The global foam materials market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as packaging, construction, automotive, and healthcare. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global flexible foam market size was valued at USD 55.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. Dense foam sheets, known for their durability, impact resistance, and thermal insulation properties, are a key segment within this expanding market. This growing demand has spurred innovation and competition among manufacturers worldwide. Based on production capacity, market presence, product quality, and industry reputation, the following nine companies have emerged as leading producers of dense foam sheets, setting benchmarks in performance and sustainability.
Top 9 Dense Foam Sheets Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Foam Factory, Inc.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: foambymail.com
Key Highlights: We proudly offer traditional foam products like cushions, insulation, and packaging materials, as well as memory foam and latex mattresses, toppers, and even ……
#2 General Plastics
Domain Est. 1996
Website: generalplastics.com
Key Highlights: General Plastics is certified and equipped to offer polyurethane foam solutions, providing part design support and design production from start to finish….
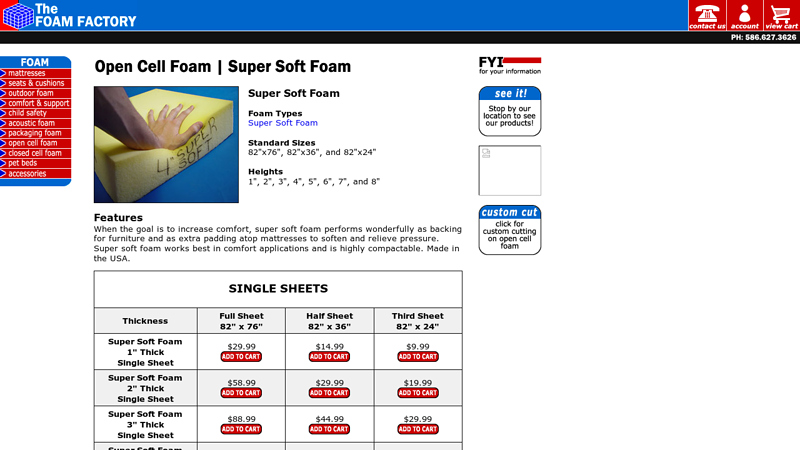
#3 The Foam Factory, Open Cell Foam, Super Soft Foam
Domain Est. 2001
Website: thefoamfactory.com
Key Highlights: Features ; Super Soft Foam 1″ Thick Single Sheet. $29.99. $14.99 ; Super Soft Foam 1″ Thick Half Pallet. $1761.00 (72 sheets). $1761.00 (144 sheets)….
#4 Worldwide Foam
Domain Est. 2008
Website: worldwidefoam.com
Key Highlights: We offer one-day lead time from our seven strategic locations while providing the widest ranges of closed cell cross-linked polyethylene foam….
#5 Zotefoams
Domain Est. 1996
Website: zotefoams.com
Key Highlights: Zotefoams offers lightweight, high-performance AZOTE and ZOTEK foam solutions for aerospace, automotive, and construction industries….
#6 Wholesale Supplier of Foam Sign Board & 4×8 Foam Sheets
Domain Est. 1996
Website: grimco.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsGrimco offers wholesale pricing and quick delivery on an extensive line of foam sign materials including 4×8 foam core sheets and HDU ……
#7 Flexible Foams
Domain Est. 1999
Website: americanexcelsior.com
Key Highlights: This includes Amcel polyethylene foam sheets or rolls available from 1/32″ to 1/2″, all the way to PE plank fabrication for heavy bracing of your finished ……
#8 New England Foam Products
Domain Est. 2002
Website: newenglandfoam.com
Key Highlights: New England Foam provides the finest quality foam products, the most competitive pricing and the shortest lead times in the entire foam fabrication industry….
#9 Polyurethane Foam
Domain Est. 2012
Website: solutions.covestro.com
Key Highlights: Our extensive range of high-performance polyurethane raw materials offer solutions for flexible, rigid and integral skin foams….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Dense Foam Sheets

2026 Market Trends for Dense Foam Sheets
The dense foam sheets market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by shifting industrial demands, sustainability imperatives, and technological advancements. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
Heightened Demand in Construction and Insulation:
The global push for energy-efficient buildings will continue to boost demand for dense foam sheets—particularly extruded polystyrene (XPS) and polyisocyanurate (PIR)—in insulation applications. With stricter building codes and green certification standards (e.g., LEED, BREEAM) gaining traction worldwide, manufacturers are focusing on high R-value, moisture-resistant foam solutions for walls, roofs, and foundations.
