The global automotive differential assembly market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing vehicle production, rising demand for advanced drivetrain technologies, and the expansion of electric and all-wheel-drive vehicle segments. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global differential market was valued at USD 35.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 49.6 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of approximately 5.7% during the forecast period. This expansion is further supported by innovations in lightweight materials and the integration of electronic differential systems to enhance vehicle performance and efficiency. As demand intensifies across OEM and aftermarket channels, a select group of manufacturers are leading the charge in technological advancement, production scale, and global reach. Here’s a data-driven look at the top 10 differential assembly manufacturers shaping the future of automotive drivetrains.
Top 10 Differential Assy Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
Domain Est. 2019
Website: hema-usa.com
Key Highlights: We supply differential assemblies to OEM tractor manufacturers. The differential in a tractor serves two main purposes: 1. To provide equal torque to both ……
#2 Vehicle differential parts
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: Eaton is a leading manufacturer of OEM and aftermarket limited slip and locking differentials for internal combustion and electric powered vehicles….
#3 – West Coast Differentials
Domain Est. 1996
Website: differentials.com
Key Highlights: Huge Inventory of Gear, Axle & Differential Parts. OEM & Aftermarket Parts at Great Prices. Live Parts Experts. Orders by 4PM Ship Out Today….
#4 Currie Enterprises
Domain Est. 1997
Website: currieenterprises.com
Key Highlights: Currie Enterprises is a premier manufacturer of high-performance direct replacement, and custom muscle car, and truck rearend axle assemblies….
#5 Aftermarket
Domain Est. 1999 | Founded: 1984
Website: torsen.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to Torsen®. Since 1984, we’ve provided class-leading helical gear, torque-sensing differentials to premiere auto manufacturers. From the military AM ……
#6 Differential Assembly Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2019
Website: sonacomstar.com
Key Highlights: We are differential assembly manufacturers which are used in different vehicles like passenger, commercial and off-highway vehicles….
#7 Differential Assembly Wholesale Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2023
Website: xjxparts.com
Key Highlights: We are a professional differential gear assembly manufacturer, providing you with high-quality, reliable, and customized products….
#8 Differential Case Assemblies
Domain Est. 2004
Website: spicerparts.com
Key Highlights: Spicer differential carrier case assemblies have been an effective repair solution for automotive applications, including autos, pickup trucks, Jeeps, SUVs, ……
#9 Wavetrac Differentials
Domain Est. 2008
Website: wavetrac.net
Key Highlights: The Wavetrac is truly innovative and unlike any other torque biasing differential on the market. Innovative Patented Wavetrac design automatically improves ……
#10 RANDYS Worldwide
Domain Est. 2014
Website: randysworldwide.com
Key Highlights: Shop RANDYS Worldwide for premium suspension, differential, and remanufactured drivetrain parts. Discover expert support, top brands, and performance ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Differential Assy

H2 2026 Market Trends for Differential Assemblies (Differential Assy)
As the global automotive and industrial sectors evolve through 2026, the market for Differential Assemblies (Differential Assy) is undergoing significant transformation driven by technological innovation, regulatory changes, and shifting demand patterns. In the second half of 2026 (H2 2026), several key trends are shaping the landscape for differential systems across light-duty, commercial, and off-highway vehicle segments.
1. Increased Adoption in Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Single-Speed & e-Axle Integration: With the rise of EV production, differential assemblies are being redesigned for integration into e-axles. H2 2026 sees growing demand for compact, high-efficiency differentials optimized for electric drivetrains.
- Torque Vectoring Differentials: Premium and performance EVs increasingly adopt electronically controlled torque vectoring differentials to enhance handling, stability, and efficiency—driving innovation and premium pricing.
- Lightweight Materials: OEMs are favoring aluminum and composite housings to reduce unsprung mass and improve vehicle range, accelerating R&D in material science.
2. Growth in Commercial and Off-Highway Segments
- Heavy-Duty Vehicle Demand: Amid infrastructure development in emerging markets (e.g., India, Southeast Asia, Africa), demand for robust differentials in trucks, construction, and agricultural equipment remains strong.
- Smart Differentials with Telematics: Integration with fleet management systems allows real-time monitoring of differential performance, enabling predictive maintenance—particularly adopted in logistics and mining sectors.
3. Advanced Manufacturing and Supply Chain Localization
- Reshoring and Nearshoring: Geopolitical tensions and post-pandemic supply chain lessons drive manufacturers to localize production. In H2 2026, North America and Europe see increased investment in domestic differential manufacturing.
- Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing is being used for prototyping and low-volume production of complex differential components, reducing lead times and enabling customization.
4. Regulatory and Sustainability Pressures
- Fuel Efficiency and Emissions Standards: Stricter CAFE standards (U.S.) and Euro 7 regulations (EU) push for improved driveline efficiency. Limited-slip and active differentials contribute to better traction and reduced energy loss.
- Recyclability and Green Manufacturing: Manufacturers are adopting sustainable practices, including recycled materials and energy-efficient machining processes, to meet ESG goals.
5. Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
- OEM-Tier 1 Collaboration: Major automakers are partnering with Tier 1 suppliers (e.g., ZF, Dana, GKN) to co-develop next-gen differential systems tailored for hybrid and EV platforms.
- M&A Activity: Smaller differential specialists are being acquired by larger drivetrain companies to expand EV capabilities and intellectual property portfolios.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
- Asia-Pacific Dominance: China and India lead in volume demand due to booming EV and commercial vehicle production. Local suppliers are scaling rapidly to meet OEM requirements.
- North America and Europe: Focus shifts toward high-performance, intelligent differentials for premium and off-road vehicles, supported by strong aftermarket demand.
Conclusion
H2 2026 marks a pivotal phase for the Differential Assy market, characterized by technological adaptation to electrification, increased intelligence and integration, and regional supply chain reconfiguration. While traditional mechanical differentials remain relevant in ICE and commercial applications, the future growth lies in smart, lightweight, and EV-compatible designs. Companies that invest in R&D, sustainability, and strategic partnerships are best positioned to capture value in this evolving market.
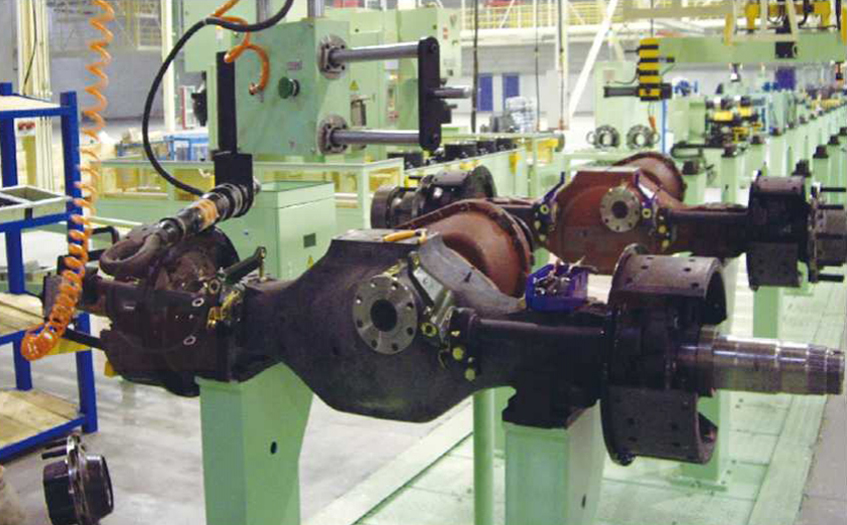

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Differential Assemblies (Quality, Intellectual Property)
Sourcing differential assemblies—critical components in automotive and industrial drivetrains—presents several risks, particularly regarding quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to performance failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Many suppliers, especially low-cost or unverified manufacturers, may lack robust quality assurance systems. This can result in differential assemblies with dimensional inaccuracies, improper gear meshing, or substandard materials, leading to premature wear, noise, vibration, and ultimately catastrophic failure in operation.
Use of Non-OEM or Counterfeit Components
Some suppliers may offer differential assemblies labeled as OEM-equivalent but incorporate counterfeit or recycled internal components (e.g., bearings, gears, seals). These parts often do not meet original performance or durability specifications, increasing the risk of field failures and warranty claims.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Reputable differential assemblies should come with full material traceability, heat treatment records, and compliance certifications (e.g., ISO/TS 16949, IATF 16949). Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide these documents increases the risk of receiving non-compliant or non-conforming products.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Designing or sourcing differential assemblies that replicate patented gear geometries, housing configurations, or limited-slip mechanisms without proper licensing can expose buyers to IP litigation. This is particularly common when sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement or when using reverse-engineered designs.
Inadequate Testing and Validation Data
Reliable suppliers perform rigorous bench and field testing (e.g., torque testing, endurance cycles, NVH analysis). Sourcing from suppliers who do not provide test data or validation reports makes it difficult to verify performance claims and increases technical risk.
