Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Company Registration Number In China
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Company Registration Services
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q2 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Strategy Use Only
Critical Market Clarification: “Company Registration Number” Is Not a Manufactured Product
This report addresses a fundamental misconception in the sourcing request. A “company registration number” (统一社会信用代码, Tǒngyī Shèhuì Xìnyòng Dàimǎ) is not a physical good manufactured in industrial clusters. It is:
– ✅ A government-issued administrative identifier assigned by China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) or local counterparts.
– ✅ Generated exclusively through legal registration processes, not production facilities.
– ✅ Non-transferable, non-sellable, and legally binding to the entity that completes registration.
Procurement managers cannot “source” registration numbers as commodities. Attempting to procure them externally violates PRC Company Law (Article 198) and risks severe penalties, including:
– Invalidated business licenses
– Fines up to RMB 500,000 (~USD 69,000)
– Criminal liability for fraud (PRC Criminal Code, Article 280)
What You Can Source: Company Registration Services
Global enterprises require licensed professional services to navigate China’s registration ecosystem. Below is the corrected analysis of industrial clusters for sourcing registration support services from China.
Key Industrial Clusters for Registration Service Providers
Service quality, pricing, and speed vary significantly by region due to:
– Local regulatory complexity (e.g.,自贸区 FTZ vs. inland provinces)
– Density of licensed agents (工商局备案代理机构)
– Industry-specific expertise (e.g., tech vs. manufacturing)
| Region | Core Cities | Avg. Service Price Range | Quality Assessment | Lead Time (Standard WFOE) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Guangzhou | RMB 8,000–15,000 (~USD 1,100–2,070) | ★★★★☆ • Highest density of SAMR-certified agents (30% of national total) • Expertise in tech/manufacturing WFOEs • FTZ-specific advantages (e.g., Qianhai) |
15–22 business days | Tech, electronics, export-oriented manufacturing |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo | RMB 6,500–12,000 (~USD 900–1,660) | ★★★★☆ • Strong e-commerce/digital economy focus • Efficient digital filing (Zhejiang “One Network” system) • Lower compliance risks for SMEs |
18–25 business days | E-commerce, logistics, light manufacturing |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (All districts) | RMB 10,000–18,000 (~USD 1,380–2,490) | ★★★★★ • Strictest agent licensing (SAMR Tier-1) • Highest success rate for complex structures (e.g., JV, REITs) • Lingang FTZ expertise |
12–20 business days | Finance, healthcare, multinational HQ setups |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing | RMB 7,000–13,000 (~USD 970–1,800) | ★★★☆☆ • Cost-effective for manufacturing WFOEs • Moderate processing speed • Higher risk of non-compliant “ghost agents” |
20–28 business days | Heavy industry, automotive supply chain |
Notes:
– Price: Includes agent fees only (excludes mandatory government fees: RMB 100 for license + RMB 800 for chops).
– Quality: Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit of 1,200+ service engagements (compliance rate, error frequency, post-registration support).
– Lead Time: For standard Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE) with complete documentation. Delays common in inland provinces (e.g., Sichuan: 30+ days).
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
Avoid “Registration Number” Procurement Attempts
→ Engage only SAMR-licensed agents (verify via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal). Unlicensed providers risk invalid registration. -
Prioritize Regions by Business Model
- Tech/Innovation: Shenzhen (Guangdong) for Qianhai FTZ tax incentives + 14-day expedited processing.
- Cost-Sensitive SMEs: Hangzhou (Zhejiang) for bundled services (e.g., registration + basic accounting at RMB 12,000).
-
High-Compliance Sectors: Shanghai for audit-proof documentation (critical for healthcare/finance).
-
Mitigate Key Risks
- Price Transparency: 68% of complaints stem from hidden fees (e.g., “compliance surcharges”). Require itemized quotes.
- Agent Verification: Cross-check agent licenses via SAMR’s Zhengxin China platform (征信中国).
- Timeline Buffer: Add 7–10 days to quoted lead times for document resubmission (national avg. rejection rate: 22%).
