The global cooling systems market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising industrial automation, increasing demand for temperature-sensitive storage in pharmaceuticals and food & beverage sectors, and the widespread adoption of HVAC systems in commercial and residential infrastructure. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global industrial cooling systems market size was valued at USD 21.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This sustained expansion reflects the growing need for energy-efficient and sustainable cooling solutions across regions. As industries prioritize operational efficiency and regulatory compliance, leading cooling system manufacturers are innovating to meet evolving performance and environmental standards. In this landscape, a select group of companies have emerged as key players, combining technological expertise, global reach, and scalable manufacturing capabilities. Here’s a look at the top nine cooling system manufacturers shaping the future of thermal management.
Top 9 Cooling System Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Goodman: Air Conditioning and Heating Systems
Domain Est. 1997
Website: goodmanmfg.com
Key Highlights: Goodman Manufacturing offers a range of affordable air conditioning, packaged units, heat pumps and gas furnaces for residential heating and cooling needs….
#2 Cooling Towers and Cooling Tower Parts
Domain Est. 2005
Website: spxcooling.com
Key Highlights: SPX Cooling Tech, LLC is a leading global manufacturer of cooling towers, evaporative fluid coolers, evaporative condensers and air cooled heat exchangers….
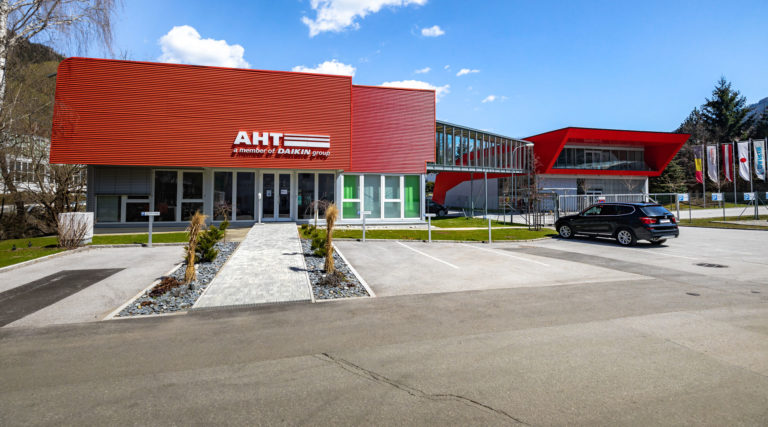
#3 AHT Cooling Systems
Website: en.aht.at
Key Highlights: Innovative, energy efficient AHT refrigeration technology. Plug in, refrigerate (freeze) and sell more – this is AHT’s motto that has been impressing customers….
#4 Rheem Manufacturing Company
Domain Est. 1995
Website: rheem.com
Key Highlights: Learn about Rheem’s innovative and efficient heating, cooling, and water heating solutions for homes and businesses….
#5 YORK
Domain Est. 1995
Website: york.com
Key Highlights: From cooling systems and heating systems to HVAC components that control humidity, YORK provides indoor air quality solutions for the way you live today….
#6 Lennox
Domain Est. 1997
Website: lennox.com
Key Highlights: Explore Lennox comfort and energy-efficient solutions for heating and cooling your space. Upgrade your home’s HVAC system with industry-leading solutions….
#7 Premier Custom Thermal Management Solutions Company
Domain Est. 2003
Website: 1-act.com
Key Highlights: Advanced Cooling Technologies, a leading thermal management solutions provider, specializes in thermal management solutions for spacecraft, electronics, ……
#8 Phoenix Manufacturing
Domain Est. 2015
Website: phoenixmanufacturing.com
Key Highlights: Phoenix Manufacturing, with 50+ years of expertise, designs and tests high-performance evaporative cooling solutions in Phoenix, Arizona….
#9 Global Leaders in Cooling Innovation
Domain Est. 2016
Website: airsysnorthamerica.com
Key Highlights: We are AIRSYS. We build engineered, sustainable, and reliable cooling solutions designed for mission-critical environments….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cooling System

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Cooling Systems
As global demand for energy efficiency, sustainability, and digital integration intensifies, the cooling systems market is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by technological innovation, regulatory changes, and shifting consumer preferences, the following key trends are expected to shape the industry landscape.
1. Increased Adoption of Energy-Efficient Cooling Technologies
By 2026, energy efficiency will remain a top priority, particularly due to rising energy costs and stricter environmental regulations. Governments worldwide are enforcing tighter standards on HVAC and industrial cooling systems, prompting manufacturers to adopt advanced heat exchangers, variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems, and low-global-warming-potential (GWP) refrigerants. Innovations such as magnetocaloric and thermoelectric cooling are expected to move from research labs into commercial applications, especially in niche markets seeking ultra-high efficiency.
