The global DC to AC power inverter market is experiencing robust growth, fueled by rising demand for renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and off-grid power solutions. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 11.67 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.8% over the forecast period from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is driven by increasing solar panel installations, government incentives for clean energy adoption, and advancements in power electronics. As demand surges, manufacturers are focusing on improving efficiency, reliability, and integration with smart energy systems. In this evolving landscape, identifying the leading DC to AC current converter manufacturers becomes critical for stakeholders across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Based on market presence, innovation, and product performance, the following ten companies represent the forefront of this growing industry.
Top 10 Dc To Ac Current Converter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 AC-DC Converters
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: AC-DC Converters. Murata Power Solutions has become the world’s leading provider of Slim redundant switching power supplies, dedicated to higher efficiency and ……
#2 Power conversion
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: Eaton has over 55 years of program heritage providing AC/DC, DC/DC and DC/AC power-conversion solutions for critical industrial applications….
#3 Cincon
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cincon.com
Key Highlights: Cincon Electronics is a leading manufacturer of DC/DC converters and AC/DC power supplies offering the high-quality and reliable power module solutions….
#4 Wall Industries
Domain Est. 1998
Website: wallindustries.com
Key Highlights: Wall Industries manufactures and markets a full line of DC DC converters and AC DC power supplies. Browse our standard and customized power solutions ……
#5 Power Supply Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1998
Website: synqor.com
Key Highlights: SynQor designs and manufactures high-efficiency, high-reliability DC-DC power converters, AC-DC power converters, EMI filters and power systems….
#6 DC
Domain Est. 2000
Website: xppower.com
Key Highlights: Choose from our extensive range of DC – DC Converters. High quality, in-house design. Approved for industrial, medical, defense & railway applications….
#7 RECOM: DC/DC & AC/DC Converter
Domain Est. 2006
Website: recom-power.com
Key Highlights: RECOM Power is a leading manufacturer of AC/DC electronic power supplies and DC/DC converters, with over 30,000 compact standard power supplies alongside ……
#8 Power Supplies
Domain Est. 1996
Website: acopian.com
Key Highlights: Acopian Made In USA Reliable ACDC/DCDC power supplies & DCDC converters-fast shipping. Order Online. Switching,Linear,Regulated,Custom,HV,Redundant,2U….
#9 Traco Power
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1944
Website: tracopower.com
Key Highlights: Reliable and Available – Since 1944. DC/DC Converters & AC/DC Power Supplies. DC-DC Converters. AC-DC Power Supplies. Find a Distributor. Get Technical Support….
#10 DC-DC Converters
Domain Est. 2001
Website: vicorpower.com
Key Highlights: Today’s most innovative companies trust Vicor to power their world-changing products. Explore DC-DC converter products, solutions and accessories….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Dc To Ac Current Converter
2026 Market Trends for DC to AC Current Converters
Rising Demand Driven by Renewable Energy Integration
By 2026, the global shift toward renewable energy will significantly boost the demand for DC to AC current converters, commonly known as inverters. Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems generate direct current (DC), which must be converted to alternating current (AC) for grid compatibility and home/industrial use. With countries accelerating solar adoption to meet climate targets, inverter demand will surge. Utility-scale solar farms, residential rooftop installations, and commercial solar projects will all require advanced, high-efficiency inverters, making this the primary growth driver.
Advancements in Inverter Technology and Efficiency
Technological innovation will define the 2026 landscape for DC to AC converters. Manufacturers are focusing on increasing conversion efficiency—modern inverters now exceed 98% efficiency—while reducing size, cost, and thermal losses. Key developments include wide-bandgap semiconductors like silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), which enable higher switching frequencies, improved thermal performance, and greater power density. These advancements will support next-generation inverters with better reliability, lower maintenance, and enhanced integration capabilities in smart energy systems.
