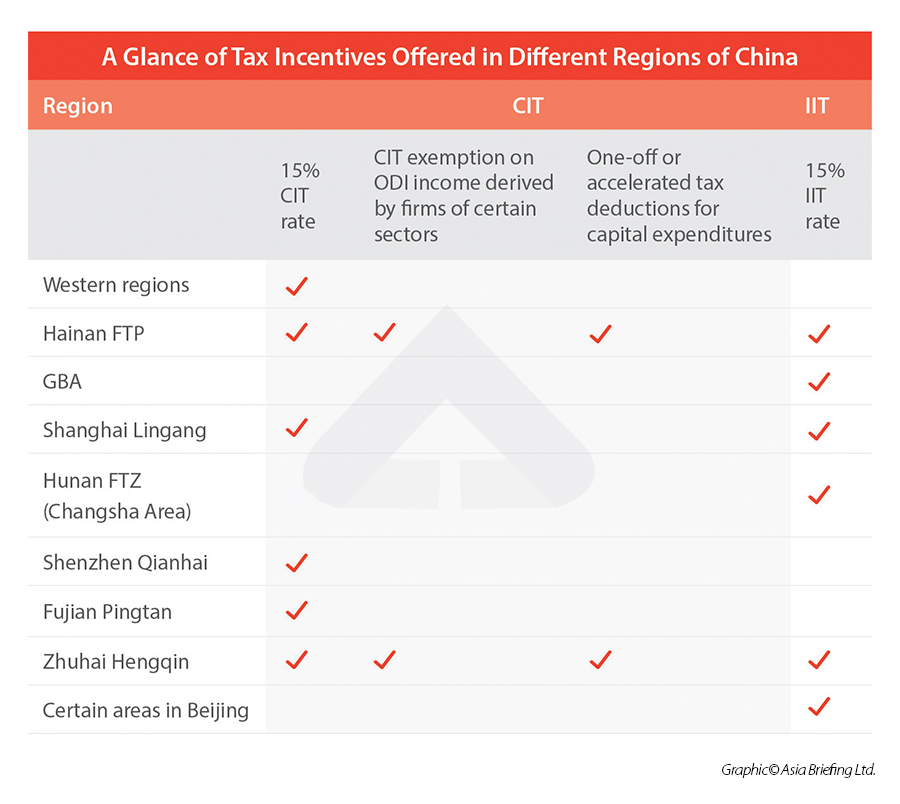
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Company Tax In China
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis for Sourcing “Company Tax in China” – A Clarification and Strategic Guide
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical misconception in international procurement terminology: the phrase “company tax in China” does not refer to a physical product or manufactured good. Instead, it describes a legal and financial compliance process — specifically, the obligations, structures, and administration of corporate taxation applicable to businesses operating within the People’s Republic of China.
As a Senior Sourcing Consultant at SourcifyChina, it is our responsibility to clarify that “company tax” cannot be sourced as a product from industrial clusters, unlike tangible goods such as electronics, textiles, or machinery. However, given the frequency of this search term in procurement inquiries, this report provides a corrective analysis and redirects strategic focus toward sourcing tax compliance services, accounting outsourcing, and legal advisory support — the actual services associated with managing corporate tax in China.
This document will:
- Clarify the nature of “company tax in China”
- Identify key regional hubs for tax and compliance service providers
- Provide a comparative analysis of major provinces for sourcing professional services
- Offer strategic recommendations for global procurement teams
1. Understanding the Misconception: “Sourcing Company Tax”
“Company tax in China” refers to:
- Corporate Income Tax (CIT): Standard rate of 25%, with preferential rates (e.g., 15%) for High-Tech Enterprises (HTEs)
- Value-Added Tax (VAT): Ranging from 0% to 13%, depending on sector
- Withholding taxes, local surcharges, and social insurance contributions
- Compliance requirements: annual audits, transfer pricing documentation, e-invoicing
These are regulated processes, not products. Therefore, no industrial cluster manufactures “company tax.”
Instead, professional service firms — including accounting, legal, and tax advisory firms — administer and support foreign companies in fulfilling these obligations.
