The lab-grown diamond market, particularly those produced via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), is experiencing rapid expansion driven by rising demand across industrial, jewelry, and technology sectors. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global lab-grown diamond market was valued at USD 20.6 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.2% from 2023 to 2030. A key enabler of this growth is the increasing adoption of CVD technology, which offers higher purity and scalability compared to traditional High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) methods. Mordor Intelligence corroborates this trend, projecting a CAGR of over 16% for the lab-grown diamond market through 2028, with CVD emerging as the preferred synthesis method due to advancements in equipment efficiency and declining production costs. As demand surges, the role of CVD diamond machine manufacturers becomes increasingly critical—shaping innovation, yield quality, and production capacity across the supply chain. Here, we spotlight the top 10 manufacturers leading this transformation with cutting-edge reactor systems and scalable solutions.
Top 10 Cvd Diamond Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Bhanderi Prime Lab Grown CVD Diamonds Manufacturer in India
Domain Est. 2021
Website: blgdlab.com
Key Highlights: Bhanderi leading manufacturer of Type IIa lab grown diamonds in India, ensures excellent quality and craftsmanship with cutting-edge technology….
#2 CVD Diamond Machine Manufacturer India
Domain Est. 2000
Website: sltl.com
Key Highlights: One-stop solution providers for diamonds have now created CVD Diamond Machines making a complete range of systems transforming diamonds from Lab to Market….
#3 CVD diamond reactors
Domain Est. 2012
Website: sekidiamond.com
Key Highlights: CVD diamond reactors from Seki Diamond are most preferred by scientists and researchers for diamond synthesis in R&D, gemstones and industrial applications….
#4 CVD Diamond Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2015
Website: cvddiamondinc.com
Key Highlights: At CVD Diamond, we manufacture and supply an extensive inventory of lab grown diamonds ranging from 0.003 to 2.00 carats….
#5 Lab Grown Diamond Machine Manufacturer and Supplier
Domain Est. 2019
Website: sltlcvdlaser.com
Key Highlights: Total Solution for Lab-Grown Diamond. World’s Largest Supplier of Technical Systems for CVD Cutting and HPHT Diamond Processing….
#6 World’s Largest Grower Of CVD Lab Grown Diamonds
Domain Est. 2023
Website: kiradiam.com
Key Highlights: Discover top-quality lab-grown diamonds at Kira, a leading manufacturer and supplier in United States & India. Trusted for excellence in CVD diamond ……
#7 HPHT and CVD Diamond Growth Processes
Domain Est. 1996
Website: gia.edu
Key Highlights: With the traditional diamond growth method, called high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT), synthetic diamonds are produced from carbon material….
#8 Chemical Vapor Deposition
Domain Est. 1997
Website: cvdequipment.com
Key Highlights: CVD Equipment Corporation provides precise and reliable chemical vapor deposition and thermal process equipment – enabling tomorrow’s technologies….
#9 Element Six
Domain Est. 1998
Website: e6.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to Element Six, a world leader in synthetic diamond and tungsten carbide supermaterials. Find out more about our excellent range today….
#10 CVD Diamond Corporation: Diamond Coated End Mills
Domain Est. 1999
Website: cvddiamond.com
Key Highlights: These high quality diamond cutting tools are used in machining graphite, machining carbon fiber, machining ceramics in the green state and in the machining of ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cvd Diamond Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for CVD Diamond Machines
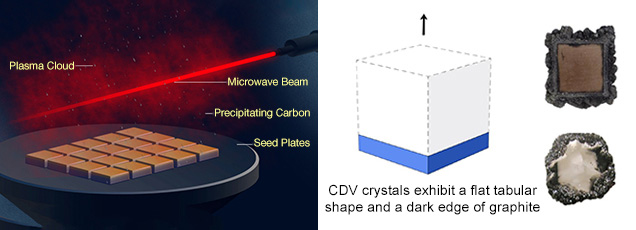
The market for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) diamond machines is poised for transformative growth and technological evolution by 2026, driven by increasing demand across high-tech industries, advancements in manufacturing capabilities, and supportive macroeconomic and environmental trends. Below is an in-depth analysis of the key market trends shaping the CVD diamond machine sector in 2026.
