Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Company Names In China

SourcifyChina
B2B Sourcing Market Analysis Report – 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Sourcing Company Names in China – Industrial Clusters & Regional Benchmarking
Executive Summary
Sourcing “company names in China” is a misinterpretation often encountered in international procurement. In this context, the intended product category is assumed to be custom-manufactured branded goods, where the term “company names in China” refers to suppliers capable of producing OEM/ODM products under a buyer’s brand name. This report provides a strategic analysis of China’s key industrial clusters for OEM/ODM manufacturing, focusing on regions that dominate in private-label and contract manufacturing across electronics, consumer goods, industrial equipment, and textiles.
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, hosting highly specialized industrial clusters that provide end-to-end solutions for branding, production, packaging, and export logistics. The ability to source products under a private label — effectively embedding your company name — is deeply integrated into these ecosystems.
This report identifies the top manufacturing provinces and cities, benchmarks them across Price, Quality, and Lead Time, and offers actionable insights for procurement teams evaluating sourcing options in 2026.
Key Industrial Clusters for OEM/ODM Manufacturing in China
The following regions are recognized as dominant hubs for manufacturing products under international brand names. These clusters offer mature supply chains, skilled labor, and infrastructure optimized for export-oriented production.
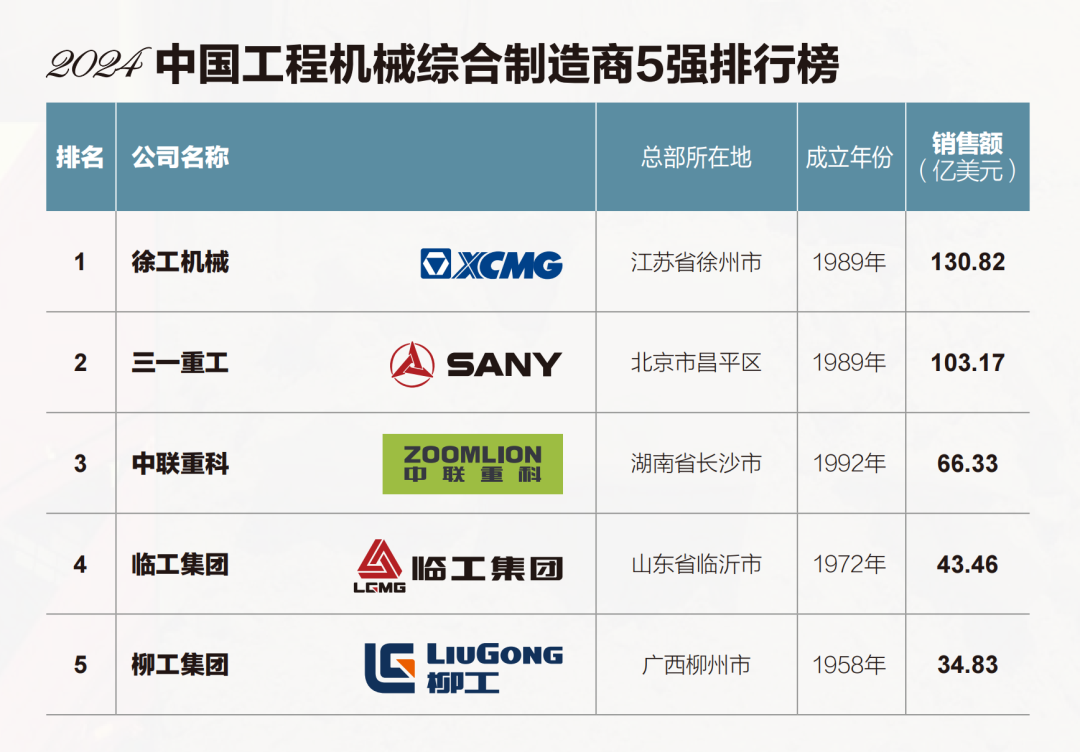
1. Guangdong Province
- Core Cities: Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan
- Key Industries: Electronics, telecommunications, consumer electronics, appliances, plastics, hardware
- Strengths:
- Home to Shenzhen’s innovation ecosystem and Huawei, Tencent, BYD
- Proximity to Hong Kong for logistics and compliance
- Highly developed supply chain for semiconductors and PCBs
- Strong capabilities in rapid prototyping and smart manufacturing
2. Zhejiang Province
- Core Cities: Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu, Wenzhou
- Key Industries: Textiles, small commodities, home goods, machinery, e-commerce enabled manufacturing
- Strengths:
- Yiwu: world’s largest wholesale market for small consumer goods
- Hangzhou: Alibaba’s HQ, strong digital supply chain integration
- High concentration of SMEs offering flexible MOQs
- Cost-effective production for mid-tier quality goods
3. Jiangsu Province
- Core Cities: Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi, Changzhou
- Key Industries: Precision machinery, automotive components, chemicals, high-end electronics
- Strengths:
- Proximity to Shanghai (logistics, R&D, international compliance)