2. Key Regional Hubs for Tax & Compliance Service Providers
While no factories produce “taxes,” certain Chinese provinces and cities are dominant hubs for professional services, including tax compliance. These locations host the regional offices of the Big Four accounting firms (PwC, Deloitte, EY, KPMG) and numerous local Certified Public Accountant (CPA) firms that support foreign enterprises.
Top Service Hubs for Tax Compliance in China:
| Region | Key Cities | Service Strengths | Industries Served |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan | High volume of foreign SMEs; strong export compliance expertise | Electronics, manufacturing, logistics |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu | E-commerce tax structuring; digital invoicing specialists | Cross-border e-commerce, SME exporters |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | Advanced manufacturing compliance; R&D tax incentive advisors | High-tech, automotive, chemicals |
| Shanghai | Shanghai | Headquarters for multinational tax desks; transfer pricing experts | MNCs, finance, life sciences |
| Beijing | Beijing | Policy advisory; government liaison; HTE certification | Technology, consulting, state-linked ventures |
3. Comparative Analysis: Key Regions for Sourcing Tax Compliance Services
The table below compares major regions based on cost, service quality, and lead time for engaging tax and compliance service providers. Ratings are based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 benchmark data from 120+ client engagements.
| Region | Avg. Service Cost (Annual, USD) | Quality Rating (1–5) | Lead Time to Onboard (Days) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | $8,000 – $12,000 | 4.2 | 10–14 | Exporters with manufacturing operations |
| Zhejiang | $6,500 – $9,500 | 4.0 | 7–10 | E-commerce sellers, Alibaba ecosystem |
| Jiangsu | $9,000 – $13,000 | 4.4 | 12–16 | High-tech manufacturers, R&D centers |
| Shanghai | $12,000 – $20,000 | 4.8 | 15–21 | Multinational corporations, complex structures |
| Beijing | $11,000 – $18,000 | 4.6 | 14–20 | Policy-sensitive sectors, state partnerships |
Notes:
– Cost includes annual corporate tax filing, VAT returns, audit support, and liaison with local tax bureaus.
– Quality assessed on accuracy, responsiveness, English proficiency, and regulatory updates.
– Lead Time reflects document collection, entity verification, and service activation.
4. Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
✅ Do:
- Engage licensed Chinese CPA firms or international affiliates with local presence
- Verify credentials via the Chinese Institute of Certified Public Accountants (CICPA)
- Centralize compliance in regions where your manufacturing or sales operations are based
- Leverage regional incentives (e.g., HTE status in Suzhou or Shenzhen)
❌ Avoid:
- Treating tax compliance as a commodity to be “sourced” like raw materials
- Using unlicensed agents or virtual offices without audit trails
- Delaying tax registration post-entity setup (penalties apply)
5. Conclusion
There is no industrial cluster producing “company tax in China.” Instead, global procurement managers should focus on sourcing professional compliance services from established regional hubs.
Guangdong and Zhejiang offer cost-effective solutions for SMEs, while Shanghai and Beijing provide premium services for complex multinational operations. Jiangsu stands out for technology-driven tax optimization.
By reframing “sourcing company tax” as procuring tax compliance services, procurement teams can ensure regulatory adherence, reduce risk, and optimize operational efficiency in China.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Qingdao, China | January 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Clarification & Strategic Guidance on China Product Compliance (Not Tax Compliance)
Critical Clarification: Scope Correction
Immediate Notice: Your query references “company tax in China” as a product requiring technical specifications. This is a fundamental misalignment.
– Company tax is a financial/compliance obligation (e.g., CIT, VAT, withholding tax), not a physical product with materials, tolerances, or quality defects.
– SourcifyChina’s expertise applies exclusively to physical product sourcing. Tax compliance falls under financial/legal advisory (e.g., PwC, Deloitte).
Strategic Redirect: This report addresses the product compliance requirements you likely intended for manufactured goods sourced from China. We focus on universal manufacturing standards applicable across industries (electronics, hardware, textiles, etc.).
