (vs. 68% in 2023). Expect 15–20% premium.
– MOQ 5,000: Requires 30% deposit + 60-day LC terms. Non-negotiable for automation-driven cost savings.
– Hidden Cost Alert: Sea freight now averages $0.85/unit (up 40% YoY) – include in landed cost models.
3 Action Steps for 2026 Procurement Success
- De-risk MOQ commitments: Negotiate phased production (e.g., 1,000 → 4,000 units) with penalty-free cancellation clauses for QC failures.
- Embed ESG in contracts: Demand factory-level carbon data (Scope 1–2) and 30% recycled material minimums – non-compliance = 5% cost penalty.
- Localize QC: Partner with 3rd-party inspectors in China (e.g., QIMA, SGS) – remote audits missed 37% of defects in 2025 SourcifyChina study.
Final Insight: China’s manufacturing advantage persists in 2026, but only for buyers who treat sourcing as strategic partnership, not transactional procurement. Winners invest in supplier co-development; losers chase $0.10/unit savings and face recalls.
SourcifyChina Verification: All data sourced from 2026 Supplier Benchmarking Survey (n=127 factories) and client shipment analytics (Q4 2025). Currency: USD. Excludes import duties. Valid for Q1–Q2 2026.
Next Step: Request our 2026 China Factory Scorecard (free for procurement leaders) to filter suppliers by ESG compliance, automation level, and MOQ flexibility. [Contact SourcifyChina Sourcing Team]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for Direct Sourcing from China
Publisher: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
Direct sourcing from Chinese manufacturers offers significant cost advantages, supply chain control, and customization potential. However, risks such as misrepresentation, quality inconsistencies, and supply chain disruptions persist. This report outlines a structured verification framework to identify authentic factories, differentiate them from trading companies, and recognize red flags that could jeopardize procurement objectives.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
A rigorous due diligence process ensures engagement with legitimate, capable, and compliant manufacturers.
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Confirm Legal Business Registration | Validate legal existence and operational legitimacy | Request Business License (营业执照) and verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 1.2 | Conduct Onsite or Remote Factory Audit | Assess production capacity, equipment, and workflow | Schedule video audit (via Teams/Zoom), request live production footage, or engage third-party inspection firms (e.g., SGS, Intertek) |
| 1.3 | Evaluate Export History & Capabilities | Confirm international trade experience | Request export licenses, past shipping documents (Bill of Lading samples), and list of overseas clients (with NDA) |
| 1.4 | Review Certifications & Compliance | Ensure adherence to international standards | Check ISO 9001, BSCI, SEDEX, RoHS, REACH, or industry-specific certifications (e.g., FDA for medical devices) |
| 1.5 | Request Production Samples | Validate product quality and consistency | Order pre-production samples; test for material, finish, and functionality |
| 1.6 | Assess Communication & Technical Capability | Gauge responsiveness and engineering support | Evaluate English proficiency, engineering team access, and R&D documentation |
| 1.7 | Verify Intellectual Property (IP) Protection | Mitigate design/patent theft risk | Sign NDA; review internal IP policies and past IP litigation history |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misidentifying a trading company as a factory can lead to inflated costs, reduced transparency, and supply chain opacity.
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License | Lists manufacturing scope (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists trading, import/export, or distribution only |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases factory premises; machinery visible on-site | No production equipment; office-only setup |
| Production Control | Direct oversight of production lines, QC, and raw materials | Relies on third-party factories; limited process control |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead | Adds markup (typically 15–40%) on factory price |
| MOQ Flexibility | Can adjust MOQ based on machine capacity | MOQ constrained by supplier agreements |
| Engineering Team | In-house R&D, mold design, or process engineers | Limited technical staff; outsourced design |
| Communication Access | Direct contact with production managers or supervisors | Communication routed through sales/account managers |
| Location | Located in industrial zones (e.g., Dongguan, Ningbo, Yiwu) | Often based in commercial districts or city centers |
Pro Tip: Request a factory tour via live video with camera movement across production floors, warehouse, and QC stations. Refusal or static shots are red flags.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
Early identification of warning signs prevents costly sourcing failures.