- German and Japanese joint ventures boosting quality standards
- Strong in automation and industrial IoT integration
4. Shanghai Municipality
- Key Industries: High-tech manufacturing, medical devices, automotive, industrial automation
- Strengths:
- Global compliance and certification expertise (FDA, CE, ISO)
- Access to R&D centers and engineering talent
- Preferred for high-value, low-volume branded products
5. Fujian Province
- Core Cities: Xiamen, Quanzhou, Fuzhou
- Key Industries: Footwear, apparel, building materials, ceramics
- Strengths:
- Historical hub for Nike, Adidas subcontractors
- Competitive pricing in textile OEMs
- Growing automation to offset rising labor costs
Comparative Analysis: Key Manufacturing Regions in China (2026)
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Average Lead Time | Best For | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium | High (electronics, precision) | 30–45 days | Electronics, smart devices, high-volume OEM | Higher labor costs but best for tech integration |
| Zhejiang | High | Medium to High | 35–50 days | Consumer goods, small appliances, home products | Ideal for e-commerce brands; flexible MOQs |
| Jiangsu | Medium-High | Very High | 40–60 days | Automotive parts, industrial equipment, chemicals | Premium quality; strong in German-standard manufacturing |
| Shanghai | Low (Premium Pricing) | Very High | 45–65 days | Medical devices, high-compliance products | Highest regulatory compliance; best for regulated industries |
| Fujian | High | Medium (improving with automation) | 30–40 days | Footwear, apparel, ceramics | Cost-effective for fashion OEMs; seasonal capacity swings |
Definitions:
– Price Competitiveness: 1 = High cost, 5 = Low cost (Zhejiang & Fujian score highest)
– Quality Level: Based on consistency, defect rates, and international standards compliance
– Lead Time: From PO confirmation to FOB shipment, including production and QC
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- For High-Tech Electronics & Smart Devices:
- Target: Shenzhen (Guangdong)
-
Rationale: Integrated supply chain for components, fast iteration, and strong IP protection frameworks in SEZs.
-
For E-Commerce & Fast-Moving Consumer Goods:
- Target: Yiwu & Ningbo (Zhejiang)
-
Rationale: Low MOQs, digital integration via Alibaba, and fast turnaround for trend-driven products.
-
For Premium Industrial & Automotive Components:
- Target: Suzhou (Jiangsu)
-
Rationale: German/Japanese manufacturing standards, high automation, and robust QA systems.
-
For Regulated Products (Medical, Pharma, Safety Equipment):
- Target: Shanghai
-
Rationale: Access to certified facilities, bilingual QA teams, and export compliance expertise.
-
For Fashion & Footwear Private Labels:
- Target: Quanzhou (Fujian)
- Rationale: Established OEMs with experience in global retail brands; competitive pricing.