1. Rising Demand from Semiconductor and Electronics Industries
A major driver for CVD diamond machines in 2026 is the semiconductor industry’s need for ultra-efficient thermal management solutions. With the proliferation of 5G, AI chips, and high-power electronic devices, CVD diamond’s exceptional thermal conductivity (up to 2,200 W/mK) makes it ideal for heat spreaders and substrates. As chip miniaturization intensifies, traditional materials like silicon carbide and copper face thermal limitations, accelerating the adoption of CVD diamond in advanced packaging and next-generation devices.
2. Expansion in Quantum Technology and Photonics
CVD diamond’s unique quantum properties—particularly nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers—are fueling demand in quantum sensing, computing, and secure communications. By 2026, investment in quantum research from governments and private sectors (especially in the U.S., EU, and China) is expected to boost the need for high-purity, single-crystal CVD diamonds. This, in turn, drives demand for advanced CVD machines capable of producing defect-free, isotopically engineered diamond wafers.
3. Advancements in Machine Efficiency and Scalability
CVD diamond machine manufacturers are focusing on improving deposition rates, energy efficiency, and batch processing capabilities. Innovations such as microwave plasma CVD (MPCVD) with enhanced plasma stability and larger chamber designs enable production of multi-inch diamond wafers at lower costs. In 2026, next-generation machines will likely feature AI-driven process control systems, allowing real-time monitoring and optimization of growth parameters, reducing defects and improving yield.
4. Growth in Industrial and Cutting Tools Market
The industrial sector, particularly in precision machining, oil & gas drilling, and aerospace, continues to adopt CVD diamond-coated tools for their extreme hardness and wear resistance. By 2026, demand for large-area, uniform diamond coatings will push machine manufacturers to develop scalable systems suitable for mass coating applications, enhancing productivity and reducing tool replacement costs.
5. Sustainability and Green Manufacturing Focus
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are influencing material choices across industries. CVD diamond is increasingly viewed as a green alternative due to its long lifespan, energy efficiency in applications, and reduced need for rare or toxic materials. In 2026, CVD machine producers are expected to emphasize lower energy consumption, reduced greenhouse gas emissions during synthesis, and recyclable components to appeal to ESG-conscious investors and customers.
6. Geopolitical and Supply Chain Shifts
Geopolitical tensions, particularly in semiconductor supply chains, are prompting countries to invest in domestic capabilities for critical materials. China, the U.S., Japan, and Germany are expected to increase funding for domestic CVD diamond R&D and production infrastructure by 2026. This may lead to regionalization of CVD machine manufacturing and tighter control over IP, affecting global market dynamics.
7. Cost Reduction and Market Democratization
Historically, high equipment and operational costs have limited CVD diamond adoption. However, by 2026, economies of scale, improved reactor designs, and automation are expected to lower the total cost of ownership. This will open new markets, including mid-tier manufacturers and academic institutions, broadening the application base beyond niche high-end sectors.
8. Strategic Collaborations and Mergers
The CVD diamond machine market is witnessing increased collaboration between equipment makers, material scientists, and end-users. Joint ventures aimed at co-developing application-specific machines (e.g., for quantum or biomedical use) are expected to accelerate innovation. Mergers among CVD technology firms may also consolidate capabilities, creating integrated solution providers.
Conclusion
By 2026, the CVD diamond machine market will be shaped by technological innovation, cross-industry demand, and global strategic interests. As machines become more efficient, affordable, and adaptable, the commercial viability of synthetic diamond will expand across semiconductors, quantum tech, industrial tools, and beyond. Companies that invest in scalable, intelligent, and sustainable CVD systems will be well-positioned to lead this high-growth market.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing CVD Diamond Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) diamond machines involves significant technical, financial, and legal considerations. Buyers—especially those new to the field—often encounter pitfalls related to machine quality and intellectual property (IP) that can compromise project success, increase costs, or lead to legal disputes. Below are key challenges to be aware of.