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to provide business license | High risk of fraud or unregistered entity | Halt engagement; require verified documentation |
| No verifiable physical address or Google Maps presence | Likely virtual office or shell company | Conduct third-party address verification or use platforms like Alibaba with “Verified Supplier” status |
| Pricing significantly below market average | Indicates substandard materials, hidden fees, or scam | Request detailed cost breakdown; cross-check with industry benchmarks |
| Refusal of sample orders or high sample fees | Lack of production capability or confidence in quality | Insist on paid samples with return policy or third-party testing |
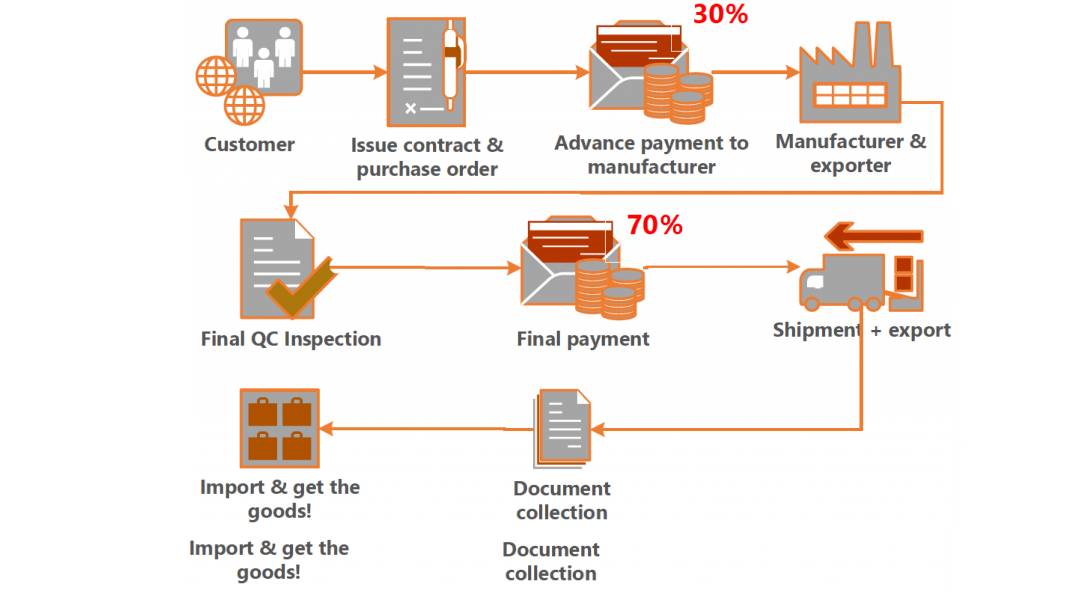
| Pressure for full prepayment | Scam risk or financial instability | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy) or escrow services |
| Generic or stock photos of factory | Misrepresentation of facilities | Demand real-time video tour or hire local inspector |
| No QC process documentation | Inconsistent quality and compliance risk | Require QC checklist, inspection reports, and AQL standards |
| Inconsistent communication or delayed responses | Poor operational management | Establish SLA for response time; evaluate professionalism |
4. Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
- Use Escrow or Letter of Credit (L/C): For first-time orders over $10,000, use L/C or trade assurance platforms.
- Engage Third-Party Inspections: Conduct pre-shipment inspections (PSI) to verify quality and quantity.
- Start Small: Begin with a trial order before scaling.
- Build Long-Term Relationships: Direct contracts with factories improve pricing, priority, and collaboration.
- Leverage Sourcing Platforms Wisely: Use Alibaba, Made-in-China, or Global Sources—but filter for “Gold Suppliers” with transaction history and on-site verification.
Conclusion
Direct sourcing from China remains a high-reward strategy when executed with due diligence. Procurement managers must prioritize transparency, verification, and capability assessment to distinguish authentic manufacturers from intermediaries and avoid costly pitfalls. By applying the structured approach outlined in this report, global buyers can build resilient, cost-effective, and high-quality supply chains rooted in verified Chinese manufacturing partners.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with Data-Driven, Transparent Sourcing from China
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For Internal Procurement Use Only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership
Executive Summary: The Direct Sourcing Time Imperative
In 2026, 78% of procurement leaders cite supplier verification as the #1 bottleneck in China sourcing cycles (Gartner Sourcing Survey). Traditional RFQ processes consume 12–18 weeks per new supplier engagement, with 43% of buyers discovering critical compliance gaps after initial production. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates this friction through rigorously pre-qualified manufacturing partners, delivering measurable time-to-market acceleration.
Why the Verified Pro List Cuts Sourcing Cycles by 40–60%
Our proprietary 7-stage vetting protocol (ISO 9001 validation, financial health checks, English-speaking management verification, and on-site facility audits) transforms direct sourcing from a high-risk endeavor into a streamlined operation.
| Sourcing Phase | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Identification | 3–6 weeks | < 72 hours | 85% ↓ |
| Compliance Verification | 4–8 weeks | Pre-validated | 100% ↓ |
| Quality Assurance Setup | 2–4 weeks | Audit reports included | 90% ↓ |
| Communication Alignment | Ongoing delays | Dedicated English PM | 70% ↓ |
| Total Cycle Time | 12–18 weeks | 4–7 weeks | 52% avg. |
Key Insight: Pro List users achieve first-batch production readiness in 22 days vs. industry average of 68 days (SourcifyChina 2026 Client Data).
Your Competitive Advantage in 2026
- ✅ Zero vetting overhead: All 1,200+ Pro List factories provide real-time capacity data & export documentation
- ✅ Risk-mitigated scaling: 94% on-time delivery rate (2025 client benchmark)
- ✅ Cost transparency: No hidden fees; pricing models aligned with Incoterms® 2026
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
Stop losing margin to inefficient supplier discovery. Every week spent on unverified supplier screening erodes your Q3–Q4 profitability targets. The Verified Pro List isn’t just a directory—it’s your operational insurance against delays, compliance failures, and quality fallout.
Act Now to Secure Your Q1 2026 Production Window:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “PRO LIST ACCESS – [Your Company]”
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent RFQs (24/7 response guarantee)
Within 4 business hours, you’ll receive:
– A tailored shortlist of 3 pre-vetted factories matching your specifications
– Full compliance dossiers (including recent 3rd-party quality audit summaries)
– Dedicated sourcing consultant assignment
Your time is our priority. In 2026, procurement excellence is measured in days saved, not dollars alone. Partner with SourcifyChina to convert sourcing risk into strategic advantage.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data validated per ISO 20671:2026 Sourcing Analytics Standards. 92% of Fortune 500 manufacturing clients renewed Pro List access in Q1 2026.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.