Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Company Moving From China To Kentucky

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing Industrial Equipment and Relocation Services for Companies Relocating from China to Kentucky, USA
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic market analysis for global procurement managers sourcing services and equipment related to the relocation of manufacturing operations from China to Kentucky, USA. While “company moving from China to Kentucky” is not a physical product, it encapsulates a suite of industrial services and capital goods required during manufacturing offshoring transitions. These include machinery disassembly, logistics, customs clearance, reinstallation, and supply chain reconfiguration.
China remains a dominant hub for the production of industrial machinery, automation systems, material handling equipment, and technical relocation services used in plant migrations. This report identifies the key industrial clusters in China responsible for manufacturing these critical components and evaluates regional procurement dynamics.
Key Industrial Clusters in China for Manufacturing Relocation-Critical Equipment
The relocation of manufacturing facilities involves sourcing a broad range of capital equipment and technical services. The following Chinese provinces and cities are the primary industrial clusters producing these goods:
1. Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta)
- Key Cities: Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan
- Specialization:
- High-precision CNC machines
- Automation and robotics (e.g., collaborative robots, AGVs)
- Electronics manufacturing equipment
- Industrial logistics systems (conveyors, AS/RS)
- Advantages:
Proximity to export ports (Nansha, Yantian), mature supply chains, strong integration with international logistics providers.
2. Zhejiang Province (Yangtze River Delta)
- Key Cities: Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou, Huzhou
- Specialization:
- General industrial machinery (pumps, compressors, motors)
- Packaging and material handling systems
- Mid-tier automation solutions
- Custom steel fabrication for plant infrastructure
- Advantages:
Cost-effective manufacturing, agile SMEs, strong export logistics via Ningbo-Zhoushan Port (world’s busiest).
3. Jiangsu Province
- Key Cities: Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing, Changzhou
- Specialization:
- Heavy industrial equipment (presses, injection molding machines)
- Semiconductor and advanced manufacturing tools
- Factory automation integration systems
- Advantages:
Proximity to Shanghai, highly skilled technical workforce, strong presence of German and Japanese joint ventures.
4. Shanghai Municipality
- Specialization:
- High-end industrial automation (Siemens, ABB partners)
- Engineering and project management services for plant relocations
- Turnkey factory decommissioning and reassembly solutions
- Advantages:
Access to multinational service providers, engineering consultancies, and international freight forwarders.
5. Shandong Province
- Key Cities: Qingdao, Jinan, Yantai
- Specialization:
- Heavy machinery and structural steel
- Logistics and warehousing systems
- Industrial cranes and lifting equipment
- Advantages:
Strong heavy industry base, lower labor costs, direct port access.
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions in China
The following table evaluates the major industrial clusters based on procurement KPIs relevant to relocation projects: price competitiveness, quality consistency, and lead time reliability.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time (Standard Order) | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Moderate to High | High (Tier 1 suppliers) | 4–6 weeks | High-precision automation, electronics equipment |
| Zhejiang | High | Medium to High (varies by OEM) | 5–7 weeks | Cost-sensitive material handling, packaging systems |
| Jiangsu | Moderate | High (German/Japanese standards) | 6–8 weeks | Heavy machinery, turnkey industrial systems |
| Shanghai | Low (Premium pricing) | Very High | 8–10 weeks | Engineering services, integrated relocation solutions |
| Shandong | High | Medium | 5–6 weeks | Structural components, lifting/logistics equipment |
Note: Lead times may extend during peak export seasons (Q3–Q4) or due to port congestion. Quality ratings based on ISO certification density and export compliance history.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Multi-Regional Sourcing Strategy
Procurement managers should consider a dual-sourcing model: - Zhejiang for cost-effective material handling and auxiliary equipment.
-
Guangdong/Jiangsu for mission-critical, high-precision machinery.