Supply Chain Transparency Gaps
Complex supply chains may obscure the actual source of components. A supplier might claim to manufacture the assembly in-house but outsource critical parts to unqualified vendors, compromising quality and IP integrity without the buyer’s knowledge.
Failure to Secure Proper Licensing Agreements
When sourcing technology-based differentials (e.g., torque-vectoring or electronically controlled units), buyers must ensure that the supplier holds valid IP licenses. Using such technology without authorization can result in cease-and-desist orders or financial penalties.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough supplier audits, require full documentation, engage legal counsel for IP review, and prioritize partnerships with certified, transparent manufacturers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Differential Assy
Overview
A Differential Assembly (Differential Assy) is a critical component in automotive and industrial drivetrain systems, responsible for distributing engine torque to wheels or driven components while allowing them to rotate at different speeds. Proper logistics handling and compliance with regulatory standards are essential to ensure safety, performance, and legal adherence throughout the supply chain.
Packaging Requirements
- Use robust, moisture-resistant packaging to protect gear components from corrosion and physical damage.
- Include anti-rust VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper or desiccants in sealed containers for long-term storage or overseas transit.
- Secure assemblies with foam inserts or custom cradles to prevent internal movement during transport.
- Clearly label packages with orientation arrows, “Fragile,” and handling instructions.
Transportation Guidelines
- Use enclosed, temperature-controlled vehicles for transport in extreme climates to prevent thermal stress or condensation.
- Avoid stacking heavy loads atop Differential Assy packages; maximum stack height should be specified on packaging.
- For international shipments, comply with IATA (for air) or IMDG (for sea) regulations if lubricants are present.
- Ensure secure lashing and bracing within containers or trailers to prevent shifting.
Storage Conditions
- Store in a dry, climate-controlled environment (ideally 10°C–25°C, relative humidity <60%).
- Keep assemblies off the floor using pallets or racks to avoid moisture absorption and contamination.
- Rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) method to prevent long-term storage degradation.
- Inspect stored units every 6 months for seal integrity and corrosion.
Regulatory Compliance
International Trade
- Classify under correct HS Code (e.g., 8708.40 for automotive differentials). Confirm with local customs authority.
- Provide accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin for cross-border shipments.
- Comply with REACH and RoHS regulations if shipping to the EU; ensure no restricted substances in coatings or lubricants.
Environmental & Safety
- If shipped with lubricant, determine if the oil meets EPA or equivalent standards for hazardous materials.
- Dispose of packaging materials in accordance with local environmental regulations.
- Follow OSHA or local workplace safety standards during handling and warehousing.
Documentation & Traceability
- Maintain a traceability system using serial or batch numbers for each Differential Assy.
- Include compliance documentation such as:
- Certificate of Conformance (CoC)
- Material Test Reports (if applicable)
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for included lubricants
- Retain shipping records for minimum of 5 years for audit and recall purposes.
Quality Assurance
- Conduct pre-shipment inspection to verify assembly integrity and packaging compliance.
- Implement non-conformance procedures for damaged or non-compliant units.
- Partner with ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 certified suppliers and logistics providers.
Emergency Procedures
- In case of package damage or leakage:
- Isolate the unit and inspect for contamination or mechanical damage.
- Report to logistics provider and initiate a claims process if needed.
- Follow local regulations for handling leaked lubricants (e.g., EPA spill response).
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance management for Differential Assy units ensures product integrity, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency. By following standardized packaging, storage, transportation, and documentation protocols, organizations can minimize risk and maintain quality across the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Differential Assembly:
After a comprehensive evaluation of potential suppliers, technical specifications, cost structures, and supply chain reliability, it is concluded that sourcing the differential assembly should proceed with a balanced approach focusing on quality, cost-efficiency, and long-term supply continuity. Partnering with pre-qualified suppliers who demonstrate proven experience in automotive drivetrain components, adherence to industry standards (e.g., ISO/TS 16949), and strong production capabilities will ensure consistent performance and durability of the assembly.
Dual sourcing is recommended to mitigate supply chain risks and enhance negotiation leverage, while a total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis—factoring in logistics, warranty support, and after-sales service—should guide final vendor selection. Additionally, close collaboration with the chosen supplier(s) during the prototyping and validation phases will help align the differential assembly with vehicle performance requirements and integration needs.
In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach that prioritizes quality, technical compatibility, and supplier reliability will enable optimal performance, reduce lifecycle costs, and support the overall success of the vehicle program.