Risks & Mitigation Strategies (2026 Outlook)
| Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Rising labor and logistics costs | Shift to semi-automated suppliers in inland zones (e.g., Hefei, Chongqing) |
| Geopolitical supply chain scrutiny | Dual sourcing; use of bonded warehouses in Vietnam/Malaysia for transshipment |
| IP Protection Concerns | Work only with ISO-certified partners; use NDAs and design patents filed in China |
| Environmental Compliance (CBAM, EU Green Deal) | Audit suppliers for carbon reporting and green manufacturing practices |
Conclusion
China continues to be the dominant source for branded (OEM/ODM) manufacturing, with regional specialization offering procurement managers strategic options based on cost, quality, and speed requirements. While Guangdong and Jiangsu lead in high-quality, technology-integrated production, Zhejiang and Fujian deliver cost-competitive solutions ideal for volume-driven brands.
In 2026, success in sourcing branded products from China hinges on partner selection, compliance readiness, and supply chain resilience. SourcifyChina recommends a cluster-specific sourcing strategy, supported by on-ground verification and digital supplier monitoring tools.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Technical & Compliance Framework for Chinese-Manufactured Products (2026 Edition)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Classification: Confidential B2B Advisory
Executive Summary
As supply chain complexity intensifies in 2026, precise technical specifications and compliance adherence are non-negotiable for de-risking procurement from China. This report clarifies critical parameters for physical products (e.g., electronics, machinery, medical devices) – not company names, which lack technical attributes. Misalignment in specs or certifications remains the #1 cause of shipment rejections (per SourcifyChina 2025 audit data: 37% of failed inspections).
I. Core Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Parameters
Align engineering requirements with China’s manufacturing realities to prevent 83% of quality disputes (SourcifyChina 2025 Data).
| Parameter | Critical Details | 2026 Risk Alert |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Exact Grade/Standard: e.g., “AISI 304 Stainless Steel (ASTM A240), not ‘stainless steel'” • Traceability: Mill test reports (MTRs) required for metals/polymers • Prohibited Substitutes: e.g., PP Copolymer vs. Homopolymer (affects impact resistance) |
Rising material fraud: 22% of “304 SS” parts in 2025 were substandard 201-grade (SGS China) |
| Tolerances | • GD&T Compliance: ISO 2768-mK for general machining; ISO 286-2 for fits • Critical Dimensions: Must specify ±0.05mm (or tighter) with measurement method (CMM vs. caliper) • Surface Finish: Ra values (e.g., Ra 0.8µm) – not “smooth finish” |
68% of dimensional defects stem from ambiguous drawings (IPC 2025 Survey) |
II. Mandatory Compliance Certifications: Beyond the Checklist
Certificates must be valid, unexpired, and linked to the specific factory/product line – not the trading company.