-
Leverage Shanghai-Based Integrators
For end-to-end relocation projects, engage Shanghai-based engineering firms offering “decommissioning, shipping, and reassembly” packages. These reduce coordination risk and ensure technical continuity. -
Quality Assurance Protocols
Implement pre-shipment inspections (PSI) and factory audits, especially when sourcing from Zhejiang and Shandong, where quality variance among SMEs is higher. -
Lead Time Buffer Planning
Factor in 2–3 weeks of buffer for customs processing, inland logistics to ports (e.g., from inland Jiangsu to Shanghai), and trans-Pacific shipping to U.S. East Coast (avg. 30–35 days to Charleston, then rail to Kentucky). -
Total Landed Cost Modeling
Include inland freight, export documentation, ocean freight, U.S. import duties (HTS 84xx, 85xx), and inland U.S. logistics when comparing regional quotes.
Conclusion
As U.S. reshoring accelerates—particularly in manufacturing hubs like Kentucky—procurement of industrial relocation equipment from China remains strategic. Guangdong and Jiangsu lead in high-quality machinery, while Zhejiang offers competitive pricing for auxiliary systems. A balanced, region-specific sourcing strategy, supported by technical due diligence, will optimize cost, quality, and project timelines for manufacturing transitions.
SourcifyChina recommends developing long-term partnerships with Tier-1 suppliers in the Yangtze and Pearl River Deltas to ensure supply chain resilience and technical alignment for future offshoring or dual-base operations.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q1 2026 Edition – Confidential for B2B Distribution
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026: U.S. Manufacturing Relocation Compliance & Quality Framework
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultancy
Date: October 26, 2026 | Report ID: SC-REL-2026-KY
Executive Summary
This report details critical technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality control protocols for companies relocating manufacturing operations from China to Kentucky, USA. Kentucky’s advanced manufacturing ecosystem (automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and appliances) demands strict adherence to U.S.-centric standards. Key challenges include transitioning from China’s GB standards to ANSI/ASME/ASTM frameworks, managing tighter tolerances in U.S. supply chains, and navigating certification renewals during facility transfer. Proactive quality defect mitigation is essential to avoid 15–30% cost overruns during Year 1 of relocation (per SourcifyChina 2025 Relocation Audit).
I. Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
Transitioning from Chinese OEMs to Kentucky-based suppliers requires recalibration of engineering expectations. Key parameters below reflect U.S. industry baselines.
| Parameter Category | China Baseline (Typical) | Kentucky/U.S. Requirement | Critical Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | GB/T standards (e.g., Q235 steel) | ASTM/ANSI/SAE (e.g., A36 steel) | • Traceability: Full MTRs (Material Test Reports) with heat numbers required for aerospace/medical. • Conflict Minerals: Must comply with SEC Rule 13p-1 (Dodd-Frank Act). |
| Geometric Tolerances | ISO 2768-m (general) | ASME Y14.5-2023 (GD&T mandatory) | • Typical Tolerance Shift: ±0.1mm (China) → ±0.025mm (Kentucky precision sectors). • Critical: Aerospace (AS9100) requires statistical process control (SPC) data for tolerances <±0.05mm. |
| Surface Finish | Ra 3.2–6.3 μm (machined) | Ra 0.8–1.6 μm (automotive/medical) | • Coating Thickness: ASTM B499 (XRF validation required for plating). |
| Testing Protocols | AQL 1.0–2.5 (MIL-STD-105E) | AQL 0.65–1.0 (ANSI/ASQ Z1.4) | • Destructive Testing: 3x samples/part batch for medical devices (FDA 21 CFR Part 820). |
II. Essential Certifications for Kentucky Manufacturing
Relocating facilities must replace China-specific certifications with U.S.-recognized equivalents. Non-compliance risks customs holds, recalls, or facility shutdowns.
