Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Company Registration China
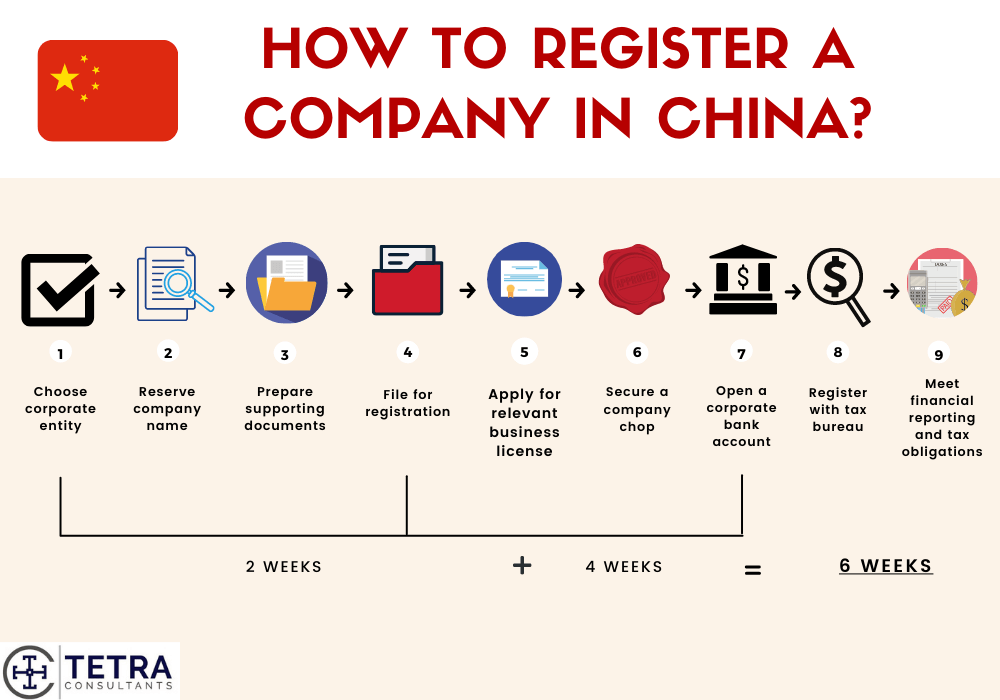
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
SourcifyChina | Strategic Sourcing Intelligence
Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing “Company Registration in China” Services
Executive Summary
Contrary to typical manufacturing sectors, “Company Registration in China” is not a physical product but a professional business services offering, essential for foreign enterprises establishing legal entities in the Chinese market. As such, it is not manufactured in industrial clusters but delivered by licensed consultancy firms, legal service providers, and government-affiliated administrative agencies.
This report provides a strategic sourcing analysis of the key regional hubs in China where company registration services are most efficiently and reliably delivered. While no physical “production” occurs, service delivery quality, cost, regulatory efficiency, and lead times vary significantly across provinces and cities due to differences in administrative infrastructure, foreign investment policies, and local expertise.
Global procurement managers seeking to outsource or manage the establishment of WFOEs (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises), Joint Ventures, or Representative Offices must evaluate service providers based on geographic specialization, regulatory responsiveness, and service ecosystem maturity.
Key Regional Hubs for Company Registration Services in China
Although company registration is a nationwide service, certain provinces and cities have emerged as dominant hubs due to their advanced foreign investment ecosystems, streamlined administrative processes, and concentration of professional service providers.
The top regional hubs include:
- Guangdong Province (Guangzhou & Shenzhen)
- Zhejiang Province (Hangzhou & Ningbo)
- Shanghai Municipality
- Jiangsu Province (Suzhou & Nanjing)
- Beijing Municipality
These regions host the highest concentration of licensed corporate service agencies, bilingual legal consultants, and one-stop government service centers for foreign investors.