Sustainability and Regulatory Pressure:
Environmental regulations targeting volatile organic compounds (VOCs), global warming potential (GWP), and end-of-life recyclability will heavily influence material formulations. By 2026, expect increased adoption of bio-based feedstocks, hydrofluoroolefin (HFO) blowing agents replacing high-GWP HFCs, and closed-loop recycling systems. Companies investing in circular economy models will gain competitive advantage.
Expansion in Transportation and Automotive Lightweighting:
As automakers strive to meet fuel efficiency and emissions targets, dense foam sheets are being integrated into electric vehicles (EVs) for battery insulation, noise dampening, and structural components. Their lightweight, thermally insulating, and vibration-absorbing properties make them ideal for EV battery enclosures and interior panels.
Growth in Protective Packaging and Industrial Applications:
E-commerce expansion and the need for durable, shock-absorbent packaging will drive demand for custom-molded dense foam sheets in electronics, medical devices, and industrial equipment. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) foams are particularly favored for their durability and reusability.
Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience:
Asia-Pacific—led by China, India, and Southeast Asia—will remain the fastest-growing region due to urbanization and infrastructure development. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will focus on innovation and compliance with environmental standards. Supply chain localization and nearshoring will gain importance to mitigate geopolitical risks and reduce lead times.
Technological Innovation and Customization:
Advancements in foam extrusion and molding technologies will enable tighter tolerances, improved surface finishes, and multi-layer composites. Demand for customized solutions—such as antimicrobial foams for healthcare or flame-retardant variants for aerospace—will push manufacturers toward more agile and responsive production systems.
In summary, the 2026 dense foam sheets market will be defined by sustainability, performance optimization, and regional diversification, offering growth opportunities for innovators who align with evolving regulatory and consumer demands.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Dense Foam Sheets (Quality, IP)
Sourcing dense foam sheets presents several challenges, particularly concerning material quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to performance failures, supply chain disruptions, or legal risks.
1. Inadequate Material Specification and Quality Control
A frequent issue is sourcing foam without clearly defined technical specifications. Buyers may assume “dense foam” implies consistent performance, but density alone doesn’t guarantee resilience, compression set, or chemical resistance. Suppliers may substitute lower-grade materials or alter formulations without notice, leading to inconsistent batch quality. Without third-party testing or material certifications (e.g., ASTM, ISO), verifying durability and performance becomes difficult.
2. Misrepresentation of Foam Properties
Some suppliers exaggerate foam characteristics such as load-bearing capacity, temperature resistance, or longevity. This is especially common with imported foams where independent verification is limited. Without access to test data or material safety data sheets (MSDS), buyers risk selecting foam that degrades prematurely under operational conditions.
3. Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Using proprietary foam formulations or patented manufacturing processes without authorization can expose companies to IP litigation. For example, sourcing foam that mimics a branded material (e.g., cross-linked polyethylene with specific cell structure) may infringe on existing patents, particularly when the supplier cannot provide freedom-to-operate documentation.
4. Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Many suppliers, especially in less-regulated markets, fail to provide lot traceability, raw material sourcing records, or compliance documentation. This absence complicates quality audits, regulatory submissions, and root cause analysis during product failures. It also increases vulnerability to counterfeit or recycled materials being passed off as virgin-grade foam.
5. Overlooking Supplier IP Ownership and Transparency
When co-developing custom foam solutions, companies may assume they own the resulting formulation or process. However, without clear contractual agreements, the supplier may retain IP rights, limiting the buyer’s ability to switch vendors or scale production. Always ensure IP ownership and usage rights are explicitly defined in supplier contracts.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: define precise technical requirements, verify supplier credentials, demand test reports, conduct site audits, and secure IP rights through legal agreements.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Dense Foam Sheets
Product Overview
Dense foam sheets are rigid or semi-rigid polymeric materials (commonly made from polyethylene, polyurethane, or PVC) used for insulation, packaging, gasketing, and industrial applications. Their low weight, durability, and compressibility require specific handling, storage, and regulatory considerations during transportation and import/export.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
- Protective Wrapping: Wrap sheets in moisture-resistant plastic (e.g., LDPE film) to prevent water damage and contamination.