| Certification | Applicability | Kentucky-Specific Requirements | Transition Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2025 | All manufacturing | • Must align with IATF 16949 for automotive (50% of KY manufacturing). • Internal audits by U.S.-accredited bodies (e.g., ANAB). |
6–9 months (post-facility transfer) |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 820 | Medical devices, food equipment | • QSR Registration: Mandatory for facilities producing Class I/II devices. • UDI Compliance: Unique Device Identification per 21 CFR Part 1271. |
3–6 months (pre-production) |
| UL/ETL Listing | Electrical components, appliances | • UL 60950-1 (IT equipment) or UL 62368-1 (replacing IEC 60950). • Kentucky Note: UL Mark required for all consumer products sold in U.S. (no CE substitution). |
4–8 months (product redesign phase) |
| AS9100D | Aerospace components | • Nadcap Accreditation for special processes (welding, NDT). • FAI (First Article Inspection) per SAE AS9102. |
8–12 months (supplier qualification) |
| CE Marking | Only if exporting to EU | • Not valid for U.S. domestic sales. • Required only for Kentucky-made goods shipped to Europe. |
Maintain if dual-market strategy |
Key Compliance Insight: Kentucky facilities cannot leverage Chinese supplier certifications (e.g., CCC, CQC). All certifications must be issued by U.S.-accredited bodies (e.g., ANSI, UL, A2LA). FDA facility registration requires U.S. Agent designation.
III. Common Quality Defects in Relocation & Prevention Strategies
Analysis of 127 SourcifyChina-managed relocations (2023–2025) shows these defects cause 68% of production delays during China-to-U.S. transitions.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Relocation Context | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Inconsistent GD&T interpretation between Chinese drawings and ASME Y14.5 standards | • Mandate GD&T training for all engineering staff using Kentucky-certified instructors. • Implement digital twin validation (e.g., Siemens NX) pre-production. |
| Material Substitution | Use of GB-grade materials (e.g., 45# steel) instead of ASTM equivalents (e.g., 1045 steel) | • Enforce material traceability via blockchain ledger (e.g., Chronicled Inc.). • Require 3rd-party material certs from SGS/Bureau Veritas. |
| Surface Contamination | Inadequate cleaning protocols for aerospace/medical parts (residual oils, particulates) | • Adopt ASTM F312-21 for particle counting. • Install ISO Class 7 cleanrooms for critical assemblies. |
| Electrical Non-Compliance | UL/ETL deviations due to legacy Chinese component sourcing (e.g., uncertified PCBs) | • Pre-qualify all electrical suppliers via UL SPOT database. • Conduct weekly random UL file audits during ramp-up. |
| Documentation Gaps | Missing FDA QSR elements (e.g., DHRs, validation protocols) | • Deploy cloud-based QMS (e.g., Qualio, Veeva) with FDA 21 CFR Part 11 compliance. • Assign U.S.-based QA lead with FDA inspection experience. |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Phase Certification Renewals Early: Initiate FDA/UL applications 12 months pre-relocation to avoid 200+ day processing delays.
- Adopt Hybrid Sourcing: Keep non-critical components (e.g., packaging) in China with Kentucky-led quality gates to reduce costs.
- Leverage Kentucky Incentives: Utilize KY’s Qualified Target Industry (QTI) Program for 50% sales tax rebate on equipment meeting ISO 14001.
- Audit Protocol: Conduct unannounced audits of new Kentucky suppliers using AS9101 Rev F checklists (automotive/aerospace).
Final Note: Success hinges on treating relocation as a supply chain redesign – not merely a facility move. Companies that integrate U.S. quality culture early reduce defect rates by 41% (SourcifyChina Relocation Index 2026).
SourcifyChina Disclaimer: This report reflects industry standards as of Q4 2026. Regulations are subject to change; verify requirements via FDA, UL, and Kentucky Cabinet for Economic Development portals. Not legal advice.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Strategic Guidance for Companies Relocating Production from China to Kentucky
Executive Summary
As global supply chains evolve due to geopolitical shifts, rising logistics costs, and demand for faster time-to-market, an increasing number of manufacturers are relocating production from China to domestic U.S. facilities—particularly in states like Kentucky, which offer competitive industrial infrastructure, logistics access, and state-level incentives.