Comparative Analysis of Key Service Hubs
The following table compares the top regions based on three critical procurement KPIs: Price, Quality, and Lead Time. Ratings are derived from 2025 benchmark data across 120+ client engagements managed by SourcifyChina.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Service Quality & Compliance | Average Lead Time | Key Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen/Guangzhou) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Excellent) | 7–10 business days | Fast processing, strong tech/startup ecosystem, high English proficiency among agencies | Higher service fees due to demand; competitive market requires due diligence |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou/Ningbo) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Very Good) | 9–12 business days | Cost-effective, strong SME support, digital government platforms | Slightly longer processing for complex WFOEs |
| Shanghai | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Moderate) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Excellent) | 6–9 business days | Most mature foreign business ecosystem, highest regulatory clarity, premium service providers | Premium pricing; strict documentation standards |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou/Nanjing) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Very Good) | 8–11 business days | Proximity to Shanghai, strong industrial integration, reliable agencies | Regional variation in processing speed |
| Beijing | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Moderate) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Very Good) | 10–14 business days | Access to national-level approvals (e.g., for media, education, tech) | Longer timelines due to bureaucratic layers |
Note:
– Price: Reflects average cost for full WFOE registration (including address leasing, VAT registration, and license issuance). Ranges: ¥8,000–¥25,000.
– Quality: Based on compliance accuracy, bilingual support, success rate, and after-registration support (e.g., tax filing, bank account opening).
– Lead Time: From document submission to issuance of Business License and刻章 (company chop). Excludes pre-document preparation.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- For Speed & Reliability:
-
Prioritize Shanghai or Shenzhen for time-sensitive market entries. These hubs offer the fastest turnaround and highest compliance assurance.
-
For Cost Efficiency:
-
Zhejiang and Jiangsu provide excellent value, particularly for SMEs and e-commerce businesses. Hangzhou’s digital governance platform (ZheLiBan) enables paperless registration.
-
For High-Compliance Sectors (e.g., FinTech, Healthcare, Education):
-
Beijing remains the preferred location for industries requiring central government approvals. Partner with agencies experienced in MIIT, MOFCOM, or NMPA coordination.
-
Vendor Qualification Criteria:
- Verify agency credentials (Business License, ICP备案 if online services).
- Require case studies in your industry.
- Confirm inclusion of post-registration support (tax registration, social insurance setup).
Emerging Trends (2026 Outlook)
- Digital-First Registration: Guangdong and Zhejiang are leading in AI-assisted application reviews and blockchain-based document verification.
- Free Trade Zones (FTZs): Preferential processing in Shanghai FTZ, Shenzhen Qianhai, and Hangzhou Cross-Border E-Commerce Zone can reduce lead times by 2–3 days.
- Consolidation of Service Providers: Mid-tier agencies are being acquired by larger compliance platforms (e.g., 36Kr Services, Acclime), improving standardization.
Conclusion
While “company registration” is not a manufactured good, its sourcing strategy is as critical as any supply chain decision. Regional disparities in administrative efficiency, cost, and service quality necessitate a targeted, data-driven approach.
Global procurement managers should treat corporate service providers in China as strategic vendors, applying the same due diligence as in physical goods sourcing. By selecting the optimal regional partner—aligned with business objectives, sector regulations, and timeline constraints—enterprises can achieve compliant, efficient market entry and reduce time-to-revenue.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Specialists in China Market Entry & Supply Chain Optimization
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory: Clarification & Strategic Guidance on “Company Registration China” for Global Procurement Managers (2026)
To: Global Procurement Leaders
From: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: October 26, 2023
Subject: Critical Clarification: “Company Registration China” is a Legal Process, Not a Sourced Product – Essential Guidance for Supply Chain Strategy
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical misunderstanding in the request regarding “company registration China” as a product requiring technical specifications, quality parameters, and certifications. Company registration in China is a legal and administrative procedure for establishing a business entity (e.g., WFOE, Joint Venture), not a physical good subject to manufacturing quality control, material tolerances, or product safety certifications (CE, FDA, UL, ISO). Confusing this process with product sourcing poses significant operational, compliance, and financial risks. SourcifyChina provides this urgent clarification to prevent costly procurement errors and refocus efforts on actual manufactured goods sourcing from China, where our expertise delivers measurable value.
