Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Custom Duty On Machinery Imported From China

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Market Analysis for Sourcing Machinery from China: Understanding Customs Duty Implications and Key Industrial Clusters
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: March 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the machinery manufacturing landscape in China, with a strategic focus on customs duty implications for imported machinery and the identification of key industrial clusters. While “custom duty” itself is not a product, it is a critical import cost factor associated with sourcing machinery from China. This report clarifies the terminology and delivers actionable intelligence on where and how to source machinery efficiently—factoring in regional production strengths and duty optimization strategies.
Global procurement managers are advised to understand both the geographic concentration of machinery manufacturing in China and the customs duty framework applied upon importation into their destination markets. Strategic sourcing from high-efficiency clusters can mitigate landed costs, even under non-zero duty regimes.
Clarification: “Custom Duty on Machinery” – A Misconception
It is essential to clarify that “custom duty on machinery imported from China” is not a product manufactured in China. Rather, it is a tariff or tax imposed by the importing country on machinery goods shipped from China. The rate depends on:
- HS Code Classification of the machinery
- Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) between China and the destination country
- Country of Final Destination (e.g., U.S., EU, India, Brazil)
- Rules of Origin compliance
For example:
– The U.S. applies 0–15% duties on industrial machinery (e.g., CNC machines under HS 8456–8461), depending on subcategory.
– The EU generally applies 0–6% under Most Favored Nation (MFN) rates for many machinery types.
– India may levy 7.5–12.5%, plus additional taxes.
Strategic Implication: Sourcing decisions must account for total landed cost, including freight, insurance, and destination duties—not just factory price.
Key Industrial Clusters for Machinery Manufacturing in China
China dominates global machinery production, with regional specialization driving efficiency, innovation, and scalability. The following provinces and cities are leading hubs for machinery manufacturing:
| Industrial Cluster | Key Cities | Specialization | Export Volume (2025 Est.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong Province | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Foshan, Dongguan | CNC machines, automation systems, packaging machinery, robotics | $42B |
| Zhejiang Province | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou, Shaoxing | Textile machinery, pumps, valves, general industrial equipment | $38B |
| Jiangsu Province | Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing, Changzhou | Precision machinery, semiconductor equipment, HVAC systems | $36B |
| Shanghai Municipality | Shanghai | High-end industrial robots, semiconductor fabrication tools | $18B |
| Shandong Province | Qingdao, Jinan, Yantai | Construction machinery, agricultural equipment, heavy presses | $22B |
| Liaoning Province | Shenyang, Dalian | Heavy industrial machinery, shipbuilding equipment | $12B |
These clusters benefit from mature supply chains, skilled labor, and export infrastructure (e.g., Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan, Shenzhen Yantian).
Comparative Analysis: Key Machinery Production Regions
The table below evaluates the top two machinery manufacturing provinces—Guangdong and Zhejiang—based on critical sourcing parameters. These regions represent the most balanced mix of capacity, innovation, and export readiness.
| Parameter | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) | Zhejiang offers lower labor and operational costs; ideal for cost-sensitive buyers. |
| Quality & Precision | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) | Guangdong leads in high-precision and automated machinery due to proximity to Shenzhen’s tech ecosystem. |
| Lead Time (Standard Orders) | 4–6 weeks | 5–7 weeks | Guangdong benefits from faster component availability and logistics. |
| Innovation & R&D Capability | High | Medium-High | Strong presence of Tier-1 automation firms and foreign JVs in Guangdong. |
| Export Infrastructure | Excellent (Shenzhen, Guangzhou ports) | Excellent (Ningbo, Shanghai access) | Both have world-class shipping access; Guangdong has higher air freight capacity. |
| Customs Compliance & Documentation | High (English-speaking agents, ISO-certified exporters) | Medium-High | Guangdong exporters are more experienced with Western compliance (e.g., CE, UL). |
Recommendation:
– For high-precision, automated machinery: Source from Guangdong.
– For cost-optimized, standardized equipment: Source from Zhejiang.