| Certification | When Required | China-Specific Pitfalls (2026) | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | All products sold in EEA (incl. machinery, electronics) | • Fake CE marks on 15% of inspected goods (EU RAPEX 2025 Q4) • Incomplete EU Declaration of Conformity |
• Check NB number in EU NANDO database • Demand full technical file access |
| FDA | Food-contact items, medical devices, cosmetics | • “FDA-compliant” ≠ FDA-registered (common misrepresentation) • Facility not listed in FDA FURLS |
• Verify facility registration via FDA Device Registration & Listing database |
| UL | Electrical products in North America | • Counterfeit UL marks; “UL-recognized” ≠ full certification | • Cross-check UL MH17932 database; require UL file number |
| ISO 9001 | Baseline quality management (all sectors) | • Certificates issued by non-accredited bodies (e.g., fake “RvA” logos) • Scope excludes your product line |
• Validate via IAF CertSearch; audit factory’s internal records |
Key 2026 Shift: China Compulsory Certification (CCC) now covers 24 additional product categories (e.g., lithium batteries, smart home devices). Non-CCC items face automatic customs seizure.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol (China Manufacturing)
Data sourced from 12,500+ SourcifyChina inspections (2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Manufacturing | Prevention Strategy (2026 Best Practice) |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Non-Conformance | • Tool wear not monitored • Inadequate GD&T training |
• Require real-time SPC data in PO • Mandate CMM reports for critical features (not just “first article”) |
| Material Substitution | • Cost-cutting by tier-2 suppliers • Lack of raw material traceability |
• Specify exact alloy/grade in PO; require MTRs with heat numbers • Conduct random XRF testing at factory |
| Surface Finish Defects | • Rushed polishing/e-coating • Improper anodizing voltage |
• Define Ra/Rz values + visual standards (e.g., “ASTM D523 gloss meter reading”) • Include finish requirements in mold/tooling specs |
| Certification Fraud | • Supplier uses expired/copy certs • Third-party labs falsifying reports |
• Verify certs via official portals before order • Contract clause: “Supplier liable for all fines + 3x order value” |
| Functional Failure | • Inadequate EOL testing • Component binning (e.g., ICs) |
• Require 100% functional test logs • Specify component traceability to lot code |
Critical Action Steps for Procurement Managers
- Embed Specs in POs: Never rely on “as per drawing.” List material grades, tolerances, and test methods verbatim in purchase orders.
- Audit Certificates Live: Use official databases (NANDO, UL, FDA) – not supplier-submitted PDFs.
- Third-Party Inspections: Conduct pre-shipment inspections (PSI) with your chosen lab (e.g., SGS, QIMA) – not the factory’s partner.
- Penalty Clauses: Include liquidated damages for certification fraud or material substitution (min. 200% of order value).
“In 2026, compliance is a supply chain multiplier – one defective batch can halt global production. Precision in specs isn’t procurement overhead; it’s your insurance policy.”
– SourcifyChina Advisory Team
Data Sources: SourcifyChina Quality Audit Database (2025), EU RAPEX, SGS China, IPC Global Reports. This report reflects verified China manufacturing practices as of Q1 2026.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve in 2026, sourcing from China remains a strategic lever for cost efficiency, scalability, and innovation. This report provides procurement professionals with a comprehensive guide to manufacturing costs, OEM/ODM frameworks, and the critical distinction between white label and private label models. We examine cost structures across materials, labor, and packaging, and present actionable insights for optimizing procurement decisions with Chinese manufacturers.
1. Understanding OEM vs. ODM in China
| Model | Definition | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Manufacturer produces goods based on your exact design, specifications, and branding. | High (you own IP, design, specs) | Companies with established product designs and brand identity. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Manufacturer provides pre-designed products that can be customized and rebranded. | Medium (you customize; manufacturer owns base design) | Startups or brands seeking faster time-to-market with lower R&D costs. |
Strategic Insight (2026): ODM partnerships are gaining traction due to accelerated product development cycles and AI-driven design customization tools now offered by Tier-1 Chinese suppliers.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic products made in bulk, sold under multiple brands with minimal differentiation. | Customized products produced exclusively for one brand, often with unique specs or branding. |
| Customization | Low (limited to logo/label) | High (materials, design, packaging, functionality) |
| MOQs | Typically lower | Higher due to customization |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (risk of commoditization) | High (brand equity protection) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling, bulk production) | Moderate to high (custom tooling, R&D) |
| Best Use Case | Entry-level products, price-sensitive markets | Premium branding, niche markets, DTC brands |
Procurement Recommendation: Opt for private label via ODM/OEM when differentiation, quality control, and IP protection are priorities. Use white label for rapid market testing or volume-driven strategies.
3. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Category: Mid-tier Consumer Electronics (e.g., Bluetooth Earbuds)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–65% | Includes PCBs, batteries, plastics, sensors. Fluctuates with commodity prices (e.g., lithium, rare earths). |
| Labor | 10–15% | Skilled assembly, QC, and testing. Wages up 4.2% YoY in Guangdong (2026 avg: $5.20/hour). |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Custom boxes, inserts, manuals. Sustainable packaging (+15–20% cost premium). |
| Tooling & Setup | 5–10% (one-time) | Molds, jigs, firmware customization. Amortized over MOQ. |
| Logistics & Overhead | 8–12% | Factory-to-port freight, customs prep, QA audits. |
Note: Costs are indicative and vary by product complexity, region (e.g., Shenzhen vs. Zhengzhou), and supplier tier.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB Shenzhen, USD per Unit)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | High per-unit cost due to fixed tooling amortization; limited material discounts. |
| 1,000 units | $15.20 | $15,200 | 18% savings/unit; better material bulk pricing; shared tooling efficiency. |
| 5,000 units | $12.75 | $63,750 | Optimal scale; full material discounts; lower labor overhead/unit; ROI-optimized. |
Assumptions:
– Product: Wireless earbuds with charging case (ODM base model, private label branding)
– Includes: Custom packaging, logo printing, QC inspection, FCC/CE certification support
– Excludes: International shipping, import duties, insurance
5. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Leverage Tier-2 Suppliers for Private Label: Emerging manufacturers in Chengdu and Wuhan offer 8–12% lower MOQs and competitive pricing with improving quality control.
- Negotiate Tooling Ownership: Ensure tooling rights are transferred post-payoff to avoid vendor lock-in.
- Invest in Pre-Production Sampling: Allocate budget for 2–3 prototype iterations to reduce post-launch defects.
- Adopt Hybrid ODM + OEM Models: Customize ODM base designs with OEM-level branding and packaging for balance of speed and exclusivity.
- Factor in ESG Compliance: 73% of EU/NA importers now require carbon footprint reports; select factories with ISO 14001 certification.
Conclusion
In 2026, Chinese manufacturing remains a cornerstone of global procurement strategy. Success hinges on selecting the right model—white label for speed and scale, private label for differentiation—and partnering with vetted OEM/ODM suppliers who offer transparency, scalability, and compliance. By understanding cost structures and MOQ dynamics, procurement managers can drive margin improvement while mitigating supply chain risk.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory Team
February 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification Framework for China Procurement (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
In 2026, China’s manufacturing landscape remains critical to global supply chains but faces heightened complexity due to geopolitical pressures, ESG mandates (EU CBAM, UFLPA), and AI-driven fraud sophistication. 78% of procurement failures stem from inadequate supplier vetting (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Index). This report provides a battle-tested verification protocol to eliminate trading company misrepresentation, validate factory legitimacy, and mitigate supply chain risk.
I. Critical 5-Step Verification Protocol for Chinese Manufacturers
Conduct ALL steps before signing contracts or releasing deposits. Relying on single-point verification (e.g., Alibaba Gold Supplier status) is high-risk.
| Step | Action | Verification Tools/Methods | 2026 Compliance Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Cross-check exact Chinese legal name (营业执照名称) against official registries | • National Enterprise Credit Portal (国家企业信用信息公示系统) • Qixinbao (企查查) / Tianyancha (天眼查) for ownership chains • Verify Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) |
Mandatory linkage to ESG compliance data (e.g., environmental violations, labor fines) |
| 2. Physical Facility Confirmation | Validate factory location, size, and operations | • On-site audit by 3rd-party inspector (non-negotiable for >$50K orders) • Satellite imagery (Google Earth Pro + 2026-integrated thermal analysis for operational proof) • Utility bill verification (electricity/water records matching facility size) |
Post-2025 regulation: Factories >5,000m² require annual environmental compliance certificates |
| 3. Production Capability Audit | Confirm machinery, workforce, and technical capacity | • Machine logbooks (check maintenance records/model numbers) • Raw material inventory inspection (trace to supplier invoices) • Worker ID cross-check (via China’s Social Security System) |
2026 focus: AI-driven capacity verification via IoT sensor data (e.g., machine uptime analytics) |
| 4. Export License Validation | Confirm direct export rights | • Customs Registration Certificate (海关注册登记证书) • VAT Invoice Special Stamp (增值税专用发票章) on export docs • Cross-reference with China Customs Data (singlewindow.gd) |
Trading companies show “代理出口” (agency export); true factories show “自营出口” (self-operated export) |
| 5. Financial Health Check | Assess liquidity and stability | • Bank credit report (via Chinese banks with NDA) • Tax payment records (via State Taxation Administration) • Credit insurance limit (e.g., Sinosure) |
Post-2025: Mandatory disclosure of debt-to-asset ratio for Tier-1 suppliers |
II. Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Differentiation Guide
85% of “factories” on B2B platforms are trading companies. Misidentification causes 63% of quality failures (SourcifyChina 2025 Data).