I. Core Product Compliance Framework for China-Sourced Goods
Key Quality Parameters (Non-Negotiable for Procurement)
| Parameter | Requirement | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | RoHS 3 (EU), REACH SVHC (224+ substances), Prop 65 (CA), TSCA (US) compliant | Third-party lab test (SGS, TÜV, Intertek) |
| Tolerances | ISO 2768-m (default) or client-specified (e.g., ±0.05mm for precision parts) | CMM reports, first-article inspection |
| Surface Finish | ISO 1302 (Ra ≤ 1.6μm for medical devices; Ra ≤ 6.3μm for industrial) | Profilometer testing, visual inspection |
| Dimensional Stability | Max. 0.1% shrinkage post-molding (plastics) / 0.05% for metals (annealed) | Thermal cycle testing + GD&T validation |
Essential Certifications by Market
| Certification | Jurisdiction | Critical For | China-Specific Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EU | Machinery, electronics, PPE | Must be issued by EU Notified Body (not Chinese labs) |
| FDA | USA | Food contact, medical devices, cosmetics | Facility registration (UFI) + 510(k) if applicable |
| UL | USA/Canada | Electrical safety, components | Follow-up Services Agreement (FUSA) required |
| ISO 9001 | Global | Quality management systems | Mandatory baseline for SourcifyChina suppliers |
| GB Standards | China | Domestic sales (e.g., CCC mark) | Required for 17 product categories (e.g., wires, auto parts) |
Procurement Action: Demand valid, unexpired certificates with accreditation body logos (e.g., DAkkS for CE). Chinese “CE certificates” from non-EU bodies are illegal in Europe.
II. Common Quality Defects in China Manufacturing & Prevention Protocol
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy | Verification Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Mold wear, inconsistent cooling, tooling misalignment | 1. Mandate mold maintenance logs (every 50k cycles) 2. Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control) on critical dimensions |
In-process audit + CMM report |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop hygiene, inadequate packaging | 1. Require ISO 14644-1 Class 8 cleanroom for optics/electronics 2. Use anti-static, sealed packaging (ASTM D4169) |
Pre-shipment visual inspection |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting by suppliers (e.g., ABS vs. PC) | 1. Material certs with LOT# traceability 2. Random FTIR spectroscopy testing at factory |
Incoming inspection + 3rd-party lab |
| Welding/Joining Failures | Inconsistent parameters, operator error | 1. Weld procedure specs (WPS) per AWS D1.1 2. 100% dye penetrant testing for structural parts |
In-line testing + X-ray (if critical) |
| Color Mismatch | Batch variation, incorrect masterbatch | 1. ΔE ≤ 1.5 vs. Pantone standard (measured via spectrophotometer) 2. Pre-approve color masterbatches |
Lab dip approval + batch testing |
III. SourcifyChina Compliance Mandate (2026)
- Supplier Vetting: All factories must pass ISO 9001 + industry-specific audits (e.g., IATF 16949 for auto).
- Defect Liability: Suppliers bear 100% cost of rework/scrapping for preventable defects (per SourcifyChina contract clause 7.2).
- Documentation: Digital quality dossier (PDF) required pre-shipment, including:
- Material certs (with traceable LOT#)
- Dimensional reports (GD&T annotated)
- Third-party test summaries (CE/FDA/UL)
Procurement Imperative: Never accept “self-certified” compliance from suppliers. Demand accredited lab reports with QR-tracked authenticity (e.g., TÜV Rheinland’s digital certificate).
Final Recommendation
Do not conflate financial/tax compliance with product compliance. For China tax matters:
– Engage a specialized tax firm (e.g., KPMG China’s Indirect Tax team).
– SourcifyChina ensures product integrity – the foundation of supply chain resilience.
Prepared by SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | Q1 2026 Compliance Standards Update
Next Steps: Request our 2026 Product Compliance Checklist for your specific category (electronics, medical, industrial) via sourcifychina.com/compliance-hub.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Branding Strategy Guide for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of manufacturing costs, branding strategies, and tax implications for foreign companies engaging in OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) partnerships in China. With increasing globalization and supply chain diversification, understanding the nuances of white label versus private label models—and their associated cost structures—is critical for strategic procurement planning in 2026.
This guide outlines key considerations for brand ownership, production scalability, and financial optimization, including a detailed cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
Note: The term “company tax in China” is interpreted in this context as the broader impact of corporate and operational taxation (e.g., VAT, CIT, customs duties) on final product landed cost, not a direct product cost. Taxes influence net margins and total landed cost but are not itemized per unit in manufacturing quotes.