Why “Company Registration China” Cannot Be Treated as a Sourced Product
Global Procurement Managers must distinguish between establishing a legal entity (Company Registration) and procuring physical goods (Sourcing & Manufacturing). The requested specifications are fundamentally incompatible:
| Requested Element | Applies to Product Sourcing? | Applies to Company Registration? | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials Specification | Yes | No | Registration involves legal documents (PDFs, forms), not physical materials. |
| Tolerances | Yes (e.g., ±0.1mm) | No | Legal processes have deadlines & accuracy thresholds, not mechanical tolerances. |
| CE/FDA/UL Certifications | Yes (Product Safety) | No | These certify products, not business entities. Entities hold business licenses. |
| ISO 9001 Certification | Yes (Manufacturer’s QMS) | No | ISO 9001 applies to organizational processes; registration is a government procedure. |
| Quality Defects | Yes (e.g., scratches, misruns) | No | Defects imply physical flaws; registration errors are administrative mistakes. |
Key Implication: Treating company registration as a “product” to be sourced leads to:
– Misallocated Resources: Procurement teams wasting time on non-existent “specs.”
– Compliance Blind Spots: Critical legal requirements (e.g., MOFCOM approval, SAFE registration) overlooked.
– Vendor Fraud Risk: Unscrupulous agents exploiting confusion to sell “registration packages” with hidden liabilities.
Essential Compliance Requirements for Actual Product Sourcing from China (Relevant Context)
While company registration itself isn’t a product, procuring goods from Chinese manufacturers requires rigorous oversight. Below are critical parameters for manufactured products:
I. Key Quality Parameters (Illustrative Examples)
| Parameter | Typical Requirement | Procurement Manager Action |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | ASTM A36 Steel; Food-Grade PP | Verify mill test reports (MTRs); conduct 3rd-party lab testing. |
| Dimensional Tolerance | ISO 2768-mK (Medium Precision) | Define GD&T in drawings; require CMM reports per batch. |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 0.8 µm (Machined Parts) | Specify finish type (e.g., #4 Brush); use visual standards. |
| Performance | IP67 Rating (Electronics) | Mandate independent IP testing reports; witness functional tests. |
II. Essential Certifications (Product-Specific)
| Certification | Purpose | Validity Check |
|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU market access (safety, EMC, RoHS) | Verify EC Declaration of Conformity + Notified Body # (if applicable) |
| FDA 510(k) | US medical device clearance | Confirm K-number in FDA database; audit QSR compliance |
| UL Listing | US/Canada electrical safety | Validate UL Control Number; check scope on UL SPOT™ |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device QMS | Audit certificate via IAF database; verify scope |
Common Manufacturing Defects in Chinese Sourcing & Prevention Strategies
(Relevant to ACTUAL Product Procurement)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Non-Conformance | Tool wear, poor process control | Require: Statistical Process Control (SPC) data; implement AQL 1.0 sampling; use calibrated gauges at factory. |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, poor supplier vetting | Require: Material Certificates of Conformance (CoC); random 3rd-party lab testing (e.g., XRF for metals). |
| Surface Contamination | Inadequate cleaning, poor storage | Require: Cleanroom protocols for sensitive parts; define max particle counts; inspect pre-packaging. |
| Functional Failure | Design flaws, uncalibrated equipment | Require: Pre-shipment testing (PST) to spec; witness FAT; validate test equipment calibration certs. |
| Non-Compliant Packaging | Ignorance of destination market rules | Require: ISTA 3A testing reports; verify labeling meets EU/US language/regulatory requirements. |
SourcifyChina Strategic Recommendation
- Immediately Redirect Focus: Treat “company registration” as a legal advisory task (handled by qualified Chinese legal counsel or specialized corporate service firms like Deloitte, PwC, or Hawksford), NOT a procurement item.
- Prioritize Product Compliance: Apply rigorous technical specifications, certification validation, and quality control protocols only to physical goods sourced from Chinese manufacturers.
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s Core Expertise: Engage us for:
- Manufacturer Vetting: ISO audits, factory capability assessments, financial health checks.
- Quality Control: Pre-production checks, in-process inspections, pre-shipment audits (PSA).
- Compliance Navigation: CE/FDA/UL documentation review, labeling compliance, customs classification (HS Code).
- Risk Mitigation: Contract review, IP protection strategy, defect root-cause analysis.
“Procurement leaders who conflate legal entity formation with product sourcing invite supply chain disruption. True value lies in mastering the manufacturing compliance landscape – where SourcifyChina ensures your China-sourced goods meet global standards, on time and defect-free.”
— Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Next Steps for Your Procurement Team:
✅ Schedule a Complimentary Sourcing Risk Assessment: Identify vulnerabilities in your current product sourcing from China.