Growth in Electric Vehicle (EV) and Charging Infrastructure
The expansion of the electric vehicle market will further stimulate demand for DC to AC inverters. EVs use inverters to convert stored DC power from batteries into AC for driving electric motors. As EV adoption grows globally, so will the need for onboard inverters. Additionally, bidirectional inverters in vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems will gain traction by 2026, allowing EVs to supply AC power back to homes or the grid. This trend reinforces the strategic importance of inverters in energy storage and grid-balancing applications.
Expansion of Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
Energy storage, particularly battery-based systems, will be a major application for DC to AC converters in 2026. As intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind expand, grid stability depends on efficient energy storage. Battery energy storage systems (BESS) require inverters to store energy in DC form and discharge it as AC. The rise of home energy storage (e.g., paired with solar panels) and large-scale grid storage will drive demand for hybrid and multi-mode inverters capable of seamless switching between grid-tied, off-grid, and backup power operations.
Smart Grids and Digitalization Integration
By 2026, DC to AC converters will increasingly feature embedded intelligence and IoT connectivity. Smart inverters will offer grid-support functions such as voltage regulation, frequency response, and fault ride-through. Utilities will deploy these intelligent devices to enhance grid resilience and integrate distributed energy resources (DERs). Software-defined inverter controls, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance will become standard, enabling real-time optimization and improved energy management in both residential and industrial settings.
Regional Market Dynamics and Regulatory Influence
Regulatory policies and regional energy strategies will shape inverter market trends. Regions like North America and Europe are expected to lead due to strong renewable mandates, carbon reduction goals, and incentives for solar plus storage. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific—led by China, India, and Japan—will see robust growth due to massive solar deployments and urban electrification. Regulatory standards for grid interconnection, safety, and cybersecurity will also influence inverter design, pushing manufacturers toward compliance with international certifications.
Competitive Landscape and Supply Chain Considerations
The DC to AC converter market will see intensified competition among established players and new entrants, especially in emerging economies. Key manufacturers will focus on vertical integration, localization, and supply chain resilience to mitigate risks from semiconductor shortages and geopolitical tensions. By 2026, partnerships between inverter makers, battery producers, and energy management software providers will become more common, aiming to deliver integrated energy solutions rather than standalone hardware.
Sustainability and End-of-Life Management
Environmental concerns will influence inverter design and lifecycle management. By 2026, manufacturers will prioritize recyclability, reduced use of rare materials, and longer product lifespans. Second-life applications for inverter components and improved end-of-life recycling processes will gain attention as part of broader circular economy initiatives in the energy sector.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing DC to AC Current Converters (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a DC to AC converter—commonly known as an inverter—requires careful evaluation to ensure reliability, safety, and performance. Overlooking key factors can lead to system failures, safety hazards, or increased long-term costs. Below are common pitfalls related to quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings that buyers should avoid.
Overlooking Build Quality and Component Reliability
Many low-cost inverters use substandard components such as inferior capacitors, inadequate heat sinks, or poor PCB layouts. These shortcuts may reduce upfront costs but often result in premature failure, inconsistent output, or overheating. Buyers should verify the use of reputable brands for critical components and consider operating environment stress (e.g., temperature cycles, vibration).
Ignoring Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings for the Application
The IP rating indicates protection against dust and moisture, but it’s frequently misunderstood or ignored. Using an IP20-rated indoor inverter in an outdoor or dusty environment can lead to corrosion, short circuits, or component failure. Always match the IP rating to the installation environment—e.g., IP65 or higher for outdoor, high-humidity, or industrial settings.
Assuming All Inverters Meet Safety and Certification Standards
Not all manufacturers comply with international safety standards such as UL, IEC, or CE. Some products may display fake or misleading certifications. Sourcing from reputable suppliers and verifying certification authenticity through official databases can prevent safety risks and ensure regulatory compliance.
Failing to Check Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Poorly designed inverters can emit high levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI), disrupting nearby electronics or violating EMC regulations. Ensure the inverter has proper shielding, filtering, and certified EMC performance—especially in sensitive environments like medical, industrial, or communication systems.
