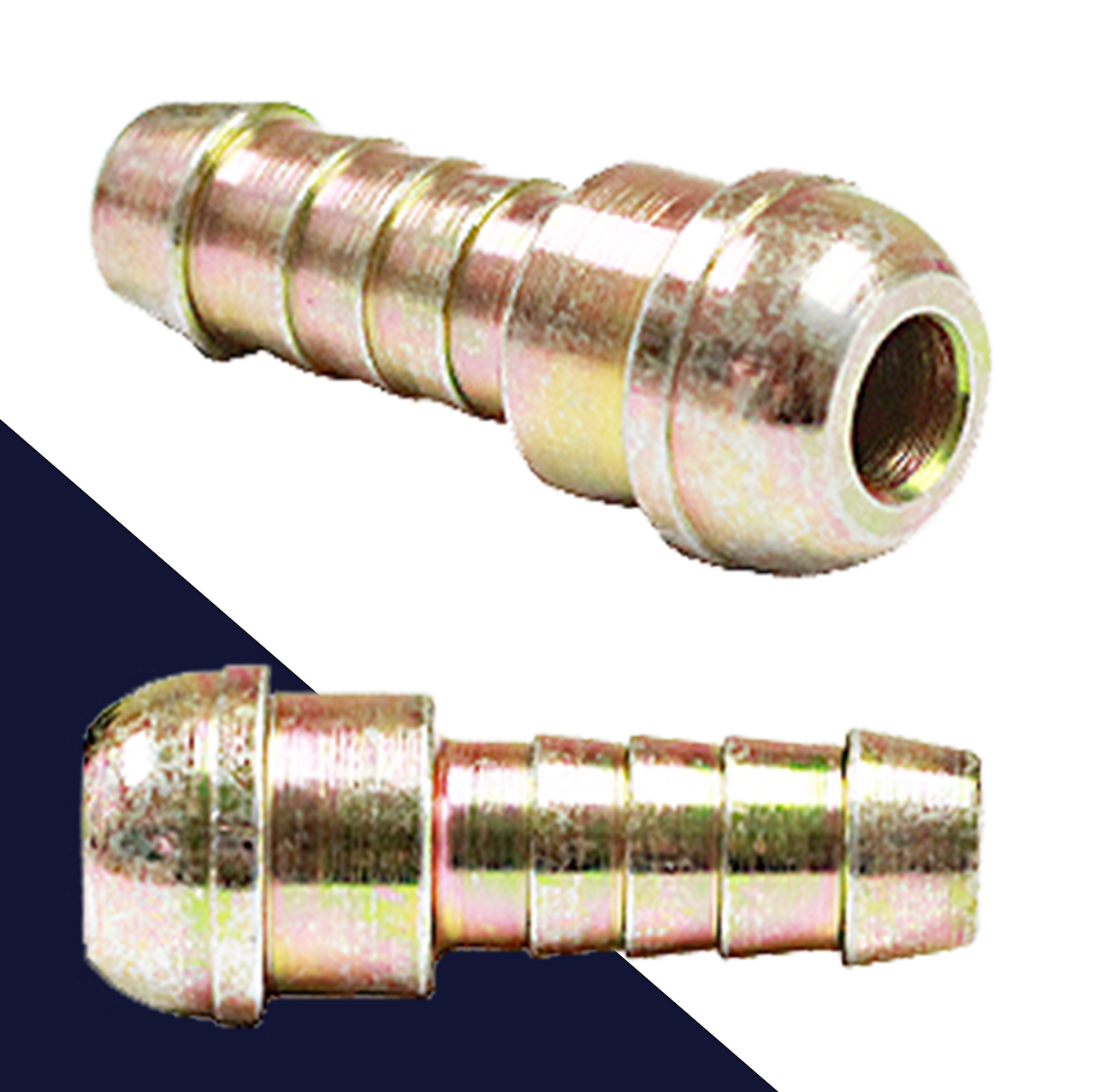
The global flexible packaging market, a key driver behind the demand for specialized components like cone nipples used in industrial and consumer goods applications, is experiencing steady growth. According to Grand View Research, the global flexible packaging market was valued at USD 232.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by rising demand for lightweight, durable, and resealable packaging solutions across food & beverage, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries—sectors where cone nipples are critical for secure dispensing and leak-proof connections.