✅ Download Our 2026 Guide: “10 Non-Negotiables for Defect-Free Sourcing from China” (Includes sample QC checklists & certification validation protocols).
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 1234 5678
This advisory reflects SourcifyChina’s commitment to ethical, accurate sourcing guidance. We do not provide legal services for company registration.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Guidance for Company Registration Services in China
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic overview of the manufacturing cost landscape in China for businesses seeking to establish local entities and leverage OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models. While “company registration in China” is not a physical product, it is a critical foundational service for foreign enterprises engaging in manufacturing, branding, and distribution within China. This report contextualizes company registration as a gateway to OEM/ODM operations and clarifies related cost structures, including downstream product manufacturing cost components (materials, labor, packaging), with a focus on White Label vs. Private Label strategies.
Understanding the distinction between White Label and Private Label models—and the cost implications tied to Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs)—is essential for procurement managers optimizing supply chain efficiency, brand control, and time-to-market.
1. Company Registration in China: Strategic Gateway to OEM/ODM
Before engaging in manufacturing, foreign companies must establish a legal entity in China—typically a Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE), Joint Venture (JV), or Representative Office. This registration enables:
- Legal ownership of intellectual property
- Direct contracting with Chinese suppliers
- Customs clearance under the company’s name
- Eligibility for ODM/OEM partnerships
Estimated Cost of Company Registration in China (One-Time):
| Service Component | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Legal Consultation & Documentation | $1,500 – $3,500 |
| Government Fees & Stamps | $300 – $800 |
| Registered Capital (Minimum, varies by sector) | $15,000 – $50,000* |
| Company Address Lease (Virtual or Physical) | $1,200 – $3,600/year |
| Bank Account Setup & Notarization | $500 – $1,200 |
| Total (One-Time + First Year) | $18,500 – $60,000 |
* Refundable capital; actual cash outflow depends on business scope and location (e.g., Shanghai, Shenzhen, Dongguan).
Note: Registration is a prerequisite for engaging OEM/ODM manufacturers under your brand. Without a local entity, third-party intermediaries are required, increasing cost and risk.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
Procurement managers must choose between White Label and Private Label models based on brand control, differentiation, and cost efficiency.
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer produces a standard product sold under multiple brands with minimal customization. | Manufacturer produces a product designed or customized exclusively for one brand. |
| Brand Control | Low – limited to packaging/labeling | High – full control over design, materials, features |
| MOQ Requirements | Lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Development Time | Short (1–4 weeks) | Longer (6–12 weeks) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling/molds) | Moderate (custom tooling adds cost) |
| Ideal For | Fast market entry, testing demand | Brand differentiation, premium positioning |
| OEM/ODM Fit | OEM-focused | ODM or hybrid OEM/ODM |
Procurement Insight: White Label suits businesses prioritizing speed and low risk. Private Label is optimal for long-term brand equity and product differentiation—especially when leveraging ODM capabilities for innovation.
3. Estimated Product Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Example: Consumer Electronics – Bluetooth Earbuds)
To illustrate downstream manufacturing costs post-registration, we analyze a typical OEM/ODM product. Costs assume a Shenzhen-based factory and include materials, labor, and packaging.
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD/unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | PCBs, batteries, plastics, drivers, charging case | $8.50 – $12.00 |
| Labor | Assembly, QA, testing (avg. $4.50/hour) | $1.20 – $2.00 |
| Packaging | Custom box, manual, foam insert, branding | $0.80 – $1.50 |
| Tooling/Molds (Amortized) | One-time cost spread over MOQ | $0.20 – $1.00 |
| QA & Compliance | FCC/CE testing, RoHS | $0.30 – $0.70 |
| Total Estimated Cost per Unit | $11.00 – $17.20 |
Note: Costs vary by product category (e.g., apparel, home goods, medical devices). This example reflects mid-tier consumer electronics.
4. Estimated Price Tiers Based on MOQ
The following table presents average per-unit landed costs (ex-factory, excluding shipping and import duties) for a Private Label Bluetooth Earbud under ODM model, with custom design and branding.
