The global rechargeable battery market is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing demand for portable electronics, medical devices, security systems, and industrial applications—many of which rely on compact, high-performance power sources like CR123 batteries. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global lithium primary battery market, which includes CR123A variants, was valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% through 2029. This growth is fueled by rising adoption in IoT devices, surveillance equipment, and tactical gear, where reliability and long shelf life are critical. As the need for safe, rechargeable alternatives to traditional non-rechargeable CR123A cells intensifies, manufacturers are innovating to deliver higher cycle life, improved charge efficiency, and enhanced safety features. In this evolving landscape, a select group of producers has emerged as leaders in developing high-quality, rechargeable CR123 batteries. Below, we spotlight the top 9 manufacturers shaping this niche yet vital segment of the battery industry.
Top 9 Cr123 Rechargeable Batteries Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China Primary Lithium Battery Custom Rechargeable Li Ion Cell …
Domain Est. 2021
Website: enhcb.com
Key Highlights: HCB Battery Co., Ltd is a leading Chinese manufacturer of primary lithium battery packs and rechargeable Li ion cells, providing custom lithium battery ……
#2 CR123A
Domain Est. 1990
Website: energy.panasonic.com
Key Highlights: CR123A:Primary Lithium Batteries ; Product Name, Primary Lithium Batteries ; Series / Type, Cylindrical type Primary Lithium Batteries (CR series Standard type)….
#3 Global Product Technical Data Sheets – Duracell Batteries
Domain Est. 1995
Website: duracell.com
Key Highlights: Global Product Technical Data Sheets – Duracell Batteries | AA, AAA, Rechargeable, Coin Button. … CR123. High Power Lithium. US. CR123. High Power Lithium. US….
#4 Lithium Batteries CR123A
Domain Est. 1998
Website: microbattery.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $40 30-day returnsThe CR123A Battery is a lithium cylindrical battery and is known for its high voltage, energy density, durability, and stable operation….
#5 ASP Lithium CR123A Batteries
Domain Est. 2003
Website: asp-usa.com
Key Highlights: ASP Lithium CR123A Batteries are packaged in a 4 cell clamshell, 12 cell box or 50 cell carton. A free Link storage case is included in each clamshell and box….
#6 Ultralife Corporation
Domain Est. 2008
Website: ultralifecorporation.com
Key Highlights: Rechargeable Systems. Li-ion and NiCd batteries for high-cycle applications. ; Primary Batteries. Ultra-long-life lithium solutions for remote ……
#7 Lithium Ion Battery Wholesale
Domain Est. 2015
Website: xtar.cc
Key Highlights: XTAR offers high-quality lithium-ion battery wholesale, including rechargeable cylindrical Li-ion 14500, 18650, 21700 & 1.5V AA lithium batteries….
#8 Rapthor Batteries
Domain Est. 2021
#9 The Ultimate Guide to CR123A Batteries
Domain Est. 2023
Website: bettlink.com
Key Highlights: This guide covers everything you need to know about CR123A batteries, CR123 vs CR123A battery naming, heavy-duty applications, and top brand considerations….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cr123 Rechargeable Batteries
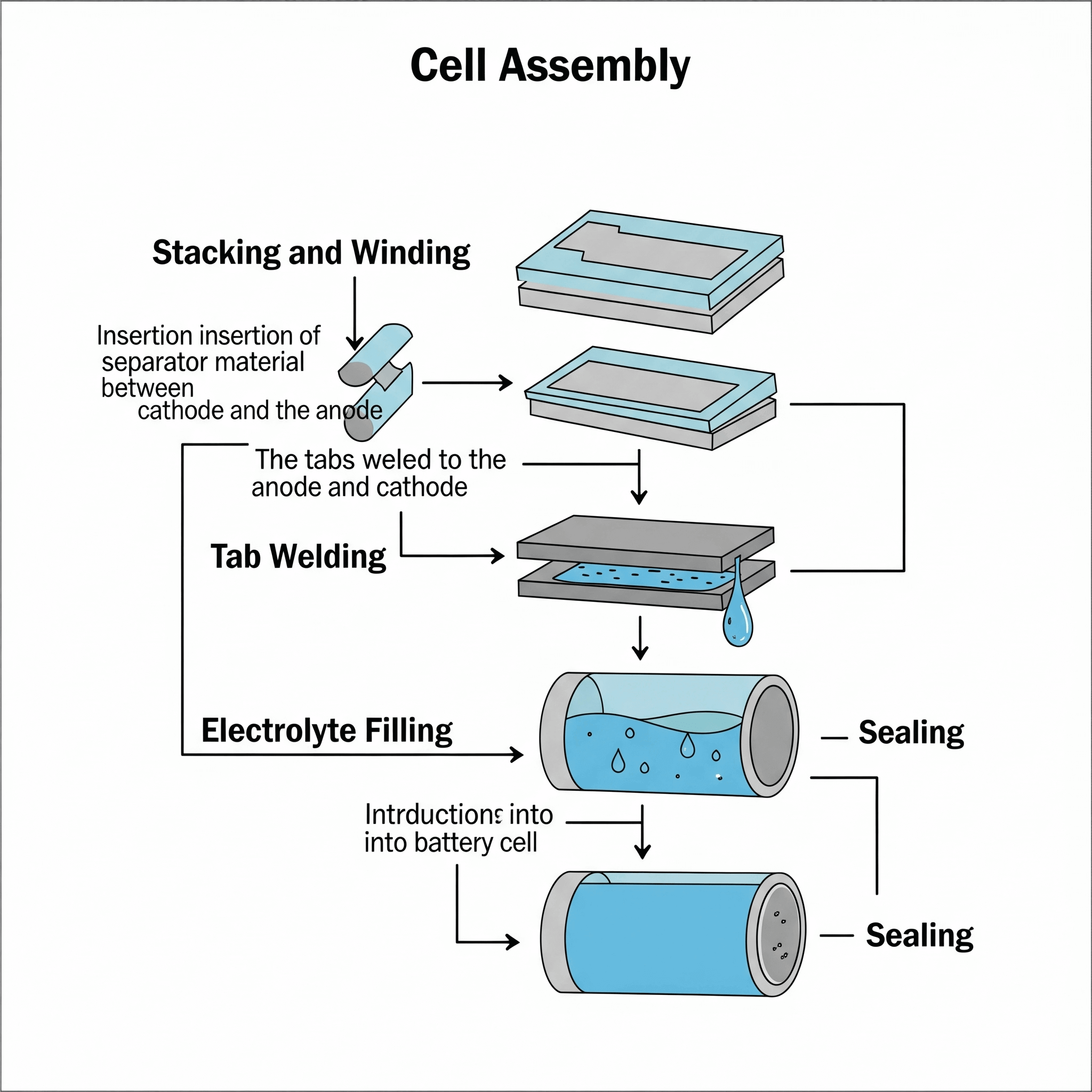
H2: Market Trends for Cr123 Rechargeable Batteries in 2026
By 2026, the market for Cr123 rechargeable batteries is projected to experience notable growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions, technological advancements in battery chemistry, and rising adoption across key sectors such as security, military, and industrial electronics.
-
Growing Demand for Sustainability
Environmental concerns are pushing consumers and businesses toward rechargeable alternatives to disposable lithium CR123A batteries. The shift aligns with global sustainability goals and regulations aimed at reducing electronic waste. Rechargeable Cr123 batteries, often based on lithium-ion (Li-ion) or lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) chemistries, offer a longer lifecycle—up to 500–1000 charge cycles—making them a cost-effective and eco-friendly option. -
Technological Improvements
By 2026, manufacturers are expected to introduce Cr123 rechargeable batteries with enhanced energy density, improved thermal stability, and faster charging capabilities. Advancements in battery management systems (BMS) will also contribute to safer performance, especially under high-drain conditions common in security cameras and tactical flashlights. These innovations are reducing the performance gap between disposable and rechargeable variants. -
Expansion in Security and Surveillance Markets
The global expansion of smart home and commercial surveillance systems is a key driver. Wireless security cameras, which often rely on Cr123 batteries, increasingly favor rechargeable models due to lower long-term operational costs. The trend toward battery-powered, easily deployable cameras supports market growth, particularly in regions with rapid urbanization. -
Military and Industrial Applications
Rechargeable Cr123 batteries are gaining traction in defense and industrial applications where reliability and power consistency are critical. Military-grade rechargeable variants with extended temperature tolerance and ruggedized designs are seeing increased procurement, especially in North America and Europe. -
Competitive Pricing and Brand Proliferation
As production scales and competition intensifies, prices for Cr123 rechargeables are expected to decline moderately by 2026. New entrants and established brands alike are launching compatible products, increasing consumer choice and driving innovation. However, concerns around counterfeit products remain, prompting calls for certification standards. -
Regional Market Dynamics
North America and Europe lead in adoption due to strong regulatory support for green technology and high penetration of smart security systems. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a fast-growing market, fueled by industrial automation and government investments in public safety infrastructure. -
Challenges and Considerations
Despite positive trends, challenges persist. Voltage compatibility (rechargeable versions typically output 3.6–3.7V vs. 3V in primary cells) can affect device performance, requiring voltage regulation in some applications. Consumer awareness and proper charging infrastructure also need improvement to maximize adoption.
In summary, the Cr123 rechargeable battery market in 2026 is poised for expansion, supported by sustainability trends, technological innovation, and growing use in high-performance applications. Stakeholders who invest in R&D, safety certifications, and consumer education are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cr123 Rechargeable Batteries (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Cr123 rechargeable batteries presents several challenges, particularly concerning quality control and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential for ensuring product reliability, safety, and legal compliance.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Cell Performance and Capacity
One of the most prevalent issues is receiving cells with significantly lower or inconsistent capacity than advertised. Many suppliers overstate capacity (e.g., claiming 800–1000 mAh), while genuine, high-quality Li-ion Cr123 cells typically deliver 600–700 mAh. Poor quality control during manufacturing leads to cell-to-cell variation, reducing the reliability of devices that depend on stable power output.
Substandard Materials and Construction
Low-cost manufacturers may use inferior cathode materials, electrolytes, or separators to cut costs. This results in shortened cycle life, increased internal resistance, and higher self-discharge rates. In extreme cases, poor construction can compromise safety mechanisms, increasing the risk of thermal runaway, leakage, or rupture—particularly dangerous in high-drain applications like security cameras or flashlights.
Lack of Safety Protections
Authentic Cr123 rechargeables should include built-in protection circuits to guard against overcharge, over-discharge, short circuit, and overheating. Many low-quality clones omit or use ineffective protection modules. Sourcing batteries without proper safety certifications (e.g., UL, CE, RoHS) exposes buyers to liability and safety hazards.
Voltage Mismatch and Compatibility Issues
Cr123A batteries are typically 3V (lithium primary) or 3.7V (Li-ion rechargeable). Some rechargeable versions output 3.6–3.7V, which may exceed the tolerance of devices designed for 3V primaries. Sourcing without verifying voltage compatibility can lead to device damage or malfunction.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Compliance Pitfalls
Counterfeit or Clone Brands
The Cr123 market is rife with counterfeit versions of reputable brands like Panasonic Eneloop, Streamlight, or SureFire. These clones often mimic packaging and branding, misleading buyers into believing they are purchasing genuine products. This not only affects performance but also exposes resellers to IP infringement claims.
Unauthorized Rebranding and OEM Misrepresentation
Some suppliers repackage low-tier cells from unknown manufacturers as premium brands or private labels without disclosure. This lack of transparency makes it difficult to trace origin or hold suppliers accountable for defects. Buyers may unknowingly violate trademark laws by distributing these rebranded products.
Missing or Falsified Certifications
Reputable suppliers provide documentation for safety and environmental compliance (e.g., UN38.3 for transport, MSDS, CE, FCC). Illegitimate suppliers often provide forged or generic certificates. Relying on falsified documentation can lead to shipment seizures, regulatory fines, or product recalls.
Weak Supply Chain Traceability
Lack of clear origin and manufacturing details makes it difficult to verify ethical sourcing, conflict mineral compliance, or adherence to environmental standards. This becomes a growing concern for businesses under ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) regulations.
Mitigation Strategies
- Source from Authorized Distributors or Verified Manufacturers: Prioritize suppliers with proven track records and direct partnerships with cell producers.
- Request and Verify Test Reports and Certifications: Demand third-party test data (e.g., capacity, cycle life) and validate certification authenticity.
- Conduct Sample Testing: Perform independent lab testing on sample batches for capacity, voltage stability, and safety compliance.
- Perform Due Diligence on IP Rights: Ensure branding and packaging do not infringe on existing trademarks; use legal agreements to clarify liability.
- Use Clear Contracts with Quality Clauses: Include specifications, penalties for non-compliance, and audit rights in supply agreements.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures safer, more reliable products and protects against legal and reputational risks in the competitive battery market.
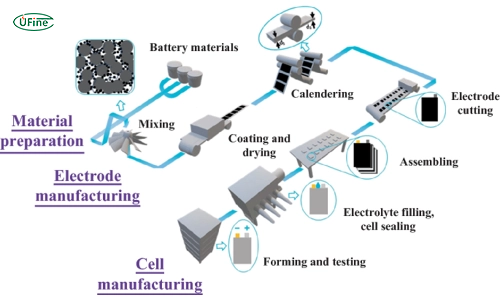
Logistics & Compliance Guide for CR123 Rechargeable Batteries
Overview
CR123 rechargeable batteries are lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries commonly used in high-drain devices such as tactical flashlights, cameras, and security systems. Due to their chemical composition, these batteries are subject to strict international and national regulations for transportation, storage, and disposal. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance requirements to ensure safe and legal handling throughout the supply chain.
Classification & Regulatory Framework
CR123 rechargeable batteries are classified as dangerous goods under the following regulatory standards:
– UN Number: UN3480 (Lithium-ion batteries, not packed with equipment)
– Class: Class 9 – Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods
– Packing Instruction: IATA PI 965, Section IB (for standalone batteries) or PI 966/967 (if packed with or contained in equipment)
– IMDG Code: Applies to maritime transport; similar requirements to IATA
– 49 CFR (DOT): Governs U.S. domestic transport by road, rail, and air
Packaging Requirements
Proper packaging is essential to prevent short circuits, damage, and thermal runaway:
– Use non-conductive inner packaging to insulate terminals (e.g., individual plastic sleeves or bubble wrap).
– Secure batteries to prevent movement within outer packaging.
– Use UN-certified packaging tested and marked for Class 9 dangerous goods.
– Clearly label packages with:
– Proper shipping name: “LITHIUM ION BATTERIES, UN3480”
– Class 9 hazard label
– Lithium battery handling label
– Shipper and consignee information
Labeling & Marking
- Hazard Class Label: Class 9 diamond label with “9” and “MISC.”
- Lithium Battery Mark: Rectangular mark including:
- “LITHIUM ION BATTERIES”
- UN3480
- Phone number for emergency response
- 25 kg gross weight limit for Section IB shipments
- Orientation Arrows: Required if package exceeds 30 kg
- No recycling symbols unless compliant with local regulations
Air Transport Regulations (IATA DGR)
- Passenger Aircraft: Prohibited for bulk shipments of standalone lithium-ion batteries.
- Cargo Aircraft: Permitted under PI 965, Section IB with limits on quantity and packaging.
- State & Operator Variations: Always check for airline-specific restrictions.
Ground & Sea Transport
- Road (ADR – Europe): Class 9 labeling, safety data sheets (SDS), and trained drivers required for large quantities.
- Rail (RID): Aligns with ADR standards.
- Sea (IMDG Code): Requires proper stowage, segregation from incompatible goods, and documentation.
Documentation
- Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (required for air and sea)
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) in compliance with GHS
- Commercial Invoice with accurate UN number and battery description
- Emergency Response Information
Storage & Handling
- Store in a cool, dry, non-conductive environment away from flammable materials.
- Maintain separation between charged and discharged batteries.
- Use fire-resistant storage cabinets where large quantities are kept.
- Avoid extreme temperatures (ideally 15–25°C).
- Implement a no-metal-tools policy near storage areas to prevent short circuits.
Training & Compliance
- Personnel involved in shipping must be trained per IATA, IMDG, or 49 CFR requirements (refresher training every 2 years).
- Maintain records of training and certifications.
- Conduct periodic audits of packaging, labeling, and documentation processes.
Returns & Reverse Logistics
- Returned CR123 batteries are also regulated as dangerous goods.
- Assess condition: damaged or swollen batteries require special containment and handling.
- Use the same packaging and labeling standards as outbound shipments.
- Follow local regulations for recycling or disposal (e.g., EPA in the U.S., WEEE in the EU).
Environmental & Disposal Compliance
- Do not dispose of in regular trash.
- Recycle through certified battery recycling programs (e.g., Call2Recycle, RBRC).
- Comply with local regulations such as:
- EU Battery Directive 2006/66/EC
- U.S. EPA guidelines for universal waste
- China’s Administrative Measures on the Recycling and Disposal of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment
Summary
CR123 rechargeable batteries require careful attention to classification, packaging, labeling, documentation, and training to meet global logistics and compliance standards. Non-compliance can lead to shipment rejection, fines, or safety incidents. Always consult the latest edition of relevant regulations and work with certified dangerous goods specialists when in doubt.
In conclusion, sourcing rechargeable CR123 batteries requires careful consideration of compatibility, safety, performance, and long-term value. While traditional CR123A batteries are typically non-rechargeable lithium primaries, rechargeable alternatives—such as Li-ion-based 16340 or dual-voltage CR123A equivalents—offer a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution when used correctly. It is essential to verify device compatibility, as not all equipment is designed to handle the slightly lower voltage (3.6V–3.7V) of rechargeable cells compared to the 3V of standard lithium CR123As. Prioritizing high-quality batteries from reputable brands (e.g., SureFire, Fenix, AW, or Keeppower) ensures reliable performance and built-in protection circuits to prevent overcharging, overheating, or short circuits.
Additionally, investing in a compatible smart charger designed for lithium-ion batteries enhances safety and extends battery life. Although the upfront cost is higher than disposable options, rechargeable CR123As provide significant savings and reduced environmental impact over time, especially for high-drain devices like tactical flashlights, security systems, or cameras. Ultimately, with proper research and adherence to manufacturer guidelines, sourcing rechargeable CR123 batteries is a smart, sustainable choice for users seeking reliable power with long-term benefits.