Poor Machine Quality and Performance Inconsistencies
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing CVD diamond machines is receiving equipment that fails to meet technical specifications or deliver consistent results. Many suppliers, particularly in emerging markets, may offer lower-cost machines that appear compliant on paper but underperform in real-world conditions. Issues include inadequate temperature uniformity, unstable plasma generation, poor vacuum integrity, and insufficient gas flow control—all of which directly impact diamond quality, growth rate, and reproducibility. Without rigorous third-party validation or on-site testing, buyers risk acquiring machinery that cannot produce gem-quality or industrial-grade diamonds reliably.
Lack of After-Sales Support and Technical Expertise
Even high-quality machines require ongoing maintenance, calibration, and technical support. A common pitfall is partnering with suppliers who offer limited or unreliable after-sales service. This includes delayed response times, difficulty sourcing spare parts, or lack of access to trained engineers. Without proper support, machine downtime increases, and operational efficiency drops—especially for users without in-house expertise in plasma physics or vacuum systems. It’s essential to vet suppliers not only on machine specifications but also on their service network, training offerings, and long-term support capabilities.
Inadequate or Misrepresented Process Know-How
CVD diamond growth depends heavily on proprietary process parameters—such as gas mixtures, pressure, power settings, and substrate preparation—not just the machine hardware. Some suppliers may deliver a machine without providing sufficient process know-how, or worse, offer misleading process recipes that do not yield viable diamond growth. Buyers may find themselves unable to produce usable diamonds despite having functional equipment. Always clarify what process support is included and, if possible, validate the supplier’s claims through pilot runs or references from existing customers.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing CVD equipment from unverified manufacturers can expose buyers to serious intellectual property (IP) risks. Some suppliers may use designs, components, or software that infringe on patented technologies owned by established players. If a machine incorporates such IP, the end-user could face legal action, equipment seizure, or prohibitions on commercial use of the diamonds produced. This is particularly concerning when sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s IP portfolio and request warranties that the machine does not infringe on third-party patents.
Hidden Technology Transfer Limitations
Even when a machine is legally sound, suppliers may embed limitations that restrict technology transfer. For example, closed-source software, encrypted control systems, or proprietary gas delivery modules can prevent users from optimizing or modifying the process. This lack of transparency locks buyers into vendor dependency and hampers innovation. Ensure that contracts include rights to full technical documentation, software access, and the ability to modify or service the equipment independently.
Insufficient Validation and Testing Protocols
Many buyers skip or underestimate the importance of on-site performance validation before finalizing a purchase. Relying solely on factory test reports or video demonstrations is risky. Without witnessing diamond growth firsthand under your desired conditions, you cannot verify the machine’s capabilities. Always arrange for a performance qualification (PQ) test, ideally producing diamonds that meet your specific application requirements (e.g., size, purity, growth rate) before accepting delivery.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence, legal review of contracts, and engagement with reputable, transparent suppliers. Prioritize vendors with proven track records, clear IP ownership, and comprehensive support frameworks to ensure a successful CVD diamond production operation.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for CVD Diamond Machine
Overview
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) diamond machines are advanced manufacturing systems used to synthesize high-purity synthetic diamonds. Due to their technical complexity, high value, and potential dual-use applications, shipping and operating these machines require strict adherence to international logistics protocols and regulatory compliance standards.
Export Controls & Regulatory Classifications
CVD diamond machines may be subject to export control regulations due to their use in high-tech and industrial applications. Key classification systems include:
– EAR (Export Administration Regulations – USA): Check the Commerce Control List (CCL). CVD machines may fall under ECCN 3B001 (equipment for manufacturing semiconductor materials) or similar, depending on technical specs (e.g., vacuum levels, temperature control, gas handling).
– Wassenaar Arrangement: Equipment capable of producing synthetic diamond for electronic or optical applications may be listed under dual-use technologies.