Additionally, Mordor Intelligence projects that the Asia-Pacific region will witness the fastest growth in packaging innovation, driven by urbanization and expanding manufacturing bases in countries like China, India, and Vietnam. As automation and precision engineering become standard in production lines, the need for high-quality, reliable cone nipple components has surged. This demand has elevated the importance of specialized manufacturers who combine material science expertise with scalable production capacity. The following list highlights the top 8 cone nipple manufacturers positioned to meet these evolving industry requirements based on production scale, engineering capabilities, geographic reach, and compliance with international quality standards.
Top 8 Cone Nipple Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
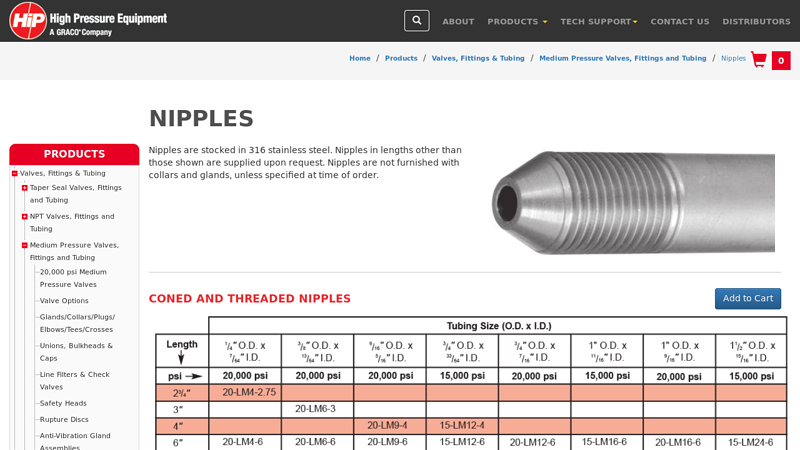
#1 Nipples
Domain Est. 1997
Website: highpressure.com
Key Highlights: Nipples are stocked in 316 stainless steel. Nipples in lengths other than those shown are supplied upon request. Nipples are not furnished with collars and …Missing: cone manufa…
#2 lubricating nipple (cone)
Domain Est. 2012
Website: elf-mh.com
Key Highlights: Product.Nr.: 180016. lubricating nipple (cone). price. Properties. Manufacturer, LINDE. Accessories; Often ordered with. switch. Product.Nr.: 212133….
#3
Domain Est. 1995
Website: parker.com
Key Highlights: As the global leader in motion and control technologies, Parker Hannifin plays a pivotal role in applications that have a positive impact on the world….