Underestimating Thermal Management and Long-Term Durability
Inadequate thermal design leads to reduced lifespan and efficiency. Inverters operating in high ambient temperatures without proper cooling mechanisms (e.g., fans, heat sinks) may derate output or fail prematurely. Evaluate thermal performance data and real-world reliability reports before purchasing.
Disregarding Warranty and Manufacturer Support
Short or limited warranties often reflect low confidence in product quality. Lack of technical support or spare parts availability can make troubleshooting and maintenance difficult. Prioritize suppliers offering comprehensive warranties and responsive customer service, especially for mission-critical applications.
By addressing these pitfalls early in the sourcing process, buyers can ensure they select a DC to AC converter that delivers safe, efficient, and long-lasting performance tailored to their specific environmental and operational needs.
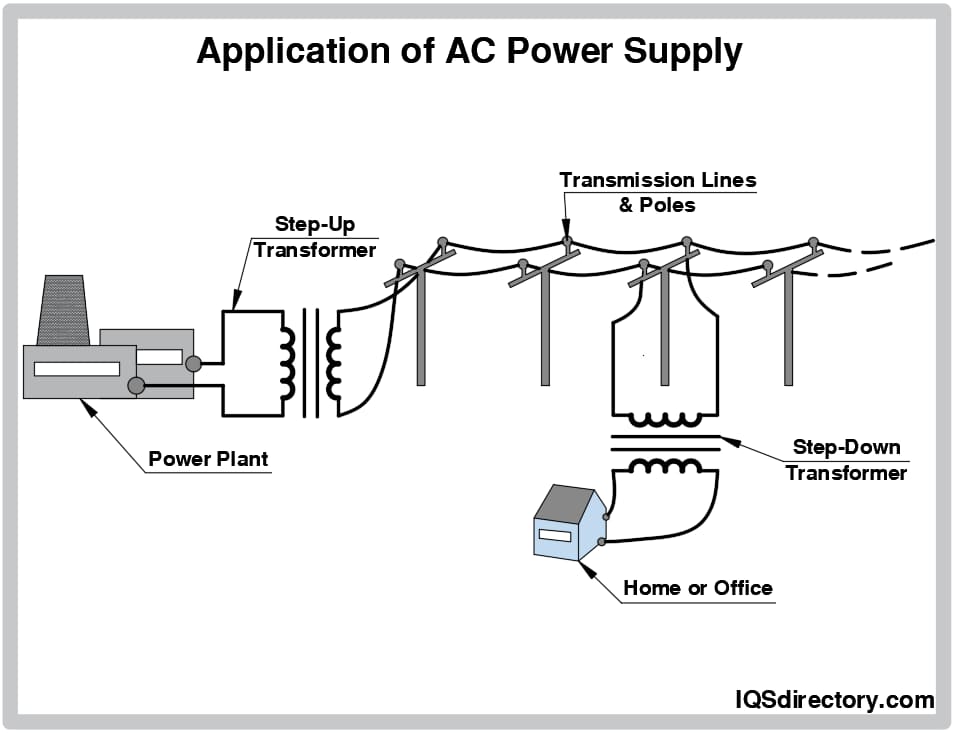
Logistics & Compliance Guide for DC to AC Current Converters
Product Classification and HS Code
DC to AC current converters, commonly known as inverters, are typically classified under Harmonized System (HS) codes related to electrical power conversion equipment. The most common HS code is 8504.40, which covers static converters (including rectifiers and inverters). However, classification may vary by country and specific product specifications (e.g., power rating, intended use, integrated battery). Accurate classification is essential for determining import duties, taxes, and regulatory requirements. Consult local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker to confirm the correct HS code for your product in each target market.
Import Regulations and Documentation
Importing DC to AC converters requires compliance with destination country regulations. Required documentation typically includes a commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading or air waybill, and a certificate of origin. Some countries may require additional forms such as an import license, conformity assessment certificate, or pre-shipment inspection (PSI) report. Ensure that technical specifications (input/output voltage, frequency, power rating) are clearly stated on all documents to avoid customs delays. For regulated markets, registration with national electrical or product safety authorities may be mandatory prior to import.