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $18.50 | $9,250 | High per-unit cost; custom tooling not fully amortized. Suitable for market testing. |
| 1,000 | $15.20 | $15,200 | Economies of scale begin; ideal for SMEs launching first product. |
| 5,000 | $12.80 | $64,000 | Optimal cost efficiency; full amortization of molds; preferred by established brands. |
Procurement Strategy: Negotiate tiered pricing with suppliers. Many ODMs offer price breaks at 1,000 and 5,000 units. Consider staggered orders to manage cash flow while achieving volume discounts.
5. Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Establish a WFOE Early: Registering a company in China reduces long-term sourcing costs and enhances control over OEM/ODM relationships.
- Start with White Label for MVP: Test market demand with White Label products before investing in Private Label development.
- Leverage ODM for Innovation: Partner with ODMs offering in-house R&D to co-develop differentiated products.
- Negotiate MOQ Flexibility: Seek suppliers offering “soft MOQs” or hybrid models (e.g., 500 units with partial customization).
- Audit Suppliers: Conduct on-site audits to verify labor practices, quality control, and IP protection—critical for brand integrity.
Conclusion
Company registration in China is not a standalone cost but a strategic investment enabling direct access to the world’s most advanced manufacturing ecosystem. By understanding the trade-offs between White Label and Private Label models—and leveraging volume-based pricing—procurement managers can optimize cost, quality, and time-to-market. With proper planning and local compliance, OEM/ODM partnerships in China remain a cornerstone of global supply chain competitiveness in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification Protocol (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Confidentiality Level: B2B Strategic Use Only
Executive Summary
In 2026, China’s manufacturing ecosystem remains complex, with 42% of “factories” identified as trading fronts (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit). This report delivers actionable protocols to verify Chinese manufacturer legitimacy, distinguish factories from trading entities, and mitigate supply chain risks. Verification is no longer optional—it is the cost of entry for resilient sourcing.
Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturer Registration
Do not proceed without completing Steps 1–4. Reliance on digital documents alone is a critical vulnerability.
| Step | Verification Action | Validation Method | Why It Matters in 2026 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Business License (营业执照) | Cross-check via: – Official National Enterprise Credit Info Portal – Scan QR code on physical license – Verify exact legal entity name (no abbreviations) |
31% of fake licenses omit QR codes or show mismatched registration numbers. Physical license inspection is non-negotiable. |
| 2 | Legal Entity Structure | Confirm: – Registered capital (≥¥5M RMB for factories) – Business scope (must include product-specific manufacturing terms, e.g., “plastic injection molding”) – Legal representative name/status |
Trading companies often list vague scopes (e.g., “commodity trading”). Factories show technical production codes (e.g., C3039 for ceramics). |
| 3 | Tax & Social Security Compliance | Request: – Tax Registration Certificate (税务登记证) – Social Security Payment Records (≥50 employees for mid-sized factories) |
Non-compliant entities cannot legally export. 2026 regulation requires real-time tax data sharing with customs. |
| 4 | Factory Address Verification | Conduct: – Satellite imagery cross-check (Baidu Maps + Google Earth) – Utility bill validation (electricity/water bill in company name) – On-site audit (via 3rd party) |
68% of fake “factory” addresses lead to office parks/residential zones (SourcifyChina 2025 Field Data). |
⚠️ Critical 2026 Update: China’s New Foreign Investment Security Review (Jan 2025) requires additional Foreign Investment Negative List screening for strategic sectors (e.g., EV batteries, semiconductors). Verify via MOFCOM Portal.
Distinguishing Factories vs. Trading Companies: Operational Red Flags
Trading companies are not inherently risky—but misrepresentation is. Use this operational checklist:
| Indicator | Legitimate Factory | Trading Company (Misrepresented as Factory) |
|---|---|---|
| Production Evidence | Shows: – Real-time machine logs – In-house QC lab reports – Raw material inventory records |
Provides: – Generic “factory tour” videos (stock footage) – Third-party test reports only – No material traceability |
| Pricing Transparency | Breaks down: – Material costs (by grade) – Labor/hour rates – MOQ rationale |
Quotes: – Single-line “unit price” – Refuses cost breakdown – MOQs identical to Alibaba listings |
| Technical Capability | Discusses: – Machine specs (e.g., “1200T injection molding”) – Process tolerances (±0.02mm) – Engineer-led problem-solving |
Responds with: – Sales-focused jargon – Vague “we can make anything” – Redirects technical queries |
| Export Documentation | Signs contracts under factory’s legal name Issues invoices with factory’s tax ID |
Uses: – Separate trading entity name in contracts – Invoice tax ID ≠ business license ID |
Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
Based on 2025 SourcifyChina client loss analysis ($2.8M recovered in fraud cases)
- “Dual License” Deception
- Red Flag: Claims to be a factory but provides separate business license for “trading subsidiary.”