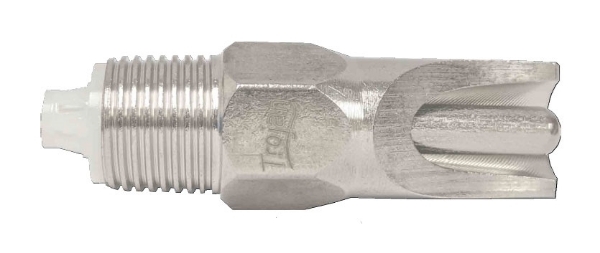
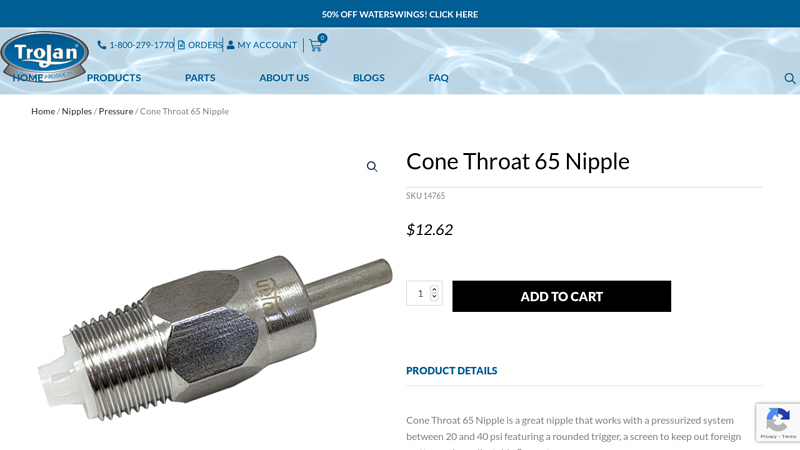
#4 Cone Throat 65 Nipple
Domain Est. 1996
#5 Swagelok
Domain Est. 1996
Website: products.swagelok.com
Key Highlights: Swagelok designs and manufactures a range of the highest quality fluid system components, including fittings, valves, regulators, gauges, hoses, and tubing….
#6 Cone Nipples Metal Hose
Domain Est. 1999
Website: hydraflex.co.uk
Key Highlights: The Cone Nipple from Hydraflex is a reliable and durable choice for a variety of applications. Offered in two main variants, one is constructed from Carbon ……
#7 AGCO
Domain Est. 2021
Website: masseytractorparts.com
Key Highlights: 5–19 day delivery 14-day returnsA close-up of the AGCO Cone-Type Lubricating Nipple – Fel108292, featuring a threaded end and a rounded top designed for attaching lubrication equip…
#8 Cone
Domain Est. 2022
Website: nrvpackers.com
Key Highlights: The conical head grease nipples have a tapered thread. They are suitable for grease points which must be lubricated often and reliably….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cone Nipple

H2: Market Trends for Cone Nipple in 2026
The global market for cone nipples—specialized components used primarily in fluid transfer systems across industries such as automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and medical devices—is poised for notable transformation by 2026. Driven by evolving manufacturing standards, material innovation, and increasing demand for leak-proof, high-performance connectors, the cone nipple segment is expected to experience steady growth and technological refinement. Below are the key market trends anticipated to shape the cone nipple industry in 2026:
1. Rising Demand in Automotive and EV Manufacturing
With the automotive industry’s continued shift toward electric vehicles (EVs), there is growing demand for precision fluid connectors that ensure reliability in cooling, braking, and battery thermal management systems. Cone nipples, known for their secure sealing capabilities under high pressure, are increasingly adopted in EV powertrain and coolant loop applications. By 2026, automakers are projected to prioritize lightweight, corrosion-resistant cone nipples made from advanced alloys or engineered polymers to improve efficiency and durability.
2. Adoption of High-Performance Materials
Material innovation is a major driver in the cone nipple market. By 2026, stainless steel grades such as 316L and titanium will dominate high-end applications due to their resistance to extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. Additionally, the use of PEEK (polyether ether ketone) and other high-strength thermoplastics is expected to rise in medical and semiconductor equipment, where sterility and chemical resistance are critical.
3. Expansion in Industrial Automation and Smart Manufacturing
As industries embrace Industry 4.0, the need for reliable, modular fluid handling systems is increasing. Cone nipples are being integrated into automated assembly lines and smart pneumatics systems, where leak prevention and quick maintenance are essential. The trend toward plug-and-play fluid components supports demand for standardized cone nipple designs compatible with digital monitoring systems.
4. Regional Growth in Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region—particularly China, India, and South Korea—is expected to lead market growth by 2026, fueled by expanding manufacturing bases, infrastructure development, and rising investments in clean energy and electric mobility. Local production of cone nipples is increasing to meet just-in-time supply chain demands, reducing reliance on imports and accelerating product customization.