– National Regulations: Countries such as China, EU member states, and Japan have their own export control frameworks. Verify local requirements before shipment.
Action: Obtain an official ECCN or equivalent classification. Apply for export licenses if required, especially for destinations under embargo or with sensitive end-users.
Required Documentation
Ensure all shipments include accurate and complete documentation:
– Commercial Invoice (with detailed technical description and value)
– Packing List (itemizing all components, weights, and dimensions)
– Certificate of Origin
– Export License (if applicable)
– Technical Specifications Sheet (including power requirements, dimensions, and materials)
– End-User Statement or End-Use Certificate (for controlled destinations)
Packaging & Handling Requirements
CVD machines are sensitive to shock, vibration, moisture, and static. Proper packaging is critical:
– Use custom wooden crates with internal bracing and anti-vibration materials.
– Include humidity control (desiccants) and ESD-safe packaging for electronic components.
– Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Sensitive Equipment.”
– Secure all moving parts and cover optical or vacuum ports.
Transportation Considerations
- Mode of Transport: Air freight is preferred for speed and reduced handling; sea freight is cost-effective for large systems but increases exposure to environmental risks.
- Climate Control: Maintain stable temperature and humidity during transit. Avoid condensation during air-to-ground transfers.
- Insurance: Procure all-risk cargo insurance covering full replacement value.
- Freight Forwarder: Use a logistics partner experienced in high-value scientific equipment with capabilities in customs clearance and regulatory compliance.
Import Compliance
Importing countries may impose additional requirements:
– Customs Duties & Taxes: Research HS codes (e.g., 8479.89 for machines with specific functions) and applicable tariffs.
– Local Approvals: Some countries require pre-shipment inspections, safety certifications (e.g., CE, CCC), or registration with technical standards bodies.
– Installation Site Preparation: Confirm power supply (voltage, phase, grounding), exhaust venting for process gases, and cleanroom compatibility if applicable.
Environmental, Health & Safety (EHS) Compliance
CVD machines use hazardous gases (e.g., methane, hydrogen) and high-energy systems:
– Comply with OSHA (USA), REACH/CLP (EU), or equivalent national EHS regulations.
– Ensure safe gas storage, leak detection, and ventilation at the installation site.
– Provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) for all consumables.
– Train operators on emergency shutdown procedures and PPE requirements.
After-Shipment Support & Compliance Monitoring
- Maintain records of export transactions for at least 5 years (per EAR requirements).
- Monitor end-use through customer agreements, especially for controlled technologies.
- Provide technical support and compliance documentation to facilitate smooth customs clearance and installation.
Conclusion
Shipping and operating a CVD diamond machine demands meticulous planning across logistics and compliance domains. Proactive classification, documentation, and coordination with regulatory experts and freight partners are essential to ensure lawful, safe, and timely deployment.
Conclusion for Sourcing a CVD Diamond Machine:
Sourcing a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) diamond machine is a strategic investment that requires careful evaluation of technical specifications, production capacity, supplier reputation, after-sales support, and total cost of ownership. CVD diamond technology offers significant advantages in producing high-purity, high-performance synthetic diamonds for applications in semiconductors, optics, cutting tools, and quantum technologies.
After assessing various suppliers, machine capabilities, and technological maturity, it is evident that selecting a reliable and proven CVD system is critical to ensure consistent diamond quality, operational efficiency, and long-term scalability. Key considerations include plasma generation method (e.g., MW-CVD vs. HFCVD), temperature and pressure control, chamber size, automation features, and energy efficiency.
Partnering with a reputable manufacturer that provides comprehensive technical support, training, and maintenance services will greatly enhance operational success. Additionally, future-proofing the investment by choosing a modular and upgradable system allows for technology advancements and expansion of application capabilities.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing decision—based on thorough technical due diligence, cost-benefit analysis, and alignment with specific application needs—will enable successful integration of CVD diamond production, supporting innovation and competitiveness in advanced material markets.