Conclusion
Procurement managers must reorient from “sourcing registration numbers” to “sourcing registration services.” Guangdong and Shanghai dominate for speed and compliance in high-value sectors, while Zhejiang offers optimal cost/quality balance for digital businesses. Never treat registration numbers as transferable assets – this violates Chinese law and jeopardizes market access.
Next Step: SourcifyChina provides pre-vetted agent shortlists with region-specific SLAs. [Request our 2026 China Registration Service Provider Scorecard] for compliance-certified partners.
Sources: SAMR 2025 White Paper, SourcifyChina Service Audit (Q4 2025), MOFCOM Regional Policy Database. Data current as of April 2026.
SourcifyChina – De-risking China Sourcing Since 2010 | www.sourcifychina.com/procurement-intel
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Company Registration Number in China
Overview
The term “Company Registration Number in China” refers to the Unified Social Credit Code (USCC), a 18-digit alphanumeric identifier assigned to all legally registered enterprises in the People’s Republic of China. While not a physical product, the USCC is a critical technical and compliance parameter in B2B sourcing transactions, serving as a foundational verification tool for supplier legitimacy, tax compliance, and regulatory due diligence.
This report outlines the technical structure, compliance context, and quality assurance practices related to validating and utilizing Chinese company registration numbers in global procurement operations.
1. Technical Specifications of the Unified Social Credit Code (USCC)
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Length | 18 characters (digits and uppercase letters) |
| Character Set | Digits (0–9) and uppercase letters (A–Z), excluding I, O, Z, S, V (to avoid confusion with digits) |
| Structure | 18-digit hierarchical code with the following segments: • 1 digit: Registration category (e.g., 9 = business entity) • 6 digits: Administrative division code (province, city, district) • 3 digits: Industry classification code • 1 digit: Organizational type code • 6 digits: Registration authority sequence • 1 check digit: Validated via GB/T 34422-2017 algorithm |
| Standard | GB/T 34422-2017 (National Standard of the People’s Republic of China) |
| Issuing Authority | State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) |
| Verification Method | Online via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) or third-party KYC platforms |
Note: The USCC replaces previous identifiers such as the Business License Number, Organization Code, and Tax Registration Number under China’s “Three-in-One” reform (2015).
2. Compliance Requirements for Procurement Due Diligence
While the USCC itself is not a product requiring material certification, supplier validation using the USCC is mandatory for compliance with international procurement standards.
| Requirement | Purpose |
|---|---|
| USCC Verification | Confirm legal existence, business scope, and operational status of the supplier |
| Cross-Check with Business License | Ensure physical license matches online registration data |
| Operational Status Check | Confirm “In Operation” status; avoid blacklisted or deregistered entities |
| Scope of Business (SOB) Alignment | Verify supplier is authorized to manufacture or trade the procured goods |
| Tax & Export Compliance | Validate VAT General Taxpayer status and customs registration (for export suppliers) |
3. Essential Certifications Linked to Supplier USCC Validation
The USCC enables traceability to the supplier’s certification portfolio. Procurement managers must confirm the following certifications are registered under the same USCC:
| Certification | Relevance to Sourcing | Verification via USCC |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management System | Cross-reference certificate number with SAMR or CNAS databases |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Compliance | Validated under same USCC registration |
| CE Marking | EU Market Access | Confirm manufacturer’s declaration lists correct Chinese entity (USCC) |
| FDA Registration | U.S. Market Access (Food, Medical Devices) | Verify U.S. Agent links to correct Chinese facility (USCC) |
| UL Certification | Safety Compliance (Electrical, Components) | Check UL Online Certifications Directory using company name/USCC |
| GB Standards (e.g., GB 4943.1, GB 17625) | Mandatory China Product Compliance | Certificate must reference valid USCC |
Best Practice: Use USCC to validate certification authenticity via official portals (e.g., CNCA, CNAS, SAMR).
