The global CPU memory stick market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for high-performance computing, increasing adoption of data-intensive applications, and the proliferation of cloud infrastructure. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global DRAM market size was valued at USD 67.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.4% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts steady market expansion, attributing growth to advancements in AI, 5G, and edge computing, which require faster and more efficient memory solutions. Against this backdrop, key manufacturers are intensifying R&D investments and scaling production to meet surging demand across consumer electronics, enterprise servers, and automotive sectors. Here, we spotlight the top 10 CPU memory stick manufacturers leading innovation and market share in this dynamic landscape.
Top 10 Cpu Memory Stick Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Kingston Technology
Domain Est. 1993
Website: kingston.com
Key Highlights: With over 35 years of expertise, Kingston has the knowledge and resources you need to choose memory with confidence….
#2 Memory
Domain Est. 1994
Website: micron.com
Key Highlights: Explore Micron’s memory solutions, driving innovation with DRAM, NAND, and NOR Flash technology to meet diverse industry needs….
#3 RAM Configurator
Domain Est. 2004
Website: gskill.com
Key Highlights: To find a list of compatible memory kit for a motherboard: 1. Select a motherboard manufacturer, chipset, and motherboard model. 2. Click the “Search” button….
#4 Integral Memory
Domain Est. 2000
Website: integralmemory.com
Key Highlights: Experts in computer memory and data storage – DRAM, Memory Cards, USB Drives, SSDs, encrypted products and industrial memory solutions….
#5 Patriot Memory
Domain Est. 2004 | Founded: 1985
Website: patriotmemory.com
Key Highlights: Patriot is a technology brand founded in 1985 in the San Francisco Bay Area. It designs, manufactures and markets high-performance DRAM memory, solid-state ……
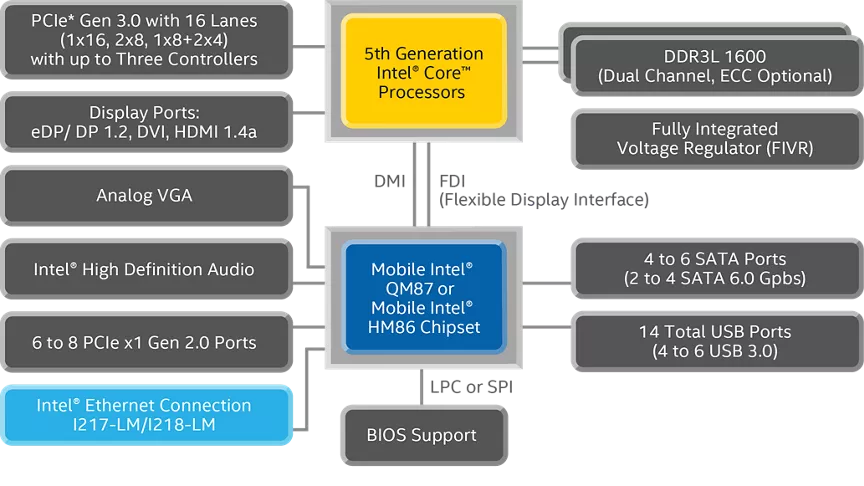
#6 Intel® Product Specifications
Domain Est. 1986
Website: intel.com
Key Highlights: Intel® product specifications, features and compatibility quick reference guide and code name decoder. Compare products including processors, desktop boards ……
#7 PC RAM
Domain Est. 1995
Website: corsair.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $79 · Free 60-day returnsUnlock your system’s potential with CORSAIR high-performance gaming RAM. Professional memory tested for reliability & compatibility. Sh…
#8 DRAM, Solid State Drive (SSD) & Memory Upgrades
Domain Est. 1997
Website: crucial.com
Key Highlights: Find compatible DRAM memory and SSD upgrades for your PC or Laptop with our Crucial Advisor tool or Crucial System Scanner….
#9 MediaTek
Domain Est. 2001
Website: mediatek.com
Key Highlights: MediaTek powers smarter devices with cutting-edge chipsets for smartphones, smart homes, automotive, IoT, and more. Discover innovation that connects….
#10 Memory module, Memory Card, USB Flash Drive, SSD, Mobile …
Domain Est. 2013
Website: teamgroupinc.com
Key Highlights: TEAMGROUP has a professional R&D capability, excellent product quality, fast production efficiency, extensive global sales network and good customer service ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cpu Memory Stick

2026 Market Trends for CPU Memory Stick
The CPU Memory Stick market—commonly associated with high-speed memory solutions integrated into or closely coupled with central processing units (CPUs)—is poised for significant transformation by 2026. While the term “CPU Memory Stick” may not refer to a standardized product category like DDR5 RAM or UDIMMs, it can be interpreted as emerging memory technologies designed to enhance CPU performance through tightly integrated or modular memory expansion (e.g., L4 cache modules, CXL-based memory devices, or specialized memory-on-stick solutions). The following analysis outlines key market trends expected to shape this segment by 2026.
Technological Advancements Driving Integration
By 2026, the integration of memory and processing units will deepen, driven by the need for lower latency and higher bandwidth in data-intensive applications. Technologies like Compute Express Link (CXL) are expected to mature, enabling CPU-attached memory sticks that act as cache or memory pool extensions. These CXL memory expanders will allow dynamic allocation of memory resources across servers, improving utilization and reducing total cost of ownership in data centers.
Additionally, advancements in 3D-stacked memory (e.g., HBM3E and HBM4) and hybrid bonding technologies will push memory closer to the CPU, blurring the line between traditional memory modules and CPU-embedded memory. While HBM remains cost-prohibitive for mainstream use, niche applications in AI, HPC, and edge computing will increasingly adopt hybrid solutions that resemble “memory sticks” in form but function as near-CPU accelerators.
Growth in Modular and Expandable Memory Architectures
The demand for scalable computing in cloud and enterprise environments will drive adoption of modular memory solutions. By 2026, OEMs and hyperscalers are expected to adopt standardized CPU memory stick form factors that allow hot-swappable, low-latency memory expansion. These modules will likely support protocols like CXL 3.0 or beyond, enabling memory disaggregation and pooling at scale.
This shift will enable more flexible server architectures, where memory can be upgraded independently of CPU or storage components. As a result, CPU memory sticks may become a critical component in composable infrastructure, allowing IT managers to right-size memory per workload and dynamically reconfigure resources.
Rising Demand from AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and generative AI workloads are placing unprecedented demands on memory bandwidth and capacity. By 2026, specialized AI accelerators and high-end CPUs will increasingly rely on high-bandwidth memory modules that resemble “sticks” but are optimized for tensor operations and model caching. These memory sticks may incorporate logic layers or in-memory computing features to reduce data movement bottlenecks.
Edge AI devices may also adopt compact CPU memory sticks to boost local inference performance without increasing CPU footprint. As AI becomes pervasive across consumer and industrial applications, the market for performance-optimized memory modules will grow significantly.
Market Consolidation and Standardization
The CPU memory stick ecosystem will see increased standardization by 2026, led by industry consortia such as the CXL Consortium, JEDEC, and OCP (Open Compute Project). Standardized interfaces and form factors will encourage interoperability and drive down costs, facilitating broader adoption across enterprise and cloud environments.
Market consolidation is also expected, with major semiconductor players (e.g., Intel, AMD, Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron) expanding their portfolios to include CXL-based memory modules and CPU-co-optimized memory solutions. Smaller firms may focus on niche applications, such as secure or radiation-hardened memory sticks for defense and aerospace.
Sustainability and Power Efficiency
Energy efficiency will be a critical differentiator in the 2026 market. CPU memory sticks will incorporate advanced power management features, including dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS), deep sleep modes, and smart thermal throttling. The push for greener data centers will incentivize designs that minimize data movement and maximize memory utilization.
Moreover, sustainable manufacturing practices and recyclable packaging will become competitive advantages, especially in regulated markets like the EU, where energy efficiency standards are tightening.
Conclusion
By 2026, the CPU memory stick market will evolve beyond traditional RAM modules into a sophisticated ecosystem of high-speed, modular, and intelligent memory solutions tightly integrated with CPUs. Driven by AI, cloud computing, and open standards like CXL, these memory sticks will play a pivotal role in enabling next-generation computing architectures. Companies that invest in interoperable, energy-efficient, and scalable memory technologies will be best positioned to lead this emerging market.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing CPU Memory Sticks (Quality, IP)
Sourcing CPU memory sticks—commonly referred to as RAM (Random Access Memory) modules—can be fraught with challenges, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks. Whether for enterprise systems, consumer electronics, or industrial applications, overlooking these pitfalls can lead to performance issues, security vulnerabilities, and legal complications. Below are key areas to watch for:
Poor Quality and Counterfeit Components
One of the most prevalent risks when sourcing memory sticks is encountering substandard or counterfeit products. These can stem from unreliable suppliers, especially in gray markets or through unauthorized distributors.
- Counterfeit RAM Modules: Fake memory sticks often mimic reputable brands but use inferior chips or falsified specifications. They may overstate capacity (e.g., 8GB labeled but only 4GB functional) or speed (e.g., advertising DDR4-3200 but operating at DDR4-2400).
- Inconsistent Performance: Low-quality memory can lead to system crashes, data corruption, or boot failures. Such instability is particularly problematic in mission-critical applications like servers or medical devices.
- Lack of Testing and Certification: Reputable memory modules undergo rigorous testing (e.g., JEDEC standards), but cheaper alternatives may skip these steps, increasing failure rates.
Mitigation: Source only from authorized distributors or directly from OEMs. Verify part numbers, use authenticity-check tools provided by manufacturers (e.g., Kingston’s verification service), and request test reports or certifications.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Memory technology involves complex IP, including patents on design, controller logic, and manufacturing processes. Sourcing from unverified suppliers increases exposure to IP violations.
- Unauthorized Clones: Some manufacturers produce RAM that infringes on patented technologies—such as power management circuits or error correction methods—owned by companies like Samsung, Micron, or SK Hynix.
- Use of Stolen or Leaked Designs: In rare but serious cases, memory modules may incorporate IP obtained through industrial espionage or reverse engineering without proper licensing.
- Legal and Supply Chain Liability: If a product uses infringing components, the integrator (OEM or system builder) can face lawsuits, product recalls, or customs seizures, even if unaware of the infringement.
Mitigation: Conduct supplier due diligence. Require IP compliance statements, audit trails, and warranty terms. Prefer suppliers who openly license IP and are transparent about their component sources.
Inadequate Traceability and Documentation
Lack of full traceability increases both quality and IP risks. Without proper documentation, it’s difficult to verify the origin and legitimacy of memory components.
- Opaque Supply Chains: Components may pass through multiple intermediaries, obscuring their origin and increasing the chance of substitution with non-compliant parts.
- Missing or Falsified Documentation: Critical data such as date codes, lot numbers, and compliance certificates may be missing or forged.
Mitigation: Enforce supply chain transparency. Require full BOM (Bill of Materials) disclosure and traceability down to the wafer level when possible. Use blockchain or digital ledger solutions where feasible.
Non-Compliance with Standards and Regulations
Memory modules must comply with industry and regional standards (e.g., RoHS, REACH, UL, FCC). Sourcing non-compliant products can result in regulatory penalties or market access denial.
- Hazardous Materials: Some low-cost memory sticks may use leaded solder or other restricted substances to cut costs.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Poorly designed modules can emit excessive EMI, violating FCC or CE regulations.
Mitigation: Require compliance certificates and conduct independent testing, especially for high-volume or regulated deployments.