2. Expansion of Data Center Cooling Demand
With the proliferation of artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and 5G infrastructure, data centers will continue to expand, significantly boosting demand for high-performance cooling solutions. By 2026, liquid cooling—including direct-to-chip and immersion cooling—is projected to capture over 30% of the data center cooling market, up from less than 10% in 2022. This shift is driven by the need to manage higher heat densities associated with AI chips and high-performance computing (HPC) clusters.
3. Growth in Sustainable and Green Cooling Solutions
Sustainability will be a major differentiator in the cooling systems market. Natural refrigerants such as CO₂ (R-744), ammonia (R-717), and hydrocarbons (e.g., propane R-290) are expected to gain market share, supported by regulations like the EU’s F-Gas Regulation and the Kigali Amendment. Additionally, solar-powered cooling systems and passive cooling designs in commercial and residential buildings will see increased adoption, particularly in emerging markets with high solar irradiance.
4. Integration of IoT and Smart Cooling Systems
The Internet of Things (IoT) and AI-driven analytics will enable predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and optimization of cooling systems. By 2026, over 60% of new commercial HVAC installations are expected to include smart controls and cloud-based management platforms. These systems will leverage machine learning to adjust cooling output based on occupancy, weather patterns, and energy pricing, significantly reducing operational costs and carbon footprints.
5. Regional Market Shifts and Urbanization
Asia-Pacific will remain the fastest-growing market for cooling systems, driven by urbanization, rising middle-class incomes, and increased construction activity in India, Southeast Asia, and China. At the same time, countries in the Middle East and Africa are investing heavily in district cooling systems to combat extreme heat and ensure energy-efficient urban development. Europe and North America will focus on retrofitting aging infrastructure with smart, low-emission cooling solutions.
6. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions will push manufacturers to localize production and source components regionally. By 2026, leading cooling system suppliers are expected to establish regional manufacturing hubs, particularly in Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe, to reduce dependency on single-source suppliers and improve delivery timelines.
Conclusion
The 2026 cooling systems market will be defined by innovation, sustainability, and digital transformation. Companies that invest in energy-efficient technologies, embrace smart system integration, and align with global decarbonization goals will be best positioned to lead in this evolving landscape. As climate change intensifies and digital infrastructure expands, cooling systems will not only be essential for comfort but also critical enablers of technological and economic resilience.
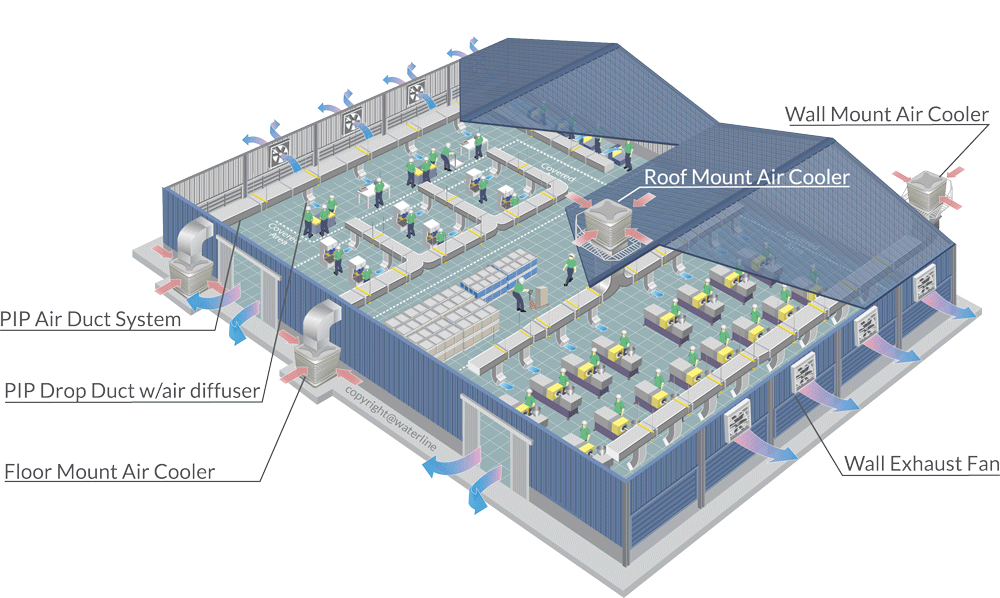
H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Cooling Systems – Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing cooling systems—whether for industrial machinery, data centers, automotive applications, or HVAC systems—can be complex, especially when balancing cost, performance, and legal considerations. Two critical areas where companies often encounter challenges are product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Below are the common pitfalls in these areas:
1. Compromised Quality Due to Cost-Cutting
- Pitfall: Selecting suppliers based solely on low pricing can lead to substandard materials, poor manufacturing processes, and inconsistent performance.