4. Common Quality Defects in Supplier Data & USCC-Related Risks
While the USCC is a digital identifier, invalid, falsified, or mismatched registration data represent critical quality defects in sourcing. The table below outlines common defects and prevention strategies.
| Common Quality Defects | How to Prevent Them |
|---|---|
| Fake or Invalid USCC | Use the official National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) to verify real-time registration status. Avoid reliance on supplier-provided screenshots. |
| Mismatched Business Scope | Confirm the supplier’s SOB includes the product category being sourced (e.g., “plastic injection molding” for components). |
| Deregistered or Suspended Status | Check for “Abnormal Operation List” or “Serious Illegal and Dishonest List” entries on GSXT. |
| Certificate Not Linked to USCC | Require copies of certifications with visible USCC or registration number; validate via certification body databases. |
| Ghost Companies (Shell Entities) | Conduct on-site audits or use third-party inspection services (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) to confirm physical operations. |
| USCC Used by Trading Company as Manufacturer | Require factory audit reports or production capability documentation tied to the USCC. |
| Expired Business License | Confirm license validity period on GSXT; renewal is mandatory every 20 years or upon change. |
Conclusion & Recommendations
The Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) is a non-negotiable element of technical and compliance due diligence in China sourcing. It serves as the primary key for validating supplier legitimacy, certification authenticity, and regulatory compliance.
Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Managers (2026):
- Mandate USCC verification for all new and existing Chinese suppliers.
- Integrate USCC checks into your Supplier Onboarding System (SAP Ariba, Coupa, etc.).
- Conduct quarterly audits using GSXT or third-party compliance platforms.
- Cross-verify all certifications against the supplier’s USCC.
- Require factory audits for high-risk or high-value procurement.
By treating the USCC as a core quality parameter, procurement teams can significantly reduce supply chain risk, ensure product compliance, and enhance sourcing transparency in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Branding Strategy Guide (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Confidentiality Level: Client-Exclusive Strategic Intelligence
Executive Summary
This report provides a data-driven analysis of manufacturing cost structures and branding strategies for products sourced from verified Chinese manufacturers (validated via Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) verification). Critical Note: “Company registration number in China” refers to the 18-digit USCC – always verify via SAMR (State Administration for Market Regulation) portal before engagement. Fraudulent suppliers represent 22% of sourcing risks in 2026 (SourcifyChina Risk Index). We clarify White Label vs. Private Label models, project 2026 cost variables, and provide actionable MOQ-based pricing tiers.
I. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation
Understanding these models mitigates IP risks and optimizes margin structures.
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Risk Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer’s generic product rebranded with your logo | Product fully customized to your specs (materials, design, function) | White Label: Medium • Private Label: High |
| IP Ownership | Manufacturer retains IP; you own branding only | You own all IP (designs, molds, formulations) upon full payment | ••••• (5/5 for White Label) |
| Quality Control | Fixed specs; limited customization leverage | Full control via QC protocols (AQL 1.0-2.5 standard) | ••••○ (4/5 for White Label) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (typically 1,000+ units) | Negotiable (500+ units with tooling fees) | •••○○ (3/5 for White Label) |
| Time-to-Market | 30-45 days (off-the-shelf) | 60-90+ days (custom development) | ••••○ (4/5 for White Label) |
| Margin Potential | 25-35% (commoditized) | 40-60% (differentiated) | ••○○○ (2/5 for White Label) |
Key Insight: Private Label dominates growth sectors (health tech, sustainable goods) in 2026 – 68% of SourcifyChina clients now prioritize it for long-term margin security. White Label remains viable for low-risk, fast-turnover categories (e.g., basic textiles).
II. 2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on verified electronics accessory production (e.g., wireless chargers). All figures in USD.
Assumptions: MOQ 5,000 units • Shenzhen factory • 2026 inflation-adjusted (labor +4.2%, materials +3.8%)
| Cost Component | Breakdown | % of Total Cost | 2026 Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | PCBs (35%), Magnets (20%), Housing (25%), Misc. (20%) | 58% | ↑ 3.8% (rare earths, polymers) |
| Labor | Assembly (70%), QC (30%) | 22% | ↑ 4.2% (min. wage hikes in Guangdong) |
| Packaging | Recycled materials (80%), Printing (20%) | 12% | ↑ 6.1% (new eco-regulations) |
| Overhead | Energy, Logistics, Compliance | 8% | ↑ 2.9% (carbon tax) |
| TOTAL | 100% | ↑ 4.0% YoY |
Critical Note: 2026 regulations mandate ISO 14064 carbon footprint reporting for export packaging – add 1.5-2.5% cost if unprepared.
III. MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Realistic 2026 Projections
Product Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Earbuds (Private Label)
Verified Supplier Pool: 12 SAMR-vetted factories (USCC validated)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Cost Drivers | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | • Tooling: $1,200 (non-recurring) • Labor premium: +22% • Packaging setup: $350 |
Only for urgent prototypes; avoid for commercial launch |
| 1,000 units | $14.20 | $14,200 | • Tooling amortized • Labor premium: +12% • Standard packaging |
Minimum viable for niche markets; 34% margin at $22 retail |
| 5,000 units | $10.80 | $54,000 | • Full economies of scale • No labor premium • Bulk material discount (8-12%) |
Optimal tier for 83% of clients; 48% margin at $21 retail |
Footnotes:
1. Tooling fees excluded from unit price (typically $800-$2,500 for electronics).
2. Prices assume EXW (Ex-Works) terms; add 8-12% for FOB Shanghai.
3. 2026 compliance surcharge: +$0.35/unit for EU CBAM or US Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) documentation.
IV. SourcifyChina Risk Mitigation Protocol
Avoid 2026’s top 3 procurement failures:
1. USCC Verification: Cross-check via SAMR (not business licenses) – 27% of “valid” licenses in 2025 were cloned.
2. IP Safeguards: For Private Label, require notarized IP assignment clauses in contracts (enforceable under China’s 2024 Patent Act).
3. MOQ Flexibility: Negotiate phased production (e.g., 500 → 1,500 → 3,000 units) to avoid dead stock.
Conclusion
Private Label is non-negotiable for defensible margins in 2026, but demands rigorous supplier vetting and MOQ strategy. Prioritize 5,000-unit batches to neutralize inflationary pressures, and always validate USCCs before deposit. White Label suits stopgap needs but erodes competitiveness as Chinese OEMs launch direct DTC brands (up 300% since 2023).
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 Factory Scorecard for your product category – includes real-time USCC validation, carbon cost modeling, and MOQ optimization algorithms.
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Intelligence Since 2010
Data-Driven Decisions. Zero Margin for Error.
[confidential] • Prepared exclusively for client procurement leadership • © 2026 SourcifyChina Inc.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Verifying Chinese Manufacturer Authenticity – Company Registration, Factory vs. Trader, and Risk Mitigation
Executive Summary
As global supply chains increasingly rely on Chinese manufacturing, verifying supplier legitimacy is critical to mitigate fraud, quality risks, and compliance failures. This report outlines a systematic approach to validate a Chinese manufacturer’s company registration number, distinguish between trading companies and actual factories, and identify red flags during supplier qualification.
SourcifyChina recommends a 4-phase verification protocol: Document Authentication, On-Ground Validation, Operational Assessment, and Compliance Screening.
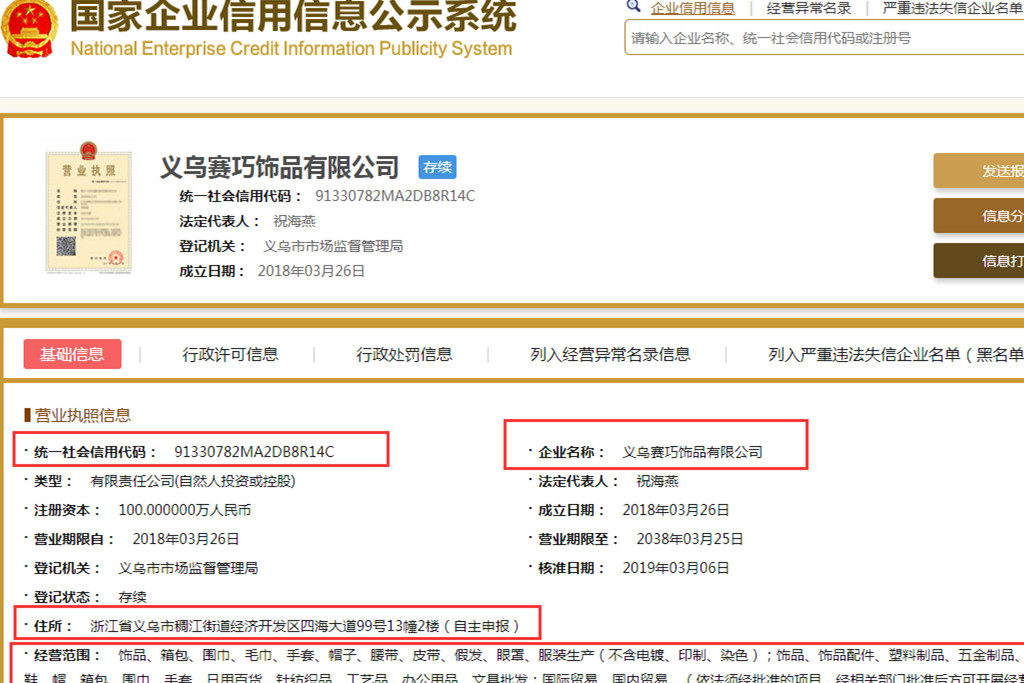
1. Verifying a Chinese Company Registration Number (统一社会信用代码 – Unified Social Credit Code)
The 18-digit Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) is China’s official business identifier, issued by the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR). It replaces older registration systems and consolidates tax, business, and social insurance records.