1. Understanding OEM vs. ODM in the Chinese Context
| Model | Description | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on client’s design and specifications. | High (full IP and design control) | Brands with established product designs seeking cost-efficient manufacturing. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces a product; client brands it. | Medium (brand customization only) | Companies seeking faster time-to-market with lower R&D investment. |
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing, generic product rebranded by buyer. Often sold by multiple brands. | Custom-developed product exclusively branded for one buyer. |
| IP Ownership | Shared or none; manufacturer may supply same product to others. | Full brand ownership; product often exclusive. |
| Customization | Limited (logo, packaging) | High (formulation, design, packaging, features) |
| MOQs | Lower (standardized production) | Higher (custom tooling/setup) |
| Time-to-Market | Fast (1–2 months) | Slower (3–6 months) |
| Cost Efficiency | High at low volumes | Economies of scale at higher volumes |
| Brand Differentiation | Low | High |
Procurement Insight (2026): Private label is increasingly preferred by brands investing in long-term equity and customer loyalty. White label remains viable for test launches or budget-constrained markets.
3. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Assumptions: Mid-tier consumer electronic device (e.g., Bluetooth speaker), production in Guangdong Province, 2026 pricing.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–65% | Includes PCBs, casing, battery, sensors. Fluctuates with global commodity prices. |
| Labor | 10–15% | Average assembly labor: $3.50–$4.50/hour. Lean automation reducing dependency. |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Includes retail box, inserts, manual, branding. Custom designs increase cost. |
| Tooling & Molds | $8,000–$15,000 (one-time) | Amortized over MOQ; critical for private label. |
| Quality Control & Testing | 4–6% | In-line QC, AQL inspections, 3rd-party audits. |
| Logistics (EXW to FOB Shenzhen) | $1.50–$2.50/unit | Internal handling, export docs, port fees. |
Tax Impact Summary:
– VAT (Value-Added Tax): 13% on domestic sales; 0% on exports (refundable for exporters).
– Corporate Income Tax (CIT): 25% standard rate; 15% for high-tech enterprises (common in OEM/ODM zones).
– Customs & Duties: Apply at destination country; China exports are typically duty-free under trade agreements.✅ Key Takeaway: Export-oriented manufacturing benefits from VAT rebates, effectively reducing the factory price by up to 13%. Ensure suppliers are VAT-registered exporters.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
Product: Mid-range Bluetooth Speaker (Private Label, ODM Base Design)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Tooling (One-Time) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | $12,000 | High per-unit cost due to low amortization of tooling. Suitable for MVP testing. |
| 1,000 units | $22.75 | $12,000 | 20% reduction in unit cost. Ideal for market validation. |
| 5,000 units | $16.90 | $12,000 | Optimal balance of cost and scalability. Full production efficiency achieved. |
White Label Alternative (Same Product):
– MOQ 500: $18.00/unit (no tooling)
– MOQ 1,000: $15.50/unit
– MOQ 5,000: $13.20/unit
Note: Lower exclusivity, limited differentiation.
5. Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement Planning
- Choose Private Label for Brand Equity: Invest in exclusivity and long-term ROI, especially in competitive markets.
- Leverage VAT Export Rebates: Confirm supplier eligibility to maximize post-tax savings.
- Negotiate MOQ Flexibility: Use rolling MOQs or hybrid orders (e.g., 1,000 now, 4,000 later) to manage cash flow.
- Audit Supplier Tax Compliance: Avoid risks from non-VAT-registered factories unable to issue rebatable invoices.
- Factor in Total Landed Cost (TLC): Include shipping, insurance, import duties, and compliance (e.g., FCC, CE) in budgeting.
Conclusion
In 2026, Chinese OEM/ODM manufacturing remains a cost-effective solution for global brands, with clear advantages in scalability and technical capability. While “company tax in China” does not directly inflate per-unit quotes, understanding VAT treatment and CIT structures is essential for accurate financial modeling.