- Impact: Cooling systems with inadequate thermal efficiency, short lifespan, or frequent failures increase downtime and maintenance costs.
- Example: Using inferior aluminum or copper alloys in heat exchangers reduces heat transfer efficiency and corrosion resistance.
Best Practice: Conduct thorough supplier audits, request material certifications (e.g., ASTM, ISO), and perform third-party quality inspections during or after production.
2. Lack of Standard Compliance and Certification
- Pitfall: Sourcing from suppliers who do not adhere to industry standards (e.g., ASME, UL, CE, ISO 9001).
- Impact: Non-compliant systems may fail safety inspections, void warranties, or pose operational risks.
- Example: A chiller unit without proper pressure vessel certification can be a safety hazard.
Best Practice: Require documented proof of compliance with relevant regional and international standards.
3. Inadequate Testing and Validation Procedures
- Pitfall: Suppliers may skip rigorous performance testing (e.g., thermal load, pressure, vibration tests).
- Impact: Undetected design flaws or manufacturing defects surface only after deployment, leading to costly recalls or retrofits.
Best Practice: Include mandatory factory acceptance tests (FAT) and performance validation protocols in procurement contracts.
4. Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
- Pitfall: Sourcing from manufacturers who replicate patented cooling technologies without authorization.
- Impact: Buyers may face legal liability, product seizures, or reputational damage for using IP-infringing components.
- Example: Purchasing a liquid cooling plate design that mimics a patented microchannel layout.
Best Practice: Conduct IP due diligence; require suppliers to warrant that their products do not infringe on third-party patents.
5. Lack of IP Ownership Clarity in Custom Designs
- Pitfall: When co-developing or customizing cooling systems, failure to define IP ownership in contracts.
- Impact: Disputes may arise over who owns the design, limiting reuse, resale, or further development.
- Example: A company funds the development of a proprietary cold plate but cannot patent it because the contract assigned IP rights to the manufacturer.
Best Practice: Clearly define IP ownership, usage rights, and confidentiality terms in supplier agreements—preferably with legal counsel.
6. Reverse Engineering and Technology Leakage
- Pitfall: Sharing detailed technical specifications with unvetted suppliers increases the risk of design cloning.
- Impact: Competitors may gain access to proprietary cooling solutions, eroding market advantage.
Best Practice: Limit technical disclosure to “black box” requirements where possible; use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and secure data-sharing protocols.
7. Overlooking Supply Chain Transparency
- Pitfall: Relying on tier-2 or tier-3 suppliers without visibility into their manufacturing practices.
- Impact: Hidden quality issues or unauthorized subcontracting can compromise both product integrity and IP security.
Best Practice: Map the full supply chain and conduct on-site assessments of key production facilities.
Conclusion
To mitigate risks when sourcing cooling systems, organizations must balance cost considerations with rigorous quality assurance and proactive IP protection. Engaging suppliers with transparent processes, strong compliance records, and clear contractual IP terms is essential for long-term reliability and competitive advantage.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cooling Systems
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, handling, installation, and operation of cooling systems. Adhering to these guidelines ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and optimal system performance.
H2: Regulatory Compliance
1. Environmental Regulations:
* Refrigerant Management: Strictly comply with the Montreal Protocol and national regulations (e.g., EPA Section 608 in the US, F-Gas Regulation in the EU) governing the use, handling, recovery, recycling, and disposal of refrigerants (CFCs, HCFCs, HFCs, HFOs). Ensure all personnel are certified (e.g., EPA 608, F-Gas certified).
* Energy Efficiency Standards: Meet minimum energy performance standards (MEPS) mandated by regions (e.g., DOE in the US, Ecodesign Directive in the EU). Verify product labeling (e.g., ENERGY STAR, EER/SEER ratings).
* Hazardous Substances: Comply with directives like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH regarding restricted materials in components.
2. Safety Standards:
* Electrical Safety: Adhere to national and international electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the US, IEC standards, local wiring regulations) for installation and electrical components.
* Pressure Equipment: Comply with pressure vessel safety codes (e.g., ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, PED in the EU) for components like condensers and receivers.
* Fire Safety: Follow building and fire codes concerning clearances, combustible materials near units, and fire suppression system integration (if applicable).
* Operational Safety: Implement safe operating procedures (SOPs) for maintenance, addressing risks like moving parts, high pressure, and electrical hazards.
3. International Trade & Customs:
* Import/Export Controls: Verify compliance with export control regulations (e.g., ITAR, EAR – if applicable to specific components/technology) and import requirements of the destination country.
* Customs Documentation: Prepare accurate documentation (Commercial Invoice, Packing List, Bill of Lading/Air Waybill, Certificate of Origin, potentially a Refrigerant Declaration). Ensure Harmonized System (HS) codes are correctly applied.