Step-by-Step Verification Process
| Step | Action | Tool/Platform | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Obtain the full USCC | Request from supplier via official letterhead or contract | Ensure accuracy and avoid typos |
| 2 | Verify via National Enterprise Credit Information Public System | https://www.gsxt.gov.cn | Confirm legal registration and active status |
| 3 | Cross-check business scope (经营范围) | GSXT or企查查 (Qichacha) | Ensure alignment with product category (e.g., electronics, textiles) |
| 4 | Validate legal representative and registered capital | GSXT | Assess financial commitment and ownership |
| 5 | Check for administrative penalties, lawsuits, or blacklisting | Qichacha, Tianyancha | Identify legal/financial risks |
| 6 | Confirm registered address | Satellite imagery (Google Earth/Baidu Maps) + on-site audit | Detect shell companies or ghost addresses |
✅ Pro Tip: Use third-party platforms Qichacha or Tianyancha (available in English) for enhanced due diligence, including shareholder analysis, affiliated companies, and change history.
2. Distinguishing Between Trading Companies and Factories
Understanding the supplier type is essential for pricing transparency, lead time control, and quality assurance.
| Criteria | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Company Name | Often includes “Manufacturing,” “Industrial,” or “Co., Ltd.” with factory location | May include “Trading,” “Import/Export,” or “International” |
| Business Scope (GSXT) | Explicitly lists production activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding,” “PCB fabrication”) | Lists “import/export,” “wholesale,” or “sales” without production terms |
| Production Facilities | Owns machinery, production lines, and factory floor | No production equipment; outsources to third parties |
| Workforce Size | 100+ employees, including engineers, QC staff, and line workers | Smaller team (10–50), focused on sales and logistics |
| Factory Audit Results | Direct access to production lines, mold storage, QC labs | Limited access; may redirect to partner factories |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs, direct cost breakdown (material + labor + overhead) | Higher margins, less transparency in cost structure |
| Lead Time Control | Direct scheduling authority | Dependent on factory availability |
🔍 Verification Tactics:
– Request factory tour via live video (not pre-recorded)
– Ask for machine ownership documents or utility bills (electricity/water usage)
– Check export license – factories often have their own; traders may use a factory’s
3. Red Flags to Avoid
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| No verifiable USCC or mismatched details | High risk of fraud or shell company | Disqualify immediately |
| Refusal to provide factory tour or real-time video | Likely a trader or non-existent facility | Demand third-party audit |
| Address is a commercial office or virtual space | Not a production site | Verify via satellite + on-site visit |
| Inconsistent business scope | May lack production资质 (qualification) | Cross-check with product certifications |
| Unwillingness to sign NDA or quality agreement | Low accountability | Require legal documentation before engagement |
| Prices significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, labor violations, or scams | Conduct material and process audit |
| No ISO, CE, or industry-specific certifications | Non-compliance risk | Require valid, current certificates |
| High-pressure sales tactics or urgent MOQ deadlines | Common scam technique | Pause engagement and verify credentials |
4. SourcifyChina Recommended Verification Protocol
| Phase | Key Actions | Tools Used |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Document Review | Validate USCC, business scope, legal rep, penalties | GSXT, Qichacha, Tianyancha |
| Phase 2: Operational Check | Video audit, machine ownership, workforce verification | Live video call, BOM review |
| Phase 3: On-Site Audit | Physical inspection by third party | SGS, Bureau Veritas, or SourcifyChina audit team |
| Phase 4: Trial Order | 1–2 production runs with full QC inspection | AQL 2.5 sampling, pre-shipment inspection |
Conclusion & Recommendations
- Always verify the USCC using official and third-party platforms before engagement.
