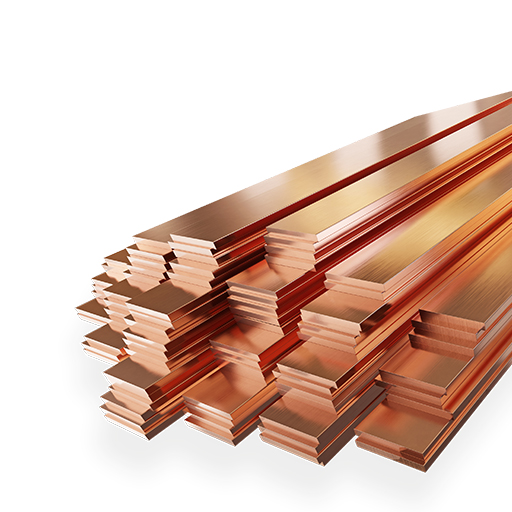
The global copper flat products market has experienced steady expansion, driven by rising demand across electrical, construction, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 50.2 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by copper’s unmatched electrical conductivity, thermal efficiency, and recyclability, making flat-rolled copper products—such as sheets, strips, and foils—critical components in renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and high-performance electronics. As demand intensifies, especially in Asia-Pacific and North America, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in production capacity, innovation, and global reach. The following analysis highlights the top nine copper flat product manufacturers shaping this evolving landscape, evaluated based on market presence, technological advancements, and strategic developments.
Top 9 Copper Flat Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Manufacturers of Industrial Copper Bus Bars, Flats, Rods, Tubes …
Domain Est. 2007
Website: barodaextrusion.com
Key Highlights: Industrial Copper Products Manufacturer – Baroda Extrusion is a leading manufacturers of copper products like copper flats, bus bars, rods, coils, billets, ……
#2 KME copper
Domain Est. 1995
Website: kme.com
Key Highlights: KME with its production plants in Germany, France, Italy, Spain, China and the USA, is one of the world’s largest manufacturers of copper and copper alloy ……
#3 Luvata
Domain Est. 2005
Website: luvata.com
Key Highlights: Luvata brings together people, innovation and technology to make the most of copper, specializing in technically demanding copper products….
#4 Copper, Busbar, Rods, Hex, Strips, Wire, Flat, Tubes Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2011
Website: gcal.co.in
Key Highlights: Manufacturers, Suppliers, Exporter and Stockist of high quality Copper Flats, Copper Strip, Copper Foils. Copper Wire, Copper Bars, Copper Rods/Hex, Copper ……
#5 Copper Bus Bars & Flats Manufacturer
Website: srcopperindustries.com
Key Highlights: Rating 5.0 (50) Copper bus bars and flats are made of high-purity copper. It is an excellent electrical conductor. Bus bars are flat, rectangular strips. They have high ……
#6 Brass / Copper / Bronze
Domain Est. 1996
Website: centralsteel.com
Key Highlights: Central Steel & Wire offers a range of copper flat bars with unique properties and applications. Among the most used grades are 101 and 110. 101 copper flat bar ……
#7 Farmers Copper, LTD.: Copper Metal Supplier
Domain Est. 1998
Website: farmerscopper.com
Key Highlights: Farmers’ Copper is a certified copper metal supplier stocking not only over 40 alloys of copper, but maintaining a very diverse inventory of other metals….
#8 Madhav Copper
Domain Est. 2013
Website: madhavcopper.com
Key Highlights: Madhav Copper manufactured Copper Busbars, and rods are available in both high conductivity electrolytic tough pitch (MCL-ETP) and high conductivity Oxygen ……
#9 MITSUBISHI MATERIALS Copper & Copper Alloy Business
Domain Est. 2020
Website: mitsubishi-copper.com
Key Highlights: We process copper materials, which originates from our smelters and refineries, into products of various shapes, such as terminal materials for automobiles….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Copper Flat

H2: Market Trends for Copper Flat in 2026
As of 2026, the market for Copper Flat—a region historically associated with mining and mineral exploration—reflects broader global shifts in industrial demand, energy transition initiatives, and commodity pricing dynamics. While “Copper Flat” may refer to a specific geographic or mining site (potentially in Nevada or another mineral-rich area), the analysis below interprets the term in the context of copper production and regional mining activity.