* Duty & Tax: Understand applicable import duties, Value Added Tax (VAT), or Goods and Services Tax (GST) for the destination.
H2: Logistics & Transportation
1. Packaging & Handling:
* Robust Packaging: Use manufacturer-recommended packaging or equivalent protection (e.g., wooden crates, pallets with corner boards, stretch wrap) to prevent damage during transit. Secure components internally.
* Fragile/Heavy Labels: Clearly mark packages as “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and indicate weight for heavy items. Protect control panels and tubing.
* Refrigerant Handling: Transport refrigerant cylinders upright, secured, and protected from direct sunlight and heat sources. Follow DOT (US) or ADR (EU) regulations for hazardous materials (Class 2.2 – Non-Flammable, Non-Poisonous Gas). Ensure cylinders are properly labeled and have safety devices.
2. Transportation Modes:
* Mode Selection: Choose appropriate transport (road, sea, air) based on urgency, cost, size/weight, and destination. Consider specialized freight for oversized units.
* Temperature Control: Protect sensitive electronic components from extreme temperatures and moisture during transit (e.g., avoid direct sun exposure in non-climate-controlled trailers or containers).
* Secure Loading: Properly secure units on vehicles/pallets using straps, braces, or other methods to prevent shifting, rolling, or impact damage.
3. Storage:
* Environment: Store cooling systems and components in a clean, dry, well-ventilated, and temperature-controlled environment (ideally 10°C – 40°C / 50°F – 104°F). Protect from moisture, dust, and direct sunlight.
* Position: Store units in their designated shipping position (usually upright). Never lay down scroll or reciprocating compressors unless explicitly approved by the manufacturer.
* Duration: Minimize storage time. Follow manufacturer guidelines for maximum storage duration before installation/commissioning.
* Refrigerant Cylinders: Store upright in a dedicated, well-ventilated, fire-resistant area, away from heat sources, combustibles, and high-traffic areas. Segregate full and empty cylinders.
H2: Installation & Commissioning Compliance
1. Site Preparation:
* Verify site meets structural requirements (weight, vibration) and has adequate space for clearances (service access, airflow).
* Ensure proper electrical supply (voltage, phase, frequency, circuit protection) and plumbing connections are ready.
* Confirm environmental permits (e.g., for condensate discharge, noise levels) are obtained if required.
2. Installation:
* Use qualified technicians adhering strictly to manufacturer’s installation manuals and local codes.
* Perform proper refrigerant line evacuation (deep vacuum) and charging procedures using calibrated equipment. Record charge weight.
* Implement leak testing protocols (e.g., electronic leak detectors, pressure holding) as required by regulations.
* Ensure proper grounding and electrical connections.
3. Commissioning & Documentation:
* Conduct thorough system testing (safety controls, operational parameters, airflow, temperatures, pressures).
* Complete mandatory compliance documentation:
* Refrigerant Log (tracking type and quantity added/recovered).
* Leak Check Records.
* Installation Certificates (electrical, pressure, refrigerant).
* Commissioning Reports.
* User Manuals and Maintenance Schedules provided to the customer.
H2: Maintenance & End-of-Life Compliance
1. Preventative Maintenance:
* Schedule regular maintenance per manufacturer recommendations to ensure efficiency, longevity, and early detection of leaks.
* Keep detailed maintenance logs, including refrigerant top-ups (which indicate potential leaks needing investigation).
2. Refrigerant Recovery & Recycling:
* Never vent refrigerant to the atmosphere. Always use EPA/F-Gas certified recovery equipment during servicing or decommissioning.
* Use certified reclaimers to process recovered refrigerant to AHRI 700 standards for reuse.
* Maintain accurate records of all refrigerant recovered, recycled, reclaimed, or disposed of.
3. End-of-Life Disposal:
* Decommission systems using certified technicians.
* Fully recover all refrigerant and oils.
* Recycle or dispose of components (metal casings, copper tubing, electronics, insulation) according to local e-waste (WEEE) and scrap metal regulations. Handle hazardous waste (e.g., PCBs in old capacitors, contaminated oil) properly.
Key Takeaway: Proactive adherence to logistics protocols and comprehensive compliance with environmental, safety, and trade regulations is critical throughout the entire lifecycle of a cooling system. Always consult the latest versions of relevant regulations and manufacturer instructions.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Cooling System:
In conclusion, the successful sourcing of a cooling system requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, operational requirements, cost efficiency, reliability, and long-term maintenance support. By aligning the selected system with the specific needs of the application—whether for industrial processes, HVAC, or data center environments—organizations can ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and sustainability. Engaging with trusted suppliers, conducting thorough due diligence, and considering total cost of ownership will ultimately lead to a resilient and cost-effective cooling solution. A well-sourced cooling system not only enhances operational efficiency but also supports safety, environmental compliance, and scalability for future demands.