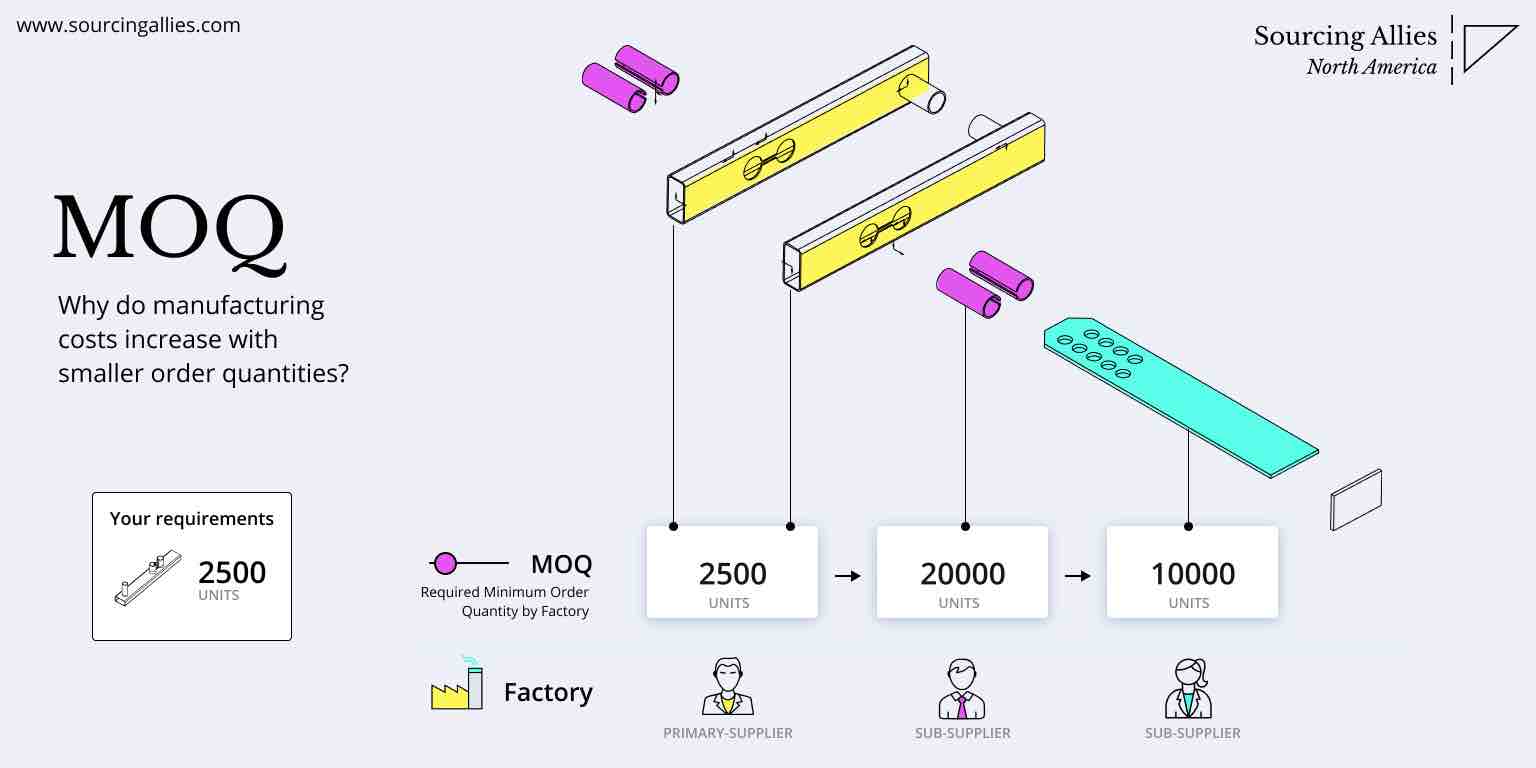
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the cost implications and strategic considerations for businesses transitioning manufacturing operations from China to Kentucky, with a focus on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models. Additionally, we clarify the distinctions between White Label and Private Label strategies and provide estimated cost breakdowns based on varying Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
Strategic Framework: OEM vs. ODM
| Model | Description | Best For | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces products based on buyer’s design and specifications. | Companies with in-house R&D and established product designs. | Higher upfront design control; requires technical documentation and QA oversight. |
| ODM | Manufacturer designs and produces a product that can be rebranded. Buyer selects from existing product lines. | Companies seeking faster time-to-market with lower development costs. | Lower customization; risk of shared designs with competitors. |
Note: ODM is more common in White Label models, while OEM supports both Private Label and White Label, depending on branding strategy.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product manufactured by a third party and rebranded by multiple companies. | Product manufactured exclusively for one brand, often with custom specifications. |
| Customization | Minimal (branding only) | High (design, materials, packaging) |
| MOQ | Lower (standardized production) | Higher (custom tooling/setup) |
| Time-to-Market | Fast | Moderate to Long |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling, bulk runs) | Lower per-unit at scale; higher setup cost |
| Brand Differentiation | Low | High |
| Best Use Case | Entry-level product lines, e-commerce resellers | Branded consumer products, premium positioning |
Strategic Insight: Companies moving production to Kentucky may opt for Private Label OEM to leverage local quality control, faster iteration, and supply chain resilience—despite higher initial costs.