1. Increased Demand Driven by Electrification and Renewable Energy
The global push toward decarbonization continues to fuel demand for copper, a critical material in electric vehicles (EVs), solar and wind infrastructure, and grid modernization. In 2026, copper demand is projected to exceed 29 million metric tons, up from approximately 26 million tons in 2023. Copper Flat, if active in production or exploration, benefits from this sustained demand, attracting investment and development interest.
2. Supply Constraints and Geopolitical Factors
Copper supply remains tight due to declining ore grades, project delays, and regulatory hurdles in major producing countries like Chile and Peru. This scarcity elevates the strategic importance of alternative sources, including underdeveloped deposits in regions such as Copper Flat. As a result, junior mining companies and exploration firms are increasingly focused on revitalizing dormant sites or advancing feasibility studies in North America to reduce import dependency.
3. Rise in North American Mining Investment
With the U.S. government emphasizing domestic critical mineral production under policies like the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, regions like Copper Flat are being reassessed for their mineral potential. In 2026, Copper Flat may see increased exploration activity, environmental reviews, and potential permitting advancements, supported by federal incentives for sustainable mining practices.
4. Technological Advancements and Sustainable Mining
Mining operations in 2026 increasingly adopt automation, AI-driven exploration, and low-carbon extraction methods. If Copper Flat progresses toward development, it is likely to incorporate these technologies to improve efficiency and meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) standards. Water recycling, renewable-powered operations, and community engagement are becoming prerequisites for project approval.
5. Commodity Price Volatility
Copper prices in 2026 remain volatile, influenced by macroeconomic trends, U.S. dollar strength, and industrial activity in China and Europe. Average prices hover between $3.80 and $4.50 per pound, making marginal projects economically viable. For Copper Flat, this pricing environment could determine whether exploration transitions into production, depending on capital availability and cost structures.
6. Indigenous and Community Relations
Growing emphasis on stakeholder engagement means that any development at Copper Flat must involve consultation with local communities and Indigenous groups. In 2026, social license to operate is as crucial as technical feasibility, with successful projects demonstrating transparent communication and shared economic benefits.
Conclusion:
By 2026, Copper Flat stands at a crossroads shaped by global copper demand, energy transition policies, and sustainable development imperatives. While not a major producer today, its potential value is rising in the context of supply chain resilience and domestic mineral security. Whether Copper Flat evolves into an active mining site will depend on successful permitting, technological integration, responsible community engagement, and favorable market conditions. Investors and policymakers are closely watching such regions as bellwethers of North America’s role in the future copper economy.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Copper Flat (Quality, IP)
Sourcing copper flat bar—commonly used in electrical, architectural, and industrial applications—can present several challenges, particularly concerning material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure reliable supply, performance, and legal compliance.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Material Composition
One of the most frequent quality issues is receiving copper flat bar that does not meet specified purity standards (e.g., C11000, C10100). Suppliers may provide material with higher levels of impurities or use recycled copper without proper certification, leading to reduced electrical conductivity and mechanical performance.
2. Poor Dimensional Tolerances
Copper flat bar must adhere to strict dimensional tolerances for fit and function. Sourcing from unreliable suppliers may result in inconsistent thickness, width, or flatness, causing fitment issues in assemblies or requiring costly post-processing.
3. Inadequate Surface Finish
Surface imperfections such as scratches, pits, or oxidation can impair conductivity, solderability, and aesthetic quality. Suppliers in less regulated markets often overlook surface quality, especially if the material is intended for visible or high-precision applications.
4. Lack of Traceability and Certification
Reputable sourcing requires mill test certificates (MTCs) or material test reports (MTRs) confirming chemical composition and mechanical properties. Many suppliers, especially intermediaries or low-cost vendors, fail to provide verifiable documentation, raising concerns about authenticity and compliance.
5. Improper Temper and Hardness
Copper flat bar is available in various tempers (e.g., soft, half-hard, hard). Receiving incorrect temper can affect formability and strength. Without proper labeling or testing, users may unknowingly use suboptimal material, leading to premature failure.
IP-Related Pitfalls
1. Infringement of Patented Alloys or Processes
Some copper alloys or manufacturing processes (e.g., specialized annealing techniques) may be protected by patents. Sourcing from suppliers who use proprietary methods without licensing can expose the buyer to legal liability, especially in regulated industries.