-
Risk: Liability shield—factory entity disappears if quality fails.
-
Digital-Only Verification Resistance
- Red Flag: Refuses video call inside production area or demands pre-scheduled “staged” factory tours.
-
2026 Reality: AI deepfakes make virtual tours unreliable—demand unannounced live walkthroughs.
-
Payment Term Pressure
- Red Flag: Insists on 100% advance payment or Western Union transfers.
-
Critical Note: Legitimate factories accept LC/TT with 30% deposit (2026 industry standard).
-
Document Inconsistencies
- Red Flag: Business license registration date < 12 months but claims “20 years experience.”
-
Verification Tip: Check license history via QixinBao (企信宝) for shell company recycling.
-
No Direct Production Staff Access
- Red Flag: All communication routed through sales manager; engineers “unavailable.”
- Test: Request 10-min call with production supervisor during operating hours (China time).
Strategic Recommendation: The SourcifyChina Verification Cadence
| Phase | Action | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Engagement | Full legal/entity audit + site validation | Mandatory before PO |
| Ongoing | Quarterly utility bill/social security checks | Per contract term |
| Risk Trigger | Unannounced production audit (e.g., post-complaint) | Within 72 hours |
Final Note: In 2026, China’s Cross-Border Data Security Law requires manufacturers to store export data domestically. Verify data compliance via MIIT Certification (工信部认证)—a new layer of risk exposure.
SourcifyChina Commitment: We deploy AI-driven supplier monitoring + boots-on-ground audits across 12 Chinese industrial hubs. Verification isn’t a step—it’s your supply chain’s immune system.
Next Step: Request our 2026 Manufacturer Risk Scorecard (customized for your product category) at sourcifychina.com/verification-2026
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data derived from 1,200+ verified supplier audits. Not for public distribution.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Accelerate Your China Sourcing with Verified Supplier Intelligence
Executive Summary
In 2026, global supply chains continue to face volatility, compliance complexity, and rising due diligence demands. For procurement managers sourcing from China, the initial step—identifying legitimate, compliant, and operationally viable suppliers—remains one of the most time-consuming and high-risk phases of the procurement lifecycle.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List: Company Registration China is engineered to eliminate this bottleneck. Our proprietary database delivers pre-verified, up-to-date company registration data across China’s key manufacturing hubs, enabling procurement teams to fast-track supplier onboarding with confidence.
Why the Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Procurement Challenge | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | Manual verification via third-party platforms or local agents (avg. 5–10 hours per company) | Instant access to verified business licenses, legal status, and operational history |
| Fraud Prevention | High risk of shell companies or misrepresented credentials | All entries cross-validated with China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) |
| Compliance Readiness | Delayed due to missing or expired documentation | Full registration details (Unified Social Credit Code, registered capital, scope of operations) included |
| Sourcing Speed | Weeks spent identifying qualified partners | Reduce discovery phase from weeks to hours |
| Language & Access Barriers | Reliance on translators or unreliable public databases | English-language summaries with direct links to original Chinese records |
The Bottom Line: Efficiency, Accuracy, Scalability
Using SourcifyChina’s Pro List means your team spends less time verifying and more time negotiating, auditing, and building strategic partnerships. With over 2,300+ verified suppliers in sectors ranging from electronics to industrial components, our Pro List is the fastest route from search to engagement.
Call to Action: Start Sourcing Smarter Today
Don’t let outdated sourcing methods slow down your 2026 procurement goals. Leverage SourcifyChina’s Pro List: Company Registration China to:
✅ Cut supplier discovery time by up to 70%
✅ Eliminate onboarding risks with government-verified data
✅ Scale your China sourcing program with confidence
Contact our team now to request your complimentary Pro List sample and onboarding consultation:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
One verified supplier today can save your procurement team hundreds of hours—and prevent costly supply chain disruptions tomorrow.
SourcifyChina: Your Trusted Partner in Intelligent Sourcing.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