- Edge Protection: Use corner boards or edge protectors to prevent chipping or cracking during transit.
- Stacking & Palletizing: Stack sheets evenly on wooden or plastic pallets. Limit stack height to prevent deformation (typically no more than 1.5 meters). Secure with stretch wrap or strapping.
- Manual Handling: Use mechanical aids (e.g., forklifts or pallet jacks) for heavy bundles to reduce worker injury risks.
Storage Conditions
- Environment: Store indoors in a dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures (ideally 10–30°C).
- Fire Safety: Keep away from ignition sources; dense foams may be flammable depending on composition. Maintain compliance with local fire codes.
- Stacking: Avoid long-term vertical leaning. Store flat to prevent warping.
Transportation Guidelines
- Mode Selection: Suitable for road, rail, air, and sea freight. Use enclosed, weatherproof containers to prevent moisture exposure.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with contents, weight, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”), and orientation arrows.
- Load Securing: Use dunnage and load-locking techniques to prevent shifting during transport. Avoid over-compression.
Regulatory Compliance
International Shipping (IMO/IMDG)
- Dense foam sheets are typically not classified as hazardous materials unless treated with flame retardants or containing regulated substances.
- Verify compliance with the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code if shipping by sea.
Air Transport (IATA)
- Most dense foam sheets are permitted as non-hazardous cargo under IATA regulations.
- Check for flammability if intended for aerospace applications—some foams may require FAA or EASA certification.
REACH & RoHS (EU Compliance)
- Ensure raw materials comply with REACH (EC 1907/2006) by declaring Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
- Confirm adherence to RoHS Directive 2011/65/EU if used in electrical/electronic equipment—restricts lead, cadmium, and other hazardous substances.
TSCA (USA)
- Comply with the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) by verifying that all chemical components are listed on the TSCA Inventory.
- Maintain a TSCA compliance statement for U.S. imports.
Prop 65 (California)
- Evaluate foam components for presence of chemicals listed under California Proposition 65. Provide warning labels if applicable.
Environmental & Disposal Regulations
- Recyclability: Confirm polymer type (e.g., PE, PU) for proper recycling streams. Some dense foams are recyclable; others require landfill or incineration.
- Waste Shipment: If classified as waste, comply with the Basel Convention for transboundary movement of hazardous waste.
- Sustainability Reporting: Consider environmental impact disclosures under frameworks such as EPDs (Environmental Product Declarations).
Documentation Requirements
- Commercial Invoice: Include detailed product description, material composition, country of origin, and HS code.
- Packing List: Specify dimensions, weight, quantity, and packaging type.
- Certificates of Compliance: Provide REACH, RoHS, TSCA, or other applicable compliance certificates upon request.
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Required under GHS if the foam contains hazardous components. Even non-hazardous foams may require an SDS for customs or workplace safety.
Customs Classification (HS Codes)
Common HS codes for dense foam sheets include:
– 3921.11 – Sheets, film, or strip of polymers of ethylene.
– 3921.12 – Of polymers of styrene.
– 3921.90 – Other plastic sheets, including polyurethane.
Note: Final classification depends on material composition, density, and additives. Consult local customs authorities for accuracy.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Supplier Audits: Verify compliance capabilities of foam suppliers.
- Testing: Conduct periodic flammability, off-gassing, and chemical composition testing.
- Training: Educate logistics staff on handling, regulatory requirements, and emergency procedures.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for dense foam sheets ensures safe transportation, regulatory adherence, and smooth customs clearance. Always verify material-specific properties and destination-country regulations to avoid delays or penalties.
In conclusion, sourcing dense foam sheets requires careful consideration of material specifications, intended application, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness. High-density foam options such as cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), polyurethane (PU), or expanded polypropylene (EPP) offer excellent durability, cushioning, thermal insulation, and resistance to compression, making them ideal for protective packaging, automotive, construction, and specialty manufacturing applications. It is essential to evaluate foam density, thickness, cell structure, and environmental resistance to ensure optimal performance. Sourcing from reputable suppliers with consistent quality control, customization capabilities, and sustainable practices can enhance long-term value. By balancing performance requirements with budget and supply chain efficiency, businesses can effectively integrate dense foam sheets into their operations, improving product protection and overall functionality.