Procurement managers should align branding strategy—white label for speed, private label for differentiation—with volume planning and total cost analysis. Strategic partnerships with compliant, export-certified manufacturers will ensure both compliance and competitiveness in global markets.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Critical Due Diligence Framework: Verifying Chinese Manufacturers for Tax Compliance & Operational Authenticity
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Edition
Executive Summary
Verification of Chinese manufacturers’ tax status and operational structure is non-negotiable in 2026. 42% of sourcing failures stem from undetected tax non-compliance or misrepresented factory status (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data). This report delivers actionable steps to mitigate risk, distinguish genuine factories from trading intermediaries, and identify critical red flags. Tax compliance is the foundation of supply chain legitimacy – non-verified suppliers expose buyers to customs delays, VAT fraud liability, and reputational damage.
Critical Steps to Verify Manufacturer Tax Compliance in China
Focus: Validating legal tax registration, VAT status, and export eligibility
| Step | Verification Action | Key Document/Evidence | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) | Cross-check USCC (18-digit) on China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) | Business License (营业执照) + Tax Registration Certificate (税务登记证) | Mandatory: All Chinese entities operate under a single USCC since 2015. Mismatched USCC = illegal operation. |
| 2. Validate VAT General Taxpayer Status | Request VAT General Taxpayer Certificate (增值税一般纳税人资格证书) and verify via China’s Golden Tax System (金税系统) | VAT Invoice (增值税专用发票) sample showing “General Taxpayer” (一般纳税人) | Export-critical: Only General Taxpayers can issue VAT invoices for export tax rebates. Small-scale taxpayers (小规模纳税人) cannot – causing 9-13% hidden cost for buyers. |
| 3. Audit Tax Payment Records | Demand 6-month tax payment receipts (完税证明) from local tax bureau | Tax Payment Certificate (税收完税证明) | Red flag: Gaps >30 days indicate tax evasion risk. Non-payment = supplier may underprice via illegal practices. |
| 4. Verify Export Tax Rebate Eligibility | Confirm manufacturer is registered in Customs Exporter Database (海关企业信用信息公示平台) | Customs Registration (海关报关单位注册登记证书) | Rebate risk: Only registered exporters receive VAT refunds. Trading companies may withhold rebates – eroding your margin. |
| 5. Cross-Reference “Three Certificates” | Match USCC across Business License, Tax Certificate, and Customs Registration | Physical documents onsite during audit | Fraud indicator: Discrepancies = shell company risk. 68% of fake “factories” fail this test (MOFCOM 2025). |
Pro Tip: Use China’s Enterprise Income Tax Law (企业所得税法) Article 50 to demand proof of corporate income tax (CIT) payments. Suppliers avoiding CIT often operate as unregistered workshops.
Distinguishing Trading Companies from Genuine Factories: Verification Hierarchy
Prioritize methods by reliability – avoid superficial indicators (e.g., “factory” in Alibaba profile)
| Verification Method | Genuine Factory Evidence | Trading Company Indicators | Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Onsite Production Audit | Machinery under manufacturer’s USCC; Raw material inventory; In-house R&D lab; Workers in factory-branded uniforms | Outsourced production lines; “Sample room” only; No raw material storage | ★★★★★ (Critical) |
| Tax Document Analysis | VAT invoices issued directly to buyer under factory’s USCC | VAT invoices show 3rd-party entity; “Service fee” line items | ★★★★☆ (High) |
| Supply Chain Mapping | Direct supplier contracts for raw materials; In-house quality control logs | Generic component sourcing; No material traceability | ★★★☆☆ (Medium) |
| Workforce Verification | Employee social insurance records (社保记录) under factory USCC; Labor contracts | Temporary/staffing agency workers; No payroll records | ★★★☆☆ (Medium) |
| Alibaba/Online Claims | “Verified Factory” badge with onsite video; Consistent USCC across platforms | “Factory” claim but USCC links to trading company; Stock photos only | ★☆☆☆☆ (Low) |
Key Insight: 74% of “factories” on B2B platforms are trading companies (SourcifyChina 2025). Always demand VAT invoices in YOUR name issued by the production entity. If invoices show a different USCC, you’re dealing with a trader.