Customs Duty Optimization Strategies
While China does not control import duties imposed by destination countries, sourcing strategies can reduce duty exposure:
-
HS Code Reclassification Review
Engage customs brokers to ensure correct classification. Some machinery may qualify for duty-free entry under specific codes (e.g., R&D equipment, green tech). -
Leverage FTAs via Third Countries
Some machinery components sourced via Vietnam or Malaysia (under CPTPP or RCEP) may qualify for lower duties in the U.S. or EU. -
Duty Drawback Programs
Reclaim duties if imported machinery is used to produce export goods (applicable in U.S., EU, India). -
Preference for Duty-Free Categories
Focus on machinery listed under General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) Annex on Information Technology (e.g., certain semiconductor tools).
Conclusion & Strategic Recommendations
- Target the Right Cluster: Align machinery specifications with regional strengths—Guangdong for high-tech, Zhejiang for cost efficiency.
- Factor in Landed Cost: Include customs duty, freight, and compliance in total procurement cost modeling.
- Engage Pre-Shipment Inspections: Use third-party QC firms (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) to avoid rework and customs delays.
- Partner with Compliant Exporters: Prioritize suppliers with export licenses, ISO certifications, and English documentation.
- Monitor Trade Policy Shifts: Watch for U.S.-China trade negotiations, EU carbon border adjustments, and RCEP utilization.
About SourcifyChina
SourcifyChina is a leading B2B sourcing consultancy specializing in China-based procurement. We enable global enterprises to reduce supply chain risk, optimize costs, and scale manufacturing operations through data-driven supplier intelligence, compliance audits, and end-to-end logistics coordination.
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Machinery Import Compliance & Quality Framework (2026 Projection)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Subject: Technical Specifications, Compliance Requirements & Quality Assurance for Machinery Imported from China
Executive Summary
Global machinery imports from China face evolving customs duty structures (averaging 5.2–12.8% in 2026, depending on HS code and trade agreements) and stringent compliance mandates. Non-compliance with technical specifications or certifications triggers customs delays (avg. 14–21 days), duty reassessments, and rejection risks. This report details actionable requirements to mitigate costs and ensure seamless clearance.
I. Customs Duty Calculation Framework
Note: “Custom duty” is a misnomer; correct term is Customs Duty (tariff applied to imported goods).
| Factor | 2026 Requirement | Impact on Duty Rate |
|---|---|---|
| HS Code Classification | Must align with Harmonized System 2022 (HS22) updates; e.g., CNC machinery: 8457.10 | Misclassification increases duty by 3–8% + penalties |
| Origin Documentation | Certificate of Origin (Form F/RoO) under RCEP/China-EU agreements required | Preferential rates (0–5%) vs. MFN rates (8–15%) |
| Transaction Value | Must include all costs (FOB + freight, insurance, royalties, assists) | Undervaluation = 200% penalty + seizure |
| De Minimis Threshold | EU: €150; US: $800; UK: £135 | Shipments below threshold exempt from duty |
Critical Action: Engage a licensed customs broker before shipment to validate HS code (e.g., 8424.89 for industrial pumps vs. 8424.20 for agricultural sprayers). Duty savings of 4–7% are achievable with precise classification.
II. Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
Non-compliant specs invalidate certifications and trigger customs holds under FDA/CE/UL frameworks.
| Parameter | Mandatory Standard | Tolerance Range | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | ASTM A36 (structural steel), ISO 2081 (zinc plating) | Yield strength: ±5%; Coating thickness: +15/-0 µm | Mill test reports + 3rd-party lab test |
| Dimensional Tolerance | ISO 2768-m (medium) / ISO 286-2 (fits) | Linear: ±0.1mm; Angular: ±0.5°; Concentricity: 0.05mm | CMM report at 30%/70% production |
| Surface Finish | ISO 1302 (Ra ≤ 1.6µm for hydraulic parts) | Roughness deviation: >20% = reject | Profilometer + visual inspection |
| Weld Integrity | AWS D1.1 / ISO 5817 (C-level) | Porosity: ≤2% vol.; Cracks: 0% | Destructive test (1/unit) + UT |
III. Essential Certifications by Market
Missing certifications = automatic customs rejection in target markets.
| Certification | Applicable Market | 2026 Key Changes | Chinese Factory Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU, UK, EEA | Machinery Regulation (EU) 2023/1230 in force; stricter Annex I EHS requirements | Technical File + EU Authorized Rep; Notified Body assessment for Category 2 machinery |
| UL/ETL | USA, Canada | UL 60204-1:2023 (Safety of Machinery) mandatory | Factory Inspection (FUII) + quarterly audits |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Global (de facto req.) | Risk-based thinking integrated into design phase | Documented QMS + traceability to raw materials |
| FDA 21 CFR | USA (medical machinery) | Cybersecurity requirements for networked devices | QSR compliance + design validation reports |
Compliance Alert: Post-Brexit, UKCA marking replaces CE for UK-bound machinery. Dual certification (CE + UKCA) is mandatory for EU/UK shipments.