Electrical and Safety Standards
DC to AC converters must comply with regional electrical safety standards to be legally sold. Key certifications include:
– UL 1741 (United States): Standard for inverters, converters, and controllers used in distributed energy systems.
– IEC 62109 (International): Safety standards for power converters used in photovoltaic systems.
– EN 62109 (European Union): Harmonized standard under the Low Voltage Directive (LVD).
– AS/NZS 4777.2 (Australia and New Zealand): Grid connection requirements for inverters.
Products should bear applicable certification marks (e.g., UL, CE, UKCA, RCM) to demonstrate compliance. Non-certified products may be rejected at customs or recalled post-import.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Requirements
Inverters must meet electromagnetic compatibility standards to prevent interference with other electronic devices. Relevant EMC directives include:
– FCC Part 15 Subpart B (USA): Regulates unintentional radiators.
– EMC Directive 2014/30/EU (EU): Requires CE marking for electromagnetic compatibility.
– CISPR 11 or CISPR 32: International standards for emissions from industrial, scientific, and medical equipment or multimedia devices.
Testing must be performed by accredited laboratories, and technical documentation (including test reports) should be maintained for market surveillance.
Packaging, Labeling, and Marking
Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transit, especially for sensitive electronic components. Use anti-static materials and secure internal bracing. Labels must include:
– Manufacturer/importer name and address
– Model number and serial number
– Input/output electrical specifications (voltage, current, frequency, power)
– Safety warnings and compliance marks (e.g., CE, UL, RoHS)
– Direction for use and caution symbols per IEC 60417
Bilingual or multilingual labeling may be required in certain markets (e.g., Canada, EU member states).
Environmental and Chemical Compliance
DC to AC converters must comply with restrictions on hazardous substances:
– RoHS (EU): Restricts lead, mercury, cadmium, and certain flame retardants.
– China RoHS: Requires labeling of hazardous substances in electronic products.
– REACH (EU): Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
Ensure that suppliers provide material declarations (e.g., IPC-1752) and that products are free of banned substances. Proper end-of-life handling instructions should be included in user manuals.
Shipping and Transportation
Due to electronic components and potential battery integration, DC to AC converters may be subject to special shipping regulations:
– IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations: Apply if the inverter contains lithium batteries (UN 3480 or UN 3481).
– IMDG Code: For sea transport of battery-equipped units.
– UN 38.3 Testing: Required for lithium batteries to certify safe transport.
Clearly label packages with appropriate hazard labels when applicable and use carriers experienced in shipping electronic or hazardous goods.
After-Sales and Warranty Logistics
Establish a service and warranty support system in the destination market. Maintain an inventory of spare parts and trained technicians, or partner with local service providers. Record product serial numbers and registration data to manage recalls or safety notices. Comply with local consumer protection laws regarding warranty duration, repair timelines, and return policies.
Recordkeeping and Audit Preparedness
Maintain comprehensive compliance records for a minimum of five to ten years, depending on jurisdiction. Records should include: certification test reports, technical files, import documentation, supplier declarations of conformity, and customer service logs. Be prepared for audits by regulatory bodies or customs authorities to demonstrate ongoing compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing a DC to AC Current Converter (Inverter):
Sourcing the right DC to AC current converter, or inverter, is a critical decision that directly impacts the performance, efficiency, and reliability of your power system. Whether for renewable energy applications, backup power, or off-grid setups, selecting an inverter involves careful consideration of key factors such as power output capacity, waveform type (pure sine wave vs. modified sine wave), input voltage compatibility, efficiency ratings, and built-in safety features.
After evaluating various options, it is evident that pure sine wave inverters are the preferred choice for sensitive electronics and long-term reliability, despite their higher initial cost. Additionally, considering brand reputation, warranty terms, and customer support will ensure long-term satisfaction and system uptime.
Ultimately, the ideal inverter should align with the specific load requirements, environmental conditions, and scalability needs of the application. By thoroughly assessing technical specifications, total cost of ownership, and supplier credibility, organizations and individuals can make informed procurement decisions that ensure efficient power conversion and system resilience.