5. Sustainability and Recycling Initiatives
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly production methods. By 2026, recyclable materials and energy-efficient machining processes for cone nipples are expected to become industry standards. Additionally, reusable and modular connector designs are gaining traction to reduce industrial waste.
6. Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The cone nipple market is witnessing increased consolidation, with major fluid system component suppliers acquiring niche manufacturers to expand their product portfolios. Strategic partnerships between cone nipple producers and system integrators are also on the rise, enabling co-development of application-specific solutions for aerospace, medical, and renewable energy sectors.
Conclusion
By 2026, the cone nipple market will be shaped by technological advancements, material innovation, and sector-specific demands. As industries prioritize efficiency, safety, and sustainability, cone nipples will evolve beyond simple connectors into intelligent, high-precision components integral to modern engineering systems. Companies that invest in R&D, global supply chain resilience, and sustainable manufacturing are likely to gain a competitive edge in this dynamic market landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cone Nipple (Quality, IP)
Sourcing cone nipples—tapered threaded fittings commonly used in plumbing, instrumentation, and hydraulic systems—can present several challenges, especially concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure reliable supply and legal compliance.
Poor Material Quality and Non-Standard Manufacturing
One of the most frequent issues is receiving cone nipples made from substandard materials or manufactured to inconsistent tolerances. Low-cost suppliers may use inferior stainless steel, brass, or carbon steel that doesn’t meet required specifications (e.g., ASTM, ISO, or DIN standards), leading to leaks, thread damage, or premature failure under pressure or corrosive environments. Inconsistent thread cutting or taper angles can also compromise sealing performance, especially in high-integrity applications.
Lack of Certification and Traceability
Many suppliers, particularly in less-regulated markets, fail to provide proper material test reports (MTRs), certificates of conformance (CoC), or batch traceability. This absence makes it difficult to verify that the cone nipples meet required industry standards (e.g., ASME B1.20.1 for NPT threads) and increases the risk of non-compliance in regulated sectors like oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, or aerospace.
Counterfeit or Non-Compliant IP-Protected Designs
Some cone nipple designs—especially proprietary or patented tapered sealing systems—are protected by intellectual property rights. Sourcing from unauthorized manufacturers may result in the procurement of counterfeit or reverse-engineered products that infringe on patents or registered designs. This exposes the buyer to legal liability, shipment seizures, and reputational damage. For example, copying a branded cone nipple with a unique sealing geometry without licensing can breach design patents.
Inadequate Quality Control Processes
Suppliers may lack robust quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001 certification), leading to inconsistent product quality across batches. Without proper inspection protocols—such as thread gauging, pressure testing, or visual inspection—defective parts can slip through, resulting in field failures and increased warranty or replacement costs.
Misrepresentation of Standards and Specifications
Some suppliers falsely claim compliance with international standards (e.g., NPT, BSPT, JIC) without actual validation. This misrepresentation can lead to compatibility issues during installation, especially when interfacing with other certified components, potentially causing safety hazards or system downtime.
Supply Chain and Ethical Sourcing Risks
Beyond technical concerns, sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement or lax labor/environmental regulations can expose companies to ethical sourcing risks. These include using forced labor, violating environmental laws, or operating without transparency—factors increasingly scrutinized by customers and regulators.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Vet suppliers through audits and request certifications (ISO, material compliance).
– Use authorized distributors for IP-protected designs.
– Require test reports and conduct third-party inspections.
– Include IP indemnity clauses in procurement contracts.
– Prioritize long-term reliability over initial cost savings.
By addressing these common issues proactively, organizations can ensure they source high-quality, compliant cone nipples while minimizing legal and operational risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cone Nipple
Product Overview
The Cone Nipple is a specialized industrial component typically used in fluid transfer systems, pneumatic applications, or plumbing connections. Its conical shape allows for secure, leak-resistant fittings when connecting hoses or tubes. This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations to ensure safe and lawful handling, transportation, and use.