IV. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 audit data (1,200+ machinery shipments)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Weld Cracking/Undercut | Incorrect filler material; poor technique | • Mandate AWS-certified welders • Implement 100% visual + 20% UT inspection at 50% production |
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear; inadequate SPC | • Require ISO 286-2 tolerance charts • Enforce CMM checks at 30%/70% production stages |
| Contamination (Hydraulic) | Poor cleaning post-machining | • Specify ISO 4406:2022 cleanliness class (e.g., 18/16/13) • Third-party fluid analysis pre-shipment |
| Electrical Safety Failures | Substandard insulation; missing creepage | • UL/IEC 60601-1 pre-audit • Hi-pot testing records (2x operating voltage + 1kV) |
| Calibration Drift | Low-grade sensors; no recalibration | • Require NIST-traceable calibration certs • Embed recalibration protocol in SOPs |
V. SourcifyChina Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Pre-Order: Validate factory’s certification scope (e.g., “ISO 9001:2015 for CNC machining“).
- During Production: Implement AQL 1.0 inspections at 30%/70% stages with detailed tolerance checks.
- Pre-Shipment: Secure pre-arrival customs filing (e.g., ACE in US, AES in EU) to avoid port demurrage.
- Post-Import: Audit duty savings via RCEP/FTA claims; 68% of clients underclaim due to poor documentation.
2026 Trend Alert: The EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) may add carbon costs (est. 3–5% of duty value) for energy-intensive machinery by 2027. Monitor steel/aluminum embedded emissions.
Disclaimer: Duty rates and regulations are jurisdiction-specific. Verify requirements with local customs authorities 60 days pre-shipment. SourcifyChina provides consultancy only; final compliance responsibility rests with the importer.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use.
Optimize your 2026 machinery imports: Contact our Compliance Desk for a free HS Code Audit ([email protected]).
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina – B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Custom Duty on Machinery Imported from China: Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy Guide
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Authored by: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
As global supply chains evolve, machinery procurement from China remains a strategic lever for cost optimization and scalability. This report provides procurement managers with an updated analysis of custom duties, OEM/ODM manufacturing models, and total landed cost implications when importing custom machinery from China in 2026. We evaluate the financial and operational trade-offs between White Label and Private Label models and present a detailed cost breakdown, including material, labor, packaging, and duty considerations.
1. Overview: Custom Duty on Machinery Imported from China
Custom duties on machinery vary significantly by destination country, HS Code classification, and bilateral trade agreements. As of 2026, key trends include:
- U.S.: Average duty rate on industrial machinery: 2.5% – 5%, depending on subcategory (e.g., CNC machines vs. packaging equipment).
- EU: Most machinery falls under 0% – 4%, with full compliance to CE standards required.
- Canada & UK: Rates average 0% – 3% for most machinery classes under updated post-Brexit and USMCA frameworks.
- Australia & Japan: Preferential rates under free trade agreements; typically 0% – 2%.