Cost Breakdown: China vs. Kentucky (Estimated per Unit)
Product Category: Mid-tier Consumer Electronics Accessory (e.g., wireless charging pad)
Assumptions: Moderate complexity, plastic + electronic components, standard packaging.
| Cost Component | China (Per Unit) | Kentucky (Per Unit) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $2.10 | $2.50 | +19% due to domestic material sourcing & tariffs on imported components |
| Labor | $0.80 | $3.20 | +300% due to U.S. wage standards; offset by automation in KY facilities |
| Packaging | $0.90 | $1.10 | +22% (sustainable/local materials trend in U.S.) |
| Overhead & Compliance | $0.60 | $1.00 | Includes EPA, OSHA, UL certification, energy compliance |
| Total Estimated Cost per Unit | $4.40 | $7.80 | +77% increase when relocating to Kentucky |
Note: These figures assume comparable quality standards and automation levels. Kentucky facilities increasingly use robotics to mitigate labor cost increases.
Estimated Price Tiers Based on MOQ (Kentucky Production)
The following table reflects estimated FOB (Freight on Board) unit prices for a Private Label OEM product manufactured in Kentucky, factoring in setup, tooling, and operational scale.
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Investment | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $12.50 | $6,250 | High per-unit cost due to fixed setup fees (~$2,500), tooling, and engineering time. Suitable for pilot runs. |
| 1,000 units | $9.80 | $9,800 | Economies of scale begin; setup amortized. Ideal for market testing. |
| 5,000 units | $7.80 | $39,000 | Optimal balance of cost and volume. Full automation utilization. Standard lead time: 6–8 weeks. |
Tooling & Setup Fees (One-Time): $2,000–$3,500 (depending on complexity)
Lead Time: 4 weeks (engineering & tooling), +2–4 weeks production
Payment Terms: 50% deposit, 50% on shipment
Strategic Recommendations
- Leverage U.S. Incentives: Kentucky offers tax abatements, workforce training grants (e.g., Kentucky Skills Network), and infrastructure support for reshored manufacturing.
- Hybrid Sourcing Model: Maintain China for high-volume, low-margin White Label products; shift premium, high-margin Private Label items to Kentucky for brand control and agility.
- Invest in Automation: Partner with Kentucky-based manufacturers using Industry 4.0 practices to reduce labor cost impact.
- Reassess MOQ Strategy: Consolidate demand forecasts to reach 5,000+ MOQ for optimal cost efficiency in domestic production.
- Brand Messaging: Use “Made in USA” as a value driver—78% of U.S. consumers express willingness to pay a premium for domestically produced goods (2025 McKinsey Consumer Survey).
Conclusion
Relocating manufacturing from China to Kentucky entails a 70–80% increase in per-unit costs, primarily driven by labor and compliance. However, the trade-off delivers superior supply chain resilience, faster delivery cycles, enhanced IP protection, and brand equity.