Classification & Harmonized System (HS) Code
Correct product classification is crucial for international shipping and customs clearance. The Cone Nipple generally falls under HS Code 7307.29 – “Tube or pipe fittings of iron or steel (e.g., couplings, elbows, sleeves), other than of cast iron.”
Note: Confirm exact classification based on material (e.g., stainless steel, brass) and intended use, as regional variations may apply.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
- Use moisture-resistant packaging to prevent corrosion, especially for steel or iron variants.
- Secure individual units in partitioned containers to avoid surface damage during transit.
- Label packages clearly with product description, material type, size, and quantity.
- For bulk shipments, use palletized loads with stretch wrapping to prevent shifting.
- Handle with care to avoid deformation of the conical end, which may affect sealing performance.
Transportation & Shipping
- Suitable for standard ground, air, and sea freight.
- Comply with International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code if applicable—typically not hazardous unless coated with or containing restricted substances.
- Ensure adequate cushioning and load distribution to prevent damage in transit.
- Include shipping documentation: commercial invoice, packing list, and certificate of origin if required.
Regulatory Compliance
- REACH (EU): Confirm the product is free from Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) listed under REACH regulations. Suppliers must provide a Declaration of Conformity if requested.
- RoHS (EU): Applies if the Cone Nipple contains electrical components; otherwise typically exempt. Verify based on full product assembly.
- TSCA (USA): Comply with Toxic Substances Control Act; ensure no banned or unlisted chemical substances are used in manufacturing.
- UKCA/UKREACH: For shipments to the United Kingdom, verify compliance with post-Brexit regulations.
Country-Specific Import Requirements
- United States: Lacey Act compliance may apply if wood packaging materials are used (ISPM 15 standard required).
- European Union: CE marking not typically required for standalone fittings unless part of a pressurized system governed by PED (Pressure Equipment Directive).
- Canada: May require compliance with CSA B137 standards if used in plumbing applications.
- Australia: Check for WaterMark certification if used in potable water systems.
Quality & Certification Documentation
- Maintain records of material test reports (MTRs) verifying composition and strength.
- Provide ISO 9001 certification from the manufacturer, if available, to demonstrate quality management compliance.
- Include dimensional specifications and performance data (e.g., pressure rating, temperature range) in technical documentation.
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Cone Nipples are typically recyclable as scrap metal.
- Do not incinerate; dispose of in accordance with local metal waste regulations.
- Avoid release into waterways or soil to prevent environmental contamination.
Storage Guidelines
- Store in a dry, indoor environment to prevent rust and corrosion.
- Keep away from acidic or alkaline substances that may cause degradation.
- Use first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory practice to minimize long-term storage risks.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and adherence to compliance standards ensure the safe, efficient distribution of Cone Nipples across global markets. Always verify regional regulations and maintain accurate documentation to avoid customs delays or non-compliance penalties.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cone Nipples
After a comprehensive evaluation of suppliers, material quality, cost, lead times, and compliance standards, sourcing cone nipples—typically used in precision fluid transfer or medical applications—requires a strategic balance between quality assurance and cost-effectiveness. It is essential to partner with reliable manufacturers that adhere to international standards such as ISO or ASTM, particularly when these components are used in critical applications like healthcare or aerospace.
Key considerations in the final sourcing decision include material compatibility (e.g., silicone, rubber, or thermoplastic elastomers), dimensional accuracy, sterilization capability, and supply chain reliability. While domestic suppliers may offer faster turnaround and easier communication, overseas manufacturers—particularly in Asia—can provide significant cost advantages if quality control processes are rigorously managed.
In conclusion, the optimal sourcing strategy for cone nipples involves a dual-supplier approach: maintaining a primary relationship with a high-quality, certified supplier for consistency and compliance, while engaging a secondary, cost-competitive supplier to mitigate supply chain risks. Continuous supplier performance monitoring, sample testing, and on-site audits are recommended to ensure long-term reliability and product integrity.