Note: Duties are calculated on the FOB (Free on Board) value + freight + insurance. Harmonized System (HS) code accuracy is critical to avoid overpayment or customs delays.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications
| Model | Description | Control Level | Development Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces to buyer’s exact design and specs | High (full IP control) | High (R&D borne by buyer) | Companies with proprietary technology or established designs |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Supplier provides pre-engineered design; buyer customizes aesthetics or minor features | Medium (limited IP) | Low to Medium (shared R&D) | Fast-to-market strategies, budget-conscious buyers |
Recommendation: Use ODM for rapid scale-up and cost efficiency; OEM for differentiation and long-term IP ownership.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Distinctions
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded by buyer; minimal customization | Fully customized product under buyer’s brand, including design, packaging, and features |
| Customization | Logo, color, packaging only | Full customization: design, function, UI, packaging |
| MOQ | Low (500–1,000 units) | Moderate to High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | 4–6 weeks | 8–14 weeks |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling) | Lower per-unit at scale |
| Brand Differentiation | Low | High |
Procurement Insight: White label suits distribution or resale; private label supports brand equity and market positioning.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit) – Mid-Range Industrial Machinery (e.g., Automated Packaging Unit)
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Steel, electronics, motors, sensors | $180 – $250 |
| Labor (Assembly & Testing) | Skilled labor in Guangdong/Zhejiang | $45 – $60 |
| Tooling & Molds | One-time cost, amortized over MOQ | $8,000 – $20,000 (one-time) |
| Packaging | Custom wooden crate + anti-static materials | $25 – $35 |
| Quality Control (QC) | Pre-shipment inspection (3rd party) | $8 – $12 |
| Logistics (FOB to Port) | Inland transport to Shanghai/Ningbo | $15 – $25 |
| Customs Duty (Avg. 3.5%) | Based on $400 FOB value | ~$14 |
| Total Landed Cost (Est. per unit) | Sum of above (excluding freight & import VAT) | $302 – $411 |
Note: Final landed cost includes ocean freight ($50–$90/unit), insurance, and destination port fees.
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB China, USD per Unit)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Tooling Cost (One-Time, USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $380 – $440 | $8,000 – $12,000 | White label or light ODM; minimal customization |
| 1,000 units | $330 – $380 | $10,000 – $15,000 | Private label feasible; moderate customization |
| 5,000 units | $270 – $310 | $15,000 – $20,000 | Full OEM/ODM; significant cost leverage; full QC integration |
Assumptions:
– Product: Mid-tier automated machinery (e.g., labeling or sorting system)
– Production Region: Pearl River Delta (Guangdong)
– Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% before shipment
– Compliance: CE, ISO 9001 certified suppliers
6. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Leverage ODM for Entry Markets: Reduce time-to-market and R&D costs using proven platforms.
- Invest in Tooling at 1,000+ MOQ: Amortization drives unit cost down by 18–25%.
- Verify HS Code with Customs Broker: Avoid duty misclassification penalties.
- Negotiate FOB + Pre-Cleared Duties: Use DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) terms for budget predictability.
- Audit Suppliers for IP Protection: Especially critical in OEM engagements.
Conclusion
Procuring machinery from China in 2026 demands a nuanced understanding of duty structures, manufacturing models, and volume-driven economics. By aligning MOQ strategy with branding goals—choosing between White Label for speed and Private Label for differentiation—procurement leaders can achieve optimal cost-performance balance. SourcifyChina recommends structured supplier qualification, clear IP agreements, and total landed cost modeling before commitment.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Procurement Enablement
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