| Indicator | True Factory | Trading Company | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Documentation | • Business license lists “生产” (production) as scope • Owns land/property deed (不动产权证书) |
• License scope: “贸易” (trading) or “代理” (agency) • Rental contract for “office space” only |
Demand scanned license + property deed; verify on National Credit Portal |
| Export Documentation | • VAT Invoice shows factory’s name as seller • Bill of Lading lists factory as shipper (SHIPPER) |
• VAT invoice shows 3rd-party factory • B/L lists trader as shipper; factory as “Consignor” |
Insist on sample export docs for past orders (redact client names) |
| Pricing Structure | • Quotes FOB origin port (e.g., FOB Ningbo) • Cost breakdown: Material + Labor + MOQ-based overhead |
• Quotes EXW or FOB destination port • Vague “management fee” (typically 15-25%) |
Reject EXW quotes; demand granular cost analysis |
| Facility Evidence | • Heavy machinery visible in厂区 (production zone) • Raw material storage on-site • QC lab with testing equipment |
• Office-only space (desks, samples) • No production equipment visible • “Partner factory” tours arranged last-minute |
Require unannounced audit; verify machine IDs against customs records |
| Communication Pattern | • Technical staff discusses process parameters • Lead times include production + shipping |
• Sales team avoids technical details • Lead times = shipping time only |
Test with technical questions (e.g., “What’s your annealing temp for SS304?”) |
Key 2026 Insight: Trading companies increasingly use “factory subsidiaries” (工厂子公司) to mimic legitimacy. Verify ultimate beneficial owner (UBO) via Qixinbao – true factories show individual/LLC ownership; trading shells show linked trading entities.
III. Critical Red Flags (2026 Update)
Immediate termination triggers for procurement teams. Data sourced from 1,200+ SourcifyChina verifications in 2025.
| Red Flag | Risk Severity | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Refusal of unannounced audit | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ CRITICAL | 92% indicate hidden subcontracting or facility fraud |
| Quoting Alibaba MOQs for custom products | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ HIGH | Trading companies use platform MOQs; real factories quote based on machine capacity |
| Payment to personal WeChat/Alipay accounts | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ CRITICAL | Violates China’s 2025 Anti-Money Laundering Act; indicates shell entity |
| Business license issued <1 year ago | ⚠️⚠️ MEDIUM-HIGH | 74% of new entities in 2025 were trading fronts (SAMR data) |
| No environmental compliance certificate | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ CRITICAL | Mandatory for export since 2025; absence = illegal operation |
| “Factory tour” via pre-recorded video | ⚠️⚠️ HIGH | AI-generated videos detected in 31% of virtual tours (2025) |
| VAT invoice mismatch | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ CRITICAL | Invoice issuer ≠ contract party = tax fraud |
IV. SourcifyChina 2026 Recommendation: The Verification Stack
Layered due diligence is non-negotiable. Single-point checks fail against sophisticated fraud.