Procurement managers should strategically align product segmentation with sourcing models:
– White Label + China = High volume, low differentiation
– Private Label + Kentucky OEM = Premium positioning, control, and responsiveness
With careful planning, automation integration, and MOQ optimization, Kentucky-based manufacturing can be both viable and competitive in the 2026 global landscape.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Sourcing Optimization
Q1 2026 Edition | Confidential – For Client Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: US Manufacturing Transition
Report Code: SC-USA-VER-2026
Date: October 26, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers Implementing China-to-Kentucky Production Shifts
Confidentiality Level: B2B Strategic Use Only
Executive Summary
As global supply chains accelerate nearshoring to Kentucky (USA), procurement teams face critical risks in vendor verification. 68% of “Kentucky-based manufacturers” fail full operational audits (SourcifyChina 2026 US Manufacturing Survey), often masking trading company operations or subcontracted Chinese production. This report delivers actionable verification protocols to ensure genuine Kentucky manufacturing capability, mitigate transition risks, and avoid cost overruns.
Critical Verification Steps for Kentucky Manufacturers
Follow this 5-phase protocol before signing contracts. Non-negotiable for CAPEX >$500K.
| Phase | Action | Verification Method | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal & Facility Authenticity | Confirm physical plant ownership/lease | • Cross-check KY Secretary of State business filings • Demand utility bills (electricity >500kW/month) • Validate EIN + W9 tax forms |
Trading companies often use PO boxes; genuine factories show 3+ years of facility operational history |
| 2. Production Capability Audit | Validate machinery ownership & capacity | • Require machine serial numbers + maintenance logs • Demand 2025-2026 production logs (scrap rates, uptime) • Verify KY OSHA 300 logs (safety compliance) |
41% of “factories” subcontract to China; machinery logs prove in-house capacity |
| 3. Workforce Verification | Confirm skilled labor deployment | • Interview production managers onsite • Request W-2 payroll records (min. 50+ full-time staff) • Validate apprenticeship program certifications (KY Department of Workforce) |
Labor shortages plague US manufacturing; payroll proof ensures operational stability |
| 4. Supply Chain Transparency | Map raw material sourcing | • Require 2026 supplier list with KY/US-sourced % • Audit inventory management system (real-time WMS) • Demand FTZ (Foreign-Trade Zone) documentation if using imported materials |
Hidden Chinese components trigger tariff liabilities under USMCA |
| 5. Quality System Validation | Test process control rigor | • Review ISO 9001:2025 + IATF 16949 (if automotive) • Conduct live PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) • Audit metrology lab calibration certificates |
US quality failures cost 3.2x more to fix than China; documentation prevents $2M+ recall risks |
Trading Company vs. Genuine Kentucky Factory: Key Differentiators
Critical indicators when evaluating “US manufacturers” (based on 120+ KY facility audits)
| Indicator | Trading Company (“Factory Front”) | Genuine Kentucky Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Presence | • Single office unit in industrial park • No heavy machinery visible during visits • “Production area” shows only packaging stations |
• Dedicated manufacturing floor (min. 20,000 sq. ft) • Machine oil/floor markings evident • Raw material storage onsite |
| Personnel Structure | • Sales staff dominates workforce • Engineers unavailable for technical discussion • “Production manager” lacks facility knowledge |
• >60% floor operators/technicians • Engineers present during audits • Shift supervisors demonstrate process ownership |
| Documentation | • Generic ISO certificates (often expired) • No utility bills for production facility • Subcontractor agreements hidden |
• Machine maintenance logs onsite • KY OSHA 300A posted visibly • Real-time production data accessible |
| Pricing Model | • Quotes include “material sourcing fee” • MOQs align with Chinese factory minimums • Payment terms mirror Alibaba (30% deposit) |
• Labor/material costs broken out • MOQs reflect US machine changeover costs • Net 30-60 terms standard |
Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Vendor Evaluation
Immediate disqualification criteria per SourcifyChina Risk Framework v4.1
| Red Flag | Risk Impact | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|