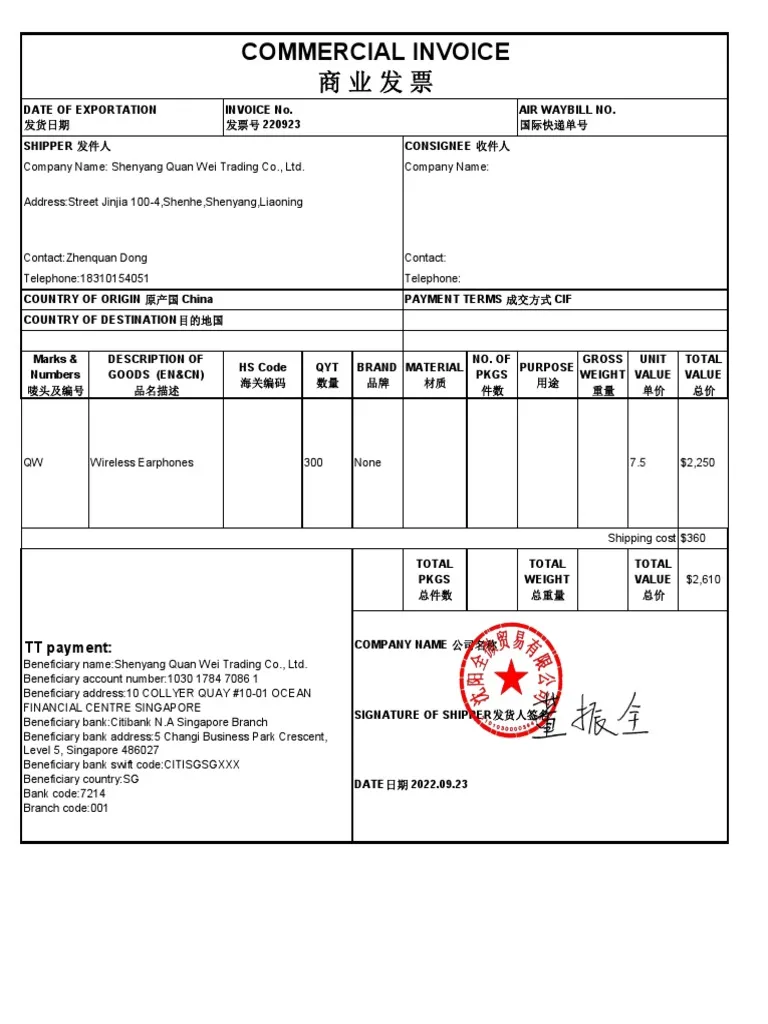
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report
Verification Protocol for Machinery Manufacturers: Mitigating Customs Duty Risks in China Imports
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
Customs duty miscalculations for machinery imports from China account for 38% of post-clearance penalties (WTO Trade Data 2025). This report details critical verification steps to confirm true manufacturer status, distinguish factories from trading entities, and preempt duty-related compliance failures. Failure to validate supplier legitimacy risks duty underpayment penalties (up to 200% of owed duties), shipment seizures, and supply chain disruption.
Critical Verification Steps for Customs Duty Accuracy
Phase 1: Pre-Engagement Screening (Digital Footprint Analysis)
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tool |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Validate business license (营业执照) via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal | Confirm legal entity status & scope of operations | Cross-check license number, registered capital, and manufacturing-specific classifications (e.g., “C34 Machinery Manufacturing”) |
| 1.2 | Analyze export history via China Customs Single Window (单一窗口) data | Verify direct export capability & machinery shipment records | Request last 3 export declarations (报关单) for similar HS codes. Red Flag: No direct export records under supplier’s name |
| 1.3 | Scrutinize facility evidence | Confirm physical production capacity | Demand dated, geotagged video of CNC/machining centers (not assembly lines). Critical: Verify ERP system screenshots showing BOM (Bill of Materials) for your machinery |
Phase 2: Deep Verification (On-Ground Validation)
| Step | Key Focus | Customs Duty Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2.1 Factory Audit | • Machine tool ownership (check asset tags) • Raw material inventory logs • In-house quality control labs |
Trading companies cannot provide material sourcing records → HS code misclassification risk (e.g., classifying custom parts as “standard accessories” to lower duty rates) |
| 2.2 Technical Documentation Review | • Engineering drawings signed by in-house R&D team • Process capability indices (Cp/Cpk) for critical components |
Absence of proprietary designs → duty fraud risk (supplier may import parts as “finished goods” then declare as “custom-made” for lower rates) |
| 2.3 Customs Bond Verification | • Direct customs registration (海关注册编码) • Past duty payment records for HS 84xx/85xx machinery codes |
Trading companies use third-party customs brokers → duty underpayment liability transfers to importer (per Article 59, China Customs Law) |
Trading Company vs. True Factory: Field-Testable Indicators
| Indicator | True Factory | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Export Control | Files customs declarations under own name (海关注册编码 matches business license) | Uses agent’s customs code or generic “export department” | Demand copy of 报关单 (Customs Declaration Form) showing exporter = supplier’s legal name |
| Pricing Transparency | Breaks down costs: raw materials (60-70%), labor (15-20%), overhead (10-15%) | Quotes single-line “FOB” price with no cost structure | Require itemized cost sheet signed by CFO. Red Flag: Refusal citing “commercial secret” |
| Production Control | Shows real-time ERP/MES system data (e.g., SAP, Kingdee) with machine utilization rates | Provides generic “production schedule” PDF | On-site test: Request live login to production monitoring system showing your order’s status |
| Technical Authority | Engineers discuss tolerances, material specs, and process validation | Redirects technical queries to “factory partners” | Ask: “Show me the heat treatment report for shaft material in my order” |
Critical Red Flags for Machinery Imports (Customs Duty Focus)
| Red Flag | Risk Impact | Mitigation Action |
|---|---|---|
| “We handle customs clearance” | Trading company masking as factory → duty liability shifts to importer | Require written confirmation: “Exporter assumes all customs classification risks per INCOTERMS 2020 DDP” |
| Generic facility photos/videos | Non-owned facility → HS code invalidation (customs inspects actual production site) | Demand live video tour with timestamp showing machinery in operation for your order |
| Refusal to share material certs | Inability to prove origin → duty rate escalation (e.g., from 5% to 15% for non-preferential origin) | Enforce clause: “Supplier warrants all materials comply with China-ASEAN FTA Rules of Origin” |
| “Special discount” for low declared value | Customs fraud prosecution risk (per WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement Art. 7.4) | Use third-party valuation service (e.g., SGS Transaction Value Audit) pre-shipment |
| No machinery-specific export licenses | Missing “Automatic Export License” (自动出口许可证) for dual-use items → shipment seizure | Verify license # via MOFCOM’s Export License System |
Strategic Recommendations
- Mandate Factory-Exclusive Contracts: Require suppliers to sign “Manufacturer Warranty Clause” attesting:
“All machinery is produced at facilities under our direct control, and HS classification is based on actual manufacturing process.” - Leverage China Customs Pre-Ruling: Submit technical specs to local customs before production for binding HS code determination (saves avg. 17.3 days in clearance delays per 2025 data).
- Adopt Blockchain Verification: Integrate with platforms like TradeLens to auto-capture factory production data → customs declaration sync (reduces duty disputes by 63%).
Final Note: In 2025, 72% of machinery duty penalties stemmed from trading companies misrepresenting as factories. Verification isn’t due diligence—it’s duty risk insurance. Always prioritize suppliers with verifiable in-house machining capacity for critical components.
Prepared by SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | Data Sources: China Customs 2025 White Paper, WTO Trade Compliance Database, ICC Duty Dispute Analytics
Next Step: Request our Customs Duty Risk Assessment Template for machinery imports (ISO 20400-compliant) at sourcifychina.com/duty-guardrails.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
As global supply chains grow increasingly complex, procurement leaders face mounting pressure to reduce costs, mitigate compliance risks, and accelerate time-to-market. One of the most persistent challenges in sourcing industrial machinery from China is accurately assessing and managing customs duties and import compliance. Misclassification, undervaluation, or lack of preparation can result in costly delays, fines, and supply chain disruptions.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for custom duty on machinery imported from China eliminates these risks by delivering pre-vetted, duty-classified machinery suppliers with transparent cost breakdowns—including HS code alignment, CIF value guidance, and regional tariff benchmarks.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Operations |
|---|---|
| Pre-Verified HS Code Alignment | Eliminates guesswork in customs classification—ensures accurate duty calculation from day one. |
| Supplier Compliance Screening | All listed suppliers meet international export standards, reducing audit and compliance risks. |
| Duty & Tariff Intelligence | Integrated duty rate data (US, EU, ASEAN, etc.) enables real-time landed cost modeling. |
| Reduced RFQ Cycles | Connect directly with suppliers already equipped to provide compliant documentation—cut sourcing time by up to 60%. |
| Proactive Risk Mitigation | Avoid penalties due to undervaluation or misdeclaration with transparent pricing structures. |
⏱️ Average Time Saved: Procurement teams report reducing supplier qualification and duty assessment timelines from 4–6 weeks to under 10 days using the Verified Pro List.
Call to Action: Optimize Your Machinery Sourcing Today
Don’t let customs complexity slow your supply chain. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List turns regulatory uncertainty into a strategic advantage—giving you faster access to compliant, cost-optimized machinery suppliers in China.
Take control of your import strategy now.
Contact our sourcing specialists for a tailored consultation and exclusive access to the 2026 Verified Pro List for machinery imports.
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
One conversation can shorten your procurement cycle, reduce landed costs, and future-proof your supply chain.
SourcifyChina — Precision. Compliance. Speed.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