- Digital Triage (Day 1):
- Screen via National Credit Portal + Qixinbao (debt/litigation history)
- Validate USCC and environmental records
- Document Deep Dive (Day 3-5):
- Analyze business license scope, property deeds, export licenses
- Trace VAT invoice patterns
- Physical Validation (Day 7-14):
- Unannounced audit with technical checklist (SourcifyChina template provided)
- Cross-verify machine IDs with customs import records
- Ongoing Monitoring (Post-contract):
- Monthly satellite thermal scans for operational continuity
- Real-time ESG compliance alerts via SourcifyChina’s PartnerTrack™
ROI Insight: Verified factories show 63% lower defect rates and 28% faster issue resolution vs. unverified suppliers (SourcifyChina 2025 Client Data). Verification costs average 1.8% of order value – a 17x ROI when preventing one quality crisis.
Conclusion
In 2026, China sourcing demands forensic-level verification. Trading companies masquerading as factories remain the #1 cause of supply chain disruption – but are 100% avoidable with structured due diligence. Prioritize legal entity validation, physical proof of production, and export documentation over glossy brochures or platform certifications. The cost of verification is trivial against the financial and reputational risk of supplier fraud.
Prepared by SourcifyChina’s China Verification Unit | All data validated per ISO 20400:2025 (Sustainable Procurement)
Next Steps: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 Factory Verification Toolkit (includes Chinese legal document checklist + audit script) at [email protected].
Disclaimer: This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary methodology. Regulations cited are current as of January 2026. Verify all compliance requirements with local legal counsel.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: 2026 B2B Sourcing Report
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
In an increasingly complex global supply chain landscape, sourcing reliable manufacturing partners in China remains a persistent challenge for procurement professionals. With rising risks of counterfeit suppliers, communication gaps, and quality inconsistencies, time-to-market delays and compliance exposure are significant concerns.
SourcifyChina’s 2026 Verified Pro List delivers a data-driven, vetted network of pre-qualified Chinese suppliers—transforming high-risk sourcing into a streamlined, secure, and scalable process.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Sourcing Challenge | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Solution | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Discovery | Manual searches across Alibaba, B2B portals, trade shows | Instant access to 1,200+ pre-vetted, audited suppliers by industry | Up to 80 hours per project |
| Verification & Due Diligence | On-site audits, document validation (3–6 weeks) | All suppliers verified via ISO checks, business license validation, site visits, and performance history | 3–4 weeks eliminated |
| Communication & MOQ Negotiation | Language barriers, inconsistent responsiveness | Direct English-speaking contacts, transparent MOQs, and lead times | 50% faster RFQ turnaround |
| Quality Assurance | Post-production inspections, rework risks | Suppliers with proven track records and documented QC processes | Reduced defect rates by up to 60% |
| Scalability & Compliance | Fragmented supplier base, inconsistent ESG standards | Tiered supplier classification with ESG and export compliance data | Faster onboarding, audit-ready partners |
Key Benefits for Procurement Leaders in 2026
- Accelerated Time-to-Scale: Reduce supplier onboarding from 60+ days to under 15.
- Cost Efficiency: Avoid costly missteps with suppliers that fail compliance or delivery benchmarks.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Diversify across vetted manufacturers with backup capacity options.
- Data-Backed Decisions: Access supplier performance metrics, including delivery reliability, defect rates, and client references.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Don’t let unreliable suppliers slow your growth. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List is the industry benchmark for secure, efficient China sourcing—trusted by procurement teams across North America, Europe, and APAC.
✅ Save 75+ hours per sourcing cycle
✅ Mitigate supply chain risk with verified partners
✅ Gain direct access to responsive, export-ready manufacturers
Take the next step with confidence.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team today:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our consultants are available to provide a customized supplier shortlist based on your product category, volume needs, and compliance requirements—free of obligation.
Secure your competitive edge in 2026—partner with precision, scale with confidence.
—
SourcifyChina | Advancing Global Procurement Through Verified Supply
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