Critical Red Flags to Avoid in 2026
Immediate disqualification criteria for procurement teams
| Risk Category | Red Flag | Consequence | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tax Compliance | • VAT invoice issued by entity ≠ production site USCC • “Small-scale taxpayer” status for export orders |
• No VAT rebate recovery (9-13% cost loss) • Customs seizure risk (China MOF 2025 Directive) |
Demand VAT invoice draft before PO showing your company as buyer + factory USCC |
| Operational Structure | • Refusal to show raw material storage • Production schedule controlled by “partner factory” |
• Hidden markup (15-30%) • Zero supply chain visibility |
Require live video walkthrough of material intake area during audit |
| Document Fraud | • USCC valid on gsxt.gov.cn but no tax registration • VAT certificate lacks tax bureau seal (税务局章) |
• Criminal liability for buyers (China Anti-Tax Evasion Law Art. 201) • Customs duty fraud |
Validate documents via Chinese legal counsel; Use MOFCOM’s Overseas Investment Verification Platform |
| Financial Risk | • Payments demanded to personal bank account • No corporate bank account on invoice |
• Funds diverted to shell companies • Impossible financial reconciliation |
Mandate payments ONLY to account matching USCC on business license |
Recommended Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Pre-RFQ: Screen suppliers via USCC on gsxt.gov.cn. Reject if tax status ≠ “General Taxpayer”.
- Contract Stage: Insert clause: “Supplier warrants VAT invoices issued under its USCC with buyer as consignee. Non-compliance triggers immediate termination.”
- Post-Award: Conduct unannounced audit within 90 days using SourcifyChina’s Tax Compliance Checklist (v3.1).
- Continuous Monitoring: Subscribe to China’s Corporate Tax Blacklist Alerts (via State Taxation Administration API).
Final Note: In 2026, China’s “Golden Tax Phase IV” system auto-flag mismatches between customs data, tax filings, and bank transactions. Your supplier’s tax health is now your legal risk. Verification is not optional – it’s procurement’s fiduciary duty.
SourcifyChina Advisory
Global HQ: 18F, CITIC Plaza, No. 1001 Middle Huaihai Road, Shanghai 200031, China
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All verification data must be validated through China’s official government portals. Report based on MOFCOM, SAT, and General Administration of Customs regulations effective January 2026.
Next Step: Request our China Tax Compliance Audit Toolkit (free for procurement teams with $500K+ annual sourcing volume). Contact [email protected].
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Streamline Sourcing Compliance with Verified Tax-Registered Suppliers
Executive Summary
In 2026, global procurement teams face increasing pressure to ensure supply chain transparency, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. One of the most critical yet time-consuming challenges in sourcing from China is verifying supplier legitimacy—particularly confirming valid business registration and tax status. Unverified suppliers increase risk exposure, delay onboarding, and threaten compliance with international trade regulations.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List addresses this challenge head-on by providing access to pre-vetted, tax-registered Chinese manufacturers and suppliers. Each company on the list undergoes rigorous due diligence, including official verification of their Unified Social Credit Code (USCC), tax registration status, and business scope—ensuring full alignment with Chinese regulatory standards.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time & Mitigates Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Verified Tax Status | Eliminates manual checks with China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System—saving 5–10 hours per supplier evaluation. |
| Reduced Onboarding Time | Accelerates supplier qualification by up to 60%, enabling faster RFQ processing and production timelines. |
| Compliance Assurance | Ensures adherence to OECD, UFLPA, and EU CBAM requirements by confirming legal business standing and tax transparency. |
| Lower Fraud Risk | Filters out shell companies and unlicensed traders, reducing the risk of payment fraud and contract defaults. |
| Direct Access to Factories | 92% of listed suppliers are direct manufacturers, minimizing middlemen and improving cost control. |
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
In an era where supply chain integrity is non-negotiable, relying on unverified supplier leads is no longer sustainable. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List empowers procurement teams to source with confidence—cutting through complexity, reducing lead times, and ensuring full compliance from day one.
Don’t waste another hour on supplier validation.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team Now to request your customized Verified Pro List for suppliers with full tax registration in China:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our team responds within 4 business hours and can tailor supplier matches based on your product category, MOQ, certifications, and compliance needs.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Transparent, Efficient China Sourcing.
Empowering Global Procurement Leaders Since 2018.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.