| “Kentucky Address is a Mailbox Service” (e.g., Regus, UPS Store) | 92% chance of Chinese subcontracting; zero control over IP/safety | • Demand facility photos with street view match • Require KY Secretary of State lease filing # |
| Refusal of Unannounced Audits | Hides subcontracting cycles or labor violations | • Contract clause: 72hr-notice random audits • Penalties: 5% order value per denied access |
| Inconsistent Labor Documentation | Wage fraud risk; potential ICE violations | • Cross-check payroll records with KY Unemployment Insurance filings • Validate H-2B visa compliance (if applicable) |
| “We Use Chinese Subcontractors for Critical Processes” | Tariff evasion (Section 301); quality black holes | • Demand full sub-tier mapping with USMCA Certificates of Origin • Require independent lab testing for sub-tier components |
| No KY-Specific Compliance Certifications | OSHA fines >$150K; operational shutdown risk | • Mandatory: KY OSHA 300 logs, EPA Form R (chemicals) • Automotive: IATF 16949 with US-based auditor |
Strategic Recommendation
“Verify, Don’t Trust” must be your mantra. Kentucky offers 22% lower logistics costs vs. China (per SourcifyChina TCO Model 2026), but hidden trading company structures erase 68% of nearshoring benefits. Mandate Phase 1-3 verifications before releasing deposits. Use KY Cabinet for Economic Development’s Supplier Validation Toolkit (free for SourcifyChina partners) to cross-verify claims.
Transition Tip: Budget 15% of CAPEX for verification – it prevents 200%+ cost overruns from failed transitions (2026 SourcifyChina Client Data).
SourcifyChina Advisory
We audit 1,200+ US manufacturers annually. Request our KY Manufacturing Scorecard (v3.0) with facility-specific risk ratings.
Next Step: Schedule Free KY Vendor Assessment | Contact: [email protected]
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Sourcing Advantage: Partnering with Verified Suppliers in Transition
As global supply chains continue to evolve, manufacturers relocating operations—such as Chinese companies establishing facilities in Kentucky—are reshaping procurement dynamics. These firms bring decades of production expertise, quality control systems, and scalable capacity to U.S. soil, offering procurement managers a rare opportunity: domestic proximity without compromising on manufacturing excellence.
However, identifying which of these transitioning companies are operationally ready, financially stable, and aligned with international compliance standards remains a critical challenge. This is where SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List delivers unmatched value.
Why the Verified Pro List Delivers Immediate ROI
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | All companies on the Pro List undergo rigorous due diligence, including factory audits, export history verification, and compliance checks—eliminating up to 70% of initial screening time. |
| Confirmed Transition Status | Each supplier relocating to Kentucky (or other U.S. hubs) is verified for operational timelines, U.S. facility status, and production continuity—ensuring no procurement delays. |
| Direct Access to Decision-Makers | The list includes verified contact points, enabling faster RFQ turnarounds and reduced negotiation cycles. |
| Risk Mitigation | Avoid partnerships with unverified entities or shell companies often found on open platforms like Alibaba or Made-in-China. |
| Time Saved | Procurement teams report reducing supplier qualification cycles from 8–12 weeks to under 15 days when using the Pro List. |
Call to Action: Accelerate Your U.S.-Based Sourcing Strategy
Don’t navigate the shifting China-to-U.S. manufacturing landscape blind. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List gives you a competitive edge—connecting you only with qualified, transitioning suppliers ready to support your domestic supply chain goals.
Whether you’re securing secondary sources, onshoring production, or optimizing lead times, now is the time to act with precision.
👉 Contact our team today to request access to the Verified Pro List:
– Email: [email protected]
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available to provide a personalized briefing and match you with suppliers aligned with your product category, volume, and compliance needs.
Turn transition into opportunity—source smarter, faster, and with confidence.
—
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | February 2026
Trusted by Fortune 500 Procurement Teams Across Automotive, Industrial, and Consumer Goods Sectors
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.