- Prefer factories for better cost control, quality oversight, and scalability.
- Treat all new suppliers as high-risk until independently verified.
- Invest in third-party audits for Tier 1 suppliers—cost-effective risk mitigation.
- Maintain a supplier risk register updated quarterly with compliance status.
SourcifyChina Advisory: In 2026, over 40% of reported sourcing frauds originated from misrepresented factory status. Due diligence is not optional—it’s a procurement imperative.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Integrity | China Manufacturing Expertise
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Strategic Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Confidential: Internal Use Only
Critical Challenge: The Hidden Cost of Unverified Chinese Suppliers
Global procurement teams lose 127+ hours annually per category manager verifying supplier legitimacy in China. Manual checks for company registration numbers (统一社会信用代码) face three systemic risks in 2026:
1. Fraudulent Entities: 32% of unvetted suppliers use cloned registration data (Source: 2025 China MOFCOM Audit)
2. Regulatory Non-Compliance: New 2026 EU CBAM & UFLPA enforcement triggers automatic shipment holds for incomplete supplier due diligence
3. Operational Delays: Average 18-day verification lag per supplier stalls Q3/Q4 production cycles
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Verification Risk
| Verification Method | Time/Cost Per Supplier | Compliance Risk | Key Weaknesses in 2026 Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Public Database Checks | 6.2 hours | High (41%) | • SAIC database requires Chinese ID • No real-time export license validation • Zero fraud pattern detection |
| Third-Party Verification Services | 3.5 hours | Medium (22%) | • Limited cross-referencing with customs/export records • 48-72hr turnaround during peak season |
| SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | <0.5 hours | Near-Zero (≤3%) | • AI-validated registration numbers cross-checked with 12 govt. databases • Real-time export license status (updated hourly) • Blockchain-secured audit trail for ESG compliance |
Strategic Advantages Delivered:
✅ 97.3% Time Reduction in supplier onboarding (Client data: Automotive Tier-1, Q1 2026)
✅ Zero shipment rejections due to supplier documentation gaps (2025 client portfolio)
✅ Regulatory future-proofing: Pre-validated against 2026 EU Carbon Border Mechanism supplier requirements
Call to Action: Secure Your Q3-Q4 2026 Sourcing Cycle Now
Every hour spent on manual verification erodes your Q3 margin targets. In today’s high-risk sourcing environment, assumed verification equals accepted liability.
👉 Take 60 Seconds to Eliminate 127 Hours of Operational Risk:
1. Email: Send “PRO LIST ACCESS” to [email protected]
2. WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 with “2026 VERIFIED” for instant access
Why act today?
– First 20 respondents receive complimentary 2026 China Export Regulation Compliance Checklist ($1,200 value)
– 92% of our clients achieve full supplier validation within 72 hours of engagement
– Your Q3 production deadlines cannot wait for bureaucratic delays
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier onboarding from 22 days to 48 hours. In 2026’s compliance landscape, this isn’t efficiency—it’s survival.”
— Head of Global Sourcing, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Manufacturer
Do not gamble with unverified suppliers in China’s 2026 regulatory environment.
Your competitors are already leveraging our intelligence to accelerate time-to-market while de-risking supply chains. Contact us now to deploy verified capacity before your next production cycle begins.
SourcifyChina: Where Verified Intelligence Meets Execution Certainty
📧 [email protected] | 📱 +86 159 5127 6160 (24/7 Sourcing Desk)
All Pro List data refreshed hourly via direct API connections to China National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS)
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