2. Counterfeit or Misrepresented Materials
There is a risk of counterfeit copper products, particularly from regions with weak IP enforcement. Suppliers may falsely claim compliance with standards (e.g., ASTM B152) or mislabel alloys to mimic higher-grade materials, which constitutes both a quality and IP violation.
3. Unauthorized Use of Branding or Specifications
Some suppliers may illegally use well-known brand names or replicate technical data sheets to appear legitimate. This misrepresentation not only breaches IP laws but also misleads buyers about the origin and quality of the product.
4. Lack of IP Due Diligence in Supplier Selection
Buyers often overlook IP compliance during supplier vetting. Failing to verify that a supplier has rights to produce and sell specific copper products can result in supply chain disruptions or legal challenges, particularly in export markets with strong IP protections.
Mitigation Strategies
- Source from certified and audited suppliers with a track record of compliance.
- Require full material documentation, including MTRs and compliance statements.
- Conduct third-party material testing upon receipt, especially for critical applications.
- Perform IP audits or legal reviews when sourcing specialized alloys or proprietary products.
- Establish clear contracts that include quality specifications and IP indemnification clauses.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures not only the performance and reliability of copper flat bar but also safeguards against legal and operational risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Copper Flat
This guide outlines the essential logistics procedures and compliance requirements for operations at Copper Flat. Adhering to these standards ensures efficient, safe, and legally compliant activities across all supply chain functions.
Transportation and Freight Management
Coordinate all inbound and outbound shipments through approved carriers that meet safety, insurance, and regulatory standards. Utilize a centralized transportation management system (TMS) to schedule deliveries, track shipments in real time, and optimize routing. Ensure documentation—including bills of lading, shipping manifests, and delivery confirmations—is accurate and retained for a minimum of seven years.
Inventory Control and Warehousing
Maintain inventory accuracy through regular cycle counts and annual physical audits. Store materials in designated areas according to compatibility, flammability, and handling requirements. Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) system for perishable or time-sensitive items. All warehouse operations must comply with OSHA standards, including proper labeling, aisle clearance, and equipment maintenance.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhere to all local, state, and federal regulations, including those set by the Department of Transportation (DOT), Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Ensure hazardous materials (if applicable) are handled, labeled, and transported in accordance with Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR). Maintain up-to-date permits, safety data sheets (SDS), and employee training records.
Import/Export Documentation
For international shipments, verify correct classification under the Harmonized System (HS) codes and ensure accurate preparation of commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Comply with U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) requirements, including entry filings and adherence to trade agreements. Conduct regular audits to prevent misclassification or undervaluation.
Safety and Environmental Standards
Implement an Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) program that includes spill response plans, waste disposal protocols, and emergency preparedness. Train employees annually on hazard communication, fire safety, and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Report all incidents promptly and conduct root cause analyses to prevent recurrence.
Vendor and Contractor Oversight
Require all third-party logistics providers and contractors to submit proof of insurance, compliance certifications, and safety program documentation prior to engagement. Conduct periodic performance and compliance reviews to ensure alignment with Copper Flat’s standards.
Recordkeeping and Audits
Maintain digital and physical records for all logistics and compliance activities. Records must be accessible and organized to support internal audits and regulatory inspections. Conduct annual compliance audits and address findings within 30 days of identification.
Training and Accountability
Provide mandatory logistics and compliance training for all relevant staff upon onboarding and annually thereafter. Assign compliance officers at key operational levels to monitor adherence and serve as points of contact for reporting concerns. Foster a culture of accountability through clear policies and open communication channels.
Conclusion on Sourcing Copper Flat:
Sourcing copper flat strip requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, supply chain reliability, and compliance with industry standards. After evaluating various suppliers, pricing models, and material specifications, it is evident that selecting the right source involves more than just competitive pricing. Key factors such as material purity (typically C11000 or C10100 copper), dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and certification (e.g., mill test reports) are critical to ensuring performance in applications like electrical conductors, busbars, and grounding systems.
Establishing long-term relationships with reputable suppliers—whether domestic or international—can enhance supply continuity and provide opportunities for volume discounts and custom fabrication options. Additionally, considerations such as lead times, logistics, and adherence to environmental and ethical sourcing practices play an increasingly important role in responsible procurement.
In conclusion, the optimal sourcing strategy for copper flat strip combines a thorough assessment of technical requirements with careful supplier vetting and risk management. By prioritizing quality, reliability, and sustainability, organizations can secure a consistent supply of high-performance copper material that supports both operational efficiency and long-term project success.