In summary, sourcing CPU memory sticks demands careful attention to quality control, IP legitimacy, and supply chain transparency. Establishing strong procurement policies and partnering with reputable suppliers are essential to avoid performance failures and legal exposure.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for CPU Memory Stick
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
CPU Memory Sticks, commonly known as RAM modules (e.g., DDR4, DDR5), are classified as electronic components under international trade regulations. They fall under Harmonized System (HS) Code 8542.90 (Integrated Circuits) or 8523.51 (Solid-State Non-Volatile Storage Devices), depending on exact specifications. Compliance with regional and international standards such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals), and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) is mandatory for market access in the EU, North America, and many other jurisdictions.
Export and Import Documentation
Accurate documentation is essential for customs clearance and regulatory compliance. Required documents include a Commercial Invoice, Packing List, Bill of Lading or Air Waybill, and, where applicable, a Certificate of Origin. For exports to regulated markets, an Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) must be determined under the U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL). Most standard memory sticks are classified under ECCN 3A991, which generally does not require a license for most destinations unless destined for embargoed countries or military end-users.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
CPU Memory Sticks are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD) and physical damage. All units must be packaged in anti-static bags or containers and placed in secure, crush-resistant outer packaging. Labeling should include ESD-sensitive warnings, product specifications (e.g., DDR type, speed, capacity), and barcodes for traceability. Temperature and humidity controls during transport should remain within 10°C–30°C and 30%–60% relative humidity to prevent condensation and component degradation.
Transportation and Freight Considerations
Air freight is recommended for high-value or time-sensitive shipments due to speed and enhanced security. Sea freight may be cost-effective for bulk orders but requires extended planning and protection against moisture and vibration. Use of tamper-evident seals and GPS-tracked containers is advised. Partner with freight forwarders experienced in handling high-tech components to ensure adherence to Incoterms (e.g., FOB, DDP) and proper insurance coverage against loss, theft, or damage.
Regulatory Compliance by Region
- European Union: Must comply with CE marking, RoHS 3 (2015/863/EU), REACH, and WEEE directives. Declarations of Conformity (DoC) are required.
- United States: FCC Part 15 Class B compliance is generally required for digital devices to limit radio frequency interference. No CE equivalent, but safety standards (e.g., UL/CSA) may apply depending on end-product integration.
- China: Requires CCC (China Compulsory Certification) for certain electronic assemblies; standalone memory modules may be exempt, but importers should verify via MIIT regulations.
- Other Markets: Countries such as South Korea (KC Mark), Japan (PSE Mark), and Canada (ISED Certification) have specific electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and safety requirements.
End-of-Life and Environmental Responsibility
Manufacturers and importers must adhere to local take-back and recycling obligations. In the EU, producers must register with national WEEE compliance schemes and finance the recycling of end-of-life equipment. Use of recyclable packaging materials and clear labeling of hazardous substances (per RoHS) supports environmental compliance and corporate sustainability goals.
Audit and Recordkeeping
Maintain records of compliance documentation, test reports, shipping manifests, and customs filings for a minimum of five years. Conduct annual audits to verify adherence to export controls, environmental regulations, and supply chain security standards (e.g., C-TPAT for U.S.-bound shipments). Implement a Quality Management System (QMS) such as ISO 9001 to support traceability and continuous improvement.
Conclusion for Sourcing a CPU Memory Stick (RAM):
When sourcing a memory stick (RAM) for a CPU, it is essential to ensure compatibility with the motherboard and existing system specifications. Key factors such as memory type (DDR4, DDR5, etc.), speed (MHz), capacity (8GB, 16GB, etc.), latency (CL timing), and physical form factor (DIMM for desktops, SO-DIMM for laptops) must align with the system’s requirements. Additionally, verifying CPU and motherboard manufacturer support for features like dual-channel configurations and XMP/DOCP profiles can significantly impact performance.
Sourcing from reputable brands and trusted vendors ensures reliability, warranty coverage, and authenticity. Whether for upgrading performance or replacing faulty modules, taking the time to research and match specifications accurately will result in a stable, efficient, and future-ready computing system. Ultimately, well-informed sourcing decisions maximize